Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Frozen Fish?: Is It Better To Buy Fresh or
Uploaded by
agubarboOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Frozen Fish?: Is It Better To Buy Fresh or
Uploaded by
agubarboCopyright:
Available Formats
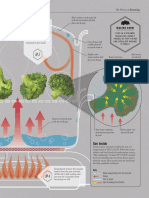
080 // 081 The Science of Fish and Seafood
Is it better to buy fresh or
FROZEN FISH?
Freezing fish halts the growth of bacteria and microbes,
and muscle-digesting enzymes in fish are stalled.
FLAVOR TRANSFER
Fragile fish oils quickly turn rancid crystal damage is negligible,
F L AV O R M O L E C U L E S F R O M
and natural bacteria that coat them and texture and taste are almost PA R C H M E N T- B A K E D F ISH
breed well in the fridge (see p68). identical to a fresh fish. But S E E P O U T IN T O T H E L IQU I D
Fish can be frozen with more low-powered home freezing will B R OT H A N D CA N B E K E PT
FOR A SAUCE BASE.
success than other meats as their damage delicate fish proteins.
flexible muscle membranes suffer So, if fish has been caught very
less damage from sharp ice crystals. recently and kept on ice, fresh is
If “flash frozen” (see below), ice best, otherwise buy it prefrozen.
KNOW THE DIFFERENCE
KNOW THE DIFFERENCE
Parchment
Flash-freezing fish Home freezing fish Baking fish in parchment, en papillote,
Industrial blast freezers freeze fish Low-powered home freezers freeze traps in moisture and gives a similar
rapidly to limit ice crystal formation. slowly, allowing ice crystals to form. effect to slow-poaching fish (see p83).
Freezing often starts on board The liquid in fish is a salty mix
ships to halt spoilage, with fish of proteins and minerals. The salt What is it? Fish is baked in a
cooled to around –22ºF (-30ºC). lowers the freezing point, which tightly sealed parchment or foil
Once on shore, industrial freezer slows home freezing even further, pouch. Parchment typically has
chambers blast fish with –40ºF increasing damage to muscle proteins a nonstick silicone coating, giving
(–40ºC) air to finish freezing rapidly. from slowly expanding ice crystals. insulation that slows heat transfer
from the pan. Most foil isn’t
nonstick and transfers heat
more rapidly.
Best for: Ideal for cooking fillets.
Herbs, spices, and vegetables can
Can I cook fish be added to suffuse the outer layers.
FROM FROZEN? Uncovered
As with oven roasting meats, the outer layers
Cooking from frozen increases cooking time, but has benefits, too. of fish baked without a covering can dry, but
this can be a good method for whole fish.
Cooking smaller fish from frozen Ice crystals melt slowly in fish, How the fish cooks: Fish is baked
in the oven without a covering, with
works perfectly well. Large cuts of increasing cooking time, but this added oils and flavorings. Cooking is
fish, and whole fish, run the risk of delay can help to achieve crisp skin slow and the outer layers dry as heat
moves into the center.
being uncooked in the center and without the center overcooking.
burnt on the outside, so should be If you do thaw fish, do this Best for: This is ideal for whole fish.
thawed before cooking. either on a rack in the fridge with Although the outer layers of the fish
dry, as the surface temperature soars,
Thin- to medium-thickness a drip tray beneath, or put fish in the skin is crisped and browned while
fillets cooked from frozen can a sealed bag in a bowl of icy water. the center cooks gently.
rival fresh fish in taste and Water speeds thawing, and
texture, and may even surpass keeping it very cold helps
them if a crispy skin is called for. prevent bacteria from breeding.
You might also like
- Seafood Recipes Cookbook: Top 75 Super Delicious Seafood Recipes To Enjoy Again And AgainFrom EverandSeafood Recipes Cookbook: Top 75 Super Delicious Seafood Recipes To Enjoy Again And AgainNo ratings yet
- Smoking Fish at Home: University of Alaska FairbanksDocument4 pagesSmoking Fish at Home: University of Alaska FairbanksmajstorNo ratings yet
- Home Preservation of Fish - OhiolineDocument6 pagesHome Preservation of Fish - Ohiolinevict57No ratings yet
- Q2 MODULE7 Cookery G10-Rosales-NHSDocument9 pagesQ2 MODULE7 Cookery G10-Rosales-NHSfishguadagraceNo ratings yet
- Different Ways in Cooking SeafoodDocument10 pagesDifferent Ways in Cooking SeafoodChristian Daniel BatoctoyNo ratings yet
- Fish and SHellfish Cooking MethodsDocument31 pagesFish and SHellfish Cooking MethodsLeslie Jane S. BlancaflorNo ratings yet
- 3-7-22 - Handling, Cooking Techniques, Methods and Guidelines For Cooking of Fish and ShellfishDocument34 pages3-7-22 - Handling, Cooking Techniques, Methods and Guidelines For Cooking of Fish and ShellfishLeslie Jane S. BlancaflorNo ratings yet
- Cookery Lecture 3rd QuarterDocument14 pagesCookery Lecture 3rd Quarteredmar aguilarNo ratings yet
- CRC Article Salmon PesachDocument2 pagesCRC Article Salmon PesachM PNo ratings yet
- Finfish and Shellfish CookeryDocument14 pagesFinfish and Shellfish CookeryBrianna GrahamNo ratings yet
- BF2 PT Fish&ShellfishDocument2 pagesBF2 PT Fish&ShellfishBernadette YurongNo ratings yet
- 6 Dasar Penanganan Ikan-Pendinginan - (1) .PPSXDocument32 pages6 Dasar Penanganan Ikan-Pendinginan - (1) .PPSXalvinaNo ratings yet
- Fish and ShellfishDocument117 pagesFish and Shellfishshanley cyra aboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Curing Fish and Other Marine ProductsDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Curing Fish and Other Marine ProductsGraceCayabyabNiduaza100% (1)
- Food TechDocument17 pagesFood TechMJ BuensucesoNo ratings yet
- FAO & SIFAR (2001) - Freezing at Sea-Advice To The Crew. Torry Advisory Note No. 34 (Revised)Document10 pagesFAO & SIFAR (2001) - Freezing at Sea-Advice To The Crew. Torry Advisory Note No. 34 (Revised)Anonymous YnnVMFpAr7No ratings yet
- Module11 HE2 C2Document7 pagesModule11 HE2 C2Ruth CesistaNo ratings yet
- Handling Offshore Catch On Board: by Jon BellDocument2 pagesHandling Offshore Catch On Board: by Jon BellMikhlal DjvNo ratings yet
- Tle 10Document62 pagesTle 10Marykie CaserNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Fishery Products - Hand OutDocument13 pagesPreparation of Fishery Products - Hand OutRushini SilvaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Region V Division of City Schools Cararayan National High SchoolDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education Region V Division of City Schools Cararayan National High SchoolLoli Gonzales ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- Part 4Document4 pagesPart 4Andrae AtinajaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood Dishes: Science Lesson - Teacher Ruru's ClassDocument51 pagesLesson 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood Dishes: Science Lesson - Teacher Ruru's ClassDanica Joy Ocampo Dianzon100% (1)
- With Their Heads On?: Is It Better To Buy ShrimpDocument1 pageWith Their Heads On?: Is It Better To Buy ShrimpagubarboNo ratings yet
- Seafood Safety: What Consumers Need To Know: Sea GrantDocument2 pagesSeafood Safety: What Consumers Need To Know: Sea GrantSotiris KourosNo ratings yet
- FNH Part 4Document15 pagesFNH Part 4JessicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood Dishes Tle 10Document10 pagesLesson 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood Dishes Tle 10Kimby Ventuzo100% (1)
- Fish and ShellfishDocument45 pagesFish and ShellfishShommer ShotsNo ratings yet
- Handling and Storage of FishDocument14 pagesHandling and Storage of Fishelara diorNo ratings yet
- Weeks 001-003 Cookery 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood Dishes (PartI)Document8 pagesWeeks 001-003 Cookery 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood Dishes (PartI)Mark John Paul Cabling100% (1)
- Q2 Grade 10 Tle W7 Handling Fresh and Frozen Sea FoodDocument35 pagesQ2 Grade 10 Tle W7 Handling Fresh and Frozen Sea Foodlemon limeNo ratings yet
- Fish Handling and ProcessingDocument31 pagesFish Handling and ProcessingSirVictor Dizon AquinoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Milkfish and Some Processed FishDocument7 pagesParts of A Milkfish and Some Processed FishJoseph Adrian PadrigaNo ratings yet
- Proper Storage of FinfishDocument6 pagesProper Storage of FinfishPrincess Althea AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Preparing Fish & Wild Game: Exceptional Recipes for the Finest of Wild Game FeastsFrom EverandPreparing Fish & Wild Game: Exceptional Recipes for the Finest of Wild Game FeastsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- TLE 10 Module 23Document2 pagesTLE 10 Module 23dustinmina21No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 ChillingDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 3 ChillingMADELNo ratings yet
- Chilling Fresh FishDocument30 pagesChilling Fresh FishRousell AndradaNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Quarter 2 SeafoodsDocument24 pagesCookery 10 Quarter 2 Seafoodsmiel park100% (6)
- The Science of Saltpatrickip3Document10 pagesThe Science of Saltpatrickip3api-475334671No ratings yet
- Akuw81002 Part5Document28 pagesAkuw81002 Part5Katiusca Alexandra Paredes SalasNo ratings yet
- Fresh FishDocument23 pagesFresh FishARLENE MORADANo ratings yet
- Processing and Fish PreservationDocument13 pagesProcessing and Fish PreservationAbdiqadir JibrilNo ratings yet
- Lesson Cook SeafoodDocument2 pagesLesson Cook SeafoodCatherine Bercasio Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Fish and Sea FoodDocument9 pagesFish and Sea Fooditzmeaneesh50% (2)
- Cooking Your Catch - A Handy Guide to Cleaning, Scaling, Gutting, Dressing, Curing, Smoking, Kippering and Drying - Including Some Serving SuggestionsFrom EverandCooking Your Catch - A Handy Guide to Cleaning, Scaling, Gutting, Dressing, Curing, Smoking, Kippering and Drying - Including Some Serving SuggestionsNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 11.1 PREPARING SEAFOOD DISHESDocument2 pagesInformation Sheet 11.1 PREPARING SEAFOOD DISHESkrizylNo ratings yet
- TVE - Methods of Fish PreservationDocument6 pagesTVE - Methods of Fish PreservationRemelyn RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Persiapan Daging, Ikan, Seafood, UnggasDocument10 pagesPersiapan Daging, Ikan, Seafood, UnggasIlmi Dewi ANo ratings yet
- Riblji ReceptiDocument33 pagesRiblji ReceptiMirza MujagicNo ratings yet
- Sai 3Document9 pagesSai 3usamaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For FinalsDocument4 pagesReviewer For FinalsKyla Gail RemendoNo ratings yet
- FishDocument13 pagesFishNalin M WeerakkodyNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 6 Preparing and Cooking Seafood Dishes UPDATEDDocument52 pagesQ2 Module 6 Preparing and Cooking Seafood Dishes UPDATEDKim Russel AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Las 6 Activity: My Family Practices in Storing Sea Food TilapiaDocument2 pagesLas 6 Activity: My Family Practices in Storing Sea Food TilapiaPRINCESS JHEA ROSACAYNo ratings yet
- Tle 10. Week 10Document31 pagesTle 10. Week 10Mary Cris TandocNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Fish MongeryDocument10 pagesChapter - 2 Fish MongeryKrishna ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- SeafoodsDocument25 pagesSeafoodschristine mae calanzaNo ratings yet
- Quarter II Week 5 To Week 8Document5 pagesQuarter II Week 5 To Week 8marilyn bristolNo ratings yet
- Preparing and Cooking Fish PPT 1114 FCDocument16 pagesPreparing and Cooking Fish PPT 1114 FCDr. Mohammed SayedNo ratings yet
- Fluffy Mashed Potatoes?: How Do I MakeDocument1 pageFluffy Mashed Potatoes?: How Do I MakeagubarboNo ratings yet
- The Science of Vegetables, Fruits, Nuts, and Seeds: Fluffy Mashed PotatoDocument1 pageThe Science of Vegetables, Fruits, Nuts, and Seeds: Fluffy Mashed PotatoagubarboNo ratings yet
- High Temperatures Can Damage A Nonstick Wok. If Using Nonstick, Fry The Garlic and Ginger in Oil Over Medium Heat, Then Add The Vegetables and Sauce, and Steam Everything Under A Tight-Fitting LidDocument1 pageHigh Temperatures Can Damage A Nonstick Wok. If Using Nonstick, Fry The Garlic and Ginger in Oil Over Medium Heat, Then Add The Vegetables and Sauce, and Steam Everything Under A Tight-Fitting LidagubarboNo ratings yet
- CocinologiaDocument1 pageCocinologiaagubarboNo ratings yet
- Perfect Vegetable Stir-Fry?: What Is The Secret of TheDocument1 pagePerfect Vegetable Stir-Fry?: What Is The Secret of TheagubarboNo ratings yet
- Optimize Nutrients?: How Do I Cook Vegetables ToDocument1 pageOptimize Nutrients?: How Do I Cook Vegetables ToagubarboNo ratings yet
- Without Them Getting Soggy?: How Do I Roast VegetablesDocument1 pageWithout Them Getting Soggy?: How Do I Roast VegetablesagubarboNo ratings yet
- Steaming: The Process ofDocument1 pageSteaming: The Process ofagubarboNo ratings yet
- See Inside: Making RoomDocument1 pageSee Inside: Making RoomagubarboNo ratings yet
- Without Crying? Peppers Taste Different?: How Do I Chop An Onion Why Do Different-ColoredDocument1 pageWithout Crying? Peppers Taste Different?: How Do I Chop An Onion Why Do Different-ColoredagubarboNo ratings yet
- Season For Oysters?: When Is The BestDocument1 pageSeason For Oysters?: When Is The BestagubarboNo ratings yet
- Green Peppers Are Peppers, Rather Than: Actually Under-Ripe A Variety in Their Own Right.Document1 pageGreen Peppers Are Peppers, Rather Than: Actually Under-Ripe A Variety in Their Own Right.agubarboNo ratings yet
- Or Scrub?: Is It Better To PeelDocument1 pageOr Scrub?: Is It Better To PeelagubarboNo ratings yet
- Better Than Non-Organic?: Are Organic Fruits and VegetablesDocument1 pageBetter Than Non-Organic?: Are Organic Fruits and VegetablesagubarboNo ratings yet
- Vegetables Raw?: Is It Better To EatDocument1 pageVegetables Raw?: Is It Better To EatagubarboNo ratings yet
- Called "Insects of The Sea" Because of Their Segmented Body and "Exoskeleton" Shell, Shrimp Are The Baby-Sized Relatives of Lobsters and Crabs. They Are The Most Widely Eaten Seafood in The WorldDocument1 pageCalled "Insects of The Sea" Because of Their Segmented Body and "Exoskeleton" Shell, Shrimp Are The Baby-Sized Relatives of Lobsters and Crabs. They Are The Most Widely Eaten Seafood in The WorldagubarboNo ratings yet
- See Inside: "The High Pan-Frying Dehydrate The Surface of Foods, Creating A CrispDocument1 pageSee Inside: "The High Pan-Frying Dehydrate The Surface of Foods, Creating A CrispagubarboNo ratings yet
- Salad Dressing From Separating?: How Can I Keep MyDocument1 pageSalad Dressing From Separating?: How Can I Keep MyagubarboNo ratings yet
- With Their Heads On?: Is It Better To Buy ShrimpDocument1 pageWith Their Heads On?: Is It Better To Buy ShrimpagubarboNo ratings yet
- Srajit Srivastava Internship Report DharaDocument22 pagesSrajit Srivastava Internship Report Dharasrajit srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Processing of FoodsDocument16 pagesThermal Processing of FoodsRounak GhoshNo ratings yet
- Amul The Taste of IndiaDocument22 pagesAmul The Taste of Indiaamansrivastava007No ratings yet
- EU ARD Final Report (Final) - 0 PDFDocument191 pagesEU ARD Final Report (Final) - 0 PDFIsaac OduhoNo ratings yet
- Wic FarmersmarketDocument2 pagesWic FarmersmarketPatricia DillonNo ratings yet
- ELC501 Purpose Tone Intended Audience answERSDocument8 pagesELC501 Purpose Tone Intended Audience answERSAidilZamriNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Dietary Requirement For Children Between 4-6 YearsDocument9 pagesProject Report: Dietary Requirement For Children Between 4-6 YearsDEBOPRIYO ROYNo ratings yet
- Restart Checklist BOHDocument2 pagesRestart Checklist BOHImee S. YuNo ratings yet
- Food Science Nutrition - 2021 - Sumardiono - Influence of Composite Flour Constituents and Extrusion Temperature in The PDFDocument9 pagesFood Science Nutrition - 2021 - Sumardiono - Influence of Composite Flour Constituents and Extrusion Temperature in The PDFAlgifary SetiyonoNo ratings yet
- Linapacan ToursDocument3 pagesLinapacan ToursLeracel Collado100% (1)
- Myfoodbook-Winter Cooking With Mushrooms 2015 PDFDocument20 pagesMyfoodbook-Winter Cooking With Mushrooms 2015 PDFPedro Luis Gutierrez O.No ratings yet
- Bac English 2020 علوم تجريبيةDocument4 pagesBac English 2020 علوم تجريبيةBouhali DjamilaNo ratings yet
- 04 - sHRIMP NUTRITION AND FEED MANAGEMENTDocument26 pages04 - sHRIMP NUTRITION AND FEED MANAGEMENTpanggilajadayNo ratings yet
- The Complete Salter Air Fryer CookbookDocument212 pagesThe Complete Salter Air Fryer CookbookHelgaNo ratings yet
- Banquet Service ProceduresDocument24 pagesBanquet Service Proceduresmackybhoyamores100% (9)
- Lesson Plan Restaurant EnglishDocument10 pagesLesson Plan Restaurant Englishemma12161216100% (2)
- Organic FarmingDocument192 pagesOrganic FarmingUNIVERSAL-CREATIONSNo ratings yet
- CAC and HACCPDocument14 pagesCAC and HACCP5zy 555No ratings yet
- (Group 12) Market Research ReportDocument11 pages(Group 12) Market Research ReportNguyen Thi Hoai AnNo ratings yet
- In The (Chinese) Kitchen: AppliancesDocument3 pagesIn The (Chinese) Kitchen: AppliancespikisecondaNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Company A. CategoryDocument4 pagesOverview of The Company A. CategoryJustineNo ratings yet
- High Value Crops Development Unit: (Vegetable, Banana, Citrus, Cacao, Mango, Coffee, Mango, Rootcrops)Document4 pagesHigh Value Crops Development Unit: (Vegetable, Banana, Citrus, Cacao, Mango, Coffee, Mango, Rootcrops)Kent AlpayNo ratings yet
- 4 Cycle Rapid Fat Loss SolutionDocument22 pages4 Cycle Rapid Fat Loss SolutionRey Johnson100% (3)
- Food, Tourism, Livelihood of Cagayan ProvinceDocument9 pagesFood, Tourism, Livelihood of Cagayan ProvinceAceAmansec100% (1)
- Meatloaf-and-Tahori EditedDocument4 pagesMeatloaf-and-Tahori EditedCloue Faye I. BasalloNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report On Gulayan Sa Paaralan With Pictures 2Document8 pagesAccomplishment Report On Gulayan Sa Paaralan With Pictures 2Randy Evangelista CalayagNo ratings yet
- Survey AnalysisDocument23 pagesSurvey AnalysisHursh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Group C Latin American Buffet MenuDocument19 pagesGroup C Latin American Buffet MenuimdkingNo ratings yet
- 200 Level EAGDocument1 page200 Level EAGEAG20033 A.M.A. MadurangaNo ratings yet
- Task 2 - Notes On HappyHour Co v3Document3 pagesTask 2 - Notes On HappyHour Co v3nanschatron26No ratings yet