Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Circulatory System Worksheets
Uploaded by
Craft CityOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Circulatory System Worksheets
Uploaded by
Craft CityCopyright:
Available Formats
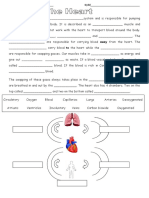
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Handout
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
VOCABULARY
blood vessel -
arteries –
veins –
capillaries –
blood –
plasma –
white blood cells –
red blood cells –
platelets –
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B46
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Look at Figure B. It shows arteries and veins within the
human body. Each artery and vein branches out to tiny
capillaries.
Write the correct term in each blank to answer the questions or
complete the sentence.
1. What pumps blood through your body?
______________
2. Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called
_______________.
3. Vessels that carry blood back to the heart are called
______________.
4. Blood moves from arteries to veins through tiny blood vessels
called ________________.
5. The heart, blood vessels and blood make up the
______________________.
Student
Handout
Examine the parts of Figure C, then answer the questions below.
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B47
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
1.
Arteries branching away from the heart become ____________________________________.
(smaller and smaller OR larger and larger)
2. Veins leading back to the heart become ________________________________________.
(smaller and smaller OR larger and larger)
3. Most of our blood vessels are ______________________________.
(arteries, veins or capillaries)
Match each term in Column A with its description in Column B. Write the correct letter in the space
provided.
Column A Column B
________ 1. circulation a) carry blood away from the heart
________ 2. heart b) pumps blood
________ 3. arteries c) connect arteries and veins
________ 4. veins d) transport of materials in living things
________ 5. capillaries e) carry blood back to the heart
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B48
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
Complete each statement using a term or terms from the list below. Write your answers
in the spaces provided. Some words may be used more than once.
heart circulation oxygen veins food
capillaries arteries blood vessel waste materials blood
1. The transport of materials in living things is called __________________.
2. In humans, circulation is carried out by the liquid called ___________________.
3. Blood is pumped by the ____________________.
4. Blood brings to cells things like ____________________ and __________________.
5. Blood picks up ___________________ from the cells.
6. Any tube that carries blood is called a(n) _______________________.
7. The three kinds of blood vessels are ______________________, ____________________,
and ________________________.
8. Blood is carried away from the heart by ___________________.
9. Blood is carried back to the heart by _____________________.
10. Arteries and veins are connected by tiny blood vessels called ______________________.
TRUE or FALSE – In the space, write a ‘T’ or ‘F’
_______ 1. Circulation is the transport of materials in living things.
_______ 2. Life stops when circulation stops.
_______ 3. Blood is pumped by the brain.
_______ 4. Blood circulates through the body only a few times a day.
_______ 5. Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
_______ 6. Arteries transport carbon dioxide to the cells.
_______ 7. Veins carry blood away from the heart.
_______ 8. Veins pick up waste materials from the cells.
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B49
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
_______ 9. Capillaries connect arteries and veins.
_______ 10. Capillaries are the largest blood vessels.
1. What percent of blood is liquid? _________
2. What is the name of the liquid part of blood?
__________________
3. a) The liquid part of blood is made up mostly of
_________________. (Hint – look back to the reading.)
b) What percent? _______
4. All of the blood cells together make up _______% of
blood.
5. Red blood cells make up _______% of blood; white
blood cells make up ______ %.
Study Figure B, then answer the questions.
1. Which blood cells are the largest? __________________________
2. Which type of blood cell is most numerous? _________________________
3. Which cells are shaped like ‘pinched’ disks? ______________________________
Study Figures C and D, then answer the questions.
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B50
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
1. What kind of blood cells is shown?
_____________
2. Describe briefly what is happening in Figure C.
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
3. When you cut yourself, which part of the blood helps you to stop bleeding?
_______________________
4. White blood cells also come to the area of a cut. Why?
_________________________________
5. Take an educated guess at this one – What happens to the number of white blood cells when
germs are in the body? _________________________________________________
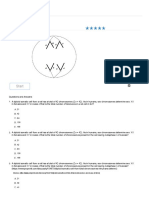
Answer the following questions about red blood cells.
1. Oxygen is _______________________________.
(needed by cells OR a cell waste)
2. Which blood cells pick up and carry oxygen? ______________________________________
(red blood cells OR white blood cells OR platelets)
3. What substance in red blood cells joins with oxygen? ______________________
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B51
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
4. Where does the blood pick up this oxygen?
a) in the heart b) in the arteries and veins c) in the lungs
5. What gives blood its color? ________________________
Ten substances carried by the blood are listed in the chart below. Indicate whether each
substance is carried to the cells or away from the cells. Place a checkmark in the proper
boxes.
Some Interesting Facts About Blood
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B52
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
• Blood makes up approximately 9% of a person’s weight. For example, if you weigh 100
pounds, 9 pounds is blood. (Can you figure out how many pounds of blood your body has?)
• An adult has about 5.7 liters of blood.
• There are about 600 times as many red blood cells as there are white blood cells. One drop
of blood contains about 5 million red blood cells. That means that there are about 25 trillion
red blood cells in the body of an average adult!
• Blood cells are produced in the marrow of bones – especially in the backbone, breast bone
and ribs.
• Every second, from 1 to 2 million red blood cells die! New cells are made to take their place.
• Plasma carries red and white blood cells. White blood cells, however, can also move by
themselves!
Adapted from What is the Circulatory System? What is Blood Made Of? , pp.70-80 Biology
Science Workshop Series
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B53
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
______
12 Name: _____________________________ Date: ________________ Period: _____
QUIZ - An Introduction to the Circulatory System
PART I – Fill in the Blanks – Choose a word from the word pool for each blank. Some words may
be used more than once. Some words may not be used at all. 9 marks
veins capillaries arteries heart
blood vessel plasma platelets white blood cells
red blood cells hemoglobin
1. ____________________ carry blood away from the heart.
2. The structures in the blood that are used to fight disease are called _______________________.
3. The substance in the blood that gives it its red color is _______________________.
4. The name given to any tube that carries blood is a(n) _______________________.
5. The straw-colored part of the blood that is made up mostly of water is ____________________.
6. ________________________ carry hemoglobin that binds to oxygen and picks up waste carbon
dioxide.
7. The smallest blood vessels are ___________________________.
8. The pumping organ of the human body is the ____________________.
9. The part of the blood that helps a wound to stop bleeding is the ______________________.
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B54
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
PART II – Diagram – Label the three components of the blood in the photo below. The words used
for labeling can be found in the word pool used in part I of this quiz. 3 marks
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B55
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B56
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
S
t
u
d
e
n
t
H
a
n
d
o
u
t
How Does Your Heart Work?
VOCABULARY
atria –
ventricles –
valve –
septum –
Place your hand on your chest and feel your beating heart. Your heart is keeping you alive! It is
made mostly of muscle tissue and pumps blood to all parts of your body.
The human heart is divided into four separate parts called chambers. There are two upper
chambers and two lower chambers.
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B57
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
The upper chambers of the heart are called the right and left atria. The singular of atria is atrium.
• The right atrium receives blood from all parts of the body. Blood in the right atrium is high in
carbon dioxide and low in oxygen. Find the right atrium in Figure A.
• The left atrium receives blood from the lungs. Blood in the left atrium is high in oxygen and
low in carbon dioxide. Find the left atrium in Figure A.
• Both atria fill with blood at the same time.
The lower chambers of the heart are the ventricles. The ventricles pump blood out of the heart.
• The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs. This blood is high in carbon dioxide and low in
oxygen.
• The left ventricle pumps blood to all parts of the body. Blood in the left ventricle is high in
oxygen. It is low in carbon dioxide.
• Both ventricles pump blood out of the heart at the same time. Every time your heart beats,
blood is being forced out of the ventricles.
1. a) When the right ventricle contracts, the valve between the upper and lower chambers is
_____________________.
(open OR closed)
b) What does this prevent?
__________________________________________________________
2. Blood pumped out of the right ventricle goes ________________________________.
(to the body OR to the lungs)
3. In the lungs, the blood gives up its _____________________ and picks up
(oxygen OR carbon dioxide)
______________________.
(oxygen OR carbon dioxide)
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B58
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
Veins carry blood back to the heart from the lungs.
4. Which chamber received fresh blood from the lungs? _________________________
(left atrium OR left ventricle)
5. a) The blood then passes into the _____________________________.
(left atrium OR left ventricle)
b) While this is happening, the valve between the left chambers is __________________.
(open OR closed)
The left ventricle contracts. This forces blood out of the heart to all parts of the body.
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B59
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
6. a) As the left ventricle contracts, the valve between the left chambers is ______________.
(open OR closed)
b) Why? _________________________________________________________________
7. Where does blood leaving the left ventricle go? ____________________________________
8. THEN, what do you think happens to the blood? ___________________________________
TRUE OR FALSE – Write a ‘T’ or an ‘F’ beside each statement.
________ 1. The heart is a muscle
________ 2. The heart has many jobs.
________ 3. A human heart has four chambers.
________ 4. Heart chambers are called arteries and veins.
________ 5. Blood moves from the atria to the ventricles.
________ 6. Ventricles receive blood from veins.
________ 7. Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
________ 8. The right and left ventricles pump at the same time.
________ 9. Your heart stops beating when you are asleep.
________ 10. Your heart beats millions of times a year.
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B60
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
SHORT ANSWER – Use Figure H to help you to answer the questions.
1 1. Arteries carry ‘fresh’ blood. There is one exception. Which
artery is the exception? __________________________
2. Veins carry ‘stale’ blood. There is one exception.
vein
Which is the exception?
_____________________________
Adapted from
How Does Your Heart Work?, pp. 82-88 Biology Science Workshop Series
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B61
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B62
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B63
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B64
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Student
Handout
a) The heart is said to be ‘self-excitable’. It generates its own contractions without having to
be commanded to do so by the brain. This is achieved by the action of natural pacemakers in
the heart – nodes of tissue that start the electrical impulses to get the heart to beat.
What is the name of the natural pacemaker that starts the heartbeat?
___________________________ (1 mark)
Where is it found? ___________________________ (1 mark)
b) On the diagram of the heart above, use arrows to show the pathway of blood through the
heart and its associated vessels. (2 marks)
c) Use a blue colored pencil to shade in all regions of the heart that carry deoxygenated blood
and a red colored pencil to shade in the regions that carry oxygenated blood. (2)
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B65
Unit: Biology C - Circulation
Science 21 Bio C - Circulation B66
You might also like
- Biology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemDocument47 pagesBiology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemMary Jewel0% (1)
- Chapter 8 Transport in Mammals - WorksheetDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Worksheetapi-3728508100% (2)
- Circulatory System Guided NoteDocument2 pagesCirculatory System Guided Noteapi-251528487No ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory ReviewDocument5 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory ReviewNur ShaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory ClozeDocument1 pageCirculatory Clozemikemaia82No ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 11.1 Locomotion and Support in Humans and AnimalsDocument7 pagesWORKSHEET 11.1 Locomotion and Support in Humans and AnimalsSakinah RahimNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Test ReviewDocument3 pagesCell Transport Test ReviewJohn Kevin NocheNo ratings yet
- Organ Systems Cloze ReadDocument1 pageOrgan Systems Cloze Readapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument117 pagesUnit 4 Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyPetrus Heinrich100% (1)
- Osmosis and Tonicity WorksheetDocument4 pagesOsmosis and Tonicity Worksheetisraa jaaboNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport QuizDocument2 pagesCell Transport QuizDoreen Khrystel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes and Heredity Key TermsDocument8 pagesChromosomes and Heredity Key TermsarurusipNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemAlba CubilloNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Animals and Plants Worksheet 9 PDFDocument2 pagesTransportation in Animals and Plants Worksheet 9 PDFParul ShahNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Worksheet AnswersDocument6 pagesCirculatory System Worksheet AnswersPak RisNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport DocumentDocument3 pagesCell Transport DocumentVictoria LoredanNo ratings yet
- Systems BookletDocument8 pagesSystems Bookletapi-383568582No ratings yet
- CH 15 WorkbookDocument10 pagesCH 15 Workbookapi-237586441100% (1)
- DNA Worksheet #2 PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Worksheet #2 PDFmineNo ratings yet
- Cell Division ExerciseDocument3 pagesCell Division ExerciseFauziah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Practice Problems & SolutionsDocument3 pagesOsmosis Practice Problems & SolutionsOlinese AugustinNo ratings yet
- Rajarshi Shahu JR Science College, Latur Screening Test - 2019 Syllabus: Physics 1 Motion 2Document7 pagesRajarshi Shahu JR Science College, Latur Screening Test - 2019 Syllabus: Physics 1 Motion 2Dr. Laxman RautNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument29 pagesCellular RespirationDominic MaderaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis BDocument3 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Bpradeep ankleshwariaNo ratings yet
- Function of The Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of The Circulatory SystemChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- Mitosi ActivityDocument3 pagesMitosi ActivityTena, CharleneNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Test BankDocument25 pagesCH 10 Test BankBiano, Fortune JayneNo ratings yet
- ST Biology Nervous System IEP TestDocument3 pagesST Biology Nervous System IEP TestDanielle WilsonNo ratings yet
- Ws1-Membrane Transport WorksheetDocument3 pagesWs1-Membrane Transport WorksheetTy BakrNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in BloodDocument12 pagesWorksheet in BloodBryan Mae H. DegorioNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetDaichi ライアン100% (1)
- Rajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyDocument2 pagesRajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyRajeem Outlaw WrightNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Document6 pagesAP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Omar LopezNo ratings yet
- Practice Chapter TestDocument4 pagesPractice Chapter Testhossam mohamedNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam - Bio1215 - Bio1214 PDFDocument15 pagesDiagnostic Exam - Bio1215 - Bio1214 PDFCarla AngelesNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer-SNC2DDocument2 pages2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer-SNC2DBob Dharam0% (1)
- Biology Chapter 4 Test ReviewDocument7 pagesBiology Chapter 4 Test ReviewCK. GohNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Mendel and Genetic CrossesDocument5 pagesWorksheet Mendel and Genetic CrossesHuma NazneyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 The Immune SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 43 The Immune System蔡旻珊No ratings yet
- Student Guide To Vce Unit 1 BiologyDocument8 pagesStudent Guide To Vce Unit 1 Biologyapi-348068677No ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: Hs Bio 002-General Biology 2Document2 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines: Hs Bio 002-General Biology 2AndreaNicoleBanzonNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - Video - Recap - of - Dna - Replication - by - Amoeba - Sisters - Newheader - v.2Document2 pagesKami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - Video - Recap - of - Dna - Replication - by - Amoeba - Sisters - Newheader - v.2Luuk Van MeursNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active Transport Internet AssignmentDocument4 pagesPassive and Active Transport Internet AssignmentShalu PundirNo ratings yet
- Genetics Chapter 2 QuestionsDocument9 pagesGenetics Chapter 2 QuestionslifecostNo ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Worksheets - of - Biology I Honors Workbook - CH - v1 - s1 PDFDocument17 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory Systems Worksheets - of - Biology I Honors Workbook - CH - v1 - s1 PDFNikki BaekNo ratings yet
- Hardy WeinbergDocument2 pagesHardy WeinbergAliye ÖzgürNo ratings yet
- Final Bioa 2015Document10 pagesFinal Bioa 2015api-237801056100% (1)
- Circulatory System WorksheetDocument3 pagesCirculatory System WorksheetLei Xandra MeiNo ratings yet
- MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesMacromoleculesSebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Content Review PacketDocument9 pagesContent Review Packetapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Lesson 21 Cellular RespirationDocument41 pagesLesson 21 Cellular RespirationJanine NacunaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4. ReproductionDocument4 pagesWorksheet 4. ReproductionrosaronceroNo ratings yet
- CirculatorySystem GizmoDocument4 pagesCirculatorySystem GizmoNashly Ramirez50% (2)
- Unit Plan Zachary Mccormic Scie 380 Natural Selection - 9 Grade BiologyDocument40 pagesUnit Plan Zachary Mccormic Scie 380 Natural Selection - 9 Grade BiologyzmccormicNo ratings yet
- ATP - The Energy Currency of CellsDocument12 pagesATP - The Energy Currency of CellsJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 3.6 OsmosisDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET 3.6 OsmosisFadhliana UzalliNo ratings yet
- MYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerDocument4 pagesMYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerRishar bokNo ratings yet
- Heart, Circulation, and Blood Unit Test: Biology 11 April 3, 2014Document8 pagesHeart, Circulation, and Blood Unit Test: Biology 11 April 3, 2014api-279500653No ratings yet
- Introduction to the Circulatory SystemDocument27 pagesIntroduction to the Circulatory SystemPapiNo ratings yet
- Biology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesBiology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemMuhammad Azrie0% (1)
- Numbers for Grade 1 StudentsDocument2 pagesNumbers for Grade 1 StudentsCraft CityNo ratings yet
- 2-3 Corrosion of Metals and Their ProtectionDocument10 pages2-3 Corrosion of Metals and Their Protectionapi-3734333100% (5)
- PW Discursive Exemplar 2Document1 pagePW Discursive Exemplar 2Craft CityNo ratings yet
- FFTCDHHDocument2 pagesFFTCDHHCraft CityNo ratings yet
- 2-3 Corrosion of Metals and Their ProtectionDocument10 pages2-3 Corrosion of Metals and Their Protectionapi-3734333100% (5)
- How Organisms Get Their FoodDocument1 pageHow Organisms Get Their FoodCraft CityNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH ON VALENCIES OF METALS and NON - METALSDocument1 pageRESEARCH ON VALENCIES OF METALS and NON - METALSCraft CityNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH ON VALENCIES OF METALS and NON - METALSDocument1 pageRESEARCH ON VALENCIES OF METALS and NON - METALSCraft CityNo ratings yet
- NAME: - ROLL NO.: - Grade: Ig 1 Date: SUBJECT: Maths (Extd) Teacher'S Signature: Assignment (15 Marks)Document1 pageNAME: - ROLL NO.: - Grade: Ig 1 Date: SUBJECT: Maths (Extd) Teacher'S Signature: Assignment (15 Marks)Craft CityNo ratings yet
- Food Chains Food Web and Energy Pyramid WorksheetDocument4 pagesFood Chains Food Web and Energy Pyramid WorksheetCraft City100% (1)
- Creative WritingDocument4 pagesCreative WritingCraft CityNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 2Document3 pagesRespiratory System 2Craft CityNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH ON VALENCIES OF METALS and NON - METALSDocument1 pageRESEARCH ON VALENCIES OF METALS and NON - METALSCraft CityNo ratings yet
- Creative WritingDocument4 pagesCreative WritingCraft CityNo ratings yet
- IGCSEDocument24 pagesIGCSECraft CityNo ratings yet
- Teacher Notes On The NecklaceDocument8 pagesTeacher Notes On The NecklaceMaria Victoria Padro100% (1)
- Astronomy NotesDocument5 pagesAstronomy NotesCraft CityNo ratings yet
- Notes On MotionDocument2 pagesNotes On MotionCraft CityNo ratings yet
- Class Ix History - The French RevolutionDocument5 pagesClass Ix History - The French RevolutionKrishna Kumar85% (46)
- Astronomy NotesDocument5 pagesAstronomy NotesCraft CityNo ratings yet
- Dead Mens PathDocument2 pagesDead Mens PathCraft CityNo ratings yet
- Physics Sound and WavesDocument11 pagesPhysics Sound and WavesCraft CityNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Basic Skills Reading Comprehension and Skills PDFDocument49 pages5th Grade Basic Skills Reading Comprehension and Skills PDFAugusto Castellano100% (3)
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants PDFDocument3 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plants PDFCraft CityNo ratings yet
- Wa0000Document30 pagesWa0000asprellaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension and Skills: Fifth Grade Basic SkillsDocument49 pagesReading Comprehension and Skills: Fifth Grade Basic SkillsCraft CityNo ratings yet
- Math IGCSE 2019 PapersDocument13 pagesMath IGCSE 2019 PapersCraft CityNo ratings yet
- GCSE Geography Revision GuideDocument9 pagesGCSE Geography Revision GuideKatie100% (1)
- CoastsDocument15 pagesCoastsburychurch100% (4)
- Manila Standard Today - Friday (September 14, 2012) IssueDocument22 pagesManila Standard Today - Friday (September 14, 2012) IssueManila Standard TodayNo ratings yet
- Classi Fications of Adverse Drug Reactions: 1. EidosDocument6 pagesClassi Fications of Adverse Drug Reactions: 1. Eidosdolemite4No ratings yet
- It PDFDocument385 pagesIt PDFCosmina UngurNo ratings yet
- Catatan Koas THT 1Document5 pagesCatatan Koas THT 1MEDS easyNo ratings yet
- Psychology All Case Studies PDFDocument54 pagesPsychology All Case Studies PDFArmeen AmirNo ratings yet
- The Incredible Journey: A Baby's Development from Conception to 1 YearDocument40 pagesThe Incredible Journey: A Baby's Development from Conception to 1 YearEli Abram CabilinNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Associates User ManualDocument20 pagesNuclear Associates User ManualvandarsNo ratings yet
- Semen AnalysisDocument2 pagesSemen AnalysisSabir KamalNo ratings yet
- Circulation: Campbell Biology: Concepts & ConnectionsDocument88 pagesCirculation: Campbell Biology: Concepts & ConnectionsBehshxbxNo ratings yet
- Boyd Et Al-2019-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDocument38 pagesBoyd Et Al-2019-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsomyNo ratings yet
- Human Blood CellsDocument3 pagesHuman Blood CellscsamarinaNo ratings yet
- MM M Hall of Femme Ebook 62463Document15 pagesMM M Hall of Femme Ebook 62463Tayaba Naim KhanNo ratings yet
- Medical Charges Reimbursement Form: Item Names Charges Details of Cash-Memos EtcDocument2 pagesMedical Charges Reimbursement Form: Item Names Charges Details of Cash-Memos EtcAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- NCP OrthoDocument2 pagesNCP OrthoJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- CH 25 Respiration Study GuideDocument2 pagesCH 25 Respiration Study Guide99646qbkdwNo ratings yet
- Sample IQ TestDocument34 pagesSample IQ TestResIpsa LoquitorNo ratings yet
- Brushing Teeth and RecessionDocument16 pagesBrushing Teeth and RecessionWayan SubadiNo ratings yet
- How to prepare your Asil for fightingDocument16 pagesHow to prepare your Asil for fightingcinna01No ratings yet
- Masters in Medical Science - MMSCDocument12 pagesMasters in Medical Science - MMSCtexilaamericanNo ratings yet
- What Is HumorDocument5 pagesWhat Is HumorWan Sek ChoonNo ratings yet
- Disturbing Art Exposes Modern Culture AbsurditiesDocument15 pagesDisturbing Art Exposes Modern Culture Absurdities2aethicusNo ratings yet
- The Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionDocument150 pagesThe Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionIsabel CarrilloNo ratings yet
- EORTC QLQ-C30 Into Indonesian VersionDocument11 pagesEORTC QLQ-C30 Into Indonesian VersionHendryNo ratings yet
- XxssDocument13 pagesXxssfkhunc07No ratings yet
- MCI - SyllabusDocument11 pagesMCI - Syllabusintaa khabNo ratings yet
- Vit KDocument22 pagesVit KKimbek BuangkeNo ratings yet
- Atlas de Acupuntura (Ingles)Document16 pagesAtlas de Acupuntura (Ingles)Medicina Tradicional China - Grupo LeNo ratings yet
- Gait Analysis: Prerequisite of Normal GaitDocument4 pagesGait Analysis: Prerequisite of Normal GaitKieran Levi100% (1)
- Petridou, Thumiger-Homo Patiens - Approaches To The Patient in The Ancient World (SAM 45)Document555 pagesPetridou, Thumiger-Homo Patiens - Approaches To The Patient in The Ancient World (SAM 45)jeremy_luckas100% (1)
- CPR and Aed: Quiz #2 ResultsDocument2 pagesCPR and Aed: Quiz #2 ResultsNathan WhiteNo ratings yet