Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematical Studies Formula Booket
Uploaded by
saloniCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematical Studies Formula Booket
Uploaded by
saloniCopyright:
Available Formats
Diploma Programme
Mathematical studies SL
formula booklet
For use during the course and in the examinations
First examinations 2014
Edited in 2015 (version 2)
© International Baccalaureate Organization 2012 5042
Contents
Prior learning 2
Topics 3
Topic 1—Number and algebra 3
Topic 2—Descriptive statistics 3
Topic 3—Logic, sets and probability 4
Topic 5—Geometry and trigonometry 5
Topic 6—Mathematical models 6
Topic 7—Introduction to differential calculus 6
Mathematical studies SL formula booklet 1
Prior learning
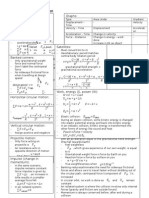
5.0 Area of a parallelogram A= b × h , where b is the base, h is the height
1
Area of a triangle =
A (b × h) , where b is the base, h is the
2
height
1
Area of a trapezium =
A (a + b) h , where a and b are the
2
parallel sides, h is the height
Area of a circle A = πr 2 , where r is the radius
Circumference of a circle C = 2πr , where r is the radius
Distance between two points ( x1 , y1 ) and
d= ( x1 − x2 ) 2 + ( y1 − y2 ) 2
( x2 , y2 )
Coordinates of the midpoint of a line segment x1 + x2 y1 + y2
with endpoints ( x1 , y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) ,
2 2
Mathematical studies SL formula booklet 2
Topics
Topic 1—Number and algebra
1.2 Percentage error vA − vE
ε= × 100% , where vE is the exact value and vA is the
vE
approximate value of v
1.7 The nth term of an un = u1 + (n − 1) d
arithmetic sequence
The sum of n terms of an n n
arithmetic sequence S n= ( 2u1 + (n − 1) d )= (u1 + un )
2 2
1.8 The nth term of a un = u1r n −1
geometric sequence
The sum of n terms of a u1 (r n − 1) u1 (1 − r n )
geometric sequence = S = , r ≠1
r −1 1− r
n
1.9 Compound interest kn
r
FV = PV × 1 + , where FV = future value, PV = present
100k
value, n = number of years, k = number of compounding periods
per year, r% = nominal annual rate of interest
Topic 2—Descriptive statistics
2.5 Mean of a set of data k
∑fx i i k
x= i =1
n
, where n = ∑f
i =1
i
2.6 Interquartile range = Q3 − Q1
IQR
Mathematical studies SL formula booklet 3
Topic 3—Logic, sets and probability
3.3 Truth tables p q ¬p p∧q p∨q p∨q p⇒q p ⇔ q
T T F T T F T T
T F F F T T F F
F T T F T T T F
F F T F F F T T
3.6
Probability of an event A P ( A) = number of outcomes in A
total number of outcomes
Complementary events P ( A′) = 1 − P ( A)
3.7 Combined events P ( A ∪ B )= P ( A) + P ( B) − P ( A ∩ B)
Mutually exclusive events P ( A ∩ B) =
0
Independent events P ( A ∩ B) =
P ( A) P ( B)
P ( A ∩ B)
Conditional probability P (A | B ) =
P ( B)
Mathematical studies SL formula booklet 4
Topic 5—Geometry and trigonometry
5.1 Equation of a straight line y = mx + c ; ax + by + d = 0
y2 − y1
Gradient formula m=
x2 − x1
5.3 a b c
Sine rule = =
sin A sin B sin C
b2 + c2 − a 2
Cosine rule a 2 = b 2 + c 2 − 2bc cos A ; cos A =
2bc
1
Area of a triangle A = ab sin C , where a and b are adjacent sides, C is the
2
included angle
5.5 Area of the curved A= 2πrh , where r is the radius, h is the height
surface of a cylinder
Surface area of a sphere A = 4πr 2 , where r is the radius
Area of the curved A = πrl , where r is the radius, l is the slant height
surface of a cone
1
Volume of a pyramid V = Ah , where A is the area of the base, h is the vertical height
3
Volume of a cuboid V =l × w × h , where l is the length, w is the width, h is the height
Volume of a cylinder V = πr 2 h , where r is the radius, h is the height
4 3
Volume of a sphere V= πr , where r is the radius
3
1 2
Volume of a cone V= πr h , where r is the radius, h is the vertical height
3
Volume of a prism V = Ah , where A is the area of cross-section, h is the height
Mathematical studies SL formula booklet 5
Topic 6—Mathematical models
6.3 Equation of the axis of b
symmetry for the graph of x= −
the quadratic function
2a
y = ax 2 + bx + c
Topic 7—Introduction to differential calculus
7.2 Derivative of ax n f ( x) =ax n ⇒ f ′( x) =nax n −1
Derivative of a sum f ( x) = ax n , g ( x) = bx m ⇒ f ′( x) + g ′( x) = nax n −1 + mbx m −1
Mathematical studies SL formula booklet 6
You might also like
- ACT 2 Explanatory Answers - ScienceDocument14 pagesACT 2 Explanatory Answers - Sciencerotat2348No ratings yet
- Physics Bowl ExamDocument7 pagesPhysics Bowl ExamShilpa GodboleNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus ReviewDocument75 pagesAP Calculus ReviewJuliaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Previous PAT Tests OxfordDocument181 pagesAnswers To Previous PAT Tests OxfordPatricia Sheppard100% (2)
- Session 1 Calculus AB 2023 AP Daily Practice SessionsDocument1 pageSession 1 Calculus AB 2023 AP Daily Practice SessionsAdel AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Linearizing Data PracticeDocument2 pagesAP Physics Linearizing Data PracticeHuiqiNo ratings yet
- MHT Cet Triumph Maths Mcqs Based On STD Xi Xii Syllabus MH Board Hints 12750 PDFDocument699 pagesMHT Cet Triumph Maths Mcqs Based On STD Xi Xii Syllabus MH Board Hints 12750 PDFvipul deshmukh100% (3)
- Strength of Materials Thin Curved BarsDocument18 pagesStrength of Materials Thin Curved Barshamza100% (1)
- Vol Prism 1Document2 pagesVol Prism 1Moneyball7No ratings yet
- CH 6 Applications of Derivatives Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)Document6 pagesCH 6 Applications of Derivatives Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)CRPF School88% (24)
- AP Calculus BC IntegrationDocument1 pageAP Calculus BC IntegrationteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Newton's 2nd Law-ProblemsDocument3 pagesNewton's 2nd Law-Problems1996andreNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Summer PacketDocument14 pagesAP Physics 1 Summer PacketAkhil DonapatiNo ratings yet
- 6 ElectrochemistryDocument20 pages6 ElectrochemistryhanifzainolNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Chapter 19 Thermodynamics - Spontaneity and Entropy KeyDocument3 pagesAP Chemistry Chapter 19 Thermodynamics - Spontaneity and Entropy Keyphuonglehuuyen100% (1)
- APES Notes - Chapter 20: The Atmosphere: Climate, Climate Change, and Ozone DepletionDocument9 pagesAPES Notes - Chapter 20: The Atmosphere: Climate, Climate Change, and Ozone DepletionirregularflowersNo ratings yet
- Question Physics1Document9 pagesQuestion Physics1Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Exam Wo AnswersDocument6 pagesUnit 6 Exam Wo AnswersHarun KianiNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C EquationsDocument3 pagesAP Physics C EquationsJoe ReiniNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B - Practice Workbook 1Document401 pagesAP Physics B - Practice Workbook 1JacobBigham100% (2)
- Practice Questions Pure Maths STD 8 12Document2 pagesPractice Questions Pure Maths STD 8 12Madhusudan G. TandaleNo ratings yet
- AP Environmental Notes From Chap 1-5Document25 pagesAP Environmental Notes From Chap 1-5wbb789No ratings yet
- Rules of Subject Verb AgreementDocument4 pagesRules of Subject Verb Agreementapi-302727717No ratings yet
- Derivatives Formula Sheet CondensedDocument1 pageDerivatives Formula Sheet CondensedintegralCALCNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument17 pagesAir PollutionAaron Mitchell100% (1)
- Introduction To IntegrationDocument4 pagesIntroduction To IntegrationwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- APES Notes - Chapter 16: Pests and Pest ControlDocument3 pagesAPES Notes - Chapter 16: Pests and Pest Controlirregularflowers100% (2)
- AP Calculus BC Quiz 3: The DerivativeDocument1 pageAP Calculus BC Quiz 3: The DerivativeteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- APES Notes - Chapter Eight: Soil: Foundation For LandDocument9 pagesAPES Notes - Chapter Eight: Soil: Foundation For LandirregularflowersNo ratings yet
- E&M Multiple Choice Answers 2004Document3 pagesE&M Multiple Choice Answers 2004KLC12345100% (1)
- Electric Potential and EnergyDocument6 pagesElectric Potential and Energykw2533No ratings yet
- ExamView - Chapter 3 ReviewDocument6 pagesExamView - Chapter 3 Reviewjfinster1987100% (2)
- Phy 105 Problem Set 1 Solutions 2012Document9 pagesPhy 105 Problem Set 1 Solutions 2012pbrowning9416No ratings yet
- Le Chatelier's PrincipleDocument2 pagesLe Chatelier's PrincipleJega SkyNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument4 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsMihir SethiNo ratings yet
- Integration Formulas PDFDocument1 pageIntegration Formulas PDFUmer ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Mock U1 Edexcel PDFDocument11 pagesMock U1 Edexcel PDFAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Formulas PDFDocument5 pagesDerivatives Formulas PDFJoe StoneNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Course OverviewDocument2 pagesAP Chemistry Course OverviewHorizonAcademyNo ratings yet
- TSHF - Healthy Habits High SchoolDocument11 pagesTSHF - Healthy Habits High Schoolapi-268502800No ratings yet
- Soil Unit Test APESDocument4 pagesSoil Unit Test APESmandarinsarecool100% (2)
- APES Notes - Chapter Three: Ecosystems: How They WorkDocument10 pagesAPES Notes - Chapter Three: Ecosystems: How They WorkirregularflowersNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass and Avogadro's Numberworked - Examples PDFDocument27 pagesAtomic Mass and Avogadro's Numberworked - Examples PDFالغزيزال الحسن EL GHZIZAL HassaneNo ratings yet
- Derivatives and Integrals FormulaDocument1 pageDerivatives and Integrals FormulaPaul Daryl CutamoraNo ratings yet
- 4 Gravitaional Constant GDocument64 pages4 Gravitaional Constant Ggomathi_nellaiNo ratings yet
- Angular MotionDocument21 pagesAngular Motionsuperman618No ratings yet
- APES Notes - Chapter 21: Atmospheric PollutionDocument1 pageAPES Notes - Chapter 21: Atmospheric PollutionirregularflowersNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry 2008 MC QuestionsDocument21 pagesAP Chemistry 2008 MC QuestionsJoanna IpNo ratings yet
- Arnold's Trivium 1991 PDFDocument10 pagesArnold's Trivium 1991 PDFKristine Rose VergaraNo ratings yet
- Using A Graph To Get The General Equation For DisplacementDocument11 pagesUsing A Graph To Get The General Equation For DisplacementAndrea KusickiNo ratings yet
- NikkuDocument36 pagesNikkuNishkarsh AroraNo ratings yet
- WorksheetsDocument22 pagesWorksheetsEljien Lumbayo100% (1)
- Transforming FunctionsDocument8 pagesTransforming FunctionsSelva RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture #15 Chapter 8 - FrictionDocument4 pagesLecture #15 Chapter 8 - FrictionArun Sankar SreetharNo ratings yet
- AP FR Quiz #5 2D MotionDocument7 pagesAP FR Quiz #5 2D MotionRobbyNo ratings yet
- AP PHYSICS B 1984 MC + SolutionsDocument19 pagesAP PHYSICS B 1984 MC + SolutionsbastardNo ratings yet
- Number Theory TutorialDocument46 pagesNumber Theory TutorialNiranjan Prasad67% (3)
- Cheat Sheet Unit 3 MotionDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Unit 3 MotionkerrevNo ratings yet
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39From EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Before the Application: How to Become the Ideal College Candidate (A Step-by-Step Guide to Making Each Year of High School Count)From EverandBefore the Application: How to Become the Ideal College Candidate (A Step-by-Step Guide to Making Each Year of High School Count)No ratings yet
- Math AA SL Booklet 2024Document10 pagesMath AA SL Booklet 2024Diana ReshetnykNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches Formula Booklet: Diploma ProgrammeDocument14 pagesMathematics: Analysis and Approaches Formula Booklet: Diploma ProgrammeKathryn TianNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Mathematics Worksheet - Understanding QuadrilateralsDocument15 pagesCBSE Class 8 Mathematics Worksheet - Understanding Quadrilateralssana100% (1)
- Set 3 P2Document2 pagesSet 3 P2Nicholson NicholsonNo ratings yet
- M A T H E M A T I C S: Bansal ClassesDocument20 pagesM A T H E M A T I C S: Bansal ClassesRahul Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Differential Geometry and Its Applications: A. PatákDocument4 pagesDifferential Geometry and Its Applications: A. PatákmiftahchoyNo ratings yet
- GLB GLBBDocument41 pagesGLB GLBBbat.laughNo ratings yet
- Voice LeadingDocument46 pagesVoice Leadingvicher2020No ratings yet
- Road AlignmentDocument17 pagesRoad Alignmentrowaters100% (1)
- CG Chapter 5Document61 pagesCG Chapter 5kiramelaku1No ratings yet
- Parallel Lines 1Document13 pagesParallel Lines 1Delia ParamithaNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Two-Dimensional MotionDocument45 pagesVectors and Two-Dimensional MotionPHAKVISETH PEMNo ratings yet
- Seamo Paper - C - 2021Document8 pagesSeamo Paper - C - 2021Bá PhongNo ratings yet
- Over-Constrained, Under-Constrained or Just Right? Goldilocks Evaluates DOF of Sketched ProfilesDocument5 pagesOver-Constrained, Under-Constrained or Just Right? Goldilocks Evaluates DOF of Sketched Profilespawanhv1454No ratings yet
- HW2 PDFDocument24 pagesHW2 PDFHimank PathakNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 Plane Trigonometry Set 1Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 Plane Trigonometry Set 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- Question Sheet + Answer Key Mid-Test Math IGCSE Grade XDocument5 pagesQuestion Sheet + Answer Key Mid-Test Math IGCSE Grade XLaurado R. SabatiniNo ratings yet
- 2 Trigonometric Functions Answers CompressedDocument71 pages2 Trigonometric Functions Answers CompressedMariela Ros TandazoNo ratings yet
- The Perse Upper School Year 9 Maths Specimen Paper 5Document12 pagesThe Perse Upper School Year 9 Maths Specimen Paper 5yukkiNo ratings yet
- 3 30149Document5 pages3 30149ali_raza117No ratings yet
- Class 6 MathsDocument9 pagesClass 6 MathssbdprasadNo ratings yet
- Applications of Sine and Cosine Functions PDFDocument1 pageApplications of Sine and Cosine Functions PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- St. Line PDFDocument40 pagesSt. Line PDFNeerraj YadavNo ratings yet
- NMTC-2022 - Previous Year Question Papers For Class 9 and 10Document10 pagesNMTC-2022 - Previous Year Question Papers For Class 9 and 10Sujai SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Geometry: Review Exercise QuestionsDocument10 pagesGeometry: Review Exercise QuestionsMustafa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture in CalculusDocument36 pagesLecture in CalculusJovelynBrozasBihisNo ratings yet
- More Than 5000 Questions Dr. BL Sharma Mathematics PageDocument4 pagesMore Than 5000 Questions Dr. BL Sharma Mathematics Pagerskr_tNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2 Axisymmetric Stagnation Point Flow and Tensor Algebra (Due Monday, Nov. 30 On Google Class)Document2 pagesAssignment #2 Axisymmetric Stagnation Point Flow and Tensor Algebra (Due Monday, Nov. 30 On Google Class)Hatem FaroukNo ratings yet