Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Asa
Uploaded by
Harold AponteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Asa
Uploaded by
Harold AponteCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Electricity
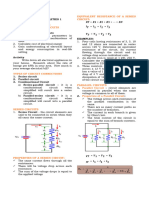
8009-1. (Refer to Figure 2.) What is the total capacitance 8011. When different rated capacitors are connected in
of a circuit containing three capacitors in parallel with parallel in a circuit, the total capacitance is
capacitances of .02 microfarad, .05 microfarad, and .10 (Note: C T = C1 + C2 + C3 . . .)
microfarad, respectively?
A— less than the capacitance of the lowest rated
A— .170 µF. capacitor.
B— 0.125 µF. B— equal to the capacitance of the highest rated
C— .0125 µF. capacitor.
You do not need to refer to Figure 2 to answer this question. C— equal to the sum of all the capacitances.
Instead, use the formula CT = C1 + C2 + C3. When capaci- When capacitors are connected in parallel, the effective
tors are connected together in parallel, the plate area of area of the plates add, and the total capacitance is the
all the capacitors add together and the total capacitance sum of the individual capacitances.
is the sum of the individual capacitances.
.02 + .05 + .10 = .170 µF
8012. When inductors are connected in series in a circuit,
the total inductance is (where the magnetic fields of each
8009-2. Convert farads to microfarads by inductor do not affect the others)
A— multiplying farads by 10 to the power of 6 (Note: L T = L 1 + L 2 + L3 . . .)
B— multiplying picofarads by 10 to the power of 6 A— less than the inductance of the lowest rated inductor.
C— multiplying microfarads by 10 to the power of 6 B— equal to the inductance of the highest rated inductor.
Each farad is equal to 10 6 microfarads. Example: 2 farads C— equal to the sum of the individual inductances.
is equal to 2 × 10 6 (2,000,000) microfarads. When several inductors are connected together in such a
way that there is no inductive coupling, the total inductance
8009-3. Convert farads to picofarads by: is the sum of the individual inductances.
A— multiplying farads by 10 to the power of 12
B— multiplying microfarads by 10 to the power of -12 8013. (Refer to Figure 3.) When more than two induc-
C— multiplying picofarads by 10 to the power of 12 tors of different inductances are connected in parallel in
a circuit, the total inductance is
Each farad is equal to 10 12 picofarads. Example: 2 farads
is equal to 2 × 10 12 (2,000,000,000) picofarads. A— less than the inductance of the lowest rated inductor.
B— equal to the inductance of the highest rated inductor.
C— equal to the sum of the individual inductances.
8010. Unless otherwise specified, any values given for
current or voltage in an AC circuit are assumed to be
A— instantaneous values.
B— effective values.
C— maximum values.
Almost all measuring instruments used for electrical
system servicing measure the effective (rms) values of
alternating current. When two or more inductors having different inductances
Unless peak values, peak-to-peak values, or average are connected in parallel, the total inductance is less than
values are specifically called out, effective values are the inductance of the lowest rated inductor.
assumed.
Answers
8009-1 [A] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8009-2 [A] (102) AMT-G Ch 4 8009-3 [A] (102) AMT-G Ch 4 8010 [B] (031) AMT-G Ch 4
8011 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8012 [C] (015) AMT-G Ch 4 8013 [A] (031) AMT-G Ch 4
Fast-Track Series General Test Guide ASA 5
Questions, Explanations, Answers & References
8014. What is the total capacitance of a certain circuit 8017. A 12-volt electric motor has 1,000 watts input and 1
containing three capacitors with capacitances of .25 micro- horsepower output. Maintaining the same efficiency, how
farad, .03 microfarad, and .12 microfarad, respectively? much input power will a 24-volt, 1-horsepower electric
(Note: C T = C1 + C2 + C3) motor require?
A— .4 µF. (Note: 1 horsepower = 746 watts)
B— .04 pF. A— 1,000 watts.
C— .04 µF. B— 2,000 watts.
C— 500 watts.
When three capacitors are connected in parallel, their total
capacitance is the sum of the individual capacitances. The power produced by an electric motor is the product
CT = C1 + C 2 + C3 of its voltage and its current.
A 12-volt motor will require 83.3 amps of current for
= 0.25 + 0.03 = 0.12 its 1,000 watts of input power to produce 746 watts (1
= 0.4 microfarad horsepower) of output power.
A 24-volt motor operating at the same efficiency will
also require 1,000 watts of input power for its 746 watts
8015. Which requires the most electrical power during of output power, but it will need only 41.7 amps of current.
operation?
(Note: 1 horsepower = 746 watts)
8018. How many amperes will a 28-volt generator be
A— A 12-volt motor requiring 8 amperes. required to supply to a circuit containing five lamps in
B— Four 30-watt lamps in a 12-volt parallel circuit. parallel, three of which have a resistance of 6 ohms each
C— Two lights requiring 3 amperes each in a 24-volt and two of which have a resistance of 5 ohms each?
parallel system.
A— 1.11 amperes.
The 12-volt motor requires 96 watts of power. B— 1 ampere.
C— 25.23 amperes.
The four 30-watt lamps require 120 watts of power.
The two 24-volt, 3-amp lights require 144 watts of power. A current of 4.67 amps flows through each of the three
six-ohm lamps. And a current of 5.6 amps flows through
each of the five-ohm lamps.
8016. How much power must a 24-volt generator furnish Since all of these lamps are in parallel, the total current
to a system which contains the following loads? is the sum of the currents flowing through each lamp. The
Unit Rating total current is 25.21 amps.
One motor (75 percent efficient).............................1/5 hp
Three position lights.................................. 20 watts each 8019. A 1-horsepower, 24-volt DC electric motor that is 80
One heating element..............................................5 amp percent efficient requires 932.5 watts. How much power
One anticollision light..............................................3 amp will a 1-horsepower, 12-volt DC electric motor that is 75
percent efficient require?
(Note: 1 horsepower = 746 watts)
(Note: 1 horsepower = 746 watts)
A— 402 watts.
B— 385 watts. A— 932.5 watts.
C— 450 watts. B— 1,305.5 watts.
C— 994.6 watts.
The motor is 1/5 HP, therefore 746 watts (1 HP) / 5 = 149
watts. This is the output of the engine. It takes more energy When we know the horsepower output and the efficiency
to produce 149 watts; find this with the efficiency rating: of an electric motor, the voltage does not enter into the
149/X = 75/100; X = 199. Therefore, the 1/5-horsepower computation. To find the number of watts required, divide
motor that is 75 percent efficient requires 199 watts. the wattage for the total horsepower by the decimal
equivalent of the efficiency.
The three position lights require a total of 60 watts.
746 ÷ 0.75 = 994.6 watts
The heating element requires 120 watts.
The anticollision light requires 72 watts.
The total power the generator must produce is 451 watts.
Answers
8014 [A] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8015 [C] (015) AMT-G Ch 4 8016 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8017 [A] (031) AMT-G Ch 4
8018 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8019 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4
6 ASA General Test Guide Fast-Track Series
Basic Electricity
8020. The potential difference between two conductors 8023. (Refer to Figure 4.) How much power is being fur-
which are insulated from each other is measured in nished to the circuit?
A— volts. A— 575 watts.
B— amperes. B— 2,875 watts.
C— coulombs. C— 2,645 watts.
The potential difference between two conductors is a
measure of the electrical pressure difference between
the conductors.
Electrical pressure is measured in volts.
8020-1. Which effect does not apply to the movement of
electrons flowing in a conductor?
A— Magnetic energy.
B— Thermal energy.
C— Static energy.
Current flowing through a conductor produces a magnetic
field and also dissipates thermal energy.
8021. A 24-volt source is required to furnish 48 watts to a
parallel circuit consisting of four resistors of equal value.
What is the voltage drop across each resistor?
A— 12 volts. This is a resistive circuit. The power is the product of the
B— 6 volts. square of the current times the resistance.
C— 24 volts. P = I 2 × R = 23 2 × 5 = 2,645 watts
Since the resistors are all in parallel across the 24-volt
power source, each resistor has the entire 24 volts dropped 8024. (Refer to Figure 5.) What is the impedance of an
across it. AC-series circuit consisting of an inductor with a reactance
of 10 ohms, a capacitor with a reactance of 4 ohms, and
a resistor with a resistance of 8 ohms?
8022. When calculating power in a reactive or inductive
AC circuit, the true power is A— 22 ohms.
B— 5.29 ohms.
A— more than the apparent power. C— 10 ohms.
B— less than the apparent power in a reactive circuit
and more than the apparent power in an inductive
circuit.
C— less than the apparent power.
True power in an AC circuit is the product of the circuit
voltage and only that part of the current in phase with
the voltage.
Apparent power is the circuit voltage multiplied by all
of the current.
True power is always less than the apparent power in
a reactive circuit which is any AC circuit containing either
inductance or capacitance. The total reactance in this circuit is the difference between
the inductive reactance and the capacitive reactance.
Total reactance is 10 – 4 = 6 ohms.
The impedance is the square root of the resistance
squared plus the reactance squared. This is the square
root of 64 plus 36, or the square root of 100.
The circuit impedance is 10 ohms.
Answers
8020 [A] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8020-1 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8021 [C] (015) AMT-G Ch 4 8022 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4
8023 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8024 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4
Fast-Track Series General Test Guide ASA 7
Questions, Explanations, Answers & References
8025. (Refer to Figure 6.) If resistor R 5 is disconnected 8026. (Refer to Figure 7.) If resistor R 3 is disconnected
at the junction of R 4 and R3 as shown, what will the ohm- at terminal D, what will the ohmmeter read?
meter read? A— Infinite resistance.
A— 2.76 ohms. B— 10 ohms.
B— 3 ohms. C— 20 ohms.
C— 12 ohms.
With resistor R5 disconnected, the ohmmeter reads the
parallel resistance of R 1 and R 2 in parallel with R4 and
R3, which are in series. The total resistance is found by
When resistor R 3 is disconnected at terminal D, it is iso-
the formula:
lated from the rest of the circuit, and the ohmmeter will
read only the resistance of R3.
Because R3 is open (it has a break in it), its resistance
is infinite.
8027. (Refer to Figure 8.) With an ohmmeter connected
into the circuit as shown, what will the ohmmeter read?
A— 20 ohms.
B— Infinite resistance.
C— 10 ohms.
The ohmmeter will read the resistance of R1 and R2 in
parallel; this is 10 ohms.
The open circuit (break) in resistor R3 gives it an infi-
nite resistance, and it does not affect the reading of the
ohmmeter.
Answers
8025 [B] (015) AMT-G Ch 4 8026 [A] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8027 [C] (015) AMT-G Ch 4
8 ASA General Test Guide Fast-Track Series
Basic Electricity
8028. (Refer to Figure 9.) How many instruments (volt- 8030. Which term means .001 ampere?
meters and ammeters) are installed correctly? A— Microampere.
A— Three. B— Kiloampere.
B— One. C— Milliampere.
C— Two.
The metric prefix “milli-” means one thousandth.
0.001 ampere is one milliampere.
8031. A cabin entry light of 10 watts and a dome light of
20 watts are connected in parallel to a 30-volt source. If
the voltage across the 10-watt light is measured, it will be
A— equal to the voltage across the 20-watt light.
B— half the voltage across the 20-watt light.
C— one-third of the input voltage.
When lights are connected in parallel across a voltage
source, the voltage across each of the lights will be the
same as the voltage of the source.
The first ammeter is installed across the voltage. This is
wrong; the ammeter will burn out.
8032. A 14-ohm resistor is to be installed in a series circuit
The first voltmeter will measure the source voltage (the
carrying .05 ampere. How much power will the resistor be
voltage of the battery), but its polarity is wrong. It will read
required to dissipate?
backward.
The voltmeter across the light bulb is installed correctly. A— At least .70 milliwatt.
The ammeter in series with the light bulb and the bat- B— At least 35 milliwatts.
tery is correct. It will read the current flowing through the C— Less than .035 watt.
light bulb.
Power dissipated in a resistor is found by multiplying its
resistance by the square of the current.
8029. The correct way to connect a test voltmeter in a P = I 2 × R = 0.05 2 × 14 = 0.035 watts.
circuit is
0.035 watts is 35 milliwatts.
A— in series with a unit.
B— between the source voltage and the load.
C— in parallel with a unit. 8033. .002KV equals
A voltmeter must always be connected in a circuit in parallel A— 20 volts.
with the unit whose voltage is to be measured. B— 2.0 volts.
C— .2 volt.
8029-1. What will a voltmeter read if properly connected A KV is a kilovolt, or 1,000 volts. Two thousandths (.002)
across a closed switch in a circuit with electrical power on? of a kilovolt is equal to 2.0 volts.
A— Voltage drop in the component(s) the switch is
connected to.
B— System voltage.
C— Zero voltage.
When a voltmeter is connected across a closed switch in
perfect condition or a good fuse, it will read zero voltage. A
voltage drop of up to 0.2 volts is acceptable with maximum
circuit current flow through the switch.
Answers
8028 [C] (015) AMT-G Ch 4 8029 [C] (015) AMT-G Ch 4 8029-1 [C] (015) AMT-G Ch 4, AC43.13 Ch 11
8030 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8031 [A] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8032 [B] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8033 [B] (015) AMT-G Ch 4
Fast-Track Series General Test Guide ASA 9
Questions, Explanations, Answers & References
8034. (Refer to Figure 10.) What is the measured voltage 8036. Which requires the most electrical power?
of the series-parallel circuit between terminals A and B? (Note: 1 horsepower = 746 watts)
A— 1.5 volts. A— A 1/5-horsepower, 24-volt motor which is 75
B— 3.0 volts. percent efficient.
C— 4.5 volts. B— Four 30-watt lamps arranged in a 12-volt parallel
circuit.
C— A 24-volt anticollision light circuit consisting of two
light assemblies which require 3 amperes each
during operation.
The 1/5-horsepower motor operating at 75 percent effi-
ciency uses 198.93 watts of power.
The four 30-watt lamps use 120 watts of power.
The anticollision light circuit uses 144 watts of power.
8037. What unit is used to express electrical power?
A— Volt.
B— Watt.
C— Ampere.
The two batteries on the left side are connected in series The volt is a measure of electrical pressure.
and the two batteries on the right side are connected in The watt is a measure of electrical power.
series. The two pairs of batteries are connected in parallel.
The series connections between terminals A and B The ampere is a measure of electrical current flow.
give this circuit a voltage of 3.0 volts.
8037-1. What is the basic unit of electrical quantity?
8035. A 24-volt source is required to furnish 48 watts to A— Electromotive Force.
a parallel circuit consisting of two resistors of equal value. B— Ampere.
What is the value of each resistor? C— Coulomb.
(Note: R t = E 2/P) The coulomb is the basic unit of electrical quantity.
A— 24 ohms. 1 coulomb is equal to 6.28 X 1018 electrons.
B— 12 ohms.
C— 6 ohms.
8038. What is the operating resistance of a 30-watt light
To solve this problem, first find the total resistance of the bulb designed for a 28-volt system?
circuit. A— 1.07 ohms.
2 B— 26 ohms.
RT = E
P C— 0.93 ohm.
2
= 24 A 30-watt light bulb operating in a 28-volt electrical system
48 has a hot resistance (operating resistance) of 26.13 ohms.
2
=
12 ohms R = E
P
There are two resistors of equal value in parallel that pro- 2
vide this resistance, therefore each resistor must have a = 28
resistance of twice this value, or 24 ohms. 30
26.13 Ω
=
Answers
8034 [B] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8035 [A] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8036 [A] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8037 [B] (031) AMT-G Ch 4
8037-1 [C] (031) AMT-G Ch 4 8038 [B] (015) AMT-G Ch 4
10 ASA General Test Guide Fast-Track Series
You might also like
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Basic Elecricity2Document26 pagesBasic Elecricity2Ismael GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- My Custom QuizDocument30 pagesMy Custom QuizIsmael GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and InductorsDocument85 pagesCapacitors and InductorsArnel E. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Ee - Module 3 - April 2012Document3 pagesEe - Module 3 - April 2012Znevba Quintano100% (2)
- Cea 223 Mod 2Document2 pagesCea 223 Mod 2PhoemelaNo ratings yet
- Where Do You Need This?: 1.maintenance Engineer 2.energy Management System 3.energy ManagerDocument31 pagesWhere Do You Need This?: 1.maintenance Engineer 2.energy Management System 3.energy Managerconference RequirementsNo ratings yet
- Physics-Revision WS - Gr9-Mrs EsraaDocument17 pagesPhysics-Revision WS - Gr9-Mrs EsraaLemar AdelNo ratings yet
- Notes Cs Physics Practical ElectricityDocument15 pagesNotes Cs Physics Practical ElectricityJervin LimNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Question BankDocument5 pagesCurrent Electricity Question BankAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Eee 1Document30 pagesEee 1MdAsaduz-ZamanNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument11 pagesElectricityskluckyskashifNo ratings yet
- Ch33 PHYS 205 Problems To Solve in Class Alternating Current CircuitsDocument3 pagesCh33 PHYS 205 Problems To Solve in Class Alternating Current CircuitsAllyson OffreyNo ratings yet
- Electricity Numerical WorksheetDocument3 pagesElectricity Numerical Worksheetayerjayaram59No ratings yet
- 10 Physics ch12 Electricity Ncert SolutioDocument19 pages10 Physics ch12 Electricity Ncert SolutiothemidnightismNo ratings yet
- Ac TestDocument2 pagesAc TestAslam FaruqiNo ratings yet
- G12 PHYSICS CHAPTER 8 Full 2023 2024 DONEDocument16 pagesG12 PHYSICS CHAPTER 8 Full 2023 2024 DONESomali YOS online FadityareNo ratings yet
- Electro N4 Test 2Document5 pagesElectro N4 Test 2Anesu MasirahaNo ratings yet
- Objectives: To Find Out More About Power in Electrical Systems, Follow The Links atDocument7 pagesObjectives: To Find Out More About Power in Electrical Systems, Follow The Links atchristheo54787No ratings yet
- Ohms N Power Law HWDocument2 pagesOhms N Power Law HWFRANCIS BALTAZARNo ratings yet
- Acdpp 1633763219Document14 pagesAcdpp 1633763219atul kumarNo ratings yet
- Electric NoteDocument6 pagesElectric NoteKucing GemukNo ratings yet
- 01 REFRESHER EE 1 - CLB - CompressedDocument12 pages01 REFRESHER EE 1 - CLB - CompressedJuphil PletoNo ratings yet
- Acdc - DC Motor - Lecture Notes 4Document34 pagesAcdc - DC Motor - Lecture Notes 4Cllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- EE ReviewerDocument13 pagesEE ReviewerZZROTNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL LectureDocument147 pagesELECTRICAL LecturejrNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument23 pagesSeries and Parallel CircuitsPrecious ChirangareNo ratings yet
- Appsc Aee Mains 2019 Electrical Engineering Paper II 0ec6f9c2Document25 pagesAppsc Aee Mains 2019 Electrical Engineering Paper II 0ec6f9c2SURYA PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Final Key: Electrical Engineering - Paper-IIDocument25 pagesFinal Key: Electrical Engineering - Paper-IISuryaCharanPaidipalliNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems of EEDocument9 pagesSample Problems of EEEdson MilanoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - 14ELE15Document6 pagesQuestion Bank - 14ELE15Rakesh ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- Chap3 - 1 Power Measurement PDFDocument22 pagesChap3 - 1 Power Measurement PDFTiffanyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 FinalDocument11 pagesExperiment 7 Finalernie5000No ratings yet
- Question Bank (ECE)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (ECE)Manav JainNo ratings yet
- Ee - Module 7 - April 2012Document4 pagesEe - Module 7 - April 2012Znevba QuintanoNo ratings yet
- Acces Point - Ee Refresher 3Document10 pagesAcces Point - Ee Refresher 3christinesarah0925No ratings yet
- Emi and Ac AssignmentDocument5 pagesEmi and Ac AssignmentMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- Circuits 22Document4 pagesCircuits 22Davis Spat TambongNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity WKSHTDocument4 pagesCurrent Electricity WKSHTrachasiNo ratings yet
- General PDFDocument98 pagesGeneral PDFrobot1945No ratings yet
- Q1. (A) A 3-ph, 6-Pole, Star Connected, Induction Motor Rated For 50Hz, 400V, Has TheDocument4 pagesQ1. (A) A 3-ph, 6-Pole, Star Connected, Induction Motor Rated For 50Hz, 400V, Has Theaman_sasanNo ratings yet
- Resistor Color Codes, Ohm Law: Principle of Electrical EngineeringDocument36 pagesResistor Color Codes, Ohm Law: Principle of Electrical EngineeringMugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Current Electricity Question BankDocument6 pagesQdoc - Tips Current Electricity Question BanknunjapiznesNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer in Electric Circuits 01Document2 pagesEnergy Transfer in Electric Circuits 01fgygNo ratings yet
- EE Looks FamDocument9 pagesEE Looks FamKate ErikaNo ratings yet
- Important Question Bank: Linear and Non Linear ElementsDocument4 pagesImportant Question Bank: Linear and Non Linear ElementsSAURAV CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class 10 NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity Class 10 NotesKota SrinadhNo ratings yet
- Assignment of EeeDocument4 pagesAssignment of EeeHarshilNo ratings yet
- EEE Assignment1 AC Fundamental1 2011-12Document8 pagesEEE Assignment1 AC Fundamental1 2011-12Arpit ShahNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Question Paper-II: - Kirchoff's LossDocument25 pagesElectrical Engineering Question Paper-II: - Kirchoff's LossbasavarajNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 PDFAbu RectifyNo ratings yet
- AssignmentsDocument28 pagesAssignmentsaly.abdulghafarNo ratings yet
- ENEE303H Homework 1Document2 pagesENEE303H Homework 1Cheng QuNo ratings yet
- Transformer:-: Equipment Used To Raise or Lower The Potential Difference of An Alternating Current SupplyDocument20 pagesTransformer:-: Equipment Used To Raise or Lower The Potential Difference of An Alternating Current SupplynazurahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Electrical Calculations: Law), Is Shown in The Triangle Below. If We Know Two Quantities We Can Calculate TheDocument8 pagesChapter 10: Electrical Calculations: Law), Is Shown in The Triangle Below. If We Know Two Quantities We Can Calculate TheReza Putra WardanaNo ratings yet
- Act. Module 4 - Resonance, Bandwidth, Non-Sinusoidal WaveformDocument6 pagesAct. Module 4 - Resonance, Bandwidth, Non-Sinusoidal WaveformSherwin PagpaguitanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 SolutionDocument26 pagesModule 2 SolutionCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Algebra Lineal - FriedbergDocument548 pagesAlgebra Lineal - FriedbergRigoberto UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- James J. Tattersall-Elementary Number Theory in Nine Chapters-Cambridge University Press (2005)Document443 pagesJames J. Tattersall-Elementary Number Theory in Nine Chapters-Cambridge University Press (2005)Harold AponteNo ratings yet
- Teoria de Estructuras, TimoshenkoDocument318 pagesTeoria de Estructuras, TimoshenkoJLSUSTAITA92% (12)
- Mecanica Moderna Del Dinero PDFDocument50 pagesMecanica Moderna Del Dinero PDFHarold AponteNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- PI-200, PI-400, PI-750, XI41B: Models / ModelosDocument31 pagesPI-200, PI-400, PI-750, XI41B: Models / ModelosRolando MaasNo ratings yet
- SSC JE Electrical SyllabusDocument4 pagesSSC JE Electrical SyllabusHarpal SainiNo ratings yet
- Week 7..Document3 pagesWeek 7..Lance Cj S. CapistranoNo ratings yet
- A Spherical Particle Is Falling Slowly. in A Viscous Liquid Such That Reynolds Number Is Less Than 1. Which Statement Is Correct For This Situation?Document6 pagesA Spherical Particle Is Falling Slowly. in A Viscous Liquid Such That Reynolds Number Is Less Than 1. Which Statement Is Correct For This Situation?Aduchelab AdamsonuniversityNo ratings yet
- MSEG 667: 3: Guided Wave OpticsDocument26 pagesMSEG 667: 3: Guided Wave OpticsJuan Carlos GarayNo ratings yet
- Marine Electrical SystemsDocument8 pagesMarine Electrical Systemssunil1237No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Plumbing ArithmeticDocument10 pagesModule 2 - Plumbing ArithmeticPermanente Health Plan Corporation PHPNo ratings yet
- Design and Hardware Implementation of L Type Resonant Step Down DC DC Converter Using Zero Current Switching Technique IJERTV5IS050623 PDFDocument8 pagesDesign and Hardware Implementation of L Type Resonant Step Down DC DC Converter Using Zero Current Switching Technique IJERTV5IS050623 PDFMouli ReddyNo ratings yet
- VOL 5 Pulse GeneratorsDocument755 pagesVOL 5 Pulse Generatorsgorods5rtNo ratings yet
- TSDOS Adv Diag Testing DW PDFDocument61 pagesTSDOS Adv Diag Testing DW PDFDhammika Dharmadasa100% (1)
- Blue SeaDocument144 pagesBlue Seabrendanc55323No ratings yet
- Question AnwerDocument23 pagesQuestion AnwerOnsoti NyaberaNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of TransformersDocument3 pagesParallel Operation of TransformersHARIHARANNo ratings yet
- Assessment Clo1 Clo2 Clo3 Clo4 Clo5 Plo1 Plo2 Plo2 Plo1Document12 pagesAssessment Clo1 Clo2 Clo3 Clo4 Clo5 Plo1 Plo2 Plo2 Plo1Ma Liu Hun VuiNo ratings yet
- DIN 15018 1 EN Version 11 1984Document38 pagesDIN 15018 1 EN Version 11 1984Tiago Lamy SilvaNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument53 pagesProject ReportMUDAM ALEKYANo ratings yet
- Statics Assgnmnt)Document20 pagesStatics Assgnmnt)Mohammed AdemNo ratings yet
- Physics Medical EntrranceDocument65 pagesPhysics Medical Entrrancewww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- SSgenUseful Free EnergyDocument15 pagesSSgenUseful Free EnergyWe RigdonNo ratings yet
- Seat No.: 3 Hours/100 MarksDocument7 pagesSeat No.: 3 Hours/100 MarksomNo ratings yet
- Installation Form - Submersible Pump of SAERDocument2 pagesInstallation Form - Submersible Pump of SAERHary FadlyNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On Energy and ThermochemistryDocument6 pagesPractice Problems On Energy and ThermochemistryMichael MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Implement Field-Oriented Control (FOC) Induction Motor Drive Model - SimulinkDocument13 pagesImplement Field-Oriented Control (FOC) Induction Motor Drive Model - SimulinkRizkia PratamaNo ratings yet
- Beam Element Formulation and Solution Procedure For Dynamic Progressive Collapse AnalysisDocument13 pagesBeam Element Formulation and Solution Procedure For Dynamic Progressive Collapse AnalysisMasnun RahmanNo ratings yet
- Transformer Inrush Current: Definition: The Transformer Inrush Current Is The Maximum Instantaneous Current Drawn by TheDocument3 pagesTransformer Inrush Current: Definition: The Transformer Inrush Current Is The Maximum Instantaneous Current Drawn by TheMilovan LukovacNo ratings yet
- Protection of MVDC Distribution SystemDocument13 pagesProtection of MVDC Distribution SystemMaqsood AhmadNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics NotesDocument115 pagesClass 12 Physics NotesAiden Pearce100% (1)
- B503D Series: Sensorless Vector Control Controller Instruction ManualDocument108 pagesB503D Series: Sensorless Vector Control Controller Instruction Manualnofal ali0% (1)
- ELEQ GSA Broschyr enDocument4 pagesELEQ GSA Broschyr enJaime Salazar ArayaNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Underdamped SystemDocument7 pagesPendulum Underdamped SystemJitender YadavNo ratings yet
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceFrom EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- A Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeFrom EverandA Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (53)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Power System Control and ProtectionFrom EverandPower System Control and ProtectionB. Don RussellRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)From EverandGuide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesFrom EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Digital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionFrom EverandDigital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Schaum's Outline of Basic Electricity, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Basic Electricity, Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (14)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsFrom EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (331)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Build Your Own Electronics WorkshopFrom EverandBuild Your Own Electronics WorkshopRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- DIY Drones for the Evil Genius: Design, Build, and Customize Your Own DronesFrom EverandDIY Drones for the Evil Genius: Design, Build, and Customize Your Own DronesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignFrom EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignNo ratings yet
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldFrom EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (87)