Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 1 - Stakeholders
Uploaded by
Chelz Rachel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThe document outlines the types of stakeholders a business has and their responsibilities to each other. The main stakeholders discussed are employees, suppliers, customers, competitors, shareholders, finance providers, and government. For each stakeholder, the document lists the business's responsibilities to them such as timely payment, fair prices, and safe working conditions. It also outlines the stakeholders' responsibilities such as providing labor, quality supplies, loyalty, and tax payments.
Original Description:
stake
Original Title
Topic 1- Stakeholders
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the types of stakeholders a business has and their responsibilities to each other. The main stakeholders discussed are employees, suppliers, customers, competitors, shareholders, finance providers, and government. For each stakeholder, the document lists the business's responsibilities to them such as timely payment, fair prices, and safe working conditions. It also outlines the stakeholders' responsibilities such as providing labor, quality supplies, loyalty, and tax payments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesTopic 1 - Stakeholders
Uploaded by
Chelz RachelThe document outlines the types of stakeholders a business has and their responsibilities to each other. The main stakeholders discussed are employees, suppliers, customers, competitors, shareholders, finance providers, and government. For each stakeholder, the document lists the business's responsibilities to them such as timely payment, fair prices, and safe working conditions. It also outlines the stakeholders' responsibilities such as providing labor, quality supplies, loyalty, and tax payments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
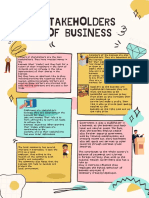
Types of Stakeholders
Types Business’s responsibilities to Stakeholders Responsibilities/Functions
Employee Timely and regular payment of wages and salaries Contributes labour and expertise
Proper working conditions and welfare amenities Usually hired to perform specific duties which are packaged into a
Opportunity for better career prospects job
Job security as well as social security like group insurance, Employee loyalty and low labour turnover
pension, retirement benefits Maintain stable employment in firm
Better living conditions like housing, transport, canteen Receive fair pay for work
Timely training and development Work in safe, comfortable environment
Suppliers Giving regular orders for purchase of goods Suppliers are businessmen who supply raw materials and other
Dealing on fair terms and conditions items required by manufacturers and traders
Timely payment of dues (Pay fair prices and pay invoices Provide the resources needed
promptly Timely delivery of quality materials
Avoid excessive pressure on smaller or weaker suppliers to Suppliers need the business to continue to buy their products in
cut prices order to maintain their own profitability and long term financial
health
“Payment holidays” may be offered to struggling businesses, if
this means keeping them as customers
Customers Products and services must be able to take care of the Known as a buyer or purchaser of a good, service, product or idea
needs of the customers Customer loyalty and repeat purchases
There must be regularity in supply of goods and services Good publicity when customers give “word of mouth”
Price of the goods and services should be reasonable and recommendations; positive customer feedback helps to improve
affordable goods and services
Giving customers assurances about quality, delivery dates, In a world of increasing free trade and international competition,
service levels and continued supplies of vital components it is essential to satisfy customers’ demands in order to stay in
and materials Business in the long term.
Not to break the laws on consumer protection and accurate
advertising
Competitors To compete fairly and within the law Avoid legal action as a consequence of uncompetitive practices
It is not a responsibility of business to provide details of its Opportunities for co-operations and joint ventures-as long as
strategic plans to competitors these do not contravene competition laws.
Not to offer to customers heavy discounts and/or free
products in every sale
Not to defame competitors through false or ambiguous
advertisements
Shareholders Annual accounts presented to shareholders Shareholders will be reluctant to sell shares and this will help
Proper use of capital avoid share price falls
To provide accurate and timely information Shareholders may be willing to buy new issues of shares to invest
Ensure growth and appreciation of owner’s capital further capital in the company
Provide regular and fair return on owners capital
Finance Payment of Interest and repayment of loans as required More willing to provide financial support in the future
Provider To raise public image of the company
Government Payment of taxes Treat businesses legally under the law
Obeying rules and regulations Prevent unfair competition
To generate employment Establish trading relations with other countries to facilitate
To provide assistance in the field of developmental international trade
research on education, medical science, technology etc Increase social welfare
You might also like
- Accounting and Its Stakeholders ExpectationsDocument9 pagesAccounting and Its Stakeholders ExpectationsLalithya Sannitha MeesalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document5 pagesChapter 5Adnan SurzoNo ratings yet
- Unit 24 - Principles of Customer Service in Hospitality LeisureDocument25 pagesUnit 24 - Principles of Customer Service in Hospitality Leisureapi-521783463No ratings yet
- Applied Economics Lesson 7Document2 pagesApplied Economics Lesson 7Calingasan, John Lloyd BañasNo ratings yet
- Besr Q4 W1Document9 pagesBesr Q4 W1Leinel Macutay MalazzabNo ratings yet
- 6) Stakeholders in Business Activities As Notes Final (D)Document12 pages6) Stakeholders in Business Activities As Notes Final (D)CRAZYBLOBY 99No ratings yet
- Understanding Apparel Quality Mid-Term Assignment: Benefits of Good Quality Products For IndustryDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Apparel Quality Mid-Term Assignment: Benefits of Good Quality Products For Industryvikash singhNo ratings yet
- What's NewDocument6 pagesWhat's NewJhay Lorraine Sadian PalacpacNo ratings yet
- Sales and Service Consultant - PD - 2016Document2 pagesSales and Service Consultant - PD - 2016James GreigNo ratings yet
- Materials Management-Unit-3Document15 pagesMaterials Management-Unit-3Garima KwatraNo ratings yet
- T3 - Ethics - Seminar - Q - AnswerDocument4 pagesT3 - Ethics - Seminar - Q - AnswerPham TungNo ratings yet
- ViniDocument34 pagesViniNishantNo ratings yet
- Social Responsibility KrajDocument15 pagesSocial Responsibility KrajShivangi GargNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Purchase TechnologyDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Purchase TechnologyHanna KabeerNo ratings yet
- Chap5 Creating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsDocument32 pagesChap5 Creating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsRajja RashadNo ratings yet
- Session - 2 - Relation MarketingDocument25 pagesSession - 2 - Relation MarketingFarhan Islam100% (1)
- Reviewer For Quiz in Business EthicsDocument8 pagesReviewer For Quiz in Business EthicsRemar BaladiaNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics and Responsibility - CLAS 1 & 2Document50 pagesBusiness Ethics and Responsibility - CLAS 1 & 2Kim Yessamin MadarcosNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management: Concepts and TechnologiesDocument39 pagesCustomer Relationship Management: Concepts and TechnologiesJaisathya 007No ratings yet
- Stakeholders in BusinessDocument14 pagesStakeholders in BusinessUtkarsh ZopeNo ratings yet
- Taco BellDocument3 pagesTaco BelldeepankarNo ratings yet
- English - Glossary Business TermsDocument7 pagesEnglish - Glossary Business TermsChoy DanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Costs and BenefitsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Costs and BenefitsAnonymous wMppXCM0No ratings yet
- Buyer - Seller RelationsDocument18 pagesBuyer - Seller Relationsaharish_iitkNo ratings yet
- Due Diligence: Dr. Rajinder S. AuroraDocument41 pagesDue Diligence: Dr. Rajinder S. AuroraaparnaskiniNo ratings yet
- The Business Responsibilities and AccountabilitiesDocument38 pagesThe Business Responsibilities and AccountabilitiesTricia mae DingsitNo ratings yet
- Valoracion de ClientesDocument8 pagesValoracion de ClientesGabriela GonzálezNo ratings yet
- 02 Task Performance - LogisticsDocument4 pages02 Task Performance - LogisticsBeyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.4 StakeholderDocument15 pagesUnit 1.4 StakeholderDavidNo ratings yet
- Ytf SwotDocument6 pagesYtf SwotWai Tseng ChongNo ratings yet
- BU111 SI Session - ReviewDocument29 pagesBU111 SI Session - ReviewGuan Jie XueNo ratings yet
- Group4 KaliDocument32 pagesGroup4 KaliPatriciamaelaoNo ratings yet
- Purchasing EthicsDocument5 pagesPurchasing EthicsMarissa GrutasNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 MGT1030 ETH VL2021220101216 Reference Material I 16-Aug-2021 2. Mission and VisionDocument26 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 MGT1030 ETH VL2021220101216 Reference Material I 16-Aug-2021 2. Mission and VisionParshv JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Challenges in The Internal EnvironmentDocument23 pagesChapter 3-Challenges in The Internal EnvironmentMulong Cabrillas100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document26 pagesChapter 5api-358995037No ratings yet
- Business Models-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesBusiness Models-WPS Officemadeja.joshuaNo ratings yet
- Business Purchasing BehaviorDocument21 pagesBusiness Purchasing BehaviorAditia SobarnaNo ratings yet
- Umar Farooq 021Document17 pagesUmar Farooq 021fatimadilawaiz1No ratings yet
- 1.4 Stakeholders: On Completion of This Chapter, You Should Be Able To: Analyse and ApplyDocument12 pages1.4 Stakeholders: On Completion of This Chapter, You Should Be Able To: Analyse and ApplyKressida BanhNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics and Social ResponsibilityDocument42 pagesBusiness Ethics and Social ResponsibilityChristian Carator MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- BECG 14 15 Corporate Social Responsibility StakeholdersDocument42 pagesBECG 14 15 Corporate Social Responsibility StakeholdersAnshuman HarshvardhanNo ratings yet
- Accenture Creating Customer Loyalty A Customer Centric ApproachDocument12 pagesAccenture Creating Customer Loyalty A Customer Centric ApproachNicholasChai100% (1)
- 7 Services MKTG Building Customer RelationshipsDocument14 pages7 Services MKTG Building Customer RelationshipsAsif PharmacistNo ratings yet
- Accounting 01Document9 pagesAccounting 01reagan blaireNo ratings yet
- Anjli Doc Aldi Case Study.Document9 pagesAnjli Doc Aldi Case Study.Mir safi balochNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentkhaebanalintlemamorieeNo ratings yet
- IC Vendor and Supplier Assessment Criteria Checklist 10842 - PDFDocument4 pagesIC Vendor and Supplier Assessment Criteria Checklist 10842 - PDFNur RochmanNo ratings yet
- Prudential Assurance Malaysia Berhad Treat Customers Fairly CharterDocument1 pagePrudential Assurance Malaysia Berhad Treat Customers Fairly CharterAhmad ZakwanNo ratings yet
- SITXFIN005 TestDocument7 pagesSITXFIN005 Testjot jotNo ratings yet
- CSR PPT CH.2Document24 pagesCSR PPT CH.2Asegid gezehagnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.stakeholders in A BusinessDocument3 pagesChapter 5.stakeholders in A BusinessKhushi PallooNo ratings yet
- Contractual Compliance PolicyDocument8 pagesContractual Compliance Policyrachel.coxlydenNo ratings yet
- Acc UpdatedDocument23 pagesAcc UpdatedEthel Jasmine VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting and Business EthicsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Accounting and Business EthicschauromweaNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 Module 1 BESRDocument6 pagesLAS 1 Module 1 BESRAnna Jessica NallaNo ratings yet
- Part A 1. Explain The Purpose of The Australian Consumer Law and How It Protects Consumers' Rights. AnswerDocument46 pagesPart A 1. Explain The Purpose of The Australian Consumer Law and How It Protects Consumers' Rights. AnswerAnil KadariyaNo ratings yet
- Stakeholders of A BusinessDocument2 pagesStakeholders of A BusinessKiano GrantNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Professional Salesmanship - Finals (Mid Term)Document12 pagesReviewer in Professional Salesmanship - Finals (Mid Term)Julia CanoNo ratings yet
- MLBB Hornbill Rules and RegulationDocument6 pagesMLBB Hornbill Rules and RegulationChelz RachelNo ratings yet
- Event ReportDocument1 pageEvent ReportChelz RachelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hospitality Fifth Edition John R. Walker: Chapter 13: Special EventsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Hospitality Fifth Edition John R. Walker: Chapter 13: Special EventsChelz RachelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Exercises 2.1 Part I & 2.2 Part I & IIDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Exercises 2.1 Part I & 2.2 Part I & IIChelz RachelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Non-Current Assets Held For Sale and Discontinued OperationsDocument35 pagesChapter 20 - Non-Current Assets Held For Sale and Discontinued OperationsVera Angraini50% (2)
- Quotation2024021303 Kitchen Renovation UpdatedDocument2 pagesQuotation2024021303 Kitchen Renovation UpdatedPearl FernandesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Competitive StrategyDocument17 pagesLecture 5 - Competitive StrategySachin kumarNo ratings yet
- Theory of Cost and ProfitDocument11 pagesTheory of Cost and ProfitCenniel Bautista100% (4)
- Roland Berger - Think-Act - Growth - # 14 2009Document59 pagesRoland Berger - Think-Act - Growth - # 14 2009apritul3539No ratings yet
- Balance Sheet: Ruchi Soya Industries Ltd. - Research CenterDocument3 pagesBalance Sheet: Ruchi Soya Industries Ltd. - Research CenterAjitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Margaret Thatcher 19252013Document2 pagesMargaret Thatcher 19252013selvamuthukumarNo ratings yet
- Nashik CDPDocument8 pagesNashik CDPSaurav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 14 - Splendour at 3950 - 1Document1 page14 - Splendour at 3950 - 1Purva PatilNo ratings yet
- Econ 101 Cheat Sheet (FInal)Document1 pageEcon 101 Cheat Sheet (FInal)Alex MadarangNo ratings yet
- The Panama Canal Expansion Plan and Its EffectDocument19 pagesThe Panama Canal Expansion Plan and Its EffectMohamed Salah El DinNo ratings yet
- Este Documento Es Aceptado Tributariamente Por SunatDocument2 pagesEste Documento Es Aceptado Tributariamente Por SunatMelissa CongonaNo ratings yet
- Company Profile PT. Nikkatsu Electric WorksDocument17 pagesCompany Profile PT. Nikkatsu Electric WorksDenny Ilyas Attamimi100% (1)
- Concept of RiskDocument21 pagesConcept of RiskAbhilash BekalNo ratings yet
- Man Kiw Chapter 16 Solutions ProblemsDocument4 pagesMan Kiw Chapter 16 Solutions ProblemsJulian Ricardo Corrales FierroNo ratings yet
- BFAR JournalizingDocument3 pagesBFAR Journalizingangelica joyce caballesNo ratings yet
- Horasis Global India Business Meeting 2010 - Programme BrochureDocument32 pagesHorasis Global India Business Meeting 2010 - Programme BrochuresaranshcNo ratings yet
- Mwakyusa Bupe Final E-Thesis (Master Copy) PDFDocument326 pagesMwakyusa Bupe Final E-Thesis (Master Copy) PDFRajendra LamsalNo ratings yet
- Cbip Manual CapitalizationDocument2 pagesCbip Manual CapitalizationMahidhar Talapaneni100% (1)
- Marine Insurance QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesMarine Insurance QuestionnaireSuraj Theruvath100% (5)
- Economic RRL Version 2.1Document8 pagesEconomic RRL Version 2.1Adrian Kenneth G. NervidaNo ratings yet
- Study Id95787 Wealth Management in IndiaDocument40 pagesStudy Id95787 Wealth Management in IndiaAbhinandhNairNo ratings yet
- BillDocument1 pageBillAskari NaqviNo ratings yet
- LKTW1 Mar 2008Document94 pagesLKTW1 Mar 2008DewiNo ratings yet
- Bank List 1502Document6 pagesBank List 1502neeraj.parasharNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2011 Beximco PharmaDocument91 pagesAnnual Report 2011 Beximco PharmaMD ABUL KHAYERNo ratings yet
- Case Study On BudgetingDocument3 pagesCase Study On BudgetingKiruthika DayanandanNo ratings yet
- Brazil Invest in Oct19Document154 pagesBrazil Invest in Oct19Giulia CamposNo ratings yet
- NumericalReasoningTest2 SolutionsDocument32 pagesNumericalReasoningTest2 SolutionsMuhammad Waseem100% (1)
- Product Release Oracle Banking Treasury Management Release 14.6.0.0.0 File NameDocument64 pagesProduct Release Oracle Banking Treasury Management Release 14.6.0.0.0 File NamenajusmaniNo ratings yet