Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Science Test Bank Key
Uploaded by
api-426620800Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Science Test Bank Key
Uploaded by
api-426620800Copyright:
Available Formats
Physical Science 2 - Assessment Bank
1. As an object falls, what happens to its gravitational energy?
a. increases
b. decreases
c. remains the same
d. more information is needed
2. Which of the following does not represent energy being converted?
a. stretching a rubber band then letting it go
b. dropping a ball
c. playing with a yo-yo
d. a book sitting on a desk
3. What are the factors that influence the amount of elastic energy in an object? Circle all that are correct.
a. stretching
b. compression
c. hardness
d. mass
4. What energy type is represented in the picture to
the right?
Which type of energy conversion is involved
when the arrow is released?
The picture represents elastic energy, which is the result of the bow being bent and the bowstring being
stretched.
When the bowstring is released, this elastic energy is transformed into kinetic energy of the arrow.
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 1
Use the diagram below to answer questions 5, 6, and 7.
5. At which point on the roller coaster will the car have the greatest amount of kinetic energy? Explain why.
Since kinetic energy is the energy of motion, the bottom of the roller coaster after the big drop is the point
at which the car is going the fastest, so it has the most kinetic energy and the least gravitational energy at
point X.
6. At which point on the roller coaster will the car have the greatest amount of gravitational energy?
Explain why.
The further from the center of the Earth, the greater the gravitational energy, so the greatest amount of
gravitational energy is at point W.
7. What energy type(s) is present at point Z? Explain your answer.
At point Z there is gravitational energy (because the roller coaster is above ground level) and kinetic energy because
the car is still moving.
8. What determines the amount of thermal energy of an object? More than one answer is possible.
e. temperature
f. speed
g. mass
h. springiness
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 2
9. Which object has more thermal energy – a large pot of water or a small pot of water at the same
temperature?
e. Both pots have the same thermal energy.
f. The large pot has more thermal energy.
g. The small pot has more thermal energy.
h. There is not enough information to answer the question.
10. Which of the following types of energy is potential energy? More than one answer is possible.
e. gravitational energy
f. kinetic energy
g. thermal energy
h. sound energy
11. A cold can of soda is taken out of the refrigerator. It slowly warms up until it is at room temperature.
Once the soda has warmed up, it has more thermal energy than it had in the refrigerator. Where did this
additional thermal energy come from?
a. The thermal energy was already in the soda.
b. The thermal energy came from the air surrounding the soda can.
c. The thermal energy came from the air surrounding the soda can and from the soda itself.
d. The thermal energy came from the refrigerator.
A student drops a ball from 5 feet above the ground. After bouncing once, it only reaches a maximum height
of 4 feet above the ground.
12. Use energy terms to explain why the ball did not reach its original height after bouncing once.
Some of the balls energy was transferred to the floor and the surrounding air so that the ball was left
with less energy than it originally had. This means that its maximum GE was smaller than it originally
was, so it only reaches a lower height.
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 3
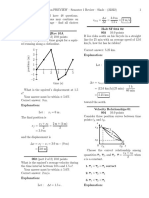
13. To the right is a diagram presenting the maximum
height the ball reaches after consecutive bounces.
Explain why the maximum height gets smaller
with every bounce.
With each bounces the ball transfers energy to the
floor and the surrounding air, leaving it with less
energy than before, so it can only reach a lower
height than before.
14. Does the diagram above contradict the idea of energy conservation? Explain your answer.
The large mug of hot tea has more thermal energy because it: A) contains more water and B) the water
in it is hotter.
15. You have a large mug with hot tea and a small mug with ice tea. Which mug has more thermal energy?
Explain your answer.
The large mug of hot tea has more thermal energy because it: A) contains more water and B) the water
in it is hotter.
16. Circle one of the following apparatuses and explain in detail how it works. Include a full explanation, an
energy conversion diagram, and an energy transfer diagram.
Pendulum Bouncing Ball Rolling Coffee Can
See full explanation of each apparatus in the teacher guide.
Energy Conversion Diagram
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 4
Energy Transfer Diagram
17. Diane and Chris are neighbors whose apartment windows face each other. They made an old-
fashioned telephone using two paper cups connected by a long string through the bottom. Each night,
they pull the string tight, and one person talks into a cup, while the other person holds the cup up to her
ear to hear. How is the sound transferred from one person’s voice to the other person’s ear?
Short-Response Rubric:
MS-PS4-2 Develop and use a model to describe that waves are reflected,
absorbed, or transmitted through various materials.
Level of Evidence of Understanding
Understanding
3 Demonstrating Student response provides clear evidence of using the
Expected dimensions* to make sense of the phenomenon. Student
Understanding is able to:
● explain how the sound energy travels from
one friend to the other.
2 Progressing Student responses provide partial evidence of using the
Toward dimensions* to make sense of the phenomenon. The
Understanding response lacks some critical information and details or
contains some errors. Student is able to:
● explain how the sound energy travels from
one friend to the other BUT the explanation
contains errors.
1 Beginning to Student response is incomplete or provides minimal
Develop evidence of using the dimensions* to make sense of the
Understanding phenomenon.
0 Not Showing Student does not respond or student response is
Understanding inaccurate, irrelevant, or contains insufficient evidence of
using the dimensions* to make sense of the
phenomenon.
*As outlined in the Performance Expectations (PE) of the NGSS, the three
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 5
dimensions are the disciplinary core ideas (DCI), science and engineering
practices (SEP), and crosscutting concepts (CCC). Note that due to the complexity
of the PEs, individual assessment items may not address all three dimensions.
Scoring Notes:
The sound energy from one person’s voice causes the air molecules inside the cup to vibrate.
The vibration transfers energy to the bottom of the cup, where the string is attached, causing
the string to vibrate. The vibration in the string travels from the bottom of the cup through the
tight string, all the way to the bottom of the other cup. This causes the air molecules inside the
other cup to vibrate and enter someone’s ear. This makes sound that they can hear as it travels
through the air when the string vibrates.
18. Miguel claims that as a ball falls, it loses potential energy. Izzy claims that as a ball falls, it gains
kinetic energy. Can both students be correct? Describe the evidence which would support either
student.
MS-PS3-5. Construct, use, and present arguments to support the claim that when the
motion energy of an object changes, energy is transferred to or from the object.
Level of Evidence of Understanding
Understanding
2 Demonstrating Student response provides clear evidence of using the
Expected dimensions* to make sense the specific phenomenon.
Understanding Student is able to:
· describe the evidence that supports either that as a ball
falls, it loses potential energy OR that as a ball falls, it gains
kinetic energy.
1 Progressing Student response provides partial evidence of using the
Toward dimensions* to make sense the specific phenomenon. The
Understanding response lacks some critical information and details or
contains some errors. Student is able to:
· describe the evidence that supports either that as a ball
falls, it loses potential energy OR that as a ball falls, it gains
kinetic energy BUT the description is partially correct or is
missing parts.
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 6
0 Not Showing Student does not respond or student response is inaccurate,
Understanding irrelevant, or contains insufficient evidence of using the
dimensions* to the specific phenomenon.
*As outlined in the Performance Expectations (PE) of the NGSS, the three dimensions are the disciplinary core ideas
(DCI), science and engineering practices (SEP), and crosscutting concepts (CCC). Note that due to the complexity of the
PEs, individual assessment items may not address all three dimensions.
Scoring notes:
● Both students can be correct. Evidence of decreasing energy is the decreasing sound
the ball makes on impact [or the decreasing height at which it rebounds]. Evidence of
jincreasing kinetic energy is that a ball falling with greater force initially has a louder
sound when it hits something, like a floor.
19. In 1908, a meteorite impact occurred in Russia. The dashed line indicates the area in which the
fireball that hit the surface of the Earth flattened millions of trees.
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 7
(Image source: https://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/ciencia/esp_ciencia_tunguska01.htm)
Content source: https://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2008/30jun_tunguska/
Part 1: Which characteristics of the meteorite are supported by the data in the map? (Select all that
apply.)
A. had a large mass
B. was falling at a high speed
C. had a large amount of kinetic energy when falling
D. was travelling from a very long distance in the solar system
Part 2: Explain your choice(s) using the map data as evidence.
To flatten trees for over 25 km, the meteorite had to hit the Earth with a great impact. Because the
amount of force is determined by mass and speed, I chose A and B. Because kinetic energy is related
to how fast something is moving, I also chose C. There is no way to know how far the meteorite
travelled, so I didn’t choose D.
20. Hydropower plants are a type of hydroelectric plant. Here are some steps in the process of
generating electricity at these types of plants.
1. Energy is stored in water found in reservoirs located at low elevations.
2. The water is pumped to higher elevations.
3. The water is then released, and then falls due to gravity.
4. Falling water enables turbines to turn, increasing energy and generating an electrical
current.
5.
Part 1: Which change would decrease the amount of potential energy in the hydropower plant system?
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 8
A. Increasing the capacity of the reservoir.
B. Increasing the length of time the water is stored in the reservoir.
C. Decreasing the amount of water falling onto the turbines.
D. Decreasing the height between the reservoir and the location where the water is
released.
Part 2: Explain your answer.
An object has more gravitational energy the further it is from Earth’s center. So, the higher the water is
when it is released (falls), the more energy it can produce. If the height of the reservoir were
decreased, the system would produce less energy as the turbine would not turn as quickly to generate
electricity.
21.
(Image source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Half-Pipe_Vert_Ramp.svg)
The diagram shows a type of ramp called a half-pipe that skateboarders and snowboarders use to
perform high jumps and tricks in the air.
Part 1: How does the energy compare when the skateboarder is on the bottom of the ramp versus
when the skateboarder is in the air performing a trick?
A. The skateboarder has less gravitational energy on the bottom and more kinetic energy in
the air.
B. The skateboarder has more gravitational energy on the bottom and less in the air.
C. The skateboarder has more kinetic energy on the bottom and more gravitational energy in
the air.
D. The skateboarder has less kinetic energy on the bottom and more kinetic energy in the air.
Part 2: Explain your answer.
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 9
The skateboarder has more kinetic energy when they are moving along the sides and bottom of the half
pipe. When they are highest in the air, and furthest from Earth, the amount of gravitational energy is the
greatest. The lose gravitational energy as they move closer to Earth’s surface, and they gain kinetic
energy at the same time.
PS2-Why Do Some Things Stop While Others Keep Going? Page 10
You might also like
- Student Activity Packet SC-1.2Document3 pagesStudent Activity Packet SC-1.2Kenneth ReedNo ratings yet
- Navigating The College Financial Aid MazeDocument33 pagesNavigating The College Financial Aid MazeMike Rosich Sr.No ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE Quarter 1 Notes (ALL)Document28 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE Quarter 1 Notes (ALL)Eunise Punzalan Oprin100% (1)
- Itemized Deductions - Taxes Paid 2021Document2 pagesItemized Deductions - Taxes Paid 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Piecewise FunctionDocument3 pagesPiecewise FunctionPauline Jann SalangaNo ratings yet
- Nosware: How To Reset Epson L3110 PrinterDocument16 pagesNosware: How To Reset Epson L3110 PrinterCristel Anne Amoranto LlamadorNo ratings yet
- Google Search - Master Class: Summary of The TricksDocument7 pagesGoogle Search - Master Class: Summary of The TricksFede HansNo ratings yet
- Physics: Chapter 2 (F4) Linear MotionDocument4 pagesPhysics: Chapter 2 (F4) Linear MotionKai YuanNo ratings yet
- Sample Formative AssessmentDocument7 pagesSample Formative AssessmentCARICRIS MARATANo ratings yet
- Physical Science Test 1 PDFDocument5 pagesPhysical Science Test 1 PDFEvan Marey AntoneNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Test - Physical ScienceDocument4 pages1st Quarter Test - Physical ScienceArven DulayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 GravitationDocument42 pagesChapter 8 GravitationNitish MehraNo ratings yet
- E Reference LibraryDocument72 pagesE Reference LibraryCheryl Morris WalderNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Motion and Forces WorksheetDocument3 pagesPhysical Science Motion and Forces WorksheetErnesto GullodNo ratings yet
- WLP-Week 6Document15 pagesWLP-Week 6Justin Abad Fernandez100% (1)
- Design Theory, Gestalt and CompositionDocument231 pagesDesign Theory, Gestalt and CompositionJojomay2100% (1)
- Problems On Fluid PropertiesDocument1 pageProblems On Fluid Propertieshibarik_475% (4)
- 10 Highest Paying PHD DegreesDocument8 pages10 Highest Paying PHD DegreesSteven OsharenaNo ratings yet
- Hse Study and Practice Test ResourcesDocument4 pagesHse Study and Practice Test ResourcesthinkpadNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: Teaching Dates and Time 9:42-10:42 Neptune, 10:42-11:42 Pluto, 2:00-3:00 SPS de Vega, 3:30-4:30 GalaxyDocument2 pagesI. Objectives: Teaching Dates and Time 9:42-10:42 Neptune, 10:42-11:42 Pluto, 2:00-3:00 SPS de Vega, 3:30-4:30 GalaxyQueeny Cor100% (1)
- Third Quarter Lesson Plan in Science VI Week 4 Day 1 ContentDocument13 pagesThird Quarter Lesson Plan in Science VI Week 4 Day 1 ContentLenz Bautista100% (1)
- Genchem1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenchem1 ReviewerCrystal Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Science8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-EnergyDocument20 pagesScience8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-EnergyJarred LazoNo ratings yet
- ESM 3124 Intermediate Dynamics, HW2Document5 pagesESM 3124 Intermediate Dynamics, HW2skyone100% (1)
- Lecture Notes On CE HeatDocument44 pagesLecture Notes On CE HeatRichard WongNo ratings yet
- Science8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Document23 pagesScience8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Keith Genesis Ruiz AglubaNo ratings yet
- Science7 q3 Mod5 Week6 Heat-TransferDocument24 pagesScience7 q3 Mod5 Week6 Heat-TransferJaken MackNo ratings yet
- IIT Class XI Phy Rotation MotionDocument70 pagesIIT Class XI Phy Rotation MotionDivyanshu Verma100% (2)
- DLP (Module 2)Document6 pagesDLP (Module 2)JeanRachoPaynandosNo ratings yet
- Signed-Off Science8 q1 Mod3 PotentialAndKineticEnergy Axaxv2Document23 pagesSigned-Off Science8 q1 Mod3 PotentialAndKineticEnergy Axaxv2sei gosa100% (4)
- Art Appreciation Course Material PrototypeDocument22 pagesArt Appreciation Course Material PrototypeJohnRowenPerjeDiana0% (1)
- Our Lady of Lourdes UniversityDocument2 pagesOur Lady of Lourdes UniversityPhysical ScienceNo ratings yet
- SP20 English Composition IIDocument9 pagesSP20 English Composition IIJacinta YandersNo ratings yet
- 1 What Is Art. Ch1Document114 pages1 What Is Art. Ch1Emily Gonzalez (Student OVHS)No ratings yet
- Problem - Counting InversionsDocument4 pagesProblem - Counting InversionsSalman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pacing Guide hs3 Spring2017Document3 pagesPacing Guide hs3 Spring2017api-319728952No ratings yet
- Earn Income - CompleteDocument20 pagesEarn Income - Completeapi-507790029No ratings yet
- Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity and Its Futuristic AspectsDocument2 pagesEinstein's Special Theory of Relativity and Its Futuristic AspectsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- CalculusSongs01 17-1Document2 pagesCalculusSongs01 17-1Cocoa SpiceNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation Lesson v1Document23 pagesArt Appreciation Lesson v1monique diane100% (1)
- Psychic Intuitive Management For Our Modern AgeDocument20 pagesPsychic Intuitive Management For Our Modern AgeCommercial ScoutsNo ratings yet
- A Survey On News Web Video Event MiningDocument3 pagesA Survey On News Web Video Event MiningAggie VargheseNo ratings yet
- Banking For Lit & L1Document37 pagesBanking For Lit & L1successintesl75% (4)
- Plate Tectonics Web Quest StudentDocument8 pagesPlate Tectonics Web Quest Studentapi-3304629350% (1)
- Managing Money Curriculum: Module 3: Applying For A LoanDocument22 pagesManaging Money Curriculum: Module 3: Applying For A LoanJerico OflariaNo ratings yet
- Scientific MethodDocument1 pageScientific MethodJason ShumwayNo ratings yet
- Softball Stealing Bases Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesSoftball Stealing Bases Lesson PlankatykohliNo ratings yet
- Exponential FormsDocument4 pagesExponential FormsWella Wella WellaNo ratings yet
- Deadliest Prisons On EarthDocument5 pagesDeadliest Prisons On Earth105705No ratings yet
- Sub Folder Contents2012-13Document7 pagesSub Folder Contents2012-13Lee Ann SpillaneNo ratings yet
- Grade5 Geometry PDFDocument4 pagesGrade5 Geometry PDFEduGainNo ratings yet
- First Quarter DLL June 26 29Document3 pagesFirst Quarter DLL June 26 29BabyrrechBalilu100% (1)
- Lesson 3. Kinetic and Potential EnergyDocument11 pagesLesson 3. Kinetic and Potential Energyellenquest528No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science Quarter 3Document13 pagesLesson Plan in Science Quarter 3Richez VillaranNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAMINATION IN STP - Analiza CentillesDocument5 pagesFINAL EXAMINATION IN STP - Analiza Centillesamiel pugatNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAMINATION IN STP - Analiza CentillesDocument5 pagesFINAL EXAMINATION IN STP - Analiza Centillesamiel pugatNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ScienceDocument13 pagesLesson Plan ScienceActions Avon100% (1)
- Quarter 1 - Module 3: Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: ScienceDocument20 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 3: Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: ScienceMarie Diana B. DagadagNo ratings yet
- For DemoDocument15 pagesFor DemoGrace T Kalif100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Grade 8Document24 pagesLesson Plan Grade 8Constantino de Guzman Batay-an Jr.100% (1)
- Tareas OptativasDocument6 pagesTareas OptativasLeomar González OlmosNo ratings yet
- 7 - Q4 ScienceDocument20 pages7 - Q4 Sciencemaximo meridaNo ratings yet
- Energy in The Playground and Amusement Park: Bridge Program in ScienceDocument26 pagesEnergy in The Playground and Amusement Park: Bridge Program in ScienceHomes EreñoNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 1 Energy Module 1Document23 pagesScience Quarter 1 Energy Module 1Yannah. cysam50% (2)
- Balawag Lesson PlanDocument14 pagesBalawag Lesson PlanGrace T KalifNo ratings yet
- Semi - Science - Work, Energy, and PowerDocument2 pagesSemi - Science - Work, Energy, and PowerCristine ObialNo ratings yet
- Science8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy FINAL07282020Document17 pagesScience8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy FINAL07282020Grayson RicardoNo ratings yet
- Energy DiagnosticDocument3 pagesEnergy Diagnosticapi-426620800No ratings yet
- What Are The Functions of The Cell Wall and Cell Membrane?Document6 pagesWhat Are The Functions of The Cell Wall and Cell Membrane?api-426620800No ratings yet
- Dramatic Growth AssessmentsDocument9 pagesDramatic Growth Assessmentsapi-426620800No ratings yet
- Book 1Document1 pageBook 1api-426620800No ratings yet
- Student RubricDocument1 pageStudent Rubricapi-426620800No ratings yet
- 1534700046-Ic2 3Document16 pages1534700046-Ic2 3api-4266208000% (1)
- Lesson 11Document7 pagesLesson 11api-426620800No ratings yet
- BuggsDocument1 pageBuggsapi-426620800No ratings yet
- API EG - USE.ELEC - KH.PC DS2 en Excel v2 4251410Document67 pagesAPI EG - USE.ELEC - KH.PC DS2 en Excel v2 4251410upper paunglaungNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 VocabularyDocument4 pagesGrade 3 VocabularyBarbyannNo ratings yet
- Dpp-3 (Electrostatic Potential)Document8 pagesDpp-3 (Electrostatic Potential)AayushNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument48 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceParvatham VijayNo ratings yet
- Physics F4C3 Gravitation BI (Student's Copy) 3.1-3.3Document30 pagesPhysics F4C3 Gravitation BI (Student's Copy) 3.1-3.3Nurul alya Qistina sulaimanNo ratings yet
- 1201gravity BINGDocument12 pages1201gravity BINGDjayusYusNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass QUESTIONDocument12 pagesCentre of Mass QUESTIONrgcsm88100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Statics. Basic Concepts and AxiomsDocument38 pagesLecture 1 Statics. Basic Concepts and AxiomsДана Қарасайқызы100% (1)
- Centripetal Force LabDocument8 pagesCentripetal Force LabGrant BrownNo ratings yet
- Ch26 Giancoli7e ManualDocument24 pagesCh26 Giancoli7e ManualRMNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Male and Female Body Segment Parameters of TheDocument8 pagesEstimation of Male and Female Body Segment Parameters of TheTitiwat Triwong100% (1)
- CJC Prelim Paper 1 AnsDocument8 pagesCJC Prelim Paper 1 Ansnewtonian_physicsNo ratings yet
- Faraday's LawDocument7 pagesFaraday's Lawlemuel mabilinNo ratings yet
- High School Chemistry WorkbookDocument197 pagesHigh School Chemistry WorkbookJeon Jungkook 전정국No ratings yet
- Momentum, Impulse, Conservation of MomentumDocument53 pagesMomentum, Impulse, Conservation of MomentumIñigo de LoyolaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Preprint Tort 1 PDFDocument5 pages2014 Preprint Tort 1 PDFElaine MarrielNo ratings yet
- Online Review AnswersDocument15 pagesOnline Review AnswersdebshistoryfairNo ratings yet
- Muma - Mulenga 1586370412 A PDFDocument8 pagesMuma - Mulenga 1586370412 A PDFBethelNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering NotesDocument216 pagesMechanical Engineering NotesvelavansuNo ratings yet
- FY4 IB 2017 WithcircularDocument15 pagesFY4 IB 2017 WithcircularTrương Quốc HuyNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument46 pagesEngineering MechanicsAnonymous Zx7EG1PaNo ratings yet
- Physics - Forces & EnergyDocument2 pagesPhysics - Forces & EnergyMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- 2.EMT Question PapersDocument3 pages2.EMT Question PapersPraveen RajkumarNo ratings yet