Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How To Decrease The PH of A Nutrient Solution
Uploaded by
samreen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Water pH is a mathematical term to denote degrees of acidity or alkalinity and is expressed by a series of positive numbers between 0 and 14 with 7 being neutral.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pagesHow To Decrease The PH of A Nutrient Solution
Uploaded by
samreenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Water pH is a mathematical term to denote degrees of
acidity or alkalinity and is expressed by a series of positive
numbers between 0 and 14 with 7 being neutral. Zero being
very acidic and 14 highly alkaline. Water pH can be
measured by a hand held pH meter operated by a small
battery.
The pH of the water has a significant impact on the
availability of certain elements in the water. Water pH
should be between 5.8 and 6.8. Values higher or lower than
5.8 and 6.8 results in either precipitation or renders some
elements unavailable to the plants for uptake.
If the pH of the water is above 6.8, nitric acid, phosphoric
acid or sulpheric acid can be used to decrease the pH to the
desired level. pH lower than 5.8 must be increased to the
desired level with potassium hydroxide (KOH), sodium
hydroxide (NaOH) or magnesium hydroxide (MgOH2).
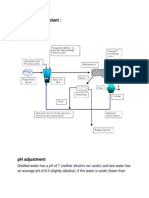
Adjusting ph of the water supply is crucial for maximum
nutrient availability. It is seldom that the water supply, even
from a well, is perfectly suitable (pH 5.8-6.8). The pH always
needs some adjustment, either up or down.
How to decrease the pH of
a nutrient solution
Lowering the pH is the most common adjustment to nutrient
solutions. That is because most waters are alkaline, with a
pH of at least 7.2 or above. The pH of the nutrient solution
should not be allowed to rise above 6.8 or decrease below
5.8. If the solution pH needs to be adjusted manually, it
should be measured at least twice a day, especially some
hours after a new nutrient solution has been added to the
nutrient tanks. There are five acids that can be used to
adjust the pH down:
nitric acid
phosphoric acid
sulphuric acid
citric acid and
acetic acid.
Acids are substances which, when added to the nutrient
solution will ionize and provide hydrogen ions. Nitric acid
produces H+ and NO3- ions. Acids are classified into strong
and weak acids. The degree of ionization will determine how
strong the acid is. Hydrochloric acid undergoes 100%
ionization so it is called a strong acid. Acetic acid only
undergoes 4% ionization so it is called a weak acid (and
hardly used commercially in hydroponic systems).
The most common acids used to lower the pH in hydroponic
nutrient solutions are phosphoric acid and nitric acid. It is
important to have a water analysis available in order to
determine which acid would be suitable for the water being
used. Nitric acid is preferred when using water with high
calcium concentrations since relatively more phosphoric
acid will be required in order to adjust the pH. If very little
calcium is in the water very little acid will be required to
decrease the pH of the water. The following reactions take
place when there is calcium in the water:
Ca(HCO3)2 + 2HNO3 = Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 + 2H2O
Ca(HCO3)2 + 2H3PO4 = Ca(H2PO4)2 + 2CO2 + 2H2O
The Important difference between using nitric acid and
phosphoric acid in waters that contain calcium is that nitric
acid produces calcium nitrate (CaNO3), carbon dioxide
(CO2) and water (H2O). In the case of phosphoric acid
calcium phosphate (Ca(H2PO4)2) is produced which as no
nutritional value to the plant since it is insoluble in water.
The nutritional loss is the phosphorus that is not available to
the plant which could be used. The amount of phosphoric
acid used and the precipitate that forms should not be of
any concern. It is not enough to cause any damage to
pumps or filters.
Acetic acid is that safest acid to use to decrease pH.
However it is not as strong as the other, so much more
volume would be required to reduce the pH of the water by
the same amount as the other acids.
When mixing concentrated solutions of acid to water it
is important to remember the following. Always add
the acid to large amounts of water. Never add the
acid first into a container and then add water. In the
later case the solution temperature can increase so
fast that it can explode cause serious damage.
How to Increase the pH of
a nutrient solution
When the water supply has a pH below 5.8 a base should
be added to the water. The most common base available is
potassium hydroxide (KOH). Other chemicals can also be
used such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and bicarbonate of
soda or baking soda (NaHCO3). Baking soda is the safest to
use. Both KOH and NaOH can burn skin if not washed of
immediately. Potassium hydroxide is available in pellets
which make handling the product very safe and easy. In
order to make a 10% solution of KOH, take 100g of KOH
pellets and add to 900ml of water. The solution can be
added to the nutrient tank until the pH of the water, without
any nutrients added, is between 5.8 and 6.8.
You might also like
- QUIZ Compressed-1.pdf - BIOCHEMISTRY LAB MODULE 1 PH OF...Document91 pagesQUIZ Compressed-1.pdf - BIOCHEMISTRY LAB MODULE 1 PH OF...B-Panganiban, Cyrus SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Lab ReportDocument6 pagesAcid Base Lab ReportYEEHSHIN JILL GAYONo ratings yet
- X Chemistry Notes Chapter 2 (Pages 6-10)Document5 pagesX Chemistry Notes Chapter 2 (Pages 6-10)Lekshmy BNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases in Everyday LifeDocument6 pagesAcids and Bases in Everyday LifeLothar GraudinsNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry NotesDocument8 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry NotesZaheer Uddin100% (1)
- Biological Buffer SystemDocument4 pagesBiological Buffer SystemVern NuquiNo ratings yet
- Acid Base SaltDocument6 pagesAcid Base SaltShaheed AnwerNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Everyday Acids and Bases: Review, Page 66Document3 pagesUnit 4: Everyday Acids and Bases: Review, Page 66Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Are Everywhere: CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesAcids and Bases Are Everywhere: CharacteristicsAzlan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Imp of PH LevelDocument1 pageImp of PH LevelTapan ShahNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument5 pagesAcids and BasesalandagocNo ratings yet
- Arrhenius Definition of An AcidDocument27 pagesArrhenius Definition of An AcidnelsonNo ratings yet
- Acid, Bases & Salts 2022-23Document34 pagesAcid, Bases & Salts 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406No ratings yet
- 25 May Acids Bases and Salts PPTDocument72 pages25 May Acids Bases and Salts PPTShubham Sharma100% (1)
- 1 Chapter 2: Acid, Bases and Salt: CH COO + Na When Small Amount of Acid Is Added CH COO + H CH COO + H ODocument6 pages1 Chapter 2: Acid, Bases and Salt: CH COO + Na When Small Amount of Acid Is Added CH COO + H CH COO + H Ojoydeep17590No ratings yet
- Solution PHDocument3 pagesSolution PHSanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Aacid Base and BuffersDocument4 pagesAacid Base and Buffersafzal sulemaniNo ratings yet
- M1 Lesson 1 - PH of Common SolutionsDocument4 pagesM1 Lesson 1 - PH of Common SolutionsPotato SquadNo ratings yet
- AlkalineWater Jan RobertsDocument5 pagesAlkalineWater Jan Robertssolmazbahary100% (1)
- H Biology Lab1Document2 pagesH Biology Lab1api-276997065No ratings yet
- Buffer SolutionsDocument10 pagesBuffer SolutionsELYANNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesAcids and Bases Lecture NotesmdonohueHGHSNo ratings yet
- PH of Food SamplesDocument11 pagesPH of Food SamplesENBONG AL-ALIM KUNSAARINo ratings yet
- Water Treatment PlantDocument2 pagesWater Treatment PlantolaelsayedNo ratings yet
- BIO CH02 L02 Synth Interactivity WKSDocument2 pagesBIO CH02 L02 Synth Interactivity WKSCamilo SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- CN BC PH Density SP GravityDocument38 pagesCN BC PH Density SP GravityTrisha MarieNo ratings yet
- Buffe by F S SHAH (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Document28 pagesBuffe by F S SHAH (Autosaved) (Autosaved)farooq shah shabbirNo ratings yet
- PH of Distilled Water: Water Stills Technical Note: T11-001Document1 pagePH of Distilled Water: Water Stills Technical Note: T11-001Alex Lopez CordobaNo ratings yet
- Acids,BasesandSalts(PrashantKirad)_14395_14402588838Document50 pagesAcids,BasesandSalts(PrashantKirad)_14395_14402588838nimodaaru123No ratings yet
- Acids bases and salts class 10 notesDocument8 pagesAcids bases and salts class 10 notesashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- Cabbage As PH IndicatorDocument2 pagesCabbage As PH IndicatormorerupaliNo ratings yet
- Presentation PHDocument19 pagesPresentation PHranbyNo ratings yet
- Making a Homemade pH Indicator from Red Cabbage to Test Household SubstancesDocument7 pagesMaking a Homemade pH Indicator from Red Cabbage to Test Household SubstancesNikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- pH Buffers Maintain Biological EnvironmentsDocument3 pagespH Buffers Maintain Biological Environmentsfaizshaikh4No ratings yet
- Presented By: Selvin Gray Che4018 Garfield Smith Dr. BramwellDocument12 pagesPresented By: Selvin Gray Che4018 Garfield Smith Dr. BramwellGarfield SmithNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Selvin Gray Che4018 Garfield Smith Dr. BramwellDocument12 pagesPresented By: Selvin Gray Che4018 Garfield Smith Dr. BramwellGarfield SmithNo ratings yet
- Total Alkalinity Determination - and Its Rule in An Aerobic Wastewater TreatmentDocument8 pagesTotal Alkalinity Determination - and Its Rule in An Aerobic Wastewater Treatmenthayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology in Biology: Lect. Name: Dr. Azmi Bin IbrahimDocument11 pagesInformation and Communication Technology in Biology: Lect. Name: Dr. Azmi Bin IbrahimAjip UzaimiNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity: The Ups and Downs of PH: Base AcidDocument4 pagesLab Activity: The Ups and Downs of PH: Base Acidpeterjo raveloNo ratings yet
- What Is PH?Document2 pagesWhat Is PH?JB BrionesNo ratings yet
- Tiếng anh 6Document78 pagesTiếng anh 6Đạo LêNo ratings yet
- Dilution, pH and Acid-Base ManufactureDocument5 pagesDilution, pH and Acid-Base ManufactureKylie smithNo ratings yet
- Litmus Paper Acidity Alkalinity PH Value: PH Values of Water Completely ExplainedDocument3 pagesLitmus Paper Acidity Alkalinity PH Value: PH Values of Water Completely ExplainedmohamedbadawyNo ratings yet
- Topic-: Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesTopic-: Chemistry Investigatory ProjectRomil TalaichNo ratings yet
- Red Cabbage As PH IndicatorDocument1 pageRed Cabbage As PH IndicatorEdmund Ocado Jr0% (1)
- How Acids & Bases Impact Our Daily LivesDocument16 pagesHow Acids & Bases Impact Our Daily LivesAhmed fatahNo ratings yet
- L5 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument21 pagesL5 Acids, Bases and SaltsQueenie EstrabilloNo ratings yet
- EC and PH: What Is It and Why Does It Matter?: Marc Van Iersel Department of Horticulture The University of GeorgiaDocument4 pagesEC and PH: What Is It and Why Does It Matter?: Marc Van Iersel Department of Horticulture The University of GeorgiaFazal KhanNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument8 pagesAcids and BasesjexNo ratings yet
- Acids and AlkalisDocument10 pagesAcids and AlkalisBirds HomeNo ratings yet
- Keila Sarahi Aguilar RuizDocument7 pagesKeila Sarahi Aguilar RuizKeilaAguilarNo ratings yet
- Study Material For ChemistryDocument7 pagesStudy Material For ChemistryBHADRANo ratings yet
- PP Asiditas + PHDocument6 pagesPP Asiditas + PHFaizah FitriahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Acid, Base and Salt: CH COO + Na When Small Amount of Acid Is Added CH COO + H CH COO + H ODocument6 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Acid, Base and Salt: CH COO + Na When Small Amount of Acid Is Added CH COO + H CH COO + H Ojoydeep17590No ratings yet
- AAH - AR - Etapa 3 - FQEDocument8 pagesAAH - AR - Etapa 3 - FQEAmi ChanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report 4.2Document4 pagesLaboratory Report 4.2Robelyn CastilloNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument26 pagesAcids and BasesAira DeomanoNo ratings yet
- Buffers in Pharmaceutical and Biologic SystemsDocument4 pagesBuffers in Pharmaceutical and Biologic SystemsGanesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Eric Visa Fee Slip PDFDocument1 pageEric Visa Fee Slip PDFsamreenNo ratings yet
- SHRM at NestleDocument23 pagesSHRM at NestlesamreenNo ratings yet
- What Is HydroponicsDocument1 pageWhat Is HydroponicssamreenNo ratings yet
- As Sapphire Applied General Model of Planned ChangeDocument3 pagesAs Sapphire Applied General Model of Planned ChangesamreenNo ratings yet
- NameDocument11 pagesNamesamreenNo ratings yet
- Name: Mariyam Mahnoor (20) Samreen Naeem (32) Zara Zaheer (36) Amna Manzoor Dar (47) Mariyam Noor (44) Class: Bpa (8) SemesterDocument3 pagesName: Mariyam Mahnoor (20) Samreen Naeem (32) Zara Zaheer (36) Amna Manzoor Dar (47) Mariyam Noor (44) Class: Bpa (8) SemestersamreenNo ratings yet
- Name: Mariyam Mahnoor (20) Samreen Naeem (32) Zara Zaheer (36) Amna Manzoor Dar (47) Mariyam Noor (44) Class: Bpa (8) SemesterDocument3 pagesName: Mariyam Mahnoor (20) Samreen Naeem (32) Zara Zaheer (36) Amna Manzoor Dar (47) Mariyam Noor (44) Class: Bpa (8) SemestersamreenNo ratings yet
- Upward and Downward Communication in SapphireDocument5 pagesUpward and Downward Communication in SapphiresamreenNo ratings yet
- What Is HydroponicsDocument7 pagesWhat Is HydroponicssamreenNo ratings yet
- QDocument2 pagesQsamreenNo ratings yet
- Upward and Downward Communication in SapphireDocument5 pagesUpward and Downward Communication in SapphiresamreenNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument13 pagesInternship ReportsamreenNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument13 pagesInternship ReportsamreenNo ratings yet
- Upward and Downward Communication in SapphireDocument5 pagesUpward and Downward Communication in SapphiresamreenNo ratings yet
- As Sapphire Applied General Model of Planned ChangeDocument3 pagesAs Sapphire Applied General Model of Planned ChangesamreenNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Numericals For PracticeDocument1 pageMole Concept Numericals For PracticemayurbuddyNo ratings yet
- Van Gogh's iconic colors for 'Starry Night' and other worksDocument5 pagesVan Gogh's iconic colors for 'Starry Night' and other worksTom HillNo ratings yet
- Discover the functions and properties of lipids through experimentsDocument8 pagesDiscover the functions and properties of lipids through experimentsJasper Ian Tan JumalaNo ratings yet
- High Temperature CorrosionDocument2 pagesHigh Temperature CorrosionIlhamChaniefNo ratings yet
- Materials Today: Proceedings: Sunita Mohapatra, Pallabi Sarkar, Ganesh BhoyeDocument6 pagesMaterials Today: Proceedings: Sunita Mohapatra, Pallabi Sarkar, Ganesh BhoyeabiliovieiraNo ratings yet
- Sulhuric Acid PDFDocument2 pagesSulhuric Acid PDFBrilian Retna AmamuhtiNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument6 pagesChemRoselyn BunquinNo ratings yet
- Materials ScienceDocument49 pagesMaterials ScienceAbhishek KaleNo ratings yet
- A Study On Durability Properties of Geopolymer Concrete Made With 100% GGBSDocument5 pagesA Study On Durability Properties of Geopolymer Concrete Made With 100% GGBSMahmoud HakimNo ratings yet
- Ammonia (EHC 54, 1986)Document153 pagesAmmonia (EHC 54, 1986)newuserNo ratings yet
- Silver Raman Ag2O RamanDocument8 pagesSilver Raman Ag2O Ramanshoeb321No ratings yet
- Top metals used in construction including steel, aluminum and moreDocument203 pagesTop metals used in construction including steel, aluminum and moreGopalakrishnan KuppuswamyNo ratings yet
- Ammonium BromideDocument4 pagesAmmonium BromideSchool pptaccNo ratings yet
- Iron Carbon Diagram (ChE Handbook)Document21 pagesIron Carbon Diagram (ChE Handbook)Mohamed Ismail100% (1)
- Inclusion Complex Formation of Cyclodextrin and PolyanilineDocument4 pagesInclusion Complex Formation of Cyclodextrin and PolyanilineElbahi DjaalabNo ratings yet
- Battery AdvancementsDocument7 pagesBattery Advancementsabhishek gowdaNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document13 pagesModule 9michaelNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics ExplainedDocument43 pagesEnzyme Kinetics ExplainedBlessings Chawinga100% (1)
- 11 Chemistry Sample PapersDocument10 pages11 Chemistry Sample PapersPc xoixaNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry Second Revision Answer KeyDocument10 pages12th Chemistry Second Revision Answer KeySubbu RajaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Hardness of WaterDocument2 pagesDetermination of Hardness of WaterNitinSrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Phosphate RockDocument3 pagesPhosphate RockManoj Kumar AcharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Carbon ChemistryDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Carbon Chemistryapi-30718309No ratings yet
- Lindab Round Duct and Fitting PDFDocument108 pagesLindab Round Duct and Fitting PDFLinh TruongNo ratings yet
- White Rust: Causes and Treatment of Zinc Coating CorrosionDocument9 pagesWhite Rust: Causes and Treatment of Zinc Coating Corrosionjljljljl4No ratings yet
- Buffers Green2018Document5 pagesBuffers Green2018pratibhauohanibtNo ratings yet
- wch11 01 Que 20231011Document28 pageswch11 01 Que 20231011Thoon Nadi Nai0% (1)
- MPS AND GWA 4th GradingDocument2 pagesMPS AND GWA 4th GradingciriloNo ratings yet
- Chem 213 LAB Notes Cover & Schedule 2018 v3Document51 pagesChem 213 LAB Notes Cover & Schedule 2018 v3Farhana Mohd RazaliNo ratings yet
- Week 1 4 Chem134 Lec ModuleDocument56 pagesWeek 1 4 Chem134 Lec ModuleMay Ann RiveraNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryFrom EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsFrom EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)