Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Suez Incident March 2019
Uploaded by
MOJIBCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Suez Incident March 2019
Uploaded by
MOJIBCopyright:
Available Formats
SAFETY ALERT
CCC CORPORATE HSE GROUP Issue Date: April 7, 2019
Multiple Fatalities – Metallurgical Failure of Spherical Tank (Not CCC)
What Happened? (Incident Description) Calculations were not completed to select the proper vaporizer
incorporating a standard safety factor to prevent liquid nitrogen from
On March 21st 2019 at approximately 08:00 AM an incident occurred entering the tank.
during the commissioning phase of a Non - CCC Project in Suez, Egypt.
3) Failure to effectively control Simultaneous Activities.
The Incident occurred when a spherical tank ruptured while being purged No permit to work System, No Supervision and No Safety Inspection
with nitrogen prior to putting the tank in service. The tank had successfully was implemented. Other ongoing activities in the tank area were not
passed leak testing at a pressure of 24 bar few days before the incident. stopped during the purging activity.
Due to the “non-availability” of a nearby nitrogen production facility, a
4) Poor site HSE Supervision and Monitoring,
mobile liquid nitrogen tank connected to a liquid nitrogen vaporizer was
The HSE and construction teams either failed to stop other activities
used to generate the needed nitrogen gas for the purging process.
around the tanks during purging activities or were not present.
Two Pressure Relieve Valves (PRVs) were installed on top of the spherical
tank and were tested earlier and it was confirmed the valves could Lessons Learned
withstand a pressure of 10 bar.
1) Ensure Effective Planning by Competent Construction and HSE
The purging plan was to vaporize the liquid nitrogen and pressurize the Engineers
spherical tank using nitrogen in the gaseous form after vaporization with A detailed Method Statement, Risk Assessment, Safe System of Work,
the expectation the PRVs would operate at a pressure of 10 bar as Supervision, HSE Checking and Inspection must be available and
previously tested. properly implemented when performing such activities. The Engineers
who develop the method statement and risk Assessment must have
At a pressure of 4 bar, the spherical tank experienced a metallurgical
sound technical competency and experience to provide informative
failure resulting in flying debris.
and detailed plans.
The scattered flying debris claimed the lives of 25 persons working below
2. Conduct Job Safety Task Instruction (JSTI)
& nearby the tank area.
Effectively communicate control measures using a JTSI to ensure all
involved workers are aware of the hazards and risks associated with
the task.
What Went Wrong? (Causes of the incident)
3) Effective Site Supervision must be enforced by the Senior Project
“Root Cause Analysis (RCA) of the Metallurgical failure revealed that liquid Management.
nitrogen flow rate was higher than the vaporizer capacity, resulting in All activities must be monitored and supervised competently,
the nitrogen reaching the spherical tank in its liquid state (–196°C). The continuously and effectively in terms of safety primarily by construction
liquid nitrogen accumulated in the spherical tank triggering steel ductile supervisors and aided by safety officers.
to brittle transition causing the tank rupture at a pressure of 4 bar”.
4) Communicate the Lessons Learned from this incident (the
content of this Alert) to the project workforce through the
1) Failure to identify the potential hazards following:
The flow rate of the liquid nitrogen was not controlled or restricted to
ensure it never exceeded the vaporizer capacity. The risk associated A Stand-down to all site workers on site (one-time Stand-down to be
with the use of liquid nitrogen was not adequately foreseen and conducted with all site workers in the presence of Project
mitigated. If the flow rate was adequately controlled, the metallurgical Management)
failure would not have occurred. The weekly TBT (Tool Box Talk). Designate one TBT to
communicate lessons learned from the incident to all site workers.
2) Failure to Plan correctly for the Task, The weekly SSMM (Safety Supervisory Management Meeting) for
The activity started without barricading the area creating a safe managers, engineers and senior supervisors
buffer zone around the purging activity to prevent any unauthorized The weekly SO Meeting (Safety Officers Meeting) for all Safety
access near the tank. Officers
The weekly CH Meeting (Charge Hand Meeting) for all Foremen
No Detailed Risk Assessment or Effective HSE Communication
and Charge-Hand
utilizing a JSTI was conducted.
You might also like
- Safety Quiz - Fire Prevention Answer Key-1Document2 pagesSafety Quiz - Fire Prevention Answer Key-1MOJIB100% (9)
- Gas Cutting Set ChecklistDocument1 pageGas Cutting Set ChecklistMOJIB83% (12)
- Case Studies Involving Incidents in A Manufacturing PlantDocument28 pagesCase Studies Involving Incidents in A Manufacturing PlantKian TecsonNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Muhammad Akif Naeem Open Ended Lab Signals and SystemDocument20 pagesMuhammad Akif Naeem Open Ended Lab Signals and SystemMuhammad Akif NaeemNo ratings yet
- Safety Alert Tank Brittle Fracture During PurgingDocument1 pageSafety Alert Tank Brittle Fracture During PurgingAndrian Prisandhie100% (2)
- Energization - Substation # 2Document2 pagesEnergization - Substation # 2Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- General Instruction Manual: Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco)Document5 pagesGeneral Instruction Manual: Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco)bryanNo ratings yet
- HSE Alert PDFDocument2 pagesHSE Alert PDFjavariam99No ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument63 pagesRisk Assessmentya9a_ya9m_ya9q2595100% (2)
- SECTION 07 8123 Intumescent Fireproofing Part 1 General 1.01 Section IncludesDocument4 pagesSECTION 07 8123 Intumescent Fireproofing Part 1 General 1.01 Section IncludesStephen KokoNo ratings yet
- Management Safety Observation Tours EssentialsDocument25 pagesManagement Safety Observation Tours EssentialsTim813100% (1)
- Basic of CorrosionDocument67 pagesBasic of Corrosionkenzsugiyanto100% (1)
- Fire Fighting TechniquesDocument75 pagesFire Fighting Techniquesscorpioss93% (27)
- HSE Policy SampleDocument1 pageHSE Policy SampleRajkumar NandaNo ratings yet
- HSE Policy SampleDocument1 pageHSE Policy SampleRajkumar NandaNo ratings yet
- Hira FormatDocument6 pagesHira FormatMOJIB33% (6)
- Nauticus 3D BeamDocument114 pagesNauticus 3D BeamMinca AndreiNo ratings yet
- Yahama Golf Cart G2e Parts ManualDocument50 pagesYahama Golf Cart G2e Parts Manualtl3883100% (1)
- Module 3 Density Altitude ExperimentDocument3 pagesModule 3 Density Altitude ExperimentIvan100% (1)
- Defect EliminationDocument4 pagesDefect EliminationHossein100% (1)
- SPE 46610 The Hazard Register: Thomas J. Dujmovich/ConocoDocument5 pagesSPE 46610 The Hazard Register: Thomas J. Dujmovich/ConocoBagas JuniarNo ratings yet
- Weekly Safety Management Walkthrough Report: Gas Compression Project DepartmentDocument12 pagesWeekly Safety Management Walkthrough Report: Gas Compression Project DepartmentSheri DiĺlNo ratings yet
- Near Miss ReportDocument2 pagesNear Miss ReportPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Disaster Aniversaries PDFDocument40 pagesDisaster Aniversaries PDFHarold Fernando Guavita ReyesNo ratings yet
- Safety Bulletin - Accident During Mooring Operation - RevDocument2 pagesSafety Bulletin - Accident During Mooring Operation - Revalberio100% (1)
- 100 Largest LossesDocument68 pages100 Largest Lossesnaqvi44100% (1)
- AI-VO-PRC-004 R1 Procedure For Inspection DefermentDocument14 pagesAI-VO-PRC-004 R1 Procedure For Inspection Defermentkhairie rahimNo ratings yet
- Safety Transportation of Hazmat 3Document66 pagesSafety Transportation of Hazmat 3upesddn2010100% (1)
- Safety Moment CsDocument1 pageSafety Moment Csramod100% (1)
- PPE Training ModuleDocument56 pagesPPE Training Modulehadeed shaikh100% (2)
- CH 15-110 Heat Stress MGMT JUL14rev0914 PDFDocument20 pagesCH 15-110 Heat Stress MGMT JUL14rev0914 PDFSnaiderNo ratings yet
- JSA For Hydro Test Activites GenericDocument4 pagesJSA For Hydro Test Activites GenericMajdiSahnounNo ratings yet
- Styrene Vapour Release Incident at LG Polymers: Harikrishnan MDocument32 pagesStyrene Vapour Release Incident at LG Polymers: Harikrishnan MHari KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Static Elect OilDocument23 pagesStatic Elect OilKudeep GargNo ratings yet
- HT & PWHT JsaDocument3 pagesHT & PWHT JsaNature BeautiesNo ratings yet
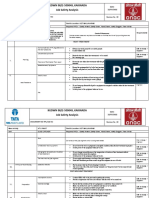
- Job Safety Analysis Baseline Risk Assessment/ Job Safety AnalysisDocument7 pagesJob Safety Analysis Baseline Risk Assessment/ Job Safety AnalysisSKH CultureNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces in Oil and Gas OperationsDocument16 pagesConfined Spaces in Oil and Gas Operationssmithyry2014No ratings yet
- IChemE - LPB 117-1994 - Flixborough 20 Years OnDocument3 pagesIChemE - LPB 117-1994 - Flixborough 20 Years Onsl1828100% (1)
- Heat Stress Management Plan For Plant 2: Gulf Union Foods CompanyDocument10 pagesHeat Stress Management Plan For Plant 2: Gulf Union Foods CompanyNithishNo ratings yet
- 07 - Tata Power Scaffold Safety ProcedureDocument24 pages07 - Tata Power Scaffold Safety Procedurehse bsjNo ratings yet
- Carbon Monoxide Safety: Marshall University Safety & HealthDocument22 pagesCarbon Monoxide Safety: Marshall University Safety & HealthIr ComplicatedNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Tool Box TalkDocument30 pagesNitrogen Tool Box Talkashaheen21100% (3)
- Jsa - Hot TappingDocument15 pagesJsa - Hot TappingAmadeo Sabanal0% (1)
- Pneumatic Test Explosion in Shanghai LNG TerminalDocument1 pagePneumatic Test Explosion in Shanghai LNG TerminalKyaw Kyaw AungNo ratings yet
- IGC3 ProjectDocument28 pagesIGC3 Projectvishnu100% (1)
- Emergency Response Flow Chart: Job Saety AnalysisDocument5 pagesEmergency Response Flow Chart: Job Saety AnalysisjneNo ratings yet
- Safety STD Audit Check ListDocument12 pagesSafety STD Audit Check Listfaraz ahmed0% (1)
- Ethanol Tank Fire Incident ReportDocument20 pagesEthanol Tank Fire Incident ReportN P Srinivasarao100% (1)
- Near Miss ReportDocument15 pagesNear Miss ReportAyaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Buncefield Final ReportDocument208 pagesBuncefield Final ReportKannanGKNo ratings yet
- 16.01.2013 Guj Ahirsalt Alled Kutch Eia 6Document128 pages16.01.2013 Guj Ahirsalt Alled Kutch Eia 6Jaime HernandezNo ratings yet
- Tunnel HSE ManualDocument13 pagesTunnel HSE Manualbabu nairNo ratings yet
- FlammablePresentation 2016Document162 pagesFlammablePresentation 2016gulfpipinggmailcomNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of Three Step Risk Assessment Method For Ship Recycling Sector 2015 Safety ScienceDocument15 pagesDevelopment and Validation of Three Step Risk Assessment Method For Ship Recycling Sector 2015 Safety ScienceEvi SiswantoNo ratings yet
- PR-2352 - Greater Birba Emergency Response PlanDocument173 pagesPR-2352 - Greater Birba Emergency Response PlanSHRISH SHUKLANo ratings yet
- XXX Revised April 6, 2005 Standard Operating Procedure No. S-100Document12 pagesXXX Revised April 6, 2005 Standard Operating Procedure No. S-100Peter Nai HoNo ratings yet
- Safe Refueling ProcedureDocument8 pagesSafe Refueling ProcedureABDUL RISHAD Kunduthode100% (1)
- Health, Safety, and Environmental Management in Offshore and Petroleum EngineeringFrom EverandHealth, Safety, and Environmental Management in Offshore and Petroleum EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ptw-Kec - Final v3 - SparkDocument1 pagePtw-Kec - Final v3 - SparkXiang JintaoNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL SAFETY - HOUSE KEEPING - 113-pDocument117 pagesINDUSTRIAL SAFETY - HOUSE KEEPING - 113-psandeep100% (1)
- The Mexico City Explosion of 1984 FinalDocument18 pagesThe Mexico City Explosion of 1984 FinalVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- HSE Annual ReportDocument12 pagesHSE Annual ReportKashifPervez1No ratings yet
- Scaffold SafetyDocument58 pagesScaffold SafetyMd Sajid HossainNo ratings yet
- OIL FILTERATION - TRA - RevDocument21 pagesOIL FILTERATION - TRA - RevBenasher IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Safety Award ApplicationDocument7 pagesSafety Award ApplicationJason Smith100% (1)
- Guidelines On Permit To Work (P.T.W.) Systems: Report No. 6.29/189 January 1993Document30 pagesGuidelines On Permit To Work (P.T.W.) Systems: Report No. 6.29/189 January 1993merajuddin64_6144004No ratings yet
- WMS Installation of PanelsDocument23 pagesWMS Installation of Panelsahmed08839494No ratings yet
- Nitrogen Info Pack 2011Document18 pagesNitrogen Info Pack 2011Nizami ShirinovNo ratings yet
- Safety Audit Report: MEIL/A/001Document6 pagesSafety Audit Report: MEIL/A/001jithin shankarNo ratings yet
- An Integrated Approach To The Safety of Surface Well Testing On Mobile Offshore RigsDocument9 pagesAn Integrated Approach To The Safety of Surface Well Testing On Mobile Offshore RigsTheNourEldenNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learned From Recent Process Safety IncidentsDocument7 pagesLessons Learned From Recent Process Safety IncidentsMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Certificate Student4Document1 pageCertificate Student4MOJIBNo ratings yet
- Portable Grinder SafetyDocument20 pagesPortable Grinder SafetysabaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Appreciation 19Document1 pageCertificate of Appreciation 19MOJIBNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Appreciation: Name SurnameDocument1 pageCertificate of Appreciation: Name SurnameMOJIBNo ratings yet
- KRA - Xls (1) Shaikh (HR)Document2 pagesKRA - Xls (1) Shaikh (HR)MOJIBNo ratings yet
- ISO 45001 2018 Versus OHSAS 18001 ClausewiseDocument6 pagesISO 45001 2018 Versus OHSAS 18001 ClausewiseEngilsh Iso80% (10)
- Unsafe Acts Safety TalkDocument1 pageUnsafe Acts Safety Talksafety86No ratings yet
- Chemical Safety Answer KeyDocument2 pagesChemical Safety Answer KeyMOJIBNo ratings yet
- Best Practices RoadsafetyDocument7 pagesBest Practices RoadsafetyMOJIBNo ratings yet
- OHSAS 18001 Audit ChecklistDocument26 pagesOHSAS 18001 Audit Checklistslamet_r100% (4)
- Crane Lift Plan Checklist-1 PDFDocument2 pagesCrane Lift Plan Checklist-1 PDFMOJIBNo ratings yet
- English Slogan 3 PDFDocument121 pagesEnglish Slogan 3 PDFMOJIBNo ratings yet
- Crane Lift Plan Checklist-1 PDFDocument2 pagesCrane Lift Plan Checklist-1 PDFMOJIBNo ratings yet
- Behavior-Based Safety For SupervisorsDocument30 pagesBehavior-Based Safety For SupervisorsMOJIBNo ratings yet
- Create ORG Chart in PowerpointDocument1 pageCreate ORG Chart in PowerpointMOJIBNo ratings yet
- Beautiful & Minimalistic Dashboard For Business Presentation Microsoft PowerPoint (PPT) TutorialDocument2 pagesBeautiful & Minimalistic Dashboard For Business Presentation Microsoft PowerPoint (PPT) TutorialPiota MdfkNo ratings yet
- Work Instruction For Cold Work Permit: Safety Management SystemsDocument4 pagesWork Instruction For Cold Work Permit: Safety Management SystemsMOJIBNo ratings yet
- Policy SampleDocument2 pagesPolicy SampleMOJIBNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Electrical Safety 1Document5 pagesRisk Assessment Electrical Safety 1MOJIBNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument9 pagesElectrical SafetyLogesh KumarNo ratings yet
- TIMELINE InfographicDocument1 pageTIMELINE InfographicMOJIBNo ratings yet
- Induction Format BHELDocument1 pageInduction Format BHELMOJIBNo ratings yet
- CS1 Course OutlineDocument2 pagesCS1 Course Outlineapi-27149177No ratings yet
- ESPRIT Milling Tutorial 02Document11 pagesESPRIT Milling Tutorial 02Sandaruwan සුජීවNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Understanding Bearing Damage Related To PWM Drives - CNFDocument7 pagesA Practical Guide To Understanding Bearing Damage Related To PWM Drives - CNFjoe4709No ratings yet
- AMICO InstallationManual PDFDocument60 pagesAMICO InstallationManual PDFfernandoNo ratings yet
- AA Holtz & Kovacs - An Introduction To Geotechnical Engineering PDFDocument746 pagesAA Holtz & Kovacs - An Introduction To Geotechnical Engineering PDFPeterNo ratings yet
- MCT Cable Transit System: Fire Rated, Environmental Cable Sealing SystemsDocument7 pagesMCT Cable Transit System: Fire Rated, Environmental Cable Sealing SystemsRaju ThamkeNo ratings yet
- Medium Voltage MZDocument86 pagesMedium Voltage MZsujiNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument13 pagesReportMamta SindhuNo ratings yet
- Pedestrian Design Guidelines PDFDocument50 pagesPedestrian Design Guidelines PDFIvan AndradeNo ratings yet
- High Carbon Steel Shot GritDocument2 pagesHigh Carbon Steel Shot Gritabdulaziz mohammedNo ratings yet
- Risk Assess T-17 - Using Portable Hand ToolsDocument4 pagesRisk Assess T-17 - Using Portable Hand ToolsMAB AliNo ratings yet
- Roofing SafetyDocument38 pagesRoofing SafetyDhârâñî KûmârNo ratings yet
- Vol Damper (Smacna)Document9 pagesVol Damper (Smacna)MohamedOmar83No ratings yet
- Potain Igo 21 PDFDocument4 pagesPotain Igo 21 PDFMarco CruzNo ratings yet
- Robotics Engineering Minor FlowchartDocument1 pageRobotics Engineering Minor FlowchartkskkingNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Memory ManagementDocument78 pagesChapter5 Memory ManagementJackYuan JinFengNo ratings yet
- Structural Concept - Helix StructureDocument6 pagesStructural Concept - Helix StructurebistsushantNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Zvs and ZVS-ZCS Bidirectional DDocument6 pagesComparison Between Zvs and ZVS-ZCS Bidirectional DSUNIL MANJHINo ratings yet
- Steering Wheel Slip - Check: Pruebas y AjustesDocument2 pagesSteering Wheel Slip - Check: Pruebas y AjustesLENIN JHAIR VALDERRAMA SEGURANo ratings yet
- Nirma University Institute of Technology B.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering Semester IVDocument2 pagesNirma University Institute of Technology B.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering Semester IVKartik aminNo ratings yet
- Material Characterization of Sugarcane Bagasseepoxy Composites For - 2022Document5 pagesMaterial Characterization of Sugarcane Bagasseepoxy Composites For - 2022bakhrul ilmiNo ratings yet
- Dual Draw/Dual Return Fuel System TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesDual Draw/Dual Return Fuel System Troubleshootinginformer techNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument9 pagesReadmewatzzupNo ratings yet
- VSSUT (EEE) SyllabusDocument47 pagesVSSUT (EEE) SyllabusAshutosh GuptaNo ratings yet
- How To Draw and Read Line Diagrams Onboard Ships?: ShareDocument9 pagesHow To Draw and Read Line Diagrams Onboard Ships?: ShareShaif uddin rifatNo ratings yet