Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geotech Chapter 11 Consolidation - Question
Uploaded by
gautamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geotech Chapter 11 Consolidation - Question
Uploaded by
gautamCopyright:
Available Formats
CIVIL ENGINEERING
Consolidation - Objective Question
Gautam Gupta - 8463016819
Q1 Consolidation of a soil is due to a load which is
a. Static and short term b. Dynamic and short term c. Dynamic and long term d. Static and long term
Q2 Time is an important parameter in the consolidation of
a. Sands only b. Clayey only c. Both sand and clay d. None
Q3 During consolidation process as water escapes out
a. Both neutral and b. Both neutral c. Gradual decrease in d. A gradual increase in Neutral
effective pressure and effective neutral pressure, a pressure and a gradual decrease in
reduce pressure gradual increase in effective pressure takes place and
increase effective pr. sum of two is constant
Q4 Primary compression is mainly due to expulsion of
a. Air b. Water c. Both air and water d. None
Q5 Secondary Consolidation is mainly due to expulsion of
a. Highly Viscous water b. Plastic readjustment c. Both a and b d. None of the above
of solid particles
Q6 The change in voids ratio due to increase in effective pressure by 1KG/cm2 is 0.1. initial voids ratio is 0.4. the
thickness of soil stratum = 7m. Consolidation settlement in cm would be
a. 5 b. 50 c. 500 d. None of above
Q7 A clay layer of thickness 10cm and initial void ratio 0.5 under goes settlement so that the final void ratio is 0.2. the
settlement of the layer in cm is
a. 1.0 b. 1.5 c. 2.0 d. 2.5
Q8 If a soil has ever been subjected to a pressure in excess of its present over burden, the soil is said to be
a. Preconsolidated b. Normally consolidate c. Under consolidated d. None of the above
Q9 Which of the following is not an assumption in Terzaghis theory of one dimensional consolidation
a. Soil mass is homogenous b. Soili is fully c. Darcy’s law is valid d. Drainage of water occurs both in
and isotropic saturated vertical and horizontal directions
Q10 Coefficient of consolidation depends upon
a. Permeability b. Coefficient of volume change c. Unit weight of water d. All the above
Q11 The unit of coefficient of consolidation is
a. Cm/sec b. Cm2 / sec c. Cm/sec2 d. No units
1|Page Gautam Gupta - 8463016819
CIVIL ENGINEERING
Q12 The ratio of settlement at any time ‘t’ to the final settlement is known as
a. Coefficient of b. Degree of c. Time factor d. Consolidation of
consolidation consolidation undisturbed soil
Q13 Isochrones are the curves showing distribution of
a. Total settlement b. Total pressure c. Excess hydrostatic pr. d. None
Q14 The slope of isochrones at any point at a given time indicates the rate of change of
a. Effective stress with b. Effective stress with c. Pore water pressure d. Pore water pressure
depth time with time with depth
Q15 Time factor is
a. A non dimensional b. A function of degree c. Directly proportional d. All the above are
parameter of consolidation to permeability of soil correct
Q16 Two identically clay samples of the same size designated as A and B are subjected to consolidation tests under
identical conditions. Drainage takes place through one face in sample A and through both the faces in sample B.
50% consolidation of sample A occurs in 10min. the required for 50% consolidation to occur in sample B in
minutes will be
a. 40 b. 10 c. 5 d. 2.5
Q17 A normally consolidated clay layer settles 1cm when the pressure increases from 1KG/cm2 to 2 KG/cm2.
Additional settlement for the same soil for further increase of pressure from 2 KG/cm2 to 4 KG/cm2 will be in
a. 1cm b. 2cm c. 3cm d. 4cm
Q18 In the soil sample of a consolidometer test, pore water pressure is
a. Minimum at the center b. Maximum at the top c. Max. at the bottom d. Max. at the centers
Q19 Which of the following soils will generally have maximum compressibility
a. Gravels b. Sands c. Silts d. Clays
Q20 If coefficient of permeability is doubled and coefficient of volume compressibility is halved, the coefficient of
consolidation
a. Increases by 2 time b. Decreases by 2 times c. Decreases by 4 times d. Increase by 4 times
Q21 The time for 50% consolidation of a sample of ‘d’cm thick with double drainage is ‘t’ hours. The time for 50%
consolidation of another sample of similar soil with 3d cm thick and single drainage Is
a. 6t b. t/6 c. 36t d. 9t
Q22 The ultimate consolidation settlement of a soil of
a. Is directly proportional to b. Decrease with the increase c. Both a and b d. None
the compression index in the initial voids ratio
2|Page Gautam Gupta - 8463016819
CIVIL ENGINEERING
Q23 A saturated clay layer with single drainage face takes 4 years to attain 50% degree of consolidation. If the clay
layer had double drainage, then the time required to attain 50%
a. 8 b. 4 c. 2 d. 1
Q24 In consolidation testing, curve fitting method is used to determine
a. Compression index b. Swelling index c. Coefficient of consolidation d. Time factor
Q25 Secondary consolidation is
a. Caused by b. Caused by c. Large for the pressures below the d. Very small for highly plastic
hydrodynamic lag creep pre consolidation pressure clays and organic clays
Q26 The recompression index is about ------- of the compression index
a. 5 times b. 1/5 c. ½ d. 1/20
Q27 Consolidation time of a soil sample
a. Increases with an b. Increases with a c. Increases with d. Increases with a
increase permeability decreases in decrease in unit decrease in
compressibility weight of water permeability
Q28 The ultimate settlement of a soil deposit increases with
a. An increase in the b. An increase in the c. A decrease in d. An increase in time
compression index initial void ratio thickness of the
stratum
Q29 A fully saturated clay specimen is subjected toa pressure of 200 KN/m2 in the consolidation test. After a period of
time when the average pore pressure is 60 KN/m2, the degree of consolidation is
a. 60 b. 70 c. 30 d. 50
Q30 A building constructed on a compressible layer settles 80mm in 4 years. Assuming that the degree of
consolidation at both the times is less than 60%, the settlement in 9 years is
a. 80mm b. 100mm c. 120mm d. None of the above
Q31 A clay layer of 4m thick undergoes 50mm ultimate consolidation settlement under single drainage conditions.
What would be the ultimate consolidation settlement for the above clay layer if it has double draining condition
a. 50mm b. 100mm c. 25mm d. None of the above
--------------------------------------------COMMON DATA---------------------------------------------------
A footing for a water tower carries a load of 900t and is 3.6m square. It rests in dense sand of 9m thickness
overlying a clay layer of 3m depth. The depth of foundation is 1.5m. the clay layer overlies hard rock. Liquid limit of
clay is 54%, void ratio is 1.08. the saturated unit weights of the sand and clay are 1.89 gm/cc and 1.79gm/cc
respectively. Assume the load distribution as 2V:1H. Assume that the site is flooded.
Q32.1 The ultimate settlement due to consolidation of the clay layer will be
a. 11.7 cm b. 4.2 cm c. 5.54cm d. 8.65 cm
3|Page Gautam Gupta - 8463016819
CIVIL ENGINEERING
Q32.2 The max. effective stress at the centre of the clay layer at the end of consolidation will be
a. 23.5 t/m2 b. 12.5 t/m2 c. 15.56 t/m2 d. 14.87 t/m2
Q33 A square footing is to be established in a clay soil at a depth of 2m, where water table has risen up to the ground
level as shown in the figure. Assume that the net load for the given is a constant and that the same is dispersed in
to clay as shown. Load dispersion is 2V:1H. ɣw = 10KN/m3 and ɣsat = 19.3 KN/m3. Net load = 500 KN. Cc = 0.36 eo
= 0.92. The width of the footing, if it is permitted to settle by 120mm, for the data given above is
a. 2.7m b. 3.5m c. 1.75m d. 2.35m
Q34 The soil profile at a building site consist of dense sand upto 2m depth, normally loaded soft clay from 2m to 6m
depth and stiff impervious rock below 6m depth. The gound water table is at the gound level. The sand has a
density of 1.85 t/m3 above water table and 1.90 t/m3 below it. For the clay natural water content is 50%, liquid
limit is 65% and grain specific gravity is 2.65. caululate the probable ultimate settlement resulting from a uniformy
distributed surface load of 4.0 t/m2, applied over an extensive area of the site.
a. 14.7 cm b. 6.2 cm c. 13.54 cm d. 29.4 cm
Q35 A saturated clay layer of 5m thickness takes 1.5 years for 50% primary consolidation when drained on both sides.
Its coefficient of volume change is 1.5 x 10 -3 m2/KN. The coefficient of permeability of the soil will be
a. 2.56 m/year b. 1.53 m/year c. 0.012 m/year d. 1.25 m/year
-------------------------COMMON DATA QUESTION -----------------------------------
Q36.1 During a pressure increment, a test specimen 20mm thick under double drainage attained 50% primary
consolidation in 45 minutes.
a. 21.4 years b. 85.6 years c. 12.6 years d. 48.5 years
Q36.2 If the clay is drained on the top surface only, then time required to reach the same degree of consolidation will
a. 34.45 years b. 85.6 years c. 62.6 years d. None
-------------------------COMMON DATA QUESTION -----------------------------------
In the laboratory test on a clay sample of thickness 25mm, drained at top only, 50% consolidation occurred in 11
minutes assume T50 = 0.197 and T70 = 0.405
Q37.1 Find the time required for the corresponding clay layer in the field of 3m thick and drained at top and bottom to
undergo 50% consolidation
a. 123 days b. 27.5 days c. 56.5 days d. 12 days
Q37.2 Find the time required to undergo 70% consolidation
a. 153 days b. 27.5 days c. 56.5 days d. 12 days
Q38 A settlement analysis carried out for a proposed structure indicates that 9cm of settlement will occur in 5 years
and the final settlement will be 45 cm based on doubled drainage condition. A detailed site investigation indicates
that only single drainage exist. Estimate the settlement at the end of 5 years for the changed condition
a. 14 cm b. 6 cm c. 4.5 cm d. 13.5 cm
4|Page Gautam Gupta - 8463016819
CIVIL ENGINEERING
-----------------------------------Common data question----------------------------------------------
A building constructed on a compressible layer with doubled drainage settles by 80mm in 4 years. The final
settlement is expected to be about 300mm
U% 60% 65% 70%
Tv 0.29 0.35 0.403
Q39.1 The settlement that would occur in 9years, will be
a. 16mm b. 162mm c. 156mm d. 120mm
Q39.2 The time required to settle by 210mm will be
a. 15.5 yrs b. 12 yrs c. 26.5 yrs d. 28.8yrs
Q39.3 The settlement that would occur in 25years will be
a. 198mm b. 195mm c. 215mm d. 235mm
Q40 The loading period for a building extended from February 1957 to February 1959. In February 1962 the average
measured settlement was found to be 90mm. the ultimate settlement was expected to be 360mm. Estimate the
settlement in February 1967. Assuming double draining to occur?
a. 54mm b. 116mm c. 135mm d. 120mm
Q41 A clay layer 6m thick under double drainage was subjected to a certain load. Its final consolidation settlement is
calculated as 120mm. if a layer of sand of negligible thickness is assumed to be present at a depth of 1.5m from
the top of the clay layer what will be its final settlement
a. 60mm b. 90mm c. 120mm d. 180mm
-------------------------Common Data Question ---------------------------------------
During a consolidation test, a sample of fully saturated clay 3cm thick is consolidated under a pressure and the
sample thickness gets reduced to 2.6cm. the pressure is then removed and the sample is allowed to expand and
take water. The final thickness is observed as 2.8cm and the final moisture content is determined as 24%. If the
specific gravity of the soil solids is 2.7.
Q42.1 The void ratio after final condition is
a. 0.648 b. 0.548 c. 0.734 d. 0.832
Q42.2 The void ratio after consolidation is
a. 0.531 b. 0.55 c. 0.734 d. 0.432
Q42.3 The void ratio before consolidation is
a. 0.668 b. 0.354 c. 0.765 d. 0.832
Q43 Representative samples of a clay layer of silty clay 5m thick, were tested in a consolidometer and the following
results were obtained initial void ratio = 0.90. pre consolidation pressure = 120 KN/m2. Recompression index =
0.03. compression index = 0.27. estimate the consolidation settlement if the present average overburden stress
5|Page Gautam Gupta - 8463016819
CIVIL ENGINEERING
on the layer is 70 KN/m2 and the increase in average stress on the layer is 80 KN/m2
a. 65mm b. 87mm c. 113mm d. 126mm
----------------------Common Data Question ----------------------------------------
A soft normally consolidated clay layer 20m thick with a moisture content of 45%. The clay has a saturated unit
weight of 20 KN/m3, a particle specific gravity of 2.7 and liquid limit of 60%. A foundation load will subject the
centre of the layer to a vertical stress increase of 10KPa. Ground water level is at the surface of clay. ɣw = 10KN/m3
Q44.1 The intial and final effective stresses at the centre of the layer will be respectively
a. 20 & 120 KN/m2 b. 100 & 110 KN/m2 c. 100 & 210 KN/m2 d. None
Q44.2 The consolidation settlement of the foundation if the initial effective stress at the centre of the soil is 100 KPa
will be
a. 64mm b. 168mm c. 112mm d. 18mm
----------------------Common Data Question---------------------------------------------
A 5m depth of sand overlies a 6m layer of clay. The water table is at top of the sand. The permeability of clay is very
low. The saturated unit weight of the sand and clay are resp. 18 and 20 KN/m3. A 4m depth of fill material of unit
weight 19 KN/m3, is placed on the surface over an extensive area. ɣw=10KN/m3
Q45.1 The effective vertical stress at the center of the clay layer immediately after the fill has been placed, assuming
this to take place rapidly, will be
a. 76 KN/m2 b. 70 KN/m2 c. 146 KN/m2 d. None
Q45.2 The effective vertical stress at the center of the clay layer, many years after the fill has been placed will be
a. 226 KN/m2 b. 70 KN/m2 c. 146 KN/m2 d. None
Q46 A consolidation test is carried out on a clay sample of thickness 20mm. during the test the void ratio was reduced
from 0.80 to 0.70. the settlement that would occur is
a. 1.23mm b. 1.56mm c. 1.11mm d. 1.45mm
-------------------------------Common Data Question ------------------------------------
A soil sample which has been subjected to consolidation test has an area of 50cm2, dry weight of sample is
190.24gm. G=2.67
Q47.1 The height of solids is
a. 1.425 cm b. 1.565 cm c. 1.725 cm d. 1.825 cm
Q47.2 If initial height of the sample was 25mm, the initial void ratio is
a. 0.65 b. 0.75 c. 0.834 d. 0.85
Q48 An 18mm thick laboratory specimen drained top and bottom reached 25% consolidation in 10min. how long will
take the same specimen to reach 50% consolidation
a. 20min b. 40min c. 80min d. 160min
6|Page Gautam Gupta - 8463016819
CIVIL ENGINEERING
Q49 The laboratory consolidation data for an undisturebed clay sample are as follows
. e1 = 1 σ1’=85 KN/m2
.e2=0.8 σ1’=465 KN/m2
The ‘e’ for a pressure of 600 KN/m2 will be
a. 0.68 b. 0.77 c. 0.584 d. 0.45
Q50 A 2m thick clay layer has Cv = 2 x 10-4 cm2/sec. if a building is constructed on it, how long will it take to attain half
the ultimate settlement under double drainage
a. 113.4 days b. 26.5 days c. 167.5 days d. None
Q51 A fully saturated clay specimen is placed in consolidometer and 2 KG/cm2 pressure is applied. After some time,
the pore pressure is found to be 0.70 KG/cm2 and change in the thickness of the sample is found to be 1mm. the
final settlement that will occur under the applied load will be
a. 1.23mm b. 1.36mm c. 1.54mm d. 1.56mm
Q52 A fully saturated clay specimen is placed in a consolidometer and 2 KG/cm2 is applied. After some time the pore
pressure is found to be 0.60 KG/cm2. Find the corresponding settlement that has occurred if the ultimate
settlement is going to be 20mm
a. 12mm b. 13mm c. 14mm d. 15mm
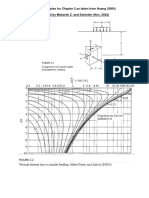
Q53 The time for a clay layer to achieve 90% consolidation in 15 years. The time required to achieve 90%
consolidation, if the layer were twice as thick, 3times more permeable and 4 times more compressible would be
a. 75 yrs b. 120 yrs c. 80 yrs d. None
Q54 A 6m thick clay layer undergoes 90% consolidation four times faster under two way drainage as compared to one
way drainage. In an identical clay layer of 15m thickness. Two way drainage will be faster as compared to one way
drainage by
a. 8 times b. 4 times c. 2.5 times d. 2 times
Q55 For the clay layer shown in fig. mv = 5 x 10 -4 m2/KN. If an earth fill of unit weight 20 KN/m3 and 2m depth is
dumped on the clay layer then the ultimate settlement of the clay layer is
a. 12mm b. 60mm c. 90mm d. 120mm
Q56 A building constructed on a compressible layer settles 80mm in 4 years. What will be the settlement in 9 years
assuming that the degree of consolidation at both the times is less than 60%
a. 65mm b. 80mm c. 40mm d. 120mm
Q57 A clay layer of 4m thick undergoes 50mm ultimate consolidation settlement under single drainage conditions.
What would be the ultimate consolidation settlement for the above clay layer if it has double draining condition
a. 10mm b. 25mm c. 50mm d. 100mm
Q58 A double draining clay layer 6m thick settles by 30mm in three years under the influence of a certain loads. Its
final consolidation settlement has been estimated to be 120mm if a thin layer of sand having negligible thickness
7|Page Gautam Gupta - 8463016819
CIVIL ENGINEERING
is introduced at a depth of 1.5m below the top surface, the final consolidation settlement of clay layer will be
a. 60mm b. 120mm c. 240mm d. None
------------------------Common Data Question ----------------------------
The average effective overburden pressure on 10m thick homogeneous saturated clay layer is 150 KPa.
Consolidation test on an undisturbed soil sample taken from the cdlay layer showed that the void ratio decreased
from 0.6 to 0.5 by increasing the stress intensity from 100 KPa to 300 KPa. G=2.65
Q59 The initial void ratio of the clay layer is
a. 0.209 b. 0.563 c. 0.746 d. 1.00
Q60 The total consolidation settlement of the clay layer due to the construction of an structure imposing an additional
stress intensity of 200 KPa is
a. 0.10m b. 0.25m c. 0.35m d. 0.50m
8|Page Gautam Gupta - 8463016819
You might also like
- Training Work in Public Work DepartmentDocument20 pagesTraining Work in Public Work Departmentaltaf_h5No ratings yet
- Design of Navigational Canal For National Waterway ProjectDocument14 pagesDesign of Navigational Canal For National Waterway ProjectMuthu Mari100% (1)
- EN8592 UNIT 2 Grey Water HarvestingDocument14 pagesEN8592 UNIT 2 Grey Water Harvesting2CIVIL3045 SONIYA ANo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering Ii: Girma Berhanu (Dr.-Ing.) Dept. of Civil Eng. Faculty of Technology Addis Ababa UniversityDocument46 pagesHighway Engineering Ii: Girma Berhanu (Dr.-Ing.) Dept. of Civil Eng. Faculty of Technology Addis Ababa Universityashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics II (Chapter 1)Document14 pagesHydraulics II (Chapter 1)Abduljebar HussienNo ratings yet
- External and Internal Stability of Soil WallsDocument4 pagesExternal and Internal Stability of Soil WallsManilaNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV Consolidation of SoilDocument64 pagesUnit - IV Consolidation of Soilgopierode4100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document40 pagesChapter 4ashuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet On ReservoirsDocument4 pagesTutorial Sheet On ReservoirsLe100% (2)
- Calculate Soil Bearing CapacityDocument20 pagesCalculate Soil Bearing CapacityjerkNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 & 2Document35 pagesChapter-1 & 2nimcan100% (2)
- IS 8237 1985 Code of Practice-Slope Protection of Reservoir EmbankmentDocument15 pagesIS 8237 1985 Code of Practice-Slope Protection of Reservoir EmbankmentJan BakosNo ratings yet
- Construction of An Ordinary Earth RoadDocument2 pagesConstruction of An Ordinary Earth Roadsathish100% (3)
- Ground Improvement Techniques PDFDocument8 pagesGround Improvement Techniques PDFBoobalan Civil100% (1)
- Hydraulic RoutingDocument25 pagesHydraulic RoutingSileshi GizachewNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Concrete With Partial Replacement of Cement With Fly Ash & Coarse Aggregate by Ceramic TilesDocument7 pagesExperimental Study On Concrete With Partial Replacement of Cement With Fly Ash & Coarse Aggregate by Ceramic TilesIJSTENo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Hydraulics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesCivil Engineering Hydraulics Multiple Choice QuestionsAbhijeeth Nagaraj100% (1)
- 17CV73 Module 1 5Document115 pages17CV73 Module 1 5shivaraj salimathNo ratings yet
- Highways and Traffic Engineering Chapter 4Document16 pagesHighways and Traffic Engineering Chapter 4EG Tiolo AbadNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Presentation on Road ConstructionDocument24 pagesSummer Training Presentation on Road ConstructionPradhumna Adhikari100% (2)
- Scheme of Examination for Extensive Survey Project Design ComponentsDocument1 pageScheme of Examination for Extensive Survey Project Design Componentskkkk1986No ratings yet
- DOcks and HarboursDocument19 pagesDOcks and HarboursijlgugNo ratings yet
- A Road Building Opportunity PURE - CRETE - Eng - 02252011Document48 pagesA Road Building Opportunity PURE - CRETE - Eng - 02252011PAYLEUNo ratings yet
- 1 What Is LevelingDocument19 pages1 What Is LevelingAbduraman Isa100% (1)
- Latihan Soal Peralatan KonstruksiDocument19 pagesLatihan Soal Peralatan KonstruksiGibral MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 10CV65 - Hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design - Drawing Question BankDocument6 pages10CV65 - Hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design - Drawing Question BankMr. Y. RajeshNo ratings yet
- Design of Surplus WeirDocument21 pagesDesign of Surplus WeirAJ AY50% (2)
- Response-Audit Report On Jalayagnam-Vol.2Document322 pagesResponse-Audit Report On Jalayagnam-Vol.2nmsusarla99950% (2)
- Pot-Holes by Supreme Court Committee Reply Version-2Document5 pagesPot-Holes by Supreme Court Committee Reply Version-2Akshay Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Claycrete English v3Document22 pagesClaycrete English v3supernaenergy100% (1)
- 7 - Hma Mix DesignDocument12 pages7 - Hma Mix Designmczen_associatesNo ratings yet
- Anna UniversityDocument131 pagesAnna UniversityDilipKumarAkkaladeviNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement Design Using AASHTO MethodDocument16 pagesFlexible Pavement Design Using AASHTO MethodNamukasa DivinaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structure PPTSummer2022part IDocument146 pagesHydraulic Structure PPTSummer2022part ITamiru OlikaNo ratings yet
- CE5018 EnvironmentalDocument37 pagesCE5018 EnvironmentalKyaw Zin HeinNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering BookDocument4 pagesIrrigation Engineering BookBanupriya BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- PierDocument4 pagesPierAtulkumar ManchalwarNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering CE-408 (2+1)Document63 pagesIrrigation Engineering CE-408 (2+1)Umer Waheed50% (2)
- Project PDFDocument50 pagesProject PDFralphlloydaloysiusNo ratings yet
- Making ways for better days with soil stabilizationDocument36 pagesMaking ways for better days with soil stabilizationJean MbuNo ratings yet
- Field TripDocument16 pagesField TripChidi HenryNo ratings yet
- Manual Small Canal Structures PDFDocument458 pagesManual Small Canal Structures PDFCristian MaximilianoNo ratings yet
- Angularity Number Test: Sushrut Gautam KCE074BCE089 Transportation Engineering II Khwopa College of EngineeringDocument5 pagesAngularity Number Test: Sushrut Gautam KCE074BCE089 Transportation Engineering II Khwopa College of EngineeringSushrutNo ratings yet
- Traffic Loading & Volume 2022.2023 v1 FinalDocument55 pagesTraffic Loading & Volume 2022.2023 v1 Finalkibiralew DestaNo ratings yet
- Soil Reinforcement Using CSA A Case Study of Indian SoilDocument6 pagesSoil Reinforcement Using CSA A Case Study of Indian SoilPj RoblesNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Sewer Appurtenances - Only Introduction (4 Hours) R2Document13 pagesUnit-4 Sewer Appurtenances - Only Introduction (4 Hours) R2Girman RanaNo ratings yet
- Design Principle of Gabion Retaining WallDocument11 pagesDesign Principle of Gabion Retaining WallAbhilash AbhiNo ratings yet
- Flood Mitigation in Hill TorrentsDocument44 pagesFlood Mitigation in Hill Torrentsyasir_mushtaq786100% (1)
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 3 PDF123No ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 4 HIGHWAY II KitDocument26 pagesCHAPTER - 4 HIGHWAY II KitAbuye HDNo ratings yet
- HW II - Chapter 5 - Unbound Pavement MaterialsDocument45 pagesHW II - Chapter 5 - Unbound Pavement Materialsabenezer abrhamNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 2 Stresses in PavementDocument49 pagesCHAPTER - 2 Stresses in PavementHaile GuebreMariamNo ratings yet
- 2 Stresses in Pavements Solved Examples With Charts of FlexibleDocument17 pages2 Stresses in Pavements Solved Examples With Charts of FlexibleNahom Esh100% (1)
- Reservoir PlanningDocument16 pagesReservoir PlanningVishal RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Soil StabilizationDocument5 pagesSoil StabilizationMarzhan KabdrakhmanNo ratings yet
- 100 TOP WATER SUPPLY Engineering Objective QuestionsDocument10 pages100 TOP WATER SUPPLY Engineering Objective QuestionsKavinMuthukumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Old Tank Project 2016Document22 pagesOld Tank Project 2016Abhishek Patil50% (2)
- Soil Mech MCQSDocument27 pagesSoil Mech MCQSUsama AhmadNo ratings yet
- ME Exam Reviewer1Document17 pagesME Exam Reviewer1Kayes MNo ratings yet
- 46C 1Document18 pages46C 1SHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Chamber: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutionDocument2 pagesChamber: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutiongautamNo ratings yet
- Product Details: Lid Ref. Wt. (122 × 2) 244 Kg. Lid Ref. Wt. 454 KGDocument2 pagesProduct Details: Lid Ref. Wt. (122 × 2) 244 Kg. Lid Ref. Wt. 454 KGgautamNo ratings yet
- U-Shape Drain (T-6) PU Series: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutionDocument3 pagesU-Shape Drain (T-6) PU Series: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutiongautamNo ratings yet
- Process Industry Practices Structural: PIP STC01015 Structural Design CriteriaDocument16 pagesProcess Industry Practices Structural: PIP STC01015 Structural Design CriteriaHarjasa AdhiNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- STC 01018Document49 pagesSTC 01018gautamNo ratings yet
- Process Industry Practices Structural: PIP STC01015 Structural Design CriteriaDocument16 pagesProcess Industry Practices Structural: PIP STC01015 Structural Design CriteriaHarjasa AdhiNo ratings yet
- Earth Retaining Wall: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutionDocument4 pagesEarth Retaining Wall: FUJI Precast Concrete SolutiongautamNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bhilai (C.G.) : "Revised"Document2 pagesDelhi Public School, Bhilai (C.G.) : "Revised"gautamNo ratings yet
- PIP STF05511 Fixed Industrial StairsDocument13 pagesPIP STF05511 Fixed Industrial StairsGiammarco Negrini100% (2)
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- Ste03020 0505Document83 pagesSte03020 0505abuzahrauNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- Temperory Schedue PDFDocument1 pageTemperory Schedue PDFgautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsDocument1 pageS.NO. Class/ Section House Name of The ParticipantsgautamNo ratings yet
- CGPSC Engineering Exam QuestionsDocument51 pagesCGPSC Engineering Exam QuestionsVenkat NiranchanaNo ratings yet
- CGPSC State Engineering Services Exam 25th April Shift 2Document74 pagesCGPSC State Engineering Services Exam 25th April Shift 2gautamNo ratings yet
- Class - 5 - Knowledge Republic-51 PDFDocument13 pagesClass - 5 - Knowledge Republic-51 PDFSreenivasa PaiNo ratings yet
- Final BookDocument98 pagesFinal BookgautamNo ratings yet
- CGPSC Engineering Exam QuestionsDocument51 pagesCGPSC Engineering Exam QuestionsVenkat NiranchanaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Stress Distribution QuestionsDocument2 pagesCivil Engineering Stress Distribution Questionsgautam25% (4)
- Geotech Chapter 3 QuestionDocument3 pagesGeotech Chapter 3 Questiongautam100% (1)
- Allahabad Sample QuestionDocument2 pagesAllahabad Sample QuestiongautamNo ratings yet
- Resume - Gautam Gupta - Civil-StructuralDocument4 pagesResume - Gautam Gupta - Civil-StructuralgautamNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument9 pagesStructuregautamNo ratings yet
- Report Ground Motion Prediction V6 - Julian Bommer EtalDocument202 pagesReport Ground Motion Prediction V6 - Julian Bommer EtalAlessandro MarascaNo ratings yet
- G9 STE Q3 Science ReviewerDocument9 pagesG9 STE Q3 Science ReviewermeNo ratings yet
- The Do-It-Yourself Dip and Strike Model (With DIY Clinometer)Document5 pagesThe Do-It-Yourself Dip and Strike Model (With DIY Clinometer)Liliana Maria Plata SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Granite - Maintenance - ManualDocument12 pagesGranite - Maintenance - Manualطارق حمدان100% (1)
- Volume-3 Technical Specification and Geological Report Part-1Document344 pagesVolume-3 Technical Specification and Geological Report Part-1Kinzang Dendup100% (1)
- GENBIO2Document16 pagesGENBIO2Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Geochemical Study of The Sakalol-Harralol Geothermal Field (Republic of Djibouti) : Evidences of A Low Enthalpy Aquifer Between Manda-Inakir and Asal Rift SettingsDocument27 pagesGeochemical Study of The Sakalol-Harralol Geothermal Field (Republic of Djibouti) : Evidences of A Low Enthalpy Aquifer Between Manda-Inakir and Asal Rift Settingsfreetime8334No ratings yet
- PalaeocopidaDocument11 pagesPalaeocopidaGitha LeatemiaNo ratings yet
- Stay Hungry, Stay Foolish .............................................................................................. 65Document96 pagesStay Hungry, Stay Foolish .............................................................................................. 65India PreparesNo ratings yet
- History of Soil MechanicsDocument9 pagesHistory of Soil Mechanicsleah yadaoNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1-Module 5Document31 pagesScience: Quarter 1-Module 5Jelly ManagaytayNo ratings yet
- FieldMove Clino Help PDFDocument39 pagesFieldMove Clino Help PDFAndy peñafiel laraNo ratings yet
- Modeling Block Cave Subsidence at The Molycorp Inc Questa Mine A Case StudyDocument14 pagesModeling Block Cave Subsidence at The Molycorp Inc Questa Mine A Case StudyDiego NunesNo ratings yet
- Ecological SuccessionDocument3 pagesEcological SuccessionArnel AsuncionNo ratings yet
- TEchnical Report PAH Silver Ore PDFDocument128 pagesTEchnical Report PAH Silver Ore PDFSubrato GhoshNo ratings yet
- Planting SystemsDocument22 pagesPlanting SystemsAlangelico Ortiz San PascualNo ratings yet
- Soil Study in IndiaDocument7 pagesSoil Study in IndiaKhalida Parveen100% (1)
- 2021 Great Lakes Landscape Supply Natural Stone BookDocument31 pages2021 Great Lakes Landscape Supply Natural Stone BookMartim MamaniNo ratings yet
- Wind DesignDocument5 pagesWind DesignSedin HodžićNo ratings yet
- Construction MethodDocument12 pagesConstruction MethodKahlua ShuzenNo ratings yet
- Vermeer 1984Document64 pagesVermeer 1984anarNo ratings yet
- Sparta in Laconia Proceedings of The 19th British Museum Classical Colloquium Held With The British School at Athens PDFDocument170 pagesSparta in Laconia Proceedings of The 19th British Museum Classical Colloquium Held With The British School at Athens PDFDavid Selec100% (1)
- Science 3rd Q RevDocument6 pagesScience 3rd Q Revethan elizaldeNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - 1st Monthly Exams - ScienceDocument21 pagesGrade 10 - 1st Monthly Exams - ScienceInah MasubayNo ratings yet
- Data MineDocument4 pagesData MineMilan LLanque CondeNo ratings yet
- Jssi Manual For Building Passive Control Technology Part - 8 Peak Response Evaluation and Design For Elasto - Plastically Damped SystemDocument9 pagesJssi Manual For Building Passive Control Technology Part - 8 Peak Response Evaluation and Design For Elasto - Plastically Damped SystemJoaquim TchamoNo ratings yet
- AA Holtz & Kovacs - An Introduction To Geotechnical Engineering PDFDocument746 pagesAA Holtz & Kovacs - An Introduction To Geotechnical Engineering PDFwarlockall100% (1)
- Group 5 PPT - Regional Geology of The PhilippinesDocument123 pagesGroup 5 PPT - Regional Geology of The PhilippinesMary JennyNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Structural Steel Pipe RacksDocument5 pagesSeismic Design of Structural Steel Pipe Racksandradeinsua0% (1)
- MahabhutasDocument203 pagesMahabhutassk11983No ratings yet