Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biostatistics and Research Methods
Uploaded by
Osama JavedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biostatistics and Research Methods
Uploaded by
Osama JavedCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOSTATISTICS AND RESEARCH METHODS
1. Introduction of Statistics: Statistical data condensation of data, presentation of data by graphs, health
related data, rates and their relative importance, presentation of quantitative data.
2. Sampling: The concept of sampling, types and methods of drawing ideal sample, sampling distribution
of sample mean, error of sampling, standard error, chi square, T-test and their uses in health.
3. Central Tendency: Concepts of central tendency, mean, median and ode and their value in health,
percentiles, measure of dispersion, coefficient of variation and skewness, normal distribution, range,
standard deviation and relative deviation.
4. Hypothesis: Concepts of hypothesis testing, null & alternative hypothesis, two types of errors,
acceptance & rejection regions, tow sided & one sided tests, general steps in hypothesis testing, test about
means, confidence interval for mean, meaning of significance in statistical procedures and methods of
inferential statistics.
5. Regression & Correlation: Scatter diagram, straight line regression model, method of least squares,
sample correlation coefficient, inference about regression coefficient and correlation coefficient.
6. Introduction to Research: The question of legitimate knowledge, knowledge & decision making, the
scientific method, quantitative vs qualitative research, application of scientific method, positivistic vs
naturalistic paradigm.
7. Classification of Research: Basic vs applied research, evaluation research, research & development
(R&D), action research.
8. Selection & Formulation of a Problem: From generic to a specific program, program statement,
getting an access to primary and secondary resources, note taking and information to management,
Review of related literature, questions and/or hypothesis of the study.
9. Development of a Research Plan: The ethical, legal and professional obligations, the rational of the
study, the research plan, evaluation of a research plan.
10. Selection of sample: sample & population, basic considerations in sampling, random sampling,
stratified random sampling cluster sampling, systematic sampling determination of sample size,
elimination of sampling bias.
11. Instrumentation and Data Collection: Tests and scales, objectivity and standardization, types of
tests and scales, validity and reliability of an instrument, assessment of validity and reliability,
development of tests/scale.
12. Data Analysis & Interpretation: Preparing data analysis, types of measurement scales, descriptive
statistics inferential statistics, using computer for data analysis.
13. Preparation of a Research Report: Format & style, citation, references & bibliography writing
theses, dissertations & journal articles.
Research paper/ Report writing related to the subject of interest of the
student
You might also like
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Bisotat For MlsDocument57 pagesBisotat For MlsABAYNo ratings yet
- 1.basic Final McqsDocument78 pages1.basic Final McqsPrabhat KcNo ratings yet
- Y Yyy Y Yyy Y YY Y Yy Yyy Y ! YY"Y#Y$Y# Y Y % Y &Y'Y (Y) +#Y"Y Y Y, Yyyy-Yyy Y.Y Y Y/Y "Y.Y Y Y YDocument15 pagesY Yyy Y Yyy Y YY Y Yy Yyy Y ! YY"Y#Y$Y# Y Y % Y &Y'Y (Y) +#Y"Y Y Y, Yyyy-Yyy Y.Y Y Y/Y "Y.Y Y Y Ydoni007No ratings yet
- Neglected Tropical DiseasesDocument84 pagesNeglected Tropical DiseasesAbhinesh Kr JhaNo ratings yet
- PSM ImagesDocument16 pagesPSM ImagesshizukaNo ratings yet
- Key Topics in PSM by DR Vivek JainDocument5 pagesKey Topics in PSM by DR Vivek Jaindocvivekjain100% (4)
- PSM Spot Community MedicineDocument20 pagesPSM Spot Community MedicinePramila MahaleNo ratings yet
- Repertory - Dissertations - FinalDocument5 pagesRepertory - Dissertations - Finalshaikh shabistaNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine PDFDocument24 pagesCommunity Medicine PDFEkambaramNo ratings yet
- Medical Law EthicsDocument30 pagesMedical Law EthicsImad AnwarNo ratings yet
- Community MCQDocument271 pagesCommunity MCQمحسن حدوان عليخان0% (1)
- Contact Us For All Medical Dvds - 03323959833: (List of Available Dvds at The End!)Document25 pagesContact Us For All Medical Dvds - 03323959833: (List of Available Dvds at The End!)ticponyNo ratings yet
- Phytochemicals, Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Profiling of Diplocyclos Palmatus (L.) C. JefferyDocument6 pagesPhytochemicals, Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Profiling of Diplocyclos Palmatus (L.) C. JefferyJovanJiEunMiNo ratings yet
- E-Scientific Booklet (AOICON)Document88 pagesE-Scientific Booklet (AOICON)DrKunal KaradeNo ratings yet
- Introduction of PharmacologyDocument33 pagesIntroduction of PharmacologykayarohanamNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Community Medicine PreventivDocument27 pagesTextbook of Community Medicine Preventivtasneem faizaNo ratings yet
- Basic BioostatisticsDocument81 pagesBasic BioostatisticsCandace Wilson ghNo ratings yet
- Research in Homoeopathy Present and Future Perspective - Homeopathic Heritage - June 2010Document5 pagesResearch in Homoeopathy Present and Future Perspective - Homeopathic Heritage - June 2010Saurav AroraNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Biostatistics MinalDocument10 pagesBasic Concept of Biostatistics MinalRohan SawantNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument100 pagesThesisVimal NishadNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive-Study-of-Organon-Nagendra-Babu.08247 - 2knowledge of PhysicianDocument6 pagesComprehensive-Study-of-Organon-Nagendra-Babu.08247 - 2knowledge of PhysicianJitendra PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- A Weekly Journal Club PresentationDocument61 pagesA Weekly Journal Club PresentationSharyKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Summary-Assessment of Clinical and Practical SkillDocument2 pagesSummary-Assessment of Clinical and Practical SkillRanjita Santra100% (1)
- Pds Social PDFDocument232 pagesPds Social PDFShambhu Ashok100% (2)
- Laboratory Test InterpretationDocument73 pagesLaboratory Test Interpretationjosieangel11No ratings yet
- Teach ManualDocument78 pagesTeach ManualShouvik DebnathNo ratings yet
- Case Control StudyDocument6 pagesCase Control Studyphian0No ratings yet
- Methods Used in EpidemologyDocument53 pagesMethods Used in EpidemologySameera banuNo ratings yet
- Antiallergic AgentsDocument56 pagesAntiallergic AgentsTazrian FarahNo ratings yet
- Acne ThesisDocument88 pagesAcne ThesisNafisa jaorawalaNo ratings yet
- 0 - Gall Stone ThesisDocument23 pages0 - Gall Stone ThesisAkshaya HBNo ratings yet
- Anameia PPT by Sandeep - FullDocument32 pagesAnameia PPT by Sandeep - Fullsravanthi100% (1)
- Rational Drug Prescribing Training CourseDocument78 pagesRational Drug Prescribing Training CourseAhmadu Shehu MohammedNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument13 pagesMeasures of Dispersionsabnira AfrinNo ratings yet
- Chlorination ExercisesDocument23 pagesChlorination Exercisesnandishb100% (2)
- History Taking2Document25 pagesHistory Taking2Capture UnseenNo ratings yet
- ICR Booklet FinalDocument2 pagesICR Booklet FinalAtit ShethNo ratings yet
- CME - Diabetic Foot UlcerDocument38 pagesCME - Diabetic Foot UlcerChuah Su WenNo ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument59 pagesCase Studiesstivana26100% (1)
- Qsar Stastistical Method in Drug DesignDocument54 pagesQsar Stastistical Method in Drug DesignvershaparchaNo ratings yet
- To Study Perinatal Outcome in Thyroid Disorder in PregnancyDocument34 pagesTo Study Perinatal Outcome in Thyroid Disorder in PregnancyAnkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Case-Control Study: Dr. Sourab Kumar DasDocument31 pagesCase-Control Study: Dr. Sourab Kumar DasSanjeet SahNo ratings yet
- Concept of PreventionDocument48 pagesConcept of Preventionmahmoud100% (1)
- HAP Question Paper Solution D. PharmaDocument9 pagesHAP Question Paper Solution D. PharmaSinger Rahul Sharma100% (1)
- Community Medicine OspeDocument4 pagesCommunity Medicine OspeHammad Shafi100% (1)
- Posology 151223081101Document24 pagesPosology 151223081101eswarNo ratings yet
- Bias and ConfoundingDocument27 pagesBias and ConfoundingsanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Karnataka, BangaloreDocument13 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Karnataka, BangaloreJyotiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document4 pagesCase Study 1Maddah Hussain100% (1)
- Cohort StudyDocument46 pagesCohort StudydrnareshchauhanNo ratings yet
- Magacyada Cudurada Iyo Waxa English Lagu Yiraahdo: Home Wararka Baargaal Maqaalo About Baargaal Nala Soo XiriirDocument6 pagesMagacyada Cudurada Iyo Waxa English Lagu Yiraahdo: Home Wararka Baargaal Maqaalo About Baargaal Nala Soo Xiriircankawaab100% (1)
- Community Medicine Preventive Social Medicine Balaram Jana.01500 - 2 PDFDocument6 pagesCommunity Medicine Preventive Social Medicine Balaram Jana.01500 - 2 PDFUsha vishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Lecture - 1 - IntroductionDocument36 pagesBiostatistics Lecture - 1 - IntroductionDr. Mahmoud Abbas Mahmoud Al-Naimi50% (4)
- AUDITING ANTIBIOGRAMS by Dr.T.V.RaoMDDocument55 pagesAUDITING ANTIBIOGRAMS by Dr.T.V.RaoMDtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Anti UlcerDocument14 pagesAnti UlcerUday SriNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingFrom EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováNo ratings yet
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet
- Research Methodology SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesResearch Methodology SYLLABUSKannabhiran ArumugamNo ratings yet
- IBUS 321 Forum Q and ADocument3 pagesIBUS 321 Forum Q and Amarina belmonte100% (1)
- 298 316 PDFDocument19 pages298 316 PDFOsama JavedNo ratings yet
- Dewan Cement: Internal ComparisonDocument24 pagesDewan Cement: Internal ComparisonOsama JavedNo ratings yet
- 298 316 PDFDocument19 pages298 316 PDFOsama JavedNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Motivation 1.2 ObjectiveDocument41 pages1.1 Motivation 1.2 ObjectiveOsama JavedNo ratings yet
- PovertyDocument22 pagesPovertythnddube4358No ratings yet
- A-4 Selection in Illustrator:: TaskaDocument3 pagesA-4 Selection in Illustrator:: TaskaOsama JavedNo ratings yet
- Rain Alarm Project Block DiagramDocument3 pagesRain Alarm Project Block DiagramVipulParasharNo ratings yet
- ReadmerDocument79 pagesReadmersatyajtiNo ratings yet
- Ame Ref-Books PDFDocument4 pagesAme Ref-Books PDFAjay Shokeen100% (1)
- Optimization in Operations Research 2nd Edition Rardin Solutions Manual DownloadDocument18 pagesOptimization in Operations Research 2nd Edition Rardin Solutions Manual DownloadLula Allen100% (23)
- An Overview of Maritime Logistics Trends and Research AgendaDocument21 pagesAn Overview of Maritime Logistics Trends and Research Agenday4x6kfzhc8No ratings yet
- PVDnotesDocument160 pagesPVDnotessvhanu4010No ratings yet
- Titela VILCEANU - Introduction To Pragmatics - Portfolio GuidebookDocument29 pagesTitela VILCEANU - Introduction To Pragmatics - Portfolio GuidebookRoxana PanacheNo ratings yet
- Calc 1Document138 pagesCalc 1LuisNo ratings yet
- National Academy Dharmapuri 97876 60996, 7010865319Document11 pagesNational Academy Dharmapuri 97876 60996, 7010865319Muralidharan KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- (Mathematical Modeling 5) B. v. Gnedenko, I. N. Kovalenko (Auth.) - Introduction To Queuing Theory (1989, Birkhäuser Basel)Document326 pages(Mathematical Modeling 5) B. v. Gnedenko, I. N. Kovalenko (Auth.) - Introduction To Queuing Theory (1989, Birkhäuser Basel)Jose Manuel Hernandez CarratalaNo ratings yet
- Nat Reviewer Mathematics Iv: Pre-TestDocument4 pagesNat Reviewer Mathematics Iv: Pre-TestRoziel MontalbanNo ratings yet
- C3 Algebra - Quadratics PDFDocument4 pagesC3 Algebra - Quadratics PDFمحمد الحماديNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe Faculty of Commerce Business Studies Department Second SemesterDocument4 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe Faculty of Commerce Business Studies Department Second SemesterchavoNo ratings yet
- Anachem Lesson 7 TransesDocument4 pagesAnachem Lesson 7 TransesChrischelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Modes of Convergence: N N N NDocument4 pagesModes of Convergence: N N N NMRNo ratings yet
- Paper IEEE WSCAR-Final PDFDocument6 pagesPaper IEEE WSCAR-Final PDFJalel HajlaouiNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 - Pontryagins Minimum PrincipleDocument9 pagesLecture10 - Pontryagins Minimum PrincipleAmit BansodNo ratings yet
- 2020.05.02 Recursive Expressions PDFDocument3 pages2020.05.02 Recursive Expressions PDFJames WigtonNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Operational Properties IIDocument8 pages7.4 Operational Properties IIFatimah Nik MazlanNo ratings yet
- Exam 2-1 Analytical ChemistryDocument5 pagesExam 2-1 Analytical Chemistrychrisie007100% (2)
- Functions and Quadratics Topic 2Document8 pagesFunctions and Quadratics Topic 2Syed Abdul Mussaver ShahNo ratings yet
- 4.3 The Normal Distribution With EXCEL Functions PDFDocument35 pages4.3 The Normal Distribution With EXCEL Functions PDFDenise SeseNo ratings yet
- Analysis III: Measure and Integration Theory of Several Variables (Lecture Notes) - Peter PhilipDocument201 pagesAnalysis III: Measure and Integration Theory of Several Variables (Lecture Notes) - Peter Philipvic1234059No ratings yet
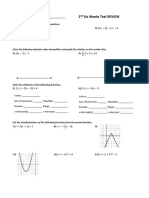
- 2nd Six Weeks Test ReviewDocument2 pages2nd Six Weeks Test ReviewAbigail WileyNo ratings yet
- Written Lesson: Utkarsh Narayan March 19, 2014Document2 pagesWritten Lesson: Utkarsh Narayan March 19, 2014Prashanth KumarNo ratings yet
- M4 Mod 1Document2 pagesM4 Mod 1Padmabnabha KamathNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus: Calculus and Integral Calculus. The Concept ofDocument19 pagesDifferential Calculus: Calculus and Integral Calculus. The Concept ofMark Niño JavierNo ratings yet
- A Little Modification in Least Cost Method For Unbalanced Transportation ProblemDocument5 pagesA Little Modification in Least Cost Method For Unbalanced Transportation ProblemAqib abdullahNo ratings yet
- Probability Test BankDocument2 pagesProbability Test Bankamul65100% (3)
- Chapter 1 - Perspective DrawingDocument23 pagesChapter 1 - Perspective DrawingChe Nora Che HassanNo ratings yet
- Statistics SPSS ProjectDocument12 pagesStatistics SPSS Projectrishabhsethi1990No ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Test Shooting Method: X X DX y DDocument4 pagesMultiple-Choice Test Shooting Method: X X DX y DDr Razak Olusegun Alli-OkeNo ratings yet
- Implementing MACD in PythonDocument1 pageImplementing MACD in PythonSyed Muhammad ShahbazNo ratings yet