Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JEPP'S Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 3rd - Navigation Aids PDF
Uploaded by
Marcos BragaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JEPP'S Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 3rd - Navigation Aids PDF
Uploaded by
Marcos BragaCopyright:
Available Formats
The Chart Clinic – Third in a Series
great circle route — the shortest distance between
two points on our curved earth.
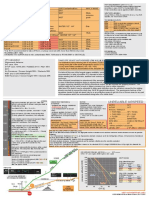
Navigation Aids
VOR, VORTAC, NDB, ILS and LF — these
Once you have selected the correct chart,
terms are bantered around frequently by pilots.
how do you locate your position fix or destination
I have even heard it said that pilots learn their
airport? Latitude and longitude lines and their
language very well so they cannot be understood
values are shown throughout the chart. In the
by the “lesser” of their peers.
chart illustration, just to the northwest of the
Every VOR facility has a compass rose
BY JAMES E. TERPSTRA Lincoln VOR, is the intersection of 41° north
surrounding the location of the VOR. A single line
latitude and 97° west longitude. The coordinate
extends from the 360° radial to indicate magnetic
values are shown adjacent to the latitude and
north. The small tick at the end of the line is used
lying off the edge of an enroute chart is not longitude lines. This makes it relatively easy to find
F quite as hazardous as flying off the edge of a
flat earth, but if the chart border data is not
utilized, it could be as disconcerting. Running out
locations on the chart, such as the Wahoo,
Nebraska Airport at N41°14.4’ W96°35.7’.
More examples of border information
to measure angles with the PV-5 plotter. A box
immediately adjacent to the VOR compass rose
gives the name, frequency, three-letter identifier
and Morse code identifier for the VOR and its
of chart seems to happen at the most inopportune showing “off-the-chart” facilities are also on the
class. This information is shown in
time, but the changes can be made easily if the chart illustration. On the top and right edges
the example for the Drummond
border information is used. outside the neatline, the next VORs used on the
VOR. The shadow area on the
When approaching the edge of a chart, there airways are Columbus and Omaha. When an
right and bottom of the box
is a way to tell which adjoining chart to use — the intersection is the next enroute fix beyond the
denotes that the Drummond
shaded blue line about two inches from the top chart edge, the intersection name and the distance
VOR is part of the enroute
of the chart (see illustration below) indicates that to that intersection are indicated just inside the
structure.
US(LO)18 is the next chart to the north and west. neatline. This can be seen just above the Lincoln
There are two ways of
If the chart and map makers had been VOR on V-6-8 at the right of the chart. The Grett
determining if a VOR has
allowed input, the earth would not have been a Intersection is 23 miles beyond Yutan Intersection
DME capability. A VORTAC
sphere — it would have been a cube. Trying to on V-6-8.
station that provides DME
project a curved surface onto a flat piece of paper The Panny Intersection just southeast of the
information is indicated by both a scalloped circle
is like fitting a round peg into a square hole. To Lincoln VORTAC is formed by the 137° radial from
inside the compass rose and a small letter “D” to
solve this problem, Jeppesen has selected the Lincoln and the 219° radial from the Omaha (OVR)
the left of the VORTAC frequency. For example,
Lambert Conformal Conic Projection for most VORTAC that is just outside the chart border.
the Bozeman VORTAC in the illustration shows
enroute charts, as indicated in the upper right When this situation occurs, the three-letter ident
both symbols.
or left corner of each chart. The reason for from the navaid off the chart will be included plus
mentioning projection? You can draw a straight its frequency and the radial forming the
line between two points on a chart to represent a intersection.
Reporting Points
The Bozeman VOR is a compulsory reporting
point, as indicated by the solid triangle in the
center of the compass rose. In the past, and on
international charts, an open triangle in the center
of a VOR shows that it is a noncompulsory reporting
point. By looking at the actual enroute charts for
the United States, you will see that all the
noncompulsory triangles are missing from the
center of the VOR symbols. Why? All navaids,
when used for overflights on either airways or
direct flights, are potentially reporting points. The
navaids are mostly noncompulsory reporting
points so there is no need to add the triangle
symbol in the middle of each VOR symbol.
Over the years, the FAA has reduced the
number of compulsory reporting points because of
the large increase in radar capability and coverage.
There are only a handful of compulsory reporting
points remaining in areas where radar coverage is
minimal. As an example of the decrease in
compulsory reporting points, there is only one
compulsory intersection on US(LO)7 that covers
the less populated areas of Montana and northern
Wyoming and Idaho.
Note the number “9” on the navaid facility
box for Bozeman. This indicates additional
A Major Breakthrough
II NN LL OO W
W -- CC OO SS TT FF LL II GG HH TT SS II M
M UU LL AA TT II OO NN
information somewhere on the same enroute chart
panel. On the chart, a note on the top half of the
panel states there is a crossing altitude for V-86 and
V-365 that is formed by the Bozeman VOR. In
Canada, there are no crossing altitudes that are
separately stated because the MEA of the next
airway segment always indicates the crossing
altitude at a VOR or intersection.
Terminal VORs and VORTACs are normally
used only in the terminal area for approaches and
usually have a range not more than 25 NM. In the
illustration, the letter “T” just to the left of the
VOR frequency of 109.4 MHZ shows that the
Buffalo VOR is a terminal VOR. The terminal
VOR name, frequency and three-letter
identifier are not enclosed in a box that
indicates it is not part of an airway. Most
terminal VORs are for IFR use, but the
letters “VFR only” enclosed in parentheses indicate
that Buffalo can only be used for VFR navigation.
Other Navaids
Pure TACANs do not have compass roses
since the azimuth cannot be used by most civilian Introducing, Jeppesen’s All New
pilots. When the TACAN channel is compatible
with the civilian VHF frequencies, the VHF
FS-200™ v5.0 for WINDOWS 95 ®
frequency will be placed below the TACAN name in The newest FS-200 is the first Personal Computer-based Aviation Training Device featuring a
parentheses. For example, the Malstrom TACAN 32-bit Windows 95 platform. This results in an easy, very intuitive, aviation simulator that has
been specifically designed for flight and procedural training. The new FS-200 includes all of the
can be used for DME information by
great features that made it so popular, plus many new features including:
tuning to 115.8 MHZ. The code “TAC-
105” is used solely by military y A Windows 95 look and feel y On-screen help menus y Enhanced instrument and system
failure capabilities y A more flexible and powerful map screen
navigation receivers to tune TACAN channel
y More user options in the flight replay mode
numbers.
A series of dots forming three concentric Whether you’re a CFII, an instrument pilot, or an instrument student, the FS-200 can increase
circles show the location of non-directional radio your proficiency, making you a safer pilot while lowering your flying expenses. Our new packages
include software, hardware consoles that eliminate the use of the keyboard or mouse for flight
beacons (NDBs). The NDBs are normally presented
control inputs, and a high quality yoke and rudder pedal system, all at an attractive price.
in a green color on enroute charts and each has a Complete systems start at $924.95.
magnetic north tick mark above
the facility the same as VORs. The Call Us Today!
Phone 1-800-894-3893 or 1-303-784-4274 Fax 1-303-784-4153
Hauser NDB transmits on 386 Visit our web site at http://www. jeppesen.com
kHz and has an identifier of HAU.
The Morse code identifier for each NDB is ®
included.
Localizers are currently included only when
they are used to form an enroute intersection. In
the illustration, the Butte, Montana localizer enroute charts will also depict all the localizers to James E. Terpstra is senior
transmits on 110.9 MHZ indicate their availability. The localizers that per- corporate vice president, flight
information technology at
and has an ident of IBEY. form an enroute function will be included with
Jeppesen. His ratings include
It is used to form the their frequencies, and the ones depicted to show ATP, single and multi-engine,
Ketch Intersection. Since the Butte localizer localizer availability will be shown without their fre- airplane and instrument flight
is a LOC-DME facility, the formation of quencies. instructor. His 6,000+ hours
Ketch is also made by the 30 DME In the next article, we will talk about all the include 3,200 instructing.
from the localizer DME. communication information found on the face of For comments, please Email:
JimTerps@jeppesen.com
Beginning in June, the Jeppesen the chart as well as the front panel.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- DODAR or FORDEC - Which Is Better?Document2 pagesDODAR or FORDEC - Which Is Better?Marcos Braga100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- MB A32F Ground Speed Mini - BulletinDocument7 pagesMB A32F Ground Speed Mini - BulletinMarcos Braga100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- MB Eng Failure ECAM - PpsDocument42 pagesMB Eng Failure ECAM - PpsMarcos Braga100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- MB A32F Engine Failure ECAMDocument42 pagesMB A32F Engine Failure ECAMMarcos Braga100% (4)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- #1 Airbus Safety First Mag - Jan 2005Document14 pages#1 Airbus Safety First Mag - Jan 2005upsasaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Wet With Sand or Dust: LPC Calculation Take-Off Is Not Authorised (Om A 8.3 8.3.3)Document1 pageWet With Sand or Dust: LPC Calculation Take-Off Is Not Authorised (Om A 8.3 8.3.3)Marcos Braga100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- MB A32F FOQA Parameters A319 320Document3 pagesMB A32F FOQA Parameters A319 320Marcos BragaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Wright Brothers, A History From Beginning To EndDocument38 pagesThe Wright Brothers, A History From Beginning To EndMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- JEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 10th - Off-Airway Navigation Long DistancesDocument2 pagesJEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 10th - Off-Airway Navigation Long DistancesMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Chart Clinic - Ninth in A Series: Vors For Direct Route NavigationDocument2 pagesThe Chart Clinic - Ninth in A Series: Vors For Direct Route Navigation222hornetNo ratings yet
- Airbus Versus Boeing RevisitedDocument11 pagesAirbus Versus Boeing RevisitedArif PranandaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Chart Clinic - Ninth in A Series: Vors For Direct Route NavigationDocument2 pagesThe Chart Clinic - Ninth in A Series: Vors For Direct Route Navigation222hornetNo ratings yet
- MB Holding EntryDocument6 pagesMB Holding EntryMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- JEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 7th - Special Use Airspace (SUA)Document2 pagesJEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 7th - Special Use Airspace (SUA)Marcos BragaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Brazil's Airline HistoryDocument52 pagesBrazil's Airline HistoryMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- JEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 8th - Airway Designation SymbolsDocument2 pagesJEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 8th - Airway Designation SymbolsMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- The Chart Clinic - Fifth in A Series: Center FrequenciesDocument2 pagesThe Chart Clinic - Fifth in A Series: Center Frequencies222hornetNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- JEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 4th - Communications TabulationsDocument2 pagesJEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 4th - Communications TabulationsMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- A32F Electrical Priority - JPGDocument1 pageA32F Electrical Priority - JPGMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- JEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 6th - Controlled AirspaceDocument2 pagesJEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 6th - Controlled AirspaceMarcos Braga100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- JEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 2nd - Enroute ChartsDocument2 pagesJEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 2nd - Enroute ChartsMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Rules of Thumb 2Document3 pagesRules of Thumb 2Marcos BragaNo ratings yet
- JEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 1st - Chart LayoutDocument2 pagesJEPP's Briefing - The Chart Clinic - 1st - Chart LayoutMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- A32F Electrical PriorityDocument1 pageA32F Electrical PriorityMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Solutions in Surveillance: Presentation ToDocument39 pagesAdvanced Solutions in Surveillance: Presentation ToMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- Wing Tip ShapesDocument6 pagesWing Tip ShapesMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- MB Adirs & Apu BleedDocument14 pagesMB Adirs & Apu BleedMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- MB Fordec & NitesDocument1 pageMB Fordec & NitesMarcos BragaNo ratings yet
- A320 FMGS Codes BragaDocument25 pagesA320 FMGS Codes BragaMarcos Braga92% (13)
- Tour Guiding and Escort Services - 301Document95 pagesTour Guiding and Escort Services - 301Zane 19531No ratings yet
- Employer'S Virtual Pag-Ibig Enrollment Form: Address and Contact DetailsDocument2 pagesEmployer'S Virtual Pag-Ibig Enrollment Form: Address and Contact DetailstheffNo ratings yet
- My Parenting DnaDocument4 pagesMy Parenting Dnaapi-468161460No ratings yet
- ITC Green Centre: Gurgaon, IndiaDocument19 pagesITC Green Centre: Gurgaon, IndiaAgastya Dasari100% (2)
- Custom Belt Buckles: Custom Brass Belt Buckles - Hand Made in The USA - Lifetime Guarantee of QualityDocument1 pageCustom Belt Buckles: Custom Brass Belt Buckles - Hand Made in The USA - Lifetime Guarantee of QualityAndrew HunterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3C Problem Solving StrategiesDocument47 pagesChapter 3C Problem Solving StrategiesnhixoleNo ratings yet
- Nandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Document336 pagesNandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Digitaladda IndiaNo ratings yet
- Michael M. Lombardo, Robert W. Eichinger - Preventing Derailmet - What To Do Before It's Too Late (Technical Report Series - No. 138g) - Center For Creative Leadership (1989)Document55 pagesMichael M. Lombardo, Robert W. Eichinger - Preventing Derailmet - What To Do Before It's Too Late (Technical Report Series - No. 138g) - Center For Creative Leadership (1989)Sosa VelazquezNo ratings yet
- The BreakupDocument22 pagesThe BreakupAllison CreaghNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Borer (2013) Advanced Exercise Endocrinology PDFDocument272 pagesBorer (2013) Advanced Exercise Endocrinology PDFNicolás Bastarrica100% (1)
- BP TB A2PlusDocument209 pagesBP TB A2PlusTAMER KIRKAYA100% (1)
- Bootstrap DatepickerDocument31 pagesBootstrap DatepickerdandczdczNo ratings yet
- Trenching Shoring SafetyDocument29 pagesTrenching Shoring SafetyMullapudi Satish KumarNo ratings yet
- 60617-7 1996Document64 pages60617-7 1996SuperhypoNo ratings yet
- Volvo D16 Engine Family: SpecificationsDocument3 pagesVolvo D16 Engine Family: SpecificationsJicheng PiaoNo ratings yet
- Churches That Have Left RCCG 0722 PDFDocument2 pagesChurches That Have Left RCCG 0722 PDFKadiri JohnNo ratings yet
- Atelierul Digital Pentru Programatori: Java (30 H)Document5 pagesAtelierul Digital Pentru Programatori: Java (30 H)Cristian DiblaruNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior (Perception & Individual Decision Making)Document23 pagesOrganizational Behavior (Perception & Individual Decision Making)Irfan ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Nikulin D. - Imagination and Mathematics in ProclusDocument20 pagesNikulin D. - Imagination and Mathematics in ProclusannipNo ratings yet
- KBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race ScheduleDocument2 pagesKBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race SchedulezainNo ratings yet
- Army Public School Recruitment 2017Document9 pagesArmy Public School Recruitment 2017Hiten BansalNo ratings yet
- What Is SCOPIC Clause - A Simple Overview - SailorinsightDocument8 pagesWhat Is SCOPIC Clause - A Simple Overview - SailorinsightJivan Jyoti RoutNo ratings yet
- Information Security Policies & Procedures: Slide 4Document33 pagesInformation Security Policies & Procedures: Slide 4jeypopNo ratings yet
- Rebecca Young Vs CADocument3 pagesRebecca Young Vs CAJay RibsNo ratings yet
- Genomics - FAODocument184 pagesGenomics - FAODennis AdjeiNo ratings yet
- LM213 First Exam Notes PDFDocument7 pagesLM213 First Exam Notes PDFNikki KatesNo ratings yet
- Matthew DeCossas SuitDocument31 pagesMatthew DeCossas SuitJeff NowakNo ratings yet
- MPU Self Reflection Peer ReviewDocument3 pagesMPU Self Reflection Peer ReviewysaNo ratings yet
- Imogen Powerpoint DesignDocument29 pagesImogen Powerpoint DesignArthur100% (1)
- EMI - Module 1 Downloadable Packet - Fall 2021Document34 pagesEMI - Module 1 Downloadable Packet - Fall 2021Eucarlos MartinsNo ratings yet