Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Madhuri Madam
Uploaded by
akshay75730 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesOriginal Title
madhuri madam.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesMadhuri Madam
Uploaded by
akshay7573Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Sr No Practical Outcomes
Trace your electrical engineering Laboratories
draw layout of electrical laboratory
prepare charts of electrical safety and demonstrate the operation of Fire
1.
extinguisher equipments
demonstrate and use electric tools such as pliers screwdriver insulation cutter
tester
Measure of EMF of DC source and to calculate its internal resistance by connecting
2.
it to an external load part 1
Measure of EMF of DC source and to calculate its internal resistance by connecting
3.
it to an external load part 2
4. determine the equivalent resistance of series connection
5. Determine the equivalent resistance of parallel connection
Use case of current law and gift shops Voltage law to determine current and voltages
6.
in electric circuits part 1
Use case of current law and Kirchhoff's Voltage law to determine current and
7.
voltages in electric circuits part 2
8. In the series connected circuits determine the equivalent capacitance
9. In The parallel connected circuits determine the equivalent capacitance
Determine the time constant of RC circuit analytically and graphically including
10. plotting the charging and discharging curves of a capacitor see through resistor R
part 1
Determine the time constant of RC circuit analytically and graphically including
11. plotting the charging and discharging curves of a capacitor see through resistor R
part 2
12. For the given magnetic material find the BH curve and hysteresis loop part 1
13. For the given magnetic material find the BH curve and hysteresis loop part 2
14. For the given magnetic material find the BH curve and hysteresis loop part 3
Use Faraday's first law of electromagnetic induction to analyse the behaviours of
15.
statically induced EMF and dynamically induced EMF in the given circuit part 1
Use Faraday's first law of electromagnetic induction to analyse the behaviours of
16.
statically induced EMF and dynamically induced EMF in the given circuit part 2
Sr No Unit Outcomes Topis and Subtopics
1. Basic Electrical Parameters 1. Direct current DC alternating
current AC voltage source and
Unit 1 basic electrical parameters current source ideal and practical
2. Electric current electric potential,
1. Distinguish the features of the potential difference PD
given electrical parameters electromotive force EMF
2. Explain the given terms 3. Electric work power and energy
3. Describe the given effect of the 4. Resistance resistivity conductivity
electric current with a relevant effect of temperature on resistance
application 5. Types of resistor and their
4. Calculate work power and application
energy for given circuits 6. Heating effect magnetic effect
chemical effect of electric current
7. DC Circuits 1. Ohm's law internal resistance of
Apply Ohm's law to calculate internal source internal voltage drop
resistance of given circuit distinguish terminal voltage
the given two parameters calculate 2. Resistance in series resistance in
equivalent resistance for a given parallel
circuit apply Kirchhoff law to 3. Active passive linear nonlinear
determine current and voltage in the circuits unilateral circuits bilateral
given circuit circuits passive and active network
node branch loop mesh
4. Kirchhoff's current law jobs
Voltage law
8. Capacitors 1. Capacitor parallel plate capacitor
2. Various connections of capacitor
Determine the construction of the 3. Energy stored in capacitor
given type capacitor describe the 4. Charging and discharging of
working of the capacitor in given capacitor
circuit calculate equivalent 5. Breakdown voltage and dielectric
capacitance in given DC circuit plot strength type of capacitor and
charging and discharging curves for application
the given capacitor
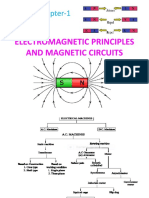
6. Magnetic Circuits 1. Magnetic lines of force flux, flux
density magnetic flux intensity
Distinguish the given terms related to 2. Magneto motive force MMF
magnetic circuit calculate various ampere turns 80 reluctance
parameters of given magnetic circuit Permeance reluctivity electric and
plot BH curve and hysteresis loop of a magnetic circuits series magnetic
given magnetic materials compare the and parallel magnetic circuit
performance of the given series and 3. Magnetization curve BH curve
parallel magnetic circuit 4. Magnetic hysteresis hysteresis
loop application
7. Electromagnetic Induction 1. Development of induced EMF and
current Faraday's law of
Describe the use of Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction
electromagnetic induction in the given 2. Static and dynamic EMF lenz law
application distinguish between the Fleming's right hand rule
given types of EMF apply Faraday's 3. self inductance coefficient of self
law to calculate induced EMF in the inductance mutual inductance
given circuit calculate self inductance coefficient of mutual inductance
and energy stored in magnetic field in and self induced EMF and
given circuits mutually induced EMF coefficient
of coupling
4. inductance in series
5. types of inductors and their
application and energy stored in
magnetic field
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Quick Study For Computer Keyboard Short CutsDocument2 pagesQuick Study For Computer Keyboard Short Cutsmahazari100% (3)
- Quick Study For Computer Keyboard Short CutsDocument2 pagesQuick Study For Computer Keyboard Short Cutsmahazari100% (3)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Magnetic CircuitsDocument38 pagesMagnetic CircuitsHanan KemalNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Magnetic CircuitsDocument52 pagesMagnetic Circuitsgopi_905100% (1)
- Lab Volt PWM AC Motor DrivesDocument103 pagesLab Volt PWM AC Motor Drivesumer farooqNo ratings yet
- IR Remote Controlled Home Automation Using ArduinoDocument10 pagesIR Remote Controlled Home Automation Using Arduinoakshay7573No ratings yet
- Ies 1Document9 pagesIes 1akshay7573No ratings yet
- Digital Techniques & Microprocessor (DEM)Document13 pagesDigital Techniques & Microprocessor (DEM)akshay7573No ratings yet
- Applied Electronics (AEL)Document8 pagesApplied Electronics (AEL)akshay7573No ratings yet
- Digital Communication (DCO)Document8 pagesDigital Communication (DCO)akshay7573No ratings yet
- REPORTDocument16 pagesREPORTakshay7573No ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Switchyard Equipment PDFDocument16 pagesChapter-8 Switchyard Equipment PDFmsnsaikiranNo ratings yet
- Need of Electrical SubstationDocument3 pagesNeed of Electrical Substationakshay7573No ratings yet
- Draw Electrical Symbols, Components & Layouts in CADDocument2 pagesDraw Electrical Symbols, Components & Layouts in CADakshay7573No ratings yet
- Substation Enclosed Switchgear PCC FundamentalsDocument85 pagesSubstation Enclosed Switchgear PCC FundamentalsAlezsander RguezArNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuits (LIC)Document10 pagesLinear Integrated Circuits (LIC)akshay7573No ratings yet
- Ie Rules-1956Document191 pagesIe Rules-1956Murali MohanNo ratings yet
- Fuse and Isometric View of Pole of DC MachineDocument3 pagesFuse and Isometric View of Pole of DC Machineakshay7573No ratings yet
- Industry QuestionsDocument3 pagesIndustry Questionsakshay7573No ratings yet
- Madhuri MadamDocument4 pagesMadhuri Madamakshay7573No ratings yet
- W.E.F. Academic Year 2012-13 G' SchemeDocument50 pagesW.E.F. Academic Year 2012-13 G' Schemeakshay7573No ratings yet
- 2.domestic WiringDocument7 pages2.domestic Wiringakshay7573No ratings yet
- ObjectiveDocument1 pageObjectiveakshay7573No ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics Notes For Class 1st To 10th PDFDocument47 pagesBasic Mathematics Notes For Class 1st To 10th PDFakshay757350% (2)
- Pamas EnergyDocument24 pagesPamas Energyakshay7573No ratings yet
- Production EngineeringDocument7 pagesProduction Engineeringakshay7573No ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics Notes For Class 1st To 10th PDFDocument47 pagesBasic Mathematics Notes For Class 1st To 10th PDFakshay757350% (2)
- Basic Electronics (Set 1)Document1 pageBasic Electronics (Set 1)akshay7573No ratings yet
- Ee8401 - em Ii - Question Bank - Unit1Document4 pagesEe8401 - em Ii - Question Bank - Unit1DEVINo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Free Energy Permanent Magnet MotorDocument10 pagesDesign and Simulation of Free Energy Permanent Magnet MotorCristian IonescuNo ratings yet
- Theory & Practice of Electromagnetic Design of DC Motors & ActuatorsDocument178 pagesTheory & Practice of Electromagnetic Design of DC Motors & ActuatorsNoel Dunn100% (2)
- EFT Finalterm Fall 2021Document2 pagesEFT Finalterm Fall 2021Tayyab AbbasNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication Engineering (EC) - 21.03.18Document280 pagesElectronics and Communication Engineering (EC) - 21.03.18Deep DiwakarNo ratings yet
- DTU B.Tech Scheme of Examination and Course Curriculum for Polymer Science & Chemical TechnologyDocument29 pagesDTU B.Tech Scheme of Examination and Course Curriculum for Polymer Science & Chemical TechnologySajal GargNo ratings yet
- FoEEE - 1Document10 pagesFoEEE - 1Kumar SunnyNo ratings yet
- Technical Guide For Bicron DC Solenoids - Bicron ElectronicsDocument12 pagesTechnical Guide For Bicron DC Solenoids - Bicron ElectronicsAbirami RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Syllabus UEE001 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGDocument2 pagesSyllabus UEE001 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGWarden Hostel GNo ratings yet
- Unit - No.:1 (Magnetic Circuits & Magnetic Materials) : CoimbatoreDocument3 pagesUnit - No.:1 (Magnetic Circuits & Magnetic Materials) : CoimbatoreVenkata SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Bee AssignmentDocument2 pagesBee AssignmentlinuxNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits ExplainedDocument47 pagesMagnetic Circuits ExplainedCrytpo MaxiNo ratings yet
- Ee2251 Electrical Machines PDFDocument120 pagesEe2251 Electrical Machines PDFJohn RivasNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Transformer Model for Transient Simulation: Part IDocument8 pagesHybrid Transformer Model for Transient Simulation: Part IJosNo ratings yet
- Magnetic circuit flux calculationsDocument3 pagesMagnetic circuit flux calculationsMausam BasnetNo ratings yet
- ET Tut5 AUT2017-18Document3 pagesET Tut5 AUT2017-18Chekuri Srinivasa VarmaNo ratings yet
- Temperatue and DiplacementDocument63 pagesTemperatue and Diplacementaregawi weleabezgi100% (1)
- "Magnetic Abrasive Finishing Machine": A Project ReportDocument42 pages"Magnetic Abrasive Finishing Machine": A Project Reportvarun dhavanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions on Magnetic CircuitsDocument5 pagesElectrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions on Magnetic CircuitsHussam GujjarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document11 pagesExperiment 1Aneef Azlan50% (2)
- Allied Physics Papers 2007-08Document9 pagesAllied Physics Papers 2007-08Jostin Punnassery50% (4)
- Design of Wireless Power Transfer System For RailwDocument9 pagesDesign of Wireless Power Transfer System For Railw19TK5AO265 V.NavaneethaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering FundamentalsDocument16 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering FundamentalsMonkey dragon10No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocument25 pagesBasic Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Magnetic Circuits and TransformerDocument33 pagesChapter 3 Magnetic Circuits and TransformerTanu AryaNo ratings yet
- BE3252 QB Unit2Document2 pagesBE3252 QB Unit2rkanthimathi86No ratings yet