Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Free Distribution - Booklet Final
Uploaded by
gautamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Free Distribution - Booklet Final
Uploaded by
gautamCopyright:
Available Formats
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
SAMPLE COPY – BOOK
PSC / VYAPAM
JUNIOR / SUB / ASSISTANT ENGINEER
P a g e |1 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Author’s Message
Chattisgarh has witnessed a large increase in both Degree and Diploma holders.
Also the competition has increased in competitive exams for public sector
vacancies. Students need to apply high level effort to take an edge over other
competitors.
CGPSC / CGVYAPAM require an approach that is different from any University
Exam. The following tips may increase the efficiency and will let u achieve
success.
• Develop Basic knowledge from standard books
• Be self motivated
• Group study and discussion on regular basis
• Apply short-cuts and learn standard result and formulae
• Understanding the exam pattern
The book includes questions with answers for the benefit of the students. Our
institute GATE-CIVIL helps the students to study and practice the concept and
questions in a simplified manner which is very useful for exams.
I would appreciate further suggestions from the readers for the modification of
the book.
Gautam Gupta
(Principal Consultant – Oil and Gas, Nuclear)
gautam.gupta23@gmail.com
+91-8463016819
P a g e |2 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
GAUTAM GUPTA
B.TECH / M.TECH. (CIVIL / STRUCTURE)
14 - YRS EXPERIENCE (INDUSTRY/EDUCATION)
INDUSTRY EXPERIENCE
A wide experience from Graduate to
Principal/Lead Engineer in Aluminum Smelter
management and construction, Remote
sensing network integration for American
firms, Design of Railway units, Designing of
Structures for Oil & Gas and Nuclear units in
middle east.
He has been engaged with the projects of the
following major companies BALCO, RMSI, L&T
– RLBU, Petrochemical, PETROFAC INTL.,
FLUOR DANIEL, TECNIMONT ICB, NARGAN.
EDUCATION EXPERIENCE
A mentor for most of the students joining the main stream of private and public
sector jobs. Under his guidance a large number of students have benefitted in
terms of knowledge, innovation, training, interview.
Under the Banner of GATE CIVIL provides coaching for engineering graduates
preparing for GATE / IES / PSU.
P a g e |3 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
4 If the strain energy of a deformed
elastic body is represented as a
1 The zero
function of the displacement
force
d1,d2,…. dn a partial derivative of
members in
that function with respect to any
the truss
choosen displacement gives the
shown are
corresponding force. This statement
a. 1,9 / principle is called as
b. 2,8 a. Principle of strain energy
c. 3,7 b. Maxwell’s reciprocal theorem
d. 5,6 c. Conjugate beam method
e. No members have zero forces d. Betti’s law
e. First theorem of castigliano’s
2 The adjacent
frame is 5 Which of the following does not
indeterminate to apply to statically determinate
the degree of structures
a. Stresses are caused due to
a. 1 temperature variations
b. 5 b. No stresses are caused due to lack of
c. 0 fit
d. 3 c. Bending moment at a section is
e. 4 independent of cross sectional area
of the component
d. Force in a component is
3 For a pin jointed frame at points independent of the material
A,B,C (point B is pin jointed )the e. Conditions of the equilibrium are
horizontal component of reaction at sufficient to fully analyze the
A is structure
6 A 2D structure in general is classified
as a statically inderterminacy
structure if it cannot be analysed by
which of the following equations of
equilibrium
a. ΣFx = 0
a. 11.25 KN towards left
b. ΣFy = 0
b. 15KN towards left
c. ΣM = 0
c. 15 KN towards right
d. a,b
d. 7 KN towards right
e. ab,c
e. 0 KN
P a g e |4 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
7 The moment distribution method is c. Mbc = 0.5 EI(2θb+ θc)
best suited for d. Mbc = 0.5 EI(θc – θb)
a. Pin jointed truss e. Mbc = 3.0 EI(2θc – θb)
b. Space truss
c. Eccentric column
d. Rigid frames
e. Trussed beams
8 The ratio of the stiffness of a
member to the total stiffness of all
the members meeting at a joint is 1 A purely compression member(with
called as negligible eccentricity) having its
a. Relative stiffness effective length equal to 9 times its
b. Distribution factor for that member radius of gyration should be treated
c. End correction as
d. Stiffness for that member a. Pedestal
e. None of the above b. Long column
c. Strut
9 Two wheel loads 80 KN and 200 KN, d. Short column
spaced 2m. apart moves on a girder e. Member subjected to bending and
of span 16m. if any wheel load can shear
lead the other, the maximum
positive and negative SF at a section 2 The maximum compressive strain
4m. from the left end respectively according to limit state design as per
will be (in KN) IS456-2000 at the highly compressed
a. 120,-60 extreme fibre in concrete subjected
b. 120,-120 to axial compression and bending
c. 200, -60 when there is no tension on the
d. 60, -200 section will be
e. 200, -200 a. 0.002
b. 0.0035
10 The slope deflection equation at B c. 0.002 ext-0.75
of elements BC in the following d. 0.0035 ext -0.75
frame is BC = 6m, AB=CD=8m e. None of these
3 In working stress method, the
modular ratio, m has a value of
(280/3 x permissible compressive
stress) the expression for m is
a. Partially takes into account the long
a. Mbc = 0.5 EI(2θc – θb) term effects such as creep
b. Mbc = 0.5 EI(2θb – θc) b. Fully takes into account the long
P a g e |5 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
term effects such as creep classes can be reduced by R kg/cm
c. Does not take into account the long while changing the maximum size of
term effects such as creep aggregate from 20mm to 40mm
d. Is the same as the modular ratio where R is
based on the value of the elastic a. 10
modulus of structural member b. 15
e. Takes into account twice the long c. 20
term effect like creep d. 30
e. 25
4 According to IS456, when high
strength deformed bars are used, 8 As per IS 456 nominal mix concrete
the reinforcement shall not be less may be used for concrete of grades
than p percent of the total cross upto
sectional area of the slab, when p is a. 10 Mpa
a. 0.12 b. 15 Mpa
b. 0.15 c. 20 Mpa
c. 0.10 d. 200 Mpa
d. 0.13 e. 25 Mpa
e. 0.04
9 As per IS 456 the weighing or
5 Splices shall not be used without batching accuracy of cement ,
additional precautions beyond bar aggregate , water and admixture
diameter of shall respectively be
a. 28mm a. 2,2,2,2
b. 30mm b. 2,3,3,3
c. 32mm c. 2,3,2,3
d. 36mm d. 2,2,3,3
e. 40mm e. 3,2,2,2
6 The redistribution of moments in a 10 The minimum period before striking
statically indeterminate beams is the props to a beam spanning 7.5m
restricted to ‘q’ percent as per IS 456 is
limit state design method where q is a. 3days
a. 10% b. 16-24 hrs
b. 70% c. 7 days
c. 30% d. 14 days
d. 50% e. 21 days
e. 40%
7 As per IS456, the minimum cement
content for the respective durability
P a g e |6 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
P a g e |7 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
c. 7.5 Mpa
d. 10 Mpa
1 Which of the following prestressing e. 4.5 Mpa
system is employed in
manufacturing concrete sleepers for
5 In the post tensioning the elastic loss
railway
in a stressed tendon resulting from
a. Post tensioning
the shortening of the member when
b. Pre tensioning
additional tendons are stressed is
c. Pre tensioning followed by post
called as
tensioning
a. Loss of pre stress
d. b, c both
b. Bond loss
e. None of these
c. Sequence stressing loss
d. Anchorage loss
2 According IS 1343, the limit state of e. Shrinkage loss
serviceability of pre stressed
concrete sections shall satisfy
6 The method of pre stressing in which
a. Deflection and cracking
prestressing is done against
b. Deflection and corrosion
hardened concrete is called
c. Deflection, cracking and maximum
a. Partial tensioning
compression
b. Post tensioning
d. b, c, both
c. Pre tensioning
e. None of these
d. Partial pre stressing
3 As per IS 1343, at the time of initial
7 As per IS 1343, at the time of initial
tensioning, the maximum tensile
tensioning, the maximum tensile
stress immediately behind the
stress immediately behind the
anchorages shall be limited to p
anchorages shall be limited to
percent of the ultimate tensile
a. 80% of ultimate tensile strength
strength of tgeh wire, where p is
b. 90% of ultimate tensile strength
a. 85
c. 67% of ultimate tensile strength
b. 50
d. 83% of ultimate tensile strength
c. 67
d. 70
e. 80 8 Minimum grade of concrete used for
post tensioning pre stressed
concrete construction is
4 According to IS 1343, the flexural
a. M25
strength of a concrete member
b. M30
having a measured compressive
c. M40
strength of 50 MPa, will
d. M45
approximately equal to
a. 5 Mpa
b. 7 Mpa 9 Post tensioning system used
P a g e |8 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
generally in required to withstand during design
a. Low rise buildings life is called
b. Bridges a. Cutoff strength
c. Government offices b. Yield strength
d. None of these c. Fatigue strength
d. Plastic strength
10 The minimum cube strength of e. Fire strength
concrete for a pre stressed member
is 4 In a roof truss over an industrial
2
a. 50 Kg/cm buildings, purlins are provided to
2
b. 150 Kg/cm carry dead load, live loads and wind
2
c. 250 Kg/cm loads. As per IS 800, the support
2
d. 350 Kg/cm conditions assumed for these would
be
a. Continuous
b. Cantilever
c. Fixed
d. Simply supported
e. Propped cantilever
1 In a simply supported beam of span ;
and carrying a point load at the mid 5 In order to account for the shear
length at the stage of collapse, what deformations and associated effects
part of the beam is fully elastic the effective slenderness ratio of
a. L/3 from each end laced column shall be taken as ‘k’
b. L/4 from each end times, the actual maximum
c. L/5 from each end slenderness ratio. The value of K
d. L/6 from each end specified in IS 800 is
e. None of the above a. 0.95
b. 0.85
2 As per limit state design of steel c. 1.15
structures, the IS800 stipulates the d. 1.10
partial safety factor for resistance of e. 1.05
member to buckling as
a. 1.10 6 For a 10mm thinner plate the
b. 1.25 distance between the centre of any
c. 1.50 two fasteners shall not be more than
d. 1.00 a. 320mm
e. 1.75 b. 300mm
c. 250mm
3 According to IS 800, the stress range d. 280mm
for a category of detail, depending e. 150mm
upon the number of cycle, it is
P a g e |9 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
7 In steel design as per IS 800
following are the limit state of
serviceability except 1 While calculating the elastic
a. Fire modulus the stress difference
b. Corrosion between two points under
c. Crack due to fatigue consideration is 40MPa and the
-6
d. Snow load strain difference is 2000 x 10 . The
e. Vibration in the structure elastic modulus of material in GPa is
a. 20000
b. 0.02
8 According to IS 800, while using
c. 2000000
plastic method of analysis, unless
d. 20
adequate ductility and plastic
e. 2000
rotation capacity are established for
design loading conditions, the yield
stress of the grade of the steel used 2 In a stress stain plot the following
shall not exceed points appear
a. 415 MPa 1. Limit of proportionality
b. 550 MPa 2. Elastic limit
c. 500 Mpa 3. Yield point
d. 450 MPa 4. Ultimate strength
e. 380 MPa 5. Point of rupture
The correct sequence of occurrence
of these points is
9 In the design of steel columns the
a. i-ii-iii-iv-v
shear resistance at the proper
b. i-ii-iv-iii-v
contact surface between steel base
c. ii-iv-i-iii-v
and concrete/grout may be
d. iv-iii-ii-v-i
calculated using a friction coefficient
e. i-iii-ii-iv-v
of
a. 0.25
b. 0.35 3 When a material is axially loaded for
c. 0.45 a long time it develops certain type
d. 0.55 of additional strain called as
e. 1.05 a. Secondary strain
b. Axial strain
c. Radial strain
10 The shape factor of a rectangular
d. Creep strain
beam of width b and depth d is
e. Shrinkage
a. 1.00
b. 1.05
c. 1.50 4 A rod of aluminum alloy (E=72GPa)
d. 1.25 has a length 0.5m and diameter
e. 2.34 10mm. the tensile stiffness (N/m) of
this rod is
P a g e | 10 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
a. 18. ߨ. 10ହ d. 0.85L
b. 36. ߨ. 10ହ e. 2L
c. 9. ߨ. 10ହ
d. 8. ߨ. 10ହ 8 If the crushing load of a column is
e. 12. ߨ. 10ହ 3000KN and Euler load is 2000KN,
then the Rankines load is (in KN)
5 A circular silicon carbide rod a. 12000
exhibiting an elastic modulus of 450 b. 1200
GPa is under a uniaxial load of 450 c. 200
MPa. The strain energy density d. 2000
stored in this specimen is e. 1000
3
a. 225 Nmm / mm
3
b. 0.225 Nmm / mm 9 In bending of beam, the point where
3
c. 22.5 Nmm / mm no bending moment occurs is known
3
d. 2250 Nmm / mm as
3
e. 2.25 Nmm / mm a. Point of zero shear
b. Point of maximum shear
6 For the state of stress shown in the c. Point of contra flexure
following figure, if Mohr’s circle is to d. Point of buckling
be plotted. If the diameter of Mohr’s e. Yield point
circle is d and the principal stresses
are p and q (magnitudes only), the 10 In the adjacent beam subjected to
value of d,p,q (in MPa) will be uniformly distributed load of a/unit
length, find the maximum bending
moment
a. 50,70,30
b. 100,70,30 a.
2
ax / 2
c. 90,70,30 b.
2
3ax / 2
d. 80,20,70 c.
2
ax / 8
e. None of these d. 2ax
2
2
e. 4ax
7 The effective length for a fixed free
(on end fixed and other is free or
supporting a load) type of column of
length L, is used in calculating the
Euler’s crippling load is
a. L
b. 0.5L
c. 0.67L
P a g e | 11 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
P a g e | 12 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
an average water demand of 200
l/day/head will be, assume that the
1 The census records indicates the filter bed is utilized for 24h/day
current population of a town as a. 125
50000, while for the 3 consecutive b. 25
decades it was 47100(one decade c. 10000
before), 43500 (two decades back), d. 2083
41000(three decades back). Using e. 50
the Arithmetic increase method, the
probable population after one 5 On comparing slow sand filter and
decade should be rapid sand filter, which of the
a. 53000 following is an incorrect statement
b. 53500 a. SSF requires larger area for its
c. 53200 installation
d. 53100 b. Cost of operation of RSF is lower
e. 52000 c. Depreciation of SSF is lower
d. SSF cannot meet variations in the
2 If the total hardness of a water demand
sample from complete analysis is e. SSF requires cleaning at a frequency
found to be 120 mg/l and the non- of one month
carbonate hardness is 50 mg/l. then
the carbonate hardness shall be 6 If the chlorination dose required for
a. 170 disinfection is 0.25mg/l and a plant
b. 70 6
disinfects 10 x 10 l/d, then the per
c. 100 day requirement of bleaching
d. 120 powder containing 25% useful
e. 20 chlorine
a. 10 kg
3 The length of a sedimentation tank b. 0.625 kg
7
for treating 6 x 10 l/d of water and c. 25 kg
having a detention period of 5hr and d. 2.5 kg
flow velocity of 15 cm/sec will be e. 62.5 kg
a. 45m
b. 72m 7 For a given discharge, efficiency of
c. 65m sedimentation tank can be increased
d. 75m by
e. 40m a. Increasing depth
b. Increasing surface area
4 The area requirement in sq.m. of a c. Decreasing surface area
rapid sand filter bed (rate of d. Both a & b
filtration is 5 cum/hr) for a town e. None of these
having a population of 50000 with
P a g e | 13 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
8 The most common cause of acidity cumec, when operated under a
in water is depression head of 3m. in a medium
a. Carbon di oxide of specific capacity (C/A) in
b. Oxygen cumec/hr/sqm/m is
0.5
c. Nitrogen a. 2/ π
0.5
d. Chlorine b. 4/ π
e. Hydrogen c. 4/ π
d. 2/ π
0.5
9 Which one of the following is not a e. 6/ π
method of layout of distribution
pipes for water distribution systems 3 Tube well irrigation has the
a. Tree system following advantage except
b. Radial system a. Serves isolated land that cannot be
c. Ring system served with canal irrigation
d. Satellite system b. Tube wells can be privately owned
e. Interlaced system c. Tubewell construction is faster and
requires less funds
10 The polluted water is one which d. Land acquisition is less
a. Contains only pathogenic bacteria e. Tube well water is much cheaper to
b. Is safe and healthy for drinking but canal water
not for domestic purpose
c. Is not contaminated 4 Specific capacity of a well
d. Can be used for concrete making a. Decrease with the diameter
e. Contains undesirable matters, b. Increase with discharge rate
making it unfit c. Varies linearly with the drawdown
d. Decrease with time from the start of
pumping
e. Is same as well irrespective of their
design
5 If a paddy crop requires 12cm depth
1 Permeable spur’s are best suited for of water at an average interval of 10
rivers which days and the crop period of 120
a. Carry heavy suspended load days, the total depth of water
b. Carry large bed load, but light (Delta) required for the crop to
suspended load achieve its maturity is
c. Need permanent protection of Dikes a. 120cm
d. Need attracting the river current b. 12cm
e. Flow in upper hilly reaches c. 144cm
d. 100cm
2 The diameter of an open well in e. 90cm
coarse sand of yield of 0.0033
P a g e | 14 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
6 Bed load is a term used to describe d. Aquitard
a. Contact load + wash load e. Perched aquifer
b. Contact + saltation load
c. Contact load + suspended load near
the bed
d. Bed material load
e. Wash load only
7 Following are the advantages of 1 For a flood control reservoir, the
canal lining except effective storage is equal to
a. Control of seepage a. Useful storage + valley storage
b. Prevention of water logging b. Useful + valley - surcharge storage
c. Reduction in maintenance cost c. Useful – valley + surcharge storage
d. Decrease in command area d. Valley + surcharge storage
e. Increase in channel capacity and e. Useful – valley storage
command area
2 Evaporation is measured by using
8 Meander ratio in an alluvial a. Raingauge
meandering river is given by b. An open pan
a. ( M L / MB ) c. Lysimeter
b. ( MB / ML ) X 100 d. Infiltrometer
c. ( M B / ML ) e. Neuron tube
d. (MB / (ML - MB )
e. None of these 3 Which of the following effects
cannot be attributed to have been
9 A geological formation which not caused by the construction of dikes
yield freely water to the well is along a river course
called as a. Faster travel of a flood wave
a. Aquifer b. Higher flood levels along the river
b. Aquiclude c. Increased peak discharges all along
c. Aquifuse the d/s points
d. Aquitard d. Decrease in meander belt
e. Perched aquifer e. Decrease in the surface slope of the
river above the leveed reach
10 Granite rock, which is negligibly
porous and highly impermeable and 4 A catchment area has 25% each of
hence neither contains nor yields water tight roofs (K=0.9), areas with
ground water is an example of many buildings (K=0.8), gardens
a. Aquifer (K=0.1), forest land (K=0.05). what is
b. Aquicllude the average impermeability factor
c. Aquifuse for the area ? (K=impermeability
factor)
P a g e | 15 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
a. 0.050 cm/hr, if the Ø index is 7.5 cm/hr,
b. 0.090 then the total runoff will be
c. 0.080 a. 22.50
d. 0.463 b. 15.00
e. 0.450 c. 30.00
d. 7.50
5 Dicken’s formula for high flood e. 3.75
discharge is useful for catchments in
a. Southern india 9 A flood of magnitude has a period of
b. Northern india 30 yrs. The permeability of its
c. Western india exceedance is
d. Eastern india a. 30.0000
b. 0.0330
6 The isohyets for annual rainfall over c. 0.0660
a catchment basin indicate the d. 0.0990
following e. 0.1200
Isohyets : Area
45-55 cm, 500 sq.km 10 A hydrograph represents
55-65 cm, 1000 sq.km a. Variation of snow fall over time
65-75 cm, 2000 sq.km b. Variation of hydraulic jump
The approximate average annual c. Variation of water temperature
precipitation depth (in cm) over the against discharge
basin is d. Variation of sediment concentration
a. 52.25 against river discharge
b. 65.25 e. Variation of river discharge over
c. 69.29 time
d. 59.29
e. 64.28
7 Which of the following factor
doesn’t effect the water infiltration
of a formation
a. Thickness of a saturated layer
b. Wind velocity
c. Temperature
d. Vegetation cover
e. Washing of fines
8 During a storm, the rates of rainfall
observed at a frequency of 15 min
for one hour are 12.5, 17.5, 22.5, 7.5
P a g e | 16 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
P a g e | 17 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
b. 21.6m
c. 51.6m
1 According to IS 73, the paving d. 67.5m
bitumen should be homogeneous e. 12m
and shall not foam when heated to -
-- degree centigrade 5 Alligator cracking is mainly due to
a. 160 a. Fatigue
b. 170 b. Foundation failure
c. 180 c. Excessive bitumen
d. 200 d. Bitumen deficiency
e. 175 e. None of these
2 While aligning a highway in a built 6 Determine the optimum cycle length
up area, it was necessary to prode a if the sum of the ratio’s of normal
horizontal circular curve of radius flows to saturation flow of two
375m. The design speed is 75 kmph. directional flow is 0.75 and the total
What is the super elevation rate lost time per cycle is 8 sec.
a. 0.200 a. 68 sec
b. 0.0667 b. 60 sec
c. 0.1600 c. 80 sec
d. 0.0600 d. 90 sec
e. 0.0750
7 Determine the no. of potential
3 While aligning a hill road with a conflicts having two way traffic
ruling gradient of 5%, a horizontal operation if road A consists of 2
urve f dius 60m is encountered. lanes and road B consists of 4 lanes
Supposing a maximum value of ade a. 24
ompensation gradient in % , for this b. 32
road would be c. 16
a. 5.00 d. 11
b. 1.25
c. 4.75
d. 3.75 8 Match the following
e. 3.00
a. 4,3,2,1
b. 2,3,4,1
4 On a level stretch designed for c. 1,2,3,4
design speed of 54 kmph, if the d. 1,3,2,4
reaction time of the driver is 2.5s
and the braking distance is 30m,
then the safe stopping sight distance 9 Depression of flexible pavement
is along the wheel path due to
a. 61.5m repetitive traffic load applications is
P a g e | 18 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
known as
a. Faulting 3 Which of the following is not a major
b. Distortion cause of buckling of rail tracks
c. Raveling a. Installation beyond specified rail
d. Rutting temperature range
b. Water logging of rails
10 Pickup the incorrect statements c. Excessive creep, jammed joints and
Improper alignment of highway sun kinks in welded tracks
would result in: d. No frequent lubrication to SEJ’s
1. Increase in construction e. None
cost
2. Decrease in accident rate 4 The density of sleepers mainly
3. Increase in vehicle depends upon all except one of the
operation cost following
4. Decease in maintenance a. Axle load the rail track is designed to
cost carry
a. 1,4 b. The nature of sleeper and the
b. 1,3 materials used
c. 2,4 c. Lateral thrust of locomotives
d. 2,3 d. Speed of the train
e. Climatic variations
5 The top width of a rail track
embankment or bottom width of
1 Creep in rails causes the following cutting, excluding the side drains is
except called as
a. The ballast is forced out of place a. Shoulder width
b. Rail joints get jammed and prevent b. Gauge offset
expansion of rails c. Formation width
c. The ride becomes bumpy and d. Safe signal distance
uncomfortable e. Track width
d. The gauge length remains the same
e. It becomes difficult to operate 6 On Indian railways, the maximum
switches and interlocking system gradient permitted in station yards is
1 in
2 The standard gauge width for board a. 150
gauge is b. 100
a. 1.2m c. 200
b. 1.767m d. 250
c. 1.752m e. 400
d. 1.676m
e. 1.525m
P a g e | 19 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
7 Maximum cant deficiency prescribed
on Indian board gauge railways is
a. 40mm 1 If the surface tension of a soap air
b. 50mm interface is 0.09N/m, the difference
c. 60mm between the internal and external
d. 150mm pressure in the soap bubble of 3 cm
e. 100mm diameter is
a. 22
b. 20
8 The maximum degree of curvature
c. 24
for broad gauge as permissible by
d. 30
the Indian railways in degrees and
e. 36
arc length are
a. 10°, 175m
b. 16°, 109m 2 Aneroid barometer measures
c. 6°, 44m a. Local atmospheric pressure
d. 20°, 275m b. Standard atmospheric pressure
e. 11°, 195m c. Difference between standard and
local atm. Pressure
d. Absolute pressure
9 In double cross overs, the crossing
e. Vaccum pressure
provided are
1. 6 acute angle crossings
2. 2 obtuse angle crossings 3 If 60000cum of water flows per min
3. 4 acute angle crossings through a pipe of diameter 3m and if
4. 4 obtuse angle crossings this pipe reduces to 1.5m diameter,
a. 1,3 what is the ratio of the velocities in
b. 1,2 these pipes
c. 2,4 a. 0.25
d. 1,4 b. 0.03
c. 0.05
d. 0.30
10 Determine the super elevation of
e. None
broad gauge track, if the
equilibrium speed of the track in
80kmph and having a chord length 4 Which of the following is not a
of 675m with versine of curve 137m method of drawing flownets
a. 206mm a. Analytical method
b. 203mm b. Helle shaw method
c. 210mm c. Relaxation method
d. 200mm d. Electrical analogy method
e. Chezy’s method
5 Which of the following is not true
regarding frictional resistance in a
P a g e | 20 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
2
laminar flow in pipes b. MT
-2
a. Depends on the velocity of flow c. MLT
-1
b. Dependent on pressure d. MLT
2 -2
c. Proportional to the area of surface e. ML T
in contact
d. Is independent of the nature of the 10 The equations of motion for laminar
contact surface flow of a real fluid are known as
e. Is affected by the temperature of a. Euler’s equation
the following fluid b. Navier – stokes equation
c. Bernoullis equation
6 In a horizontal rectangular channel, d. Froude’s equation
if the Froude number of an incoming e. None of these
supercritical flow is 6, then the jump
so formed will be
a. Undular
b. Weak
c. Steady
d. Strong
e. Oscillating
7 The hydraulic radius (in m) of a
rectangular channel 2.5m wide
carrying water to a depth of 1.25m is
a. 2.0
b. 5.0
c. 0.50
d. 0.625
e. 1.20
8 The bernoullis equation is written
2
with usual notation (p/ɣ + V /2g + Z)
= constant. In this equation , each of
the terms represent energy in
a. Kg-m/kg mass of fluid
b. N-m/kg mass of fluid
c. N-m/N weight of fluid
d. kW/kg mass of fluid
e. Unit less quantities
9 The dimension of surface tension are
-2
a. MT
P a g e | 21 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
P a g e | 22 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
c. 0.4500
d. 1.350
1 A forest land is to be surveyed e. 0.0090
without accumulating errors, the
approach to be taken should be
5 A magnetic declination of -5 degree
a. Established minor control points
indicates the meridian to the
with low precision first
a. Easter side of the true meridian
b. Locate the details first and then the
b. Western side of true meridian
major control point
c. Northern side of true meridian
c. Fix the major points with great
d. Southern side of true meridian
precision and do detailing
e. North eastern side of the true
d. Locate the animals and mark these
meridian
as control points
e. Fix the minor points and then start
detailing 6 If the correction for curvature for a
measured distance of 1200m is
0.14m, the correction for refraction
2 A vernier scale in which the smallest
in m will be
division of vernier is longer than the
a. 0.020
smallest division on the main scale,
b. 0.202
this vernier is called
c. 8.517
a. Retrograde vernier
d. 0.117
b. Direct vernier
e. 0.017
c. Double vernier
d. Simple vernier
e. Non linear vernier 7 A series of closely spaced contour
lines represent a
a. Gentle slope
3 Well condition triangle is having
b. Uniform slope
angle
c. Horizontal surface
a. 30 and 120 degree
d. Vertical stiff
b. 20 an 110 degree
e. Steep slope
c. 15 and 95 degree
d. 90 and 120 degree
e. 30 and 90 degree 8 A curve of varying radius introduced
between two branches of a
compound curve is called as
4 A steel tape weighing 6N is
a. Mean curve
suspended between two supports
b. Transition curve
and has three spans. If the pull on
c. Base curve
the tape is 100 N and each span is of
d. Common curve
10m length, then the sag correction
e. Retrograde curve
in m in the tape will be
a. 0.0045
b. 0.0135 9 The correct prismoidal formula for
P a g e | 23 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
volume is a. CL – Clay of low plasticity
a. d/3 (first Area + last Area + Σeven b. MH – silt of high plasticity, elastic silt
area + 2.Σ.odd area ) c. OH – organic clay, organic silt
b. d/3 (first Area + last Area + 4Σeven d. SC – clayey sand
area + 2.Σ.odd area ) e. CH – clay of high plasticity , fat clay
c. d/3 (first Area + last Area + 2Σeven
area + 4.Σ.odd area ) 3 The plastic limit of a sensitive clay is
d. d/3 (first Area + last Area + 2Σeven 30%, the plasticity index is 30% and
area + 2.Σ.odd area ) the natural moisture content is 63%,
the liquidity index of this soil is
10 In a closed traverse, the sum of a. 0.6
south latitudes exceeds the sum of b. 1.1
north latitudes and the sum of east c. 1.0
departures exceeds the sum of west d. 0
departures. The closing line will lie e. 1.15
in the
a. NW quadrant 4 Which of the following tests is not
b. NE quadrant used for measuring the insitu
c. SE quadrant density of compacted soil
d. SW quadrant a. Sand patch method
b. Rubber balloon method
c. Nuclear density gauge
d. Sand replacement method
e. Electrical density gauges
5 Based on the rock mass rating
(RMR), a rock having a value ranging
1 The looseness or denseness of sandy between 41-60 will be rated as
soils is numerically expressed in a. Very poor
terms of b. Poor
a. Maximum voids content c. Fair
b. Minimum voids content d. Good
c. Compaction moisture content e. Very good
d. Relative density
e. Consistency
6 In a core drilled for 100m, the
following fragments were obtained
2 A soil with sand fraction = 14%, silt 24,12,11,9,22,8,12 and loose rock.
and clay content = 86%, liquid limit The RQD of the rock is
of 55% and plasticity index of 28%. a. 17%
According to the USCS (unified soil b. 81%
classification system) this soil is of c. 2%
type
P a g e | 24 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
d. 25% d. 127
e. 4% e. 221
7 In constant head permeability test
observations were made L = 30cm,
area of the specimen = 175 sq.cm, 1 In the manufacture of cement,
constant head difference h = 50cm gypsum is added to
and water collected in a period of a. Increase the strength of cement
5min is 350 cu.m the hydraulic b. Reduce the strength of cement
conductivity in cm/s c. Control the setting time of cement
a. 0.004 d. Provide colour to the cement
b. 0.000 e. None of these
c. 0.040
d. 0.240 2 Which of the following is a PERT
e. 0.024 event
a. Transport of sand
b. Transport of cement
8 The correct order of capillary rise in c. Concreting of roof completed
increasing order in different types of d. Making of framework continues
soils is e. None of these
a. Fine sands – silt – clay – colloids
b. Silt – fine sand – colloids – clay
c. Clay – fine sands – colloids – silt 3 Bricks are soaked in water before
d. Silt – fine sands – clays – colloids use in masonry work mainly
e. Silt – clay – fine sands – colloids 1. To remove dust
2. To remove air voids
3. So that they do not absorb
9 Sheep foot rollers used for soil water from cement mortar
compaction are most suitable for Which of these statements is/are
a. Clean coarse grained soil with 4-8% correct
passing 75μ sieve a. 1,2,3
b. Coarse grained soil less than with 4- b. 1 only
8% passing 75μ sieve c. 2 and 3
c. Clean coarse grained soil with 12% d. 3 only
passing 75μ sieve e. None of these
d. Pavement sub grades
e. Fine grained soils with more than
20% passing 200μ sieve 4 The use of super plasticizers as
10 The effective stress (KN/sq.m) at admixture
point B shown in the following soil a. Increases compressive strength of
strata is concrete
a. 0 b. Permits lower water cement ratio,
b. 99 thereby strength is increased
c. 349 c. Reduces the setting time of concrete
P a g e | 25 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
d. Permits lower cement content d. All of the above have same fineness
thereby strength is increased e. None of these
e. None of these
7 PERT network time is based on
5 The type of bond in a brick masonry a. Poisson distribution
containing alternate courses of b. Exponential distribution
stretchers and headers, is called c. Beta distribution
a. Flemish bond d. Normal distribution
b. English bond e. None of these
c. Stretcher bond
d. Header bond 8 Which of the following is a limitation
e. None of these of Bar Chart
a. Interdependencies of activities
b. Project progress
6 Which of the following cement has c. Uncertainties
the lowest fineness d. All of the above
a. Low heat cement e. None of these
b. Pozzolana cement
c. Ordinary Portland cement
P a g e | 26 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
P a g e | 27 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Answers
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
b d a e a e d b c c
REINFORCED CEMENT CONCRETE DESIGN
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
d d a a d c d c b e
PRESTRESSED CONCRETE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
b c e a c b a b b d
DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
a a c a e b d d c c
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
d a d b b b e b c a
ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
a b a b a b a d e
IRRIGATION ENGINEERING
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
a c e d c b d c d c
P a g e | 28 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
HYDROLOGY
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
c b e d b e b d b e
HIGHWAY ENGINEERING
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
e b d d a a b b d c
RAILWAY ENGINEERING
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
d d b e c e b a b b
FLUID MECHANICS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
c a b e b c d c a b
SURVEY
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
c a a a b a e b b c
SOIL MECHANICS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
d e b a c b a a e b
PERT/CPM – CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
c c d b b c c d
P a g e | 29 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Questions in original book
Exam Question Exam Question
CGSES – 2015 1-16 CGSES – 2015 1-24
CGHB-AE-2015 17-31 CGHB-AE-2015 25-37
CGHB- JE- 2015 32-38 CGHB- JE- 2015 38-51
CGSES – 2016 39-58 PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 52-60
Exam Question Exam Question
CGSES – 2015 1-35 CGSES – 2015 1-5
CGHB-AE-2015 36-42 CGHB-AE-2015 6
CGHB- JE- 2015 43-56 CGHB- JE- 2015 7-8
PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 57-64 PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 9-11
CGSES – 2016 65-77 CGSES – 2016 12-14
P a g e | 30 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Questions in original book
Exam Question Exam Question
CGSES – 2015 1-32 CGSES – 2015 1-24
CGHB-AE-2015 33-35 CGHB-AE-2015 25-43
CGHB- JE- 2015 36-45 CGHB- JE- 2015
PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 46-69 PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 44-45
CGSES – 2016 70-78 CGSES – 2016 46-57
Exam Question
Exam Question
CGSES – 2015 1-12
CGSES – 2015 1-27
CGHB-AE-2015 13-17
CGHB-AE-2015 28-50
CGHB- JE- 2015
CGHB- JE- 2015 51-59
PWD-NRDA-JE-2015
PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 60-69
CGSES – 2016 18-21
CGSES – 2016 70-83
P a g e | 31 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Questions in original book
Exam Question Exam Question
CGSES – 2015 1-4 CGSES – 2015 1-32
CGHB-AE-2015 5-9 CGHB-AE-2015
CGHB- JE- 2015 10-15 CGHB- JE- 2015
PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 16-25 PWD-NRDA-JE-2015
CGSES – 2016 25-32 CGSES – 2016 33-44
Exam Question
Exam Question
CGSES – 2015 1-8
CGSES – 2015 1-8
CGHB-AE-2015 9
CGHB-AE-2015 9-14
CGHB- JE- 2015 10-25
CGHB- JE- 2015
PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 26-34
PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 15-23
CGSES – 2016 35-40
CGSES – 2016 24-28
P a g e | 32 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
THE UNDISPUTED CHAMPIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Questions in original book
Exam Question
CGSES – 2015 1-24
CGHB-AE-2015 25-38
CGHB- JE- 2015 39-49
PWD-NRDA-JE-2015 50-62
CGSES – 2016 63-77
Exam Question
CGSES – 2015
CGHB-AE-2015
CGHB- JE- 2015
PWD-NRDA-JE-2015
CGSES – 2016 1-8
P a g e | 33 BY GAUTAM GUPTA SIR Mobile / WhatsApp – 8463016819
You might also like
- StructureDocument9 pagesStructuregautamNo ratings yet
- Final BookDocument98 pagesFinal BookgautamNo ratings yet
- Ce8502 Structural Analysis I MCQDocument26 pagesCe8502 Structural Analysis I MCQRohan GadaveNo ratings yet
- Solution PRELIM STHEORY 2020-2021 PDFDocument22 pagesSolution PRELIM STHEORY 2020-2021 PDFErick MangalinoNo ratings yet
- 10 (Compatibility Mode)Document22 pages10 (Compatibility Mode)Walid Abou KhachfeNo ratings yet
- CE F320 Class Test Solutions - R2Document7 pagesCE F320 Class Test Solutions - R2YASH JUMDENo ratings yet
- Refresher Module-Structural Engineering (ACI-Moment Coefficient)Document1 pageRefresher Module-Structural Engineering (ACI-Moment Coefficient)Renz Ryan DolorNo ratings yet
- Em MergedDocument934 pagesEm Mergednakul kamatkarNo ratings yet
- Exams 2019Document5 pagesExams 2019Kirk KatamansoNo ratings yet
- Question 4 85Document13 pagesQuestion 4 85Tarun RajputNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory Eval Exam by SorianoDocument6 pagesStructural Theory Eval Exam by SorianoBenjie MorenoNo ratings yet
- 5 6223985654372499531Document15 pages5 6223985654372499531Ashis SahaNo ratings yet
- BASIC MECHANICS MC EL MN MR PE ES GL GM RN CE EE ME 167 Yellezuome PDFDocument8 pagesBASIC MECHANICS MC EL MN MR PE ES GL GM RN CE EE ME 167 Yellezuome PDFdaniel dentehNo ratings yet
- PrefiDocument1 pagePrefiJefferson Kevin LerioNo ratings yet
- ES11LE2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesES11LE2 ReviewerMarian Galvez-LuisNo ratings yet
- ES 13 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Second Departmental Examination Samplex September 28, 2017 (6:00-8:00 PM) First Semester 2017-2018Document3 pagesES 13 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Second Departmental Examination Samplex September 28, 2017 (6:00-8:00 PM) First Semester 2017-2018Carl Justin AzucenaNo ratings yet
- 2016Document896 pages2016Someshwar KoreNo ratings yet
- 2019 May CE352-B - Ktu QbankDocument5 pages2019 May CE352-B - Ktu QbankAkshaya Dheer MadugulaNo ratings yet
- ES 13 Final Exam Reviewer PDFDocument5 pagesES 13 Final Exam Reviewer PDFMarjurie Paragas OrianaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures ModuleDocument56 pagesTheory of Structures Moduleacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Enhancement Theory Part 1Document7 pagesEnhancement Theory Part 1Harold PicoNo ratings yet
- CE 420 CEM 402 Study Guide - Structural TheoryDocument5 pagesCE 420 CEM 402 Study Guide - Structural TheoryKaryl Briant FloresNo ratings yet
- Unit-Vi Indeterminate Structural AnalysisDocument5 pagesUnit-Vi Indeterminate Structural AnalysisVinodKumar100% (1)
- Unit-Vi Indeterminate Structural AnalysisDocument5 pagesUnit-Vi Indeterminate Structural AnalysisVinodKumarNo ratings yet
- Approximate Analysis of Statically Indeterminate StructuresDocument36 pagesApproximate Analysis of Statically Indeterminate StructuresRommel BaesaNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Engineering MCQ PDF Part 1 - All Exam ReviewDocument17 pagesBasic Mechanical Engineering MCQ PDF Part 1 - All Exam ReviewsabilashNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Sp03Document18 pages12 Physics Sp03Sivarama krishnan.KNo ratings yet
- 2nd Chapter ENERGY PRINCIPLESDocument7 pages2nd Chapter ENERGY PRINCIPLESpratiksha nagargojeNo ratings yet
- Lateral Load Analysis of Multi-Storey Structures Considering Axial DeformationsDocument7 pagesLateral Load Analysis of Multi-Storey Structures Considering Axial DeformationsMazen Al-arsanNo ratings yet
- 5593r09-Advanced Structural AnalysisDocument2 pages5593r09-Advanced Structural AnalysisAijaz Zende100% (1)
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument43 pagesElectricity and MagnetismCh asim100% (1)
- Moment Resistance of Column Bases - PCI Industry HandbookDocument7 pagesMoment Resistance of Column Bases - PCI Industry HandbookGuillermo AguilarNo ratings yet
- Cblephpl 05Document9 pagesCblephpl 05Harishni ArulvasagamNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory Refresher Set PDFDocument6 pagesStructural Theory Refresher Set PDFezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- C 9 - Long ColumnsDocument29 pagesC 9 - Long ColumnsRekanNo ratings yet
- MCQ For StructureDocument4 pagesMCQ For StructureRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- M.Tech-ASA I MID OBJECTIVE Q.BDocument10 pagesM.Tech-ASA I MID OBJECTIVE Q.BrforeunitedNo ratings yet
- Tos 2Document4 pagesTos 2Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Ec 301Document4 pagesEc 301Soumitra BhowmickNo ratings yet
- 2019 May CE202-EDocument3 pages2019 May CE202-ELiya WilsonNo ratings yet
- 4323Document8 pages4323KaushikBoseNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Discussion 22-6-2023 1 To100 FullDocument130 pagesQuestion Paper Discussion 22-6-2023 1 To100 FullJayakrishnan VNo ratings yet
- MCQ's Question Bank /topic Learning Outcomes Page 1of 20Document20 pagesMCQ's Question Bank /topic Learning Outcomes Page 1of 20gvnagamaniNo ratings yet
- PH Sample Paper 1 UnsolvedDocument11 pagesPH Sample Paper 1 Unsolvedudit anandNo ratings yet
- Deformable BodiesDocument4 pagesDeformable BodiesChristian M. MortelNo ratings yet
- Corre CeDocument29 pagesCorre CeKim VeneracionNo ratings yet
- CE Plastic AnalysisDocument11 pagesCE Plastic Analysisvenkat sykamNo ratings yet
- PSAD-PreBoardExam02 ManilaRoundDocument10 pagesPSAD-PreBoardExam02 ManilaRoundSharmaine FajutaganaNo ratings yet
- Review Module-Reinforced Concrete Design (RCD Columns-USD Part 2)Document3 pagesReview Module-Reinforced Concrete Design (RCD Columns-USD Part 2)Dream CatcherNo ratings yet
- Sample - Force in RedundantDocument44 pagesSample - Force in RedundantSammi YongNo ratings yet
- MCQs Unit 1physics KPK BoardDocument5 pagesMCQs Unit 1physics KPK BoardAmber ShahNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam RC IDocument4 pagesPractice Exam RC IMamush LetaNo ratings yet
- Model Examination: Adhiparasakthi College of EngineeringDocument2 pagesModel Examination: Adhiparasakthi College of EngineeringrishinathnehruNo ratings yet
- Apj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Course Code: CE352 Course Name: Comprehensive ExamDocument5 pagesApj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Course Code: CE352 Course Name: Comprehensive ExamVishnu PrasadNo ratings yet
- PPT - 07 (Compatibility Mode)Document22 pagesPPT - 07 (Compatibility Mode)Walid Abou KhachfeNo ratings yet
- Ce Te 3 KaDocument2 pagesCe Te 3 KaJunnaz BalacuitNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Beams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsFrom EverandBeams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- U-Shape Drain (T-6) PU Series: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutionDocument3 pagesU-Shape Drain (T-6) PU Series: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutiongautamNo ratings yet
- Product Details: Lid Ref. Wt. (122 × 2) 244 Kg. Lid Ref. Wt. 454 KGDocument2 pagesProduct Details: Lid Ref. Wt. (122 × 2) 244 Kg. Lid Ref. Wt. 454 KGgautamNo ratings yet
- Chamber: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutionDocument2 pagesChamber: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutiongautamNo ratings yet
- Earth Retaining Wall: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutionDocument4 pagesEarth Retaining Wall: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutiongautamNo ratings yet
- Process Industry Practices Structural: PIP STC01015 Structural Design CriteriaDocument16 pagesProcess Industry Practices Structural: PIP STC01015 Structural Design CriteriaHarjasa AdhiNo ratings yet
- PIP STF05511 Fixed Industrial StairsDocument13 pagesPIP STF05511 Fixed Industrial StairsGiammarco Negrini100% (2)
- Delhi Public School, Bhilai (C.G.) : "Revised"Document2 pagesDelhi Public School, Bhilai (C.G.) : "Revised"gautamNo ratings yet
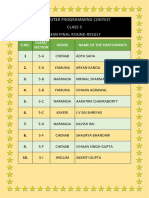
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- CGPSC State Engineering Services Exam 25th April Shift 2Document74 pagesCGPSC State Engineering Services Exam 25th April Shift 2gautamNo ratings yet
- STC 01018Document49 pagesSTC 01018gautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- Process Industry Practices Structural: PIP STC01015 Structural Design CriteriaDocument16 pagesProcess Industry Practices Structural: PIP STC01015 Structural Design CriteriaHarjasa AdhiNo ratings yet
- Ste03020 0505Document83 pagesSte03020 0505abuzahrauNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- Temperory Schedue PDFDocument1 pageTemperory Schedue PDFgautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- CGPSC State Engineering Services Exam 27th April Shift 1Document51 pagesCGPSC State Engineering Services Exam 27th April Shift 1Venkat NiranchanaNo ratings yet
- Class - 5 - Knowledge Republic-51 PDFDocument13 pagesClass - 5 - Knowledge Republic-51 PDFSreenivasa PaiNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- CGPSC State Engineering Services Exam 27th April Shift 1Document51 pagesCGPSC State Engineering Services Exam 27th April Shift 1Venkat NiranchanaNo ratings yet
- Geotech Chapter 3 QuestionDocument3 pagesGeotech Chapter 3 Questiongautam100% (1)
- Geotech Chapter 10 Stress Distribution - QuestionDocument2 pagesGeotech Chapter 10 Stress Distribution - Questiongautam25% (4)
- Allahabad Sample QuestionDocument2 pagesAllahabad Sample QuestiongautamNo ratings yet
- Resume - Gautam Gupta - Civil-StructuralDocument4 pagesResume - Gautam Gupta - Civil-StructuralgautamNo ratings yet
- Geotech Chapter 11 Consolidation - QuestionDocument8 pagesGeotech Chapter 11 Consolidation - Questiongautam100% (2)
- (Preboard Exam) : Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pages(Preboard Exam) : Multiple ChoiceNicole Rodil100% (1)
- Practical 2-Clement and DesormesDocument10 pagesPractical 2-Clement and Desormeswickedsinner767% (6)
- Structural and Thermal Analysis of A Boiler Using Finite Element AnalysisDocument5 pagesStructural and Thermal Analysis of A Boiler Using Finite Element AnalysismohanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Jet ApparatusDocument5 pagesImpact of Jet Apparatustariqafridi009_96858100% (1)
- NDC Gb7 PileDocument13 pagesNDC Gb7 PileMed El Hadi AbidiNo ratings yet
- RamjetDocument17 pagesRamjetShabeer830100% (2)
- Surge Calculation 1 - 373505Document7 pagesSurge Calculation 1 - 373505J A S JASNo ratings yet
- MEP CompanyDocument24 pagesMEP Companyniteen_mnnitNo ratings yet
- Mae 1153 Characteristics For DurabilityDocument9 pagesMae 1153 Characteristics For DurabilityMohammad AL HaririNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University Chemical EngineeringDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University Chemical EngineeringNeel ShelatNo ratings yet
- Hps Line CardDocument1 pageHps Line CardAdrianaNo ratings yet
- Mec351 - Chapter 1Document97 pagesMec351 - Chapter 1MYlearn HazimiNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids: General Chemistry 2 Engr. Jozel Bryan M. TerribleDocument30 pagesProperties of Liquids: General Chemistry 2 Engr. Jozel Bryan M. TerribleJozel Bryan Mestiola TerrìbleNo ratings yet
- 5MA039 - Introduction To Heat TransferDocument30 pages5MA039 - Introduction To Heat TransferNaveen KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- KSB Selecting Centrifugal PumpsDocument92 pagesKSB Selecting Centrifugal Pumps윤홍민100% (1)
- Physics 111 Homework Solution #7Document14 pagesPhysics 111 Homework Solution #7Carlos OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Air Exchange Rates in Greenhouses With Different Types of Ventilation Opening in The Western Mediterranean Region of TurkeyDocument2 pagesAir Exchange Rates in Greenhouses With Different Types of Ventilation Opening in The Western Mediterranean Region of Turkeypramod_20253No ratings yet
- Resistance and Propulsion Characteristics of Various Commercial Ships Based On CFD ResultsDocument18 pagesResistance and Propulsion Characteristics of Various Commercial Ships Based On CFD ResultsmarinengineerNo ratings yet
- Comparison of r22 and r407cDocument7 pagesComparison of r22 and r407cVamsi Priya KatamreddyNo ratings yet
- 9FA Failures in DabholDocument10 pages9FA Failures in Dabholsenthil031277100% (3)
- Fluid Power CircuitsDocument176 pagesFluid Power CircuitsMike Fredskilde97% (29)
- Charging and TD Chart PlusDocument1 pageCharging and TD Chart PlusFaquruddin AliNo ratings yet
- R134a Refrigerant Pressure Temperature Chart Under The Condition of SaturationDocument1 pageR134a Refrigerant Pressure Temperature Chart Under The Condition of SaturationAkhidNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 13: VentilatingDocument2 pagesHVAC Systems 13: VentilatingrohitNo ratings yet
- Assignments HMTDocument2 pagesAssignments HMTPiyush AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Activity SheetDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity SheetKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- FEEG1002 Formula Sheet S1 and S2 2015-16Document5 pagesFEEG1002 Formula Sheet S1 and S2 2015-16GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Geko Ansys CFD PDFDocument38 pagesGeko Ansys CFD PDFJulio Andrés Casal RamosNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbinesDocument51 pagesSteam TurbinesSohaib ArshadNo ratings yet
- Settlement Calculation of Composite Foundation Reinforced With Stone ColumnsDocument9 pagesSettlement Calculation of Composite Foundation Reinforced With Stone Columnsprashant maliNo ratings yet