Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guided Notes For Derivatives Lecture
Uploaded by
api-450379473Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guided Notes For Derivatives Lecture
Uploaded by
api-450379473Copyright:
Available Formats
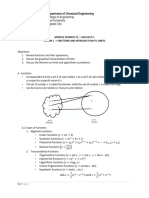
Derivatives
Guided Notes
𝐷𝑖𝑠𝑝𝑙𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡
Constant velocity=
Not constant Velocity from Halfway to Cafeteria =
Current Velocity (Not Constant) =
𝑑𝑦
Derivative is defined as 𝑑𝑥 = _____________
f(x) in this equation is equivalent to the _________ in our running example.
x in this equation is equivalent to the _________ in our running example.
𝑑𝑦
in this equation is equivalent to the _________ in our running example.
𝑑𝑥
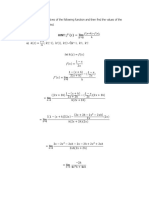
Examples f(x)=𝒙𝟐 + 𝟒
((𝑥 + ℎ)2 + 4) − (𝑥 2 + 1)
f(x)=x+1 𝑑(𝑥 2 +4) lim
𝑑(𝑥+1) lim ((𝑥 + ℎ) + 1) − (𝑥 + 1)
= ℎ→0 ℎ
𝑑𝑥 (𝑥 2 + 2𝑥ℎ + ℎ2 + 4) − (𝑥 2 + 4)
= ℎ→0 ℎ 𝑑(𝑥 2 +4) lim
𝑑𝑥 = ℎ→0 ℎ
𝑑(𝑥+1) 𝑥+ℎ+1−𝑥−1
lim
= ℎ→0 𝑑𝑥 𝑥 2 + 2𝑥ℎ + ℎ2 + 4 − 𝑥 2 − 4
𝑑𝑥 ℎ 𝑑(𝑥 2 +4) lim
ℎ = ℎ→0 ℎ
𝑑(𝑥+1) lim 𝑑𝑥
= ℎ→0 ℎ 2𝑥ℎ + ℎ2
𝑑𝑥 𝑑(𝑥 2 +4) lim
𝑑(𝑥+1) lim 1 = ℎ→0 ℎ
= ℎ→0 𝑑𝑥
𝑑𝑥 𝑑(𝑥 2 +4) lim 2𝑥 + ℎ
ℎ→0
𝑑(𝑥+1) =
=1 𝑑𝑥
𝑑𝑥 𝑑(𝑥 2 +4)
= 2x
𝑑𝑥
𝑑𝑦
What is 𝑑𝑥 of these functions?
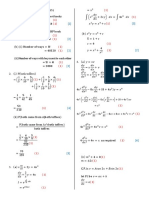
f(x)=𝑥 2 + x + 6
f(x)=√𝑥
f(x)=𝑙𝑛𝑥
f’(x) means ____________________
f’(1) means ____________________
Find f’(π) for the following functions.
f(x)=𝑥 2 − 15
f(x)=12
f(x)=cos(𝑥)
Thinking Differently Function Derivative
Derivative = _________.
𝑥2
Shortcut Method 𝑥3
For functions of the form f(x)=
𝑥 𝑛 , where n is a ________ the
derivative is ________.
4𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2
𝑥 3 + 4𝑥 2
If f(x)=n(g(x)), where n is a __________ then f’(x)= ___________.
If f(x)=g(x)+h(x) then f’(x)=______________.
Find f’(2) using the shortcut method for the following functions.
f(x)=𝑥 2 − 15
f(x)=12
f(x)=𝑥 2 + x + 6
Summary Questions:
Find f’(x) using the definition of a derivative.
f(x)=4𝑥 2 − 2x + 6
Find f’(x) using the shortcut method for finding derivatives.
f(x)=12𝑥 2 − 6x + 9821821223
You might also like
- Hyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandHyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET 2.2 (Hal. 105) : Use The Definition For 2 and 4Document14 pagesPROBLEM SET 2.2 (Hal. 105) : Use The Definition For 2 and 4Ridho PranataNo ratings yet
- Q2 General Mathematics ReviewerrrDocument1 pageQ2 General Mathematics ReviewerrrGian Carlo ValenzonNo ratings yet
- BintangChandra KalkulusDocument6 pagesBintangChandra KalkulusRising ForceNo ratings yet
- Fase 1 1. Principio de SustituciónDocument5 pagesFase 1 1. Principio de Sustituciónjuan camilo mendozaNo ratings yet
- The Derivative As The Slope of The Tangent Line: Grade 11-KeplerDocument17 pagesThe Derivative As The Slope of The Tangent Line: Grade 11-KeplerXzyle1213No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Continuity of FunctionsDocument6 pagesLesson 3 Continuity of FunctionsLarisha Jan PomboNo ratings yet
- Variable SeparableDocument7 pagesVariable SeparableJesus David Ochoa VilaroNo ratings yet
- Differenciation CalculusDocument18 pagesDifferenciation CalculusauniNo ratings yet
- EE 301 Signals & Systems Homework 2 Solutions: Problem 1Document12 pagesEE 301 Signals & Systems Homework 2 Solutions: Problem 1Cankan ÇelikNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Part 2Document4 pagesMathematics - Part 2Francis Rafael FlorNo ratings yet
- Tugas MTK (SP)Document4 pagesTugas MTK (SP)teguh imam pradhonggoNo ratings yet
- Math 130 Revesion ExamDocument9 pagesMath 130 Revesion ExamaymanNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument25 pagesReviewjfbv549No ratings yet
- Unidad III Límites y ContinuidadDocument16 pagesUnidad III Límites y ContinuidadAndy CuaicalNo ratings yet
- Actividad Nivel Inicial Julian ZabaletaDocument7 pagesActividad Nivel Inicial Julian ZabaletaJz PdNo ratings yet
- Sustituciones Trigonometricas PDFDocument4 pagesSustituciones Trigonometricas PDFJeffer MendezNo ratings yet
- Sustituciones Trigonometricas PDFDocument4 pagesSustituciones Trigonometricas PDFJeffer MendezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Working With Functions1 1Document8 pagesChapter 2.1 Working With Functions1 1Enkhjin OtgonbatNo ratings yet
- Section 2.4 Precise Definition of The LimitDocument8 pagesSection 2.4 Precise Definition of The LimitInitsigan KatangkayNo ratings yet
- 2da PC CÁLCULODocument8 pages2da PC CÁLCULOSara Liz GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Engineering Analysis: Faculty of Engineering Petroleum EngineeringDocument12 pagesEngineering Analysis: Faculty of Engineering Petroleum EngineeringNazeer AlyasNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 Integration of Distinct Quadratic Factors Examples and SolutionDocument3 pagesCalculus 2 Integration of Distinct Quadratic Factors Examples and SolutionJulie Ann MontalbanNo ratings yet
- PPTCH3SEM4pdf__2024_03_27_10_44_09Document55 pagesPPTCH3SEM4pdf__2024_03_27_10_44_09adityarajaj189No ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Derivative (Increment Method) PDFDocument5 pagesLecture 03 - Derivative (Increment Method) PDFKors Min YeolNo ratings yet
- Ejemplos de DerivadasDocument4 pagesEjemplos de Derivadascallisayagutierrezasucena4No ratings yet
- Partial Fraction Decomposition SummarisedDocument15 pagesPartial Fraction Decomposition SummarisedLuckson MulanshiNo ratings yet
- Applied Math Assignment Functions Limits ContinuityDocument2 pagesApplied Math Assignment Functions Limits ContinuityGautamNo ratings yet
- The-Derivative-as-the-Slope-of-the-Tangent-LineDocument5 pagesThe-Derivative-as-the-Slope-of-the-Tangent-Lineshprimero2020No ratings yet
- General Rules of Derivatives: Lecturer: Hakima Kh. AhmedDocument10 pagesGeneral Rules of Derivatives: Lecturer: Hakima Kh. AhmedKasar nagib 2002No ratings yet
- Calculus - Limit ConceptDocument14 pagesCalculus - Limit Conceptchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- DERIVATIVE OF A FUNCTIONDocument43 pagesDERIVATIVE OF A FUNCTIONJoey TelinNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Fundamental Definition of DerivativeDocument4 pagesLecture On Fundamental Definition of DerivativeKing HarlequinNo ratings yet
- 04 - HW Derivatives ProblemsDocument3 pages04 - HW Derivatives ProblemsMaxNo ratings yet
- Araneta All Problem Sets Exams Practice Exams Math 83Document55 pagesAraneta All Problem Sets Exams Practice Exams Math 83Marvince AranetaNo ratings yet
- Functions and Relations activity solutionsDocument3 pagesFunctions and Relations activity solutionsCeyola Audrey GazmenNo ratings yet
- Math22 1ReviewerDerivativeTrigonometricFunctionDocument6 pagesMath22 1ReviewerDerivativeTrigonometricFunctionanon_422073337No ratings yet
- Euler Substitution and Ostrogardsky Integration Method For Proper Rational FunctionsDocument5 pagesEuler Substitution and Ostrogardsky Integration Method For Proper Rational FunctionsKeith Lester Mallorca100% (1)
- LIMITSDocument23 pagesLIMITSLyka BalacdaoNo ratings yet
- The DerivativeDocument4 pagesThe Derivativesidrajaffri72No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Functions and Introduction to LimitsDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - Functions and Introduction to Limitskylahernandez2022No ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales - Puntos de LaplaceDocument7 pagesEcuaciones Diferenciales - Puntos de LaplaceJuan Pablo Ramirez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- VC & FT Worked Out Examples (R 19) (ALL UNITS)Document135 pagesVC & FT Worked Out Examples (R 19) (ALL UNITS)Harsha KumarNo ratings yet
- Solución Semana 8 Análisis MatemáticoDocument16 pagesSolución Semana 8 Análisis MatemáticoElvis CalderonNo ratings yet
- Clase Virtual - ContinuidadDocument13 pagesClase Virtual - ContinuidadPeter NarvaezNo ratings yet
- (A) (I) Number of Ways To Choose 6 BooksDocument2 pages(A) (I) Number of Ways To Choose 6 BookskkkkllllNo ratings yet
- Chain Product Quotient Tough RecapDocument7 pagesChain Product Quotient Tough RecaparinizzataNo ratings yet
- Homework On Separable and Linear ODE: Mathematics IVDocument4 pagesHomework On Separable and Linear ODE: Mathematics IVAmmar MedeniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note On CalculusDocument94 pagesLecture Note On CalculusFarhan NiloyNo ratings yet
- Activities 1-10 (Derivatives)Document12 pagesActivities 1-10 (Derivatives)Angelou FelisildaNo ratings yet
- Inverse functionsDocument10 pagesInverse functionsJerom Lexther Mission EsposoNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS DERIVATIVESDocument13 pagesCALCULUS DERIVATIVESAliza FatymaNo ratings yet
- Deribatuak 1Document6 pagesDeribatuak 1loreaxiangcanceloNo ratings yet
- D091201056 - Akbar Suparman Panggalo - TugasMatekDocument9 pagesD091201056 - Akbar Suparman Panggalo - TugasMatekhasma saniaNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo de CalculoDocument24 pagesCuadernillo de CalculoFernanda FarreraNo ratings yet
- Calculate Tangent Lines and DerivativesDocument30 pagesCalculate Tangent Lines and DerivativesLarisha Jan PomboNo ratings yet
- Practico N°2 - RUA 4445Document18 pagesPractico N°2 - RUA 4445Carlos J. F. ChoqueNo ratings yet
- Recurso - 1704387140156 - Semana 01 - ÁlgebraDocument5 pagesRecurso - 1704387140156 - Semana 01 - ÁlgebraOrlando LozanoNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Derivative of The Algebraic FunctionsDocument9 pagesCalculus - Derivative of The Algebraic Functionschristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document12 pagesModule 3Gerwin MontevirgenNo ratings yet
- Sorting Chart ActivityDocument2 pagesSorting Chart Activityapi-450379473No ratings yet
- Commute Probability 2Document3 pagesCommute Probability 2api-450379473No ratings yet
- Tic Tac Toe RubricDocument1 pageTic Tac Toe Rubricapi-450379473No ratings yet
- Derivatives: Calculus I 11th or 12 Grade David RogersDocument20 pagesDerivatives: Calculus I 11th or 12 Grade David Rogersapi-450379473No ratings yet
- Tic Tac ToeDocument1 pageTic Tac Toeapi-450379473No ratings yet
- Education HWDocument1 pageEducation HWapi-450379473No ratings yet
- Plotting Data ProjectDocument1 pagePlotting Data Projectapi-450379473No ratings yet
- Large Deflections of Cantilever BeamsDocument4 pagesLarge Deflections of Cantilever BeamsHasan Ayouby100% (1)
- Carrfoster 2Document5 pagesCarrfoster 2SauravNo ratings yet
- Surface Area of A Semi-Cylinder WorksheetDocument1 pageSurface Area of A Semi-Cylinder WorksheetvirtualmathsNo ratings yet
- Quantum NumbersDocument2 pagesQuantum NumbersWong Weng SiongNo ratings yet
- The Relevance of YS/UTS RatioDocument21 pagesThe Relevance of YS/UTS RatiocarrespmNo ratings yet
- Colless, Matthew - The New CosmologyDocument249 pagesColless, Matthew - The New CosmologyShade SemjazaNo ratings yet
- Pemfc Modeling Mvkf25Document37 pagesPemfc Modeling Mvkf25Xiaoqiang zhangNo ratings yet
- CK Osborne Reynolds PDFDocument4 pagesCK Osborne Reynolds PDFChaminduKrishanRupasingheNo ratings yet
- 2012 - Mak - NatMater - Tightly Bound Trions in Monolayer MoS2Document5 pages2012 - Mak - NatMater - Tightly Bound Trions in Monolayer MoS2Liqin SuNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - Physics Part 2Document11 pagesTerm 1 - Physics Part 2Gaming TriadNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Flawed DomainDocument4 pagesNumerical Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Flawed DomainGrit WingsNo ratings yet
- Practice paper (2021-22) Term 1 Physics (042) Class xiDocument12 pagesPractice paper (2021-22) Term 1 Physics (042) Class xiNagendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- Lang SethDocument52 pagesLang Sethrrmerlin_2No ratings yet
- EquiprobabilityDocument2 pagesEquiprobabilitydanny222No ratings yet
- Structural Control System for Water TankDocument4 pagesStructural Control System for Water TankJOSMRIVERCNo ratings yet
- Experiment #3 / Unit 6 Calorimetry - Measuring Heat Changes During A Physical or Chemical ChangeDocument2 pagesExperiment #3 / Unit 6 Calorimetry - Measuring Heat Changes During A Physical or Chemical Changeapi-368121935No ratings yet
- Compiled FluMach Problems - GROUP6 - BSME31Document58 pagesCompiled FluMach Problems - GROUP6 - BSME31Jhun Briones100% (1)
- Troskie HJ Chapter 2Document87 pagesTroskie HJ Chapter 2Saran KuttyNo ratings yet
- JJHJHHJHDocument6 pagesJJHJHHJHjayarNo ratings yet
- Shown.: Example: Determine The Vertical and Horizontal Deflections at The Point B of The TrussDocument3 pagesShown.: Example: Determine The Vertical and Horizontal Deflections at The Point B of The TrussNitin rajputNo ratings yet
- Ossd U1Document26 pagesOssd U1huangjunxiang4No ratings yet
- Lectu 14Document4 pagesLectu 14YeviraArinDiyanaNo ratings yet
- Noise Level Calculations: Example #1Document2 pagesNoise Level Calculations: Example #1Susheel WankhedeNo ratings yet
- Moments, Levers and Gears 3 QPDocument19 pagesMoments, Levers and Gears 3 QPdeepheat_008No ratings yet
- Solution Recording and Playback Vortex SheddingDocument27 pagesSolution Recording and Playback Vortex SheddingerenNo ratings yet
- Models - Mph.heat Transient AxiDocument6 pagesModels - Mph.heat Transient AxiAnonymous sAmJfcVNo ratings yet
- WKST - 1.4 Converting Graphs - ChallengeDocument8 pagesWKST - 1.4 Converting Graphs - Challengefaltu accountNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document55 pagesChapter 1nur izzah fatiniNo ratings yet
- To Determine Angle of Minimum Deviation For A Given Prism by Plotting A Graph Between Angle of Incidence and Angle of Deviation PDFDocument6 pagesTo Determine Angle of Minimum Deviation For A Given Prism by Plotting A Graph Between Angle of Incidence and Angle of Deviation PDFriyanmedhi04No ratings yet
- Catalogo Raycap Baja TensionDocument250 pagesCatalogo Raycap Baja TensionDomingo RuizNo ratings yet