Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CIDAM
Uploaded by
Nestor Abante Valiao Jr.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views2 pagesclassroom instruction delivery alignment map
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentclassroom instruction delivery alignment map
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views2 pagesCIDAM
Uploaded by
Nestor Abante Valiao Jr.classroom instruction delivery alignment map
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
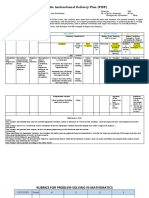
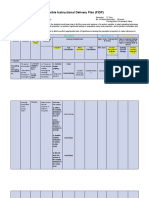
GROUP 3
Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map
Grade: 11 Semester: 2nd Semester
Core Subject Title: Statistics and Probability No. of Hours/Semester: 80 hours
Prerequisites (if needed):
Core Subject Description: At the end of the course, the students must know how to find the mean and variance of a random variable, to apply sampling techniques and
distributions, to estimate population mean and proportion, to perform hypothesis testing on population mean and proportion, and to perform correlation and regression
analyses on real – life problems.
Culminating Performance Standard: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Performance Highest Enabling Strategy to Use in
Standards Re – Developing the Highest Thinking
Learning Competencies grouped Highest Thinking Skill to Assess Skill to Assess
Compete
Content Minimum K ncies Assessment Enabling General Teaching
Content Standard Minimum U RBT Level Technique Strategy Strategy
Beyond
s Minimu D WW QA PC
m
10.formulates the
appropriate null and U 1. Applying Communication Gallery Walk
The learner is The alternative and connections
able to learne hypotheses on a Collaboration
perform r is population proportion / /
appropriate able to Discovery learning
tests of perfor
11. identifies the
hypothesis m
involving appro appropriate form of U 2. Analyzing Exploration
population priate the test statistic when
The learner mean and tests the Central Limit Interdisciplinary
demonstrat population of Theorem is to be used approach
es proportion to hypot
understandi make hesis 12. identifies the Think – Pair –
ng of key inferencing in involvi
concepts appropriate rejection U 3. Analyzing Share
Tests of real – life ng region for a given
tests of problem in popula
Hypothesis hypotheses level of significance Problem Solving
different tion
on the when the Central
disciplines. mean
population and Limit Theorem is to
mean and popula be used.
population tion
proportion. propo 13. computes for the
rtion
test – statistic value U 4. Applying
to
make (population
infere proportion)
ncing
in real 14. draws conclusion U 5. Analyzing
– life about the population
proble proportion based on
m in the test – statistic
differe value and the
nt rejection region.
discipl
ines.
15. solves problems
involving test of
hypotheses on U 6. Evaluating
population
proportion.
Performance Task: ___________________________________________________________________________
Prepared by:
FRANKLIN B. MAYO (OLGA)
DANILO A. ROBLICO JR. (CST-R)
MARY GRACE A. VICENTE (SJA)
LOIRYL KAE FERMARIN (HI)
JAN AMADEO L. UGHAYON (CCEI)
JOSE REY H. GIMENEZ (OLPMSI)
NESTOR VALIAO
You might also like
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map: First QuarterDocument2 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map: First QuarterTwinkz Oberio BarcomaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Document3 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Arniel LlagasNo ratings yet
- STATDocument9 pagesSTATRitchelle MabandosNo ratings yet
- Cidam - Statistics FfinalDocument12 pagesCidam - Statistics FfinalKyle BersaloteNo ratings yet
- FIDP TemplateDocument3 pagesFIDP TemplateMonica Joyce NaperiNo ratings yet
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapDocument3 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapMindanao Community SchoolNo ratings yet
- Cidam StatDocument4 pagesCidam StatJanisah Abdulsamad60% (5)
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Document12 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?LANY T. CATAMINNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability FIDP Delivers Key ConceptsDocument7 pagesStatistics and Probability FIDP Delivers Key ConceptsSfa Mabini BatangasNo ratings yet
- Cidam Statistics FfinalDocument12 pagesCidam Statistics FfinalNelson MaraguinotNo ratings yet
- Region4A - Validity and Falsity of Real-Life Argument - SalandananDocument3 pagesRegion4A - Validity and Falsity of Real-Life Argument - SalandananJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level 11 Teacher Learning Area General Mathematics Teaching Dates and Time Jan.6-10,2019 Quarter Third QuarterDocument52 pagesSchool Grade Level 11 Teacher Learning Area General Mathematics Teaching Dates and Time Jan.6-10,2019 Quarter Third Quarteremmanuel peraltaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Document3 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Nelson MaraguinotNo ratings yet
- CLASSROOM INSTRUCTION ALIGNMENT FOR STATISTICSDocument12 pagesCLASSROOM INSTRUCTION ALIGNMENT FOR STATISTICSMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Effects of English Language and Literature on Students' Language Ability from a Multidimensional Perspective: A Study of Indonesian StudentsDocument3 pagesEffects of English Language and Literature on Students' Language Ability from a Multidimensional Perspective: A Study of Indonesian StudentsErickson James Gregorio FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability FIDPDocument7 pagesStatistics and Probability FIDPHoney Mae VillaverNo ratings yet
- Applying Logic and Mathematics to Real-Life SituationsDocument3 pagesApplying Logic and Mathematics to Real-Life SituationsJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Statistics FIDPDocument2 pagesGrade 11 Statistics FIDPJoy TamalaNo ratings yet
- Session 1/january 23 Session 2/january 24 Session 3/january 25 Session 4/january 26Document4 pagesSession 1/january 23 Session 2/january 24 Session 3/january 25 Session 4/january 26jun del rosarioNo ratings yet
- SLOs, Bloom's Taxonomy, Cognitive, Psychomotor, and Affective DomainsDocument5 pagesSLOs, Bloom's Taxonomy, Cognitive, Psychomotor, and Affective DomainsEricka NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Document2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Rojane L. AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- ROCEL MAE L. GAMBA REGION V (Workshop No. 1)Document3 pagesROCEL MAE L. GAMBA REGION V (Workshop No. 1)Rocel Mae L. GambaNo ratings yet
- Grade: Semester: Core Subject Title: No. of Hours/ Semester: Core Subject DescriptionDocument2 pagesGrade: Semester: Core Subject Title: No. of Hours/ Semester: Core Subject DescriptionMicheal CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative MethodsDocument2 pagesQuantitative MethodsWc-mark ChuvachucHuNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: I. ObjectivesdenizsadayNo ratings yet
- FIDP Gen MathDocument19 pagesFIDP Gen MathKarl FerrerNo ratings yet
- Grades 1 to 12 School Burgos National High School Statistics ProbabilityDocument3 pagesGrades 1 to 12 School Burgos National High School Statistics ProbabilityMiller YamsonNo ratings yet
- Northwestern Mindanao State College of Science and Technology (NMSC) Labuyo, Tangub CityDocument7 pagesNorthwestern Mindanao State College of Science and Technology (NMSC) Labuyo, Tangub CityIs JulNo ratings yet
- Alignment Classroom Instructon Delivery (Acid) PlanDocument7 pagesAlignment Classroom Instructon Delivery (Acid) PlanJonory Qaquilala BojosNo ratings yet
- 2021 - For Submission 1 - GenMath Workshop 1 FIDPDocument19 pages2021 - For Submission 1 - GenMath Workshop 1 FIDPJaimie Judelle AlzolNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1- SYLLABUSDocument4 pagesGROUP 1- SYLLABUSAnna Katherine ArsolonNo ratings yet
- DLL Stat Q1W5Document3 pagesDLL Stat Q1W5Nicole MoscaNo ratings yet
- Subject: English For Academic and Professional Purposes Grade Level: Grade 11 Prepared By: Teacher Joseph Ryann J. JalagatDocument8 pagesSubject: English For Academic and Professional Purposes Grade Level: Grade 11 Prepared By: Teacher Joseph Ryann J. JalagatAngelyn LingatongNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : and To Apply Logic To Real-Life SituationsDocument19 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : and To Apply Logic To Real-Life SituationsMa. Angelica De La PenaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Learning Using Different MethodsDocument18 pagesAssessing Learning Using Different Methodsnissi guingabNo ratings yet
- Week 6.Document9 pagesWeek 6.Coco LlameraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3Document2 pagesLesson Plan 3api-449406527No ratings yet
- Session 1/january 30 Session 2/january 31 Session 3/february 1 Session 4/february 2Document3 pagesSession 1/january 30 Session 2/january 31 Session 3/february 1 Session 4/february 2jun del rosarioNo ratings yet
- COT 2 STAT PROB 11 WHLP Q4 Week 4 BELLODocument9 pagesCOT 2 STAT PROB 11 WHLP Q4 Week 4 BELLOFRECY MARZANNo ratings yet
- Myp Math Extended Unit 02Document6 pagesMyp Math Extended Unit 02vato otavNo ratings yet
- Stat&Prob 3rd Week 4Document3 pagesStat&Prob 3rd Week 4Mark Lenon VerdaderoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Thompson Aleyce Revised Equivalent Fractions Lesson Plan With Corrections 5 6 17 847pmDocument6 pagesMicrosoft Word - Thompson Aleyce Revised Equivalent Fractions Lesson Plan With Corrections 5 6 17 847pmapi-356004164No ratings yet
- CCA LossDocument5 pagesCCA LossHWNo ratings yet
- 1-FIDP TemplateDocument4 pages1-FIDP TemplateMeljoy TenorioNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Statistics FIDPDocument2 pagesGrade 11 Statistics FIDPJaneth AmorNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability FIDPDocument31 pagesStatistics and Probability FIDP123 456No ratings yet
- FIDPDocument9 pagesFIDPMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document11 pagesWeek 4Coco LlameraNo ratings yet
- CIDAM English For Academic and Professional Purposes Q2Document2 pagesCIDAM English For Academic and Professional Purposes Q2Mire-chan BaconNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template CONTENT 5Document2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template CONTENT 5Edward Barber100% (3)
- FIDP - Legaspi, Gina FeDocument3 pagesFIDP - Legaspi, Gina FeGina Fe S. Legaspi100% (2)
- Statistics WEEK 8Document10 pagesStatistics WEEK 8Elvin PretencioNo ratings yet
- CIDAM 1stDocument4 pagesCIDAM 1stMarife Hermosa - LeymaNo ratings yet
- Distance-Learning-Course-Plan Math1-StatisticsDocument13 pagesDistance-Learning-Course-Plan Math1-StatisticsHarvey RatunilNo ratings yet
- FIDP Correlation AnalysisDocument2 pagesFIDP Correlation AnalysisMeryll Joy P. MaaliwNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument15 pagesRandom Variables and Probability DistributionsJason Peña100% (1)
- Decile Grouped Data Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesDecile Grouped Data Lesson PlanMelody LagarasNo ratings yet
- STATDocument4 pagesSTATRitchelle MabandosNo ratings yet
- Local Media7448206506575993530Document4 pagesLocal Media7448206506575993530Sai GuyoNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus WorsheetDocument1 pageBasic Calculus WorsheetNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- Assessment in The K To 12 Basic Education Program - April 1Document43 pagesAssessment in The K To 12 Basic Education Program - April 1Lloyl Yosores MonteroNo ratings yet
- Simple InterestDocument19 pagesSimple InterestNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- Certificate Name SampleDocument1 pageCertificate Name SampleNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- Syllabus in Mathematics (Grade 9)Document5 pagesSyllabus in Mathematics (Grade 9)Nestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- Teaching Guide Statistics and ProbabilityDocument5 pagesTeaching Guide Statistics and ProbabilityNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- LP SampleDocument3 pagesLP SampleNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- Verbal InterpretationDocument1 pageVerbal InterpretationNestor Abante Valiao Jr.0% (1)
- Teaching Guide Stat and ProbDocument6 pagesTeaching Guide Stat and ProbNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- TestDocument2 pagesTestNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- TestDocument2 pagesTestNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- God Loves YouDocument1 pageGod Loves YouNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- Who Will Sing The Song - by Doug BatchelorDocument19 pagesWho Will Sing The Song - by Doug BatchelorDikapsNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Actuarial ScienceDocument5 pagesDissertation Actuarial ScienceWriteMyPaperIn3HoursCanada100% (1)
- I Can Statements - 4th Grade CC Math - NBT - Numbers and Operations in Base Ten Polka DotsDocument13 pagesI Can Statements - 4th Grade CC Math - NBT - Numbers and Operations in Base Ten Polka DotsbrunerteachNo ratings yet
- S Parameter BasicsDocument11 pagesS Parameter Basicslancelot795No ratings yet
- Aerodynamics MCQs on Low Speed AerodynamicsDocument4 pagesAerodynamics MCQs on Low Speed AerodynamicsHarish MathiazhahanNo ratings yet
- Structure Chap-7 Review ExDocument7 pagesStructure Chap-7 Review Exabenezer g/kirstosNo ratings yet
- Optimal f ratio for inverter chainDocument6 pagesOptimal f ratio for inverter chainVIKAS RAONo ratings yet
- Pump CavitationDocument5 pagesPump Cavitationjrri16No ratings yet
- Udl Exchange LessonDocument4 pagesUdl Exchange Lessonapi-297083252No ratings yet
- Mangaldan Distric Ii Pogo-Palua Elementary School: ND RDDocument3 pagesMangaldan Distric Ii Pogo-Palua Elementary School: ND RDFlordeliza Manaois RamosNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Site That Takes CalculationsDocument7 pagesNotes On The Site That Takes CalculationsNurdin ŠabićNo ratings yet
- Aiken 1980Document31 pagesAiken 1980Michael SanchesNo ratings yet
- Assessing Approaches To Genre ClassificationDocument72 pagesAssessing Approaches To Genre ClassificationAnonymous RrGVQjNo ratings yet
- Head Nurses Leadership Skills Mentoring and Motivating Staff Nurses On Rendering High-Quality Nursing CareDocument23 pagesHead Nurses Leadership Skills Mentoring and Motivating Staff Nurses On Rendering High-Quality Nursing CareDaniel RyanNo ratings yet
- Governor System (Electrical Part)Document142 pagesGovernor System (Electrical Part)የፐፐፐ ነገርNo ratings yet
- Rr210501 Discrete Structures and Graph TheoryDocument6 pagesRr210501 Discrete Structures and Graph TheorySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Computer Appications Project PDFDocument45 pagesGrade 10 Computer Appications Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudi100% (1)
- Rr10302 Applied MechanicsDocument12 pagesRr10302 Applied MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- FMEA Scope AnalysisDocument14 pagesFMEA Scope AnalysisAnkurNo ratings yet
- 23 Response OptimizationDocument30 pages23 Response OptimizationafonsopilarNo ratings yet
- Transcripts Moi UniversityDocument4 pagesTranscripts Moi UniversityMelanie GaksNo ratings yet
- HAL An Approach Attack To Goldbach ConjectureDocument23 pagesHAL An Approach Attack To Goldbach ConjectureEMMANUEL AUDIGÉNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques for Management DecisionsDocument4 pagesQuantitative Techniques for Management DecisionsFiraa'ool Yusuf100% (1)
- Writing Scientific NotationDocument2 pagesWriting Scientific NotationkolawoleNo ratings yet
- CE6306 NotesDocument125 pagesCE6306 Noteskl42c4300No ratings yet
- Design of Predictive Magic Cards.Document26 pagesDesign of Predictive Magic Cards.aries25th3No ratings yet
- Reed BC Quantum Mechanics An Enhanced PrimerDocument407 pagesReed BC Quantum Mechanics An Enhanced PrimerStrahinja DonicNo ratings yet
- Relation between resolution III and confounded responsesDocument50 pagesRelation between resolution III and confounded responsesrohitrealisticNo ratings yet
- Handout Diode EquationDocument1 pageHandout Diode Equationmanpreetsingh3458417No ratings yet
- Stability Analysis-Control SystemDocument29 pagesStability Analysis-Control SystemNanmaran RajendiranNo ratings yet
- 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete: Mit OpencoursewareDocument14 pages2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete: Mit Opencoursewarelovelyosmile253No ratings yet