Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Noncompetitive Inhibition: Inhibitor
Uploaded by
kasi FOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Noncompetitive Inhibition: Inhibitor
Uploaded by
kasi FCopyright:
Available Formats
Inhibitor a substance which slows down or prevents a particular chemical reaction or other
process or which reduces the activity of a particular reactant, catalyst, or enzyme.
Irreversible inhibitor they check or stop the chemical reaction by occupying active site or
destroying the globular site
Reversible inhibitor they have weak bond with enzymes and can proceed to both direction they can also
neutralized the effect of substrate concertration
Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (SS) and inhibitor (II) both bind to the same site on the enzyme. In
effect, they compete for the active site and bind in a mutually exclusive fashion. And only true enzyme can be
product
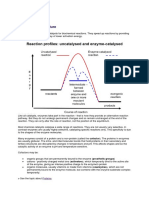
The other type of inhibition is noncompetitive inhibition . In noncompetitive inhibition, a molecule binds to an enzyme
somewhere other than the active site. This changes the enzyme's three-dimensional structure so that its active site can still bind
substrate with the usual affinity, but is no longer in the optimal arrangement to stabilize the transition state and catalyze the reation
ENZYMES a substance produced by a living organism which acts as a catalyst to bring about a
specific biochemical reaction
ENERGY OF ACTIVATION IN BIOLOGY, activation energy is the minimum energywhich must be
available to a chemical system with potential reactants to result in a chemical reaction. ... The activation
energy of a reaction is usually denoted by Ea and given in units of kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or
kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). OR
ENERGY ACTIVATION reactants must collide with some energy for starting of reaction this energy is
called energy activation
COFACTOR a substance (other than the substrate) whose presence is essential for the activity
of an enzyme
ACTIVATOR this type of cofactor change the shape of enzyme or mold the enzyme which
cause the increase the rate of particular enzyme
For eg amalase enzyme present in sliva increase its activity in the presence of chloride ions
These chloride ions are activator
PHOSTETIC GROUP this type of cofactor thightly permenetly attach with enzyme
For eg FAD HAEME(iron carrier of electron to chtochrome)
COENZYME if cofactor is organic in nature then it is called as coenzyme
For eg NADH VITAMINS
Active site a region on an enzyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction
.
You might also like
- Inhibition and RegulationDocument28 pagesInhibition and RegulationRoyal MindNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - Doc Version 1Document7 pagesEnzymes - Doc Version 1LALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- Protein Denaturation: EnzymesDocument7 pagesProtein Denaturation: EnzymescharlesNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (HL)Document26 pagesMetabolism (HL)Sapreen KaurNo ratings yet
- General Principles of CatalysisDocument12 pagesGeneral Principles of CatalysisOLUWASEGUN K AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Lesson #8 - EnzymesDocument29 pagesLesson #8 - EnzymesMaya AwadNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 3Document6 pagesEnzymes 3MituSamadderNo ratings yet
- Scienze e Rapporto Uomo NaturaDocument2 pagesScienze e Rapporto Uomo NaturaEmilia EspositoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Chapter 3Document4 pagesMicrosoft Word - Chapter 3hjhjkhdsafNo ratings yet
- Enzyme CatalysisDocument35 pagesEnzyme CatalysisMihir IyerNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Structure: OxidoreductasesDocument7 pagesEnzyme Structure: OxidoreductasesSamuel MutungaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme RegulationDocument3 pagesEnzyme RegulationgeffkryptonNo ratings yet
- AP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersDocument12 pagesAP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersMehak BectorNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Function and StructureDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Function and Structuretiyf mojaleedNo ratings yet
- Irreversible InhibitorsDocument5 pagesIrreversible InhibitorsbelabelawNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ChemistryDocument9 pagesEnzyme ChemistryVictor OmoloNo ratings yet
- GCE AS Biology 3 ENZYME NoteDocument11 pagesGCE AS Biology 3 ENZYME Notengnicole090607No ratings yet
- Enzymes and The Active SiteDocument23 pagesEnzymes and The Active SiteLaura GambaNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12Document7 pagesEnzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12almira garciaNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument31 pagesEnzymemiriam harriottNo ratings yet
- Sameer Ahmed Group: GM-01: Function and StructureDocument5 pagesSameer Ahmed Group: GM-01: Function and StructureSameer ButtNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ...Document13 pagesEnzymes ...Glen MangaliNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Mechanism of Enzymatic ActionDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Mechanism of Enzymatic ActionMoon PhạmNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Enzymes AreDocument11 pagesEnzyme: Enzymes ArePiyush BhallaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Enzymes: SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 3: Enzymes: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics Lecture NoteDocument51 pagesEnzyme Kinetics Lecture Notedowndstairs45No ratings yet
- Enzymes Are Remarkable Biological Molecules That Act As CatalystsDocument2 pagesEnzymes Are Remarkable Biological Molecules That Act As CatalystsgeffkryptonNo ratings yet
- Food SafteyDocument296 pagesFood SafteySureshkumaryadavNo ratings yet
- 12 - EnzymeDocument2 pages12 - EnzymeEnriko PalicpicNo ratings yet
- Bio EnzDocument8 pagesBio EnzbhzeenatNo ratings yet
- Jessica Lee Enzyme LabDocument15 pagesJessica Lee Enzyme LabAshalee JonesNo ratings yet
- How Do Enzymes Speed Up Chemical Reactions?: Active SiteDocument2 pagesHow Do Enzymes Speed Up Chemical Reactions?: Active SitepbNo ratings yet
- All of Those Enzymes Up and Metabolize As Fast As Possible! As It TurnsDocument11 pagesAll of Those Enzymes Up and Metabolize As Fast As Possible! As It TurnsshahzebNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - Part IIDocument71 pagesEnzymes - Part IIBarış KaplanNo ratings yet
- Enzyme RegulationDocument3 pagesEnzyme RegulationrubiomaryfloryvielNo ratings yet
- Lecture On EnzymesDocument26 pagesLecture On EnzymesDAVIE MATIASNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?: E E E EDocument15 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?: E E E EFarhana MuradNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationDocument35 pagesEnzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument80 pagesEnzymesThisha MohanNo ratings yet
- GEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam ReviewerDocument3 pagesGEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam ReviewerVanessa JimenezNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesOliver QNo ratings yet
- Ma2003 Bright Osinachi Ndubuisi - Enzyme Assay, Mechanism of Action and Kinetics of Enzymatic Catalysis.Document3 pagesMa2003 Bright Osinachi Ndubuisi - Enzyme Assay, Mechanism of Action and Kinetics of Enzymatic Catalysis.geddy D.No ratings yet
- Principles of Biochemistry - Enzymes - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Biochemistry - Enzymes - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldstanleybrowncoleNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Terms and MeaningDocument3 pagesEnzymes Terms and MeaningSubash GunasekaranNo ratings yet
- 2.enzyme Kinetics 2021Document133 pages2.enzyme Kinetics 2021Amrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Biology PresentationDocument21 pagesBiology PresentationCarolina AnnNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab Theory DiscussionDocument4 pagesEnzyme Lab Theory DiscussionQuade FrancesNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalysis: Salahaddin-University-Erbil College of Education Chemistry DepartmentDocument11 pagesEnzyme Catalysis: Salahaddin-University-Erbil College of Education Chemistry DepartmentZana EdrisNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism Lecture Part ADocument16 pagesMicrobial Metabolism Lecture Part AKashif IqbalNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document6 pagesEnzymes 1zarszNo ratings yet
- KavetaDocument2 pagesKavetaDoc_Neurologist8478No ratings yet
- 4 - EnzymesDocument31 pages4 - EnzymescheckmateNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Keshav Vashistha (Associate Professor, M.G.C.P.S., Jaipur)Document7 pagesEnzymes: Keshav Vashistha (Associate Professor, M.G.C.P.S., Jaipur)KeshavVashisthaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme StructureDocument17 pagesEnzyme Structureام احمدNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: - Sucrase - Lactase - MaltaseDocument4 pagesEnzymes: - Sucrase - Lactase - MaltaseKate Nicole EjercitoNo ratings yet
- S.5 EnzymesDocument16 pagesS.5 Enzymesmusokelukia6No ratings yet
- Chidrawi M1 C PDFDocument33 pagesChidrawi M1 C PDFZA AustraliaNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- QuestionareDocument2 pagesQuestionarekasi FNo ratings yet
- Plant Pathology CompleteDocument14 pagesPlant Pathology Completekasi FNo ratings yet
- Botany McQs GenticsDocument7 pagesBotany McQs Genticskasi FNo ratings yet
- Print Ok PP ENTDocument12 pagesPrint Ok PP ENTkasi FNo ratings yet
- Environment Factors Influencing Crop GrowthDocument5 pagesEnvironment Factors Influencing Crop GrowthjnsenguptaNo ratings yet
- SQM-Guide Mango L-EN PDFDocument52 pagesSQM-Guide Mango L-EN PDFkasi FNo ratings yet
- Sugar Cane Cultivation in PakistanDocument15 pagesSugar Cane Cultivation in Pakistankasi FNo ratings yet
- Vegetable BreedingDocument1 pageVegetable Breedingkasi FNo ratings yet
- Madam SubjectDocument3 pagesMadam Subjectkasi FNo ratings yet
- Biometric AlDocument1 pageBiometric Alkasi FNo ratings yet