Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1213 QS015 - 1
Uploaded by
Viknish ArumugamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1213 QS015 - 1
Uploaded by
Viknish ArumugamCopyright:
Available Formats
QS 015/1
Matriculation Programme
Examination
Semester 1
Session 2012/2013
Chow Choon Wooi
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
1. Find the value of x which satisfies the equation
(5 − ) − ( − 2) = 3 − (1 + )
2. Determine the solution set of the inequality
1 1
<
2 −1 +2
3. Given + 2, − 4, − 7 are the first three terms of a geometric series. Determine the
value of . Hence, find the sum to infinity of the series.
4. Given a complex number = 1 − √3 . Determine the value of if = ̅
.
3 −1
5. (a) Matrix M is given as . Show that =7 − 8 , where I is the 2 x 2
−4 4
identity matrix. Deduce that = − .
+1 −1 1
(b) Given matrix = 3 2 4 and | | = 27. Find the value of , where
−1 0 +2
is an integer.
6. The functions and are defined as ( ) = , ≠ 2 and ( ) = 3 − .
(a) Find ( ) and ( ).
(b) Evaluate ( ⃘ )(3).
(c) If ( ⃘ )( ) = , find the value of .
7. (a) Solve | − − 3| = 3.
(b) Find the solution set of the inequality < 4.
8. The first four terms of a binomial expansion (1 + ) is
1
1+ − + +⋯
2
Find
(a) the values of a and n where ≠ 0.
Chow Choon Wooi Page 2
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
(b) the value of p Hence, by substituting = , show that is approximately
equal to .
9. Given ( ) = ln(2 + 3) and ( ) = .
(a) Show that ( ) is a one-to-one function algebraically.
(b) Find ( ⃘ )( ) and ( ⃘ )( ). Hence, state the conclusion about the results.
(c) Sketch the graphs of ( ) and ( ) on the same axes. Hence, state the
domain and range of ( ).
10. Given
2 2 3
= 1 5 4
3 1 4
(a) Find the determinant of matrix .
(b) Find the minor, cofactor and adjoint of matrix .
(c) Given ( ( )) = | | where is 3 x 3 identity matrix, show that
=| ( ). Hence, find .
|
(d) By using in part ( ), solve the following simultaneous equations.
2 + 2 + 3 = 49
+ 5 + 4 = 74
3 + + 4 = 49
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Chow Choon Wooi Page 3
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
1. Find the value of x which satisfies the equation
(5 − ) − ( − 2) = 3 − (1 + )
SOLUTION
(5 − ) − ( − 2) = 3 − (1 + )
(5 − )
=3− (1 + )
( − 2)
( )
( )
+ (1 + ) = 3
= → =
(5 − )(1 + )
=3
( − 2)
(5 − )(1 + )
=2
( − 2)
(5 − )(1 + )
=8
( − 2)
(5 − )(1 + ) = 8( − 2)
5+5 − − = 8 − 16
5+4 − = 8 − 16
0= + 8 − 4 − 16 − 5
+ 8 − 4 − 16 − 5 = 0
+ 4 − 21 = 0
( + 7)( − 3) = 0
( + 7) = 0 or ( − 3) = 0
= −7 or =3
Checking
(5 − ) − ( − 2) = 3 − (1 + )
When = −7
[5 − (−7)] − (−7 − 2) = 3 − (1 − 7)
≠ −7
When =3
(5 − 3) − (3 − 2) = 3 − (1 + 3)
(2) − (1) = 3 − (4)
1−0=3−2
1 = 1√
∴ =3
Chow Choon Wooi Page 4
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
2. Determine the solution set of the inequality
1 1
<
2 −1 +2
SOLUTION
1 1
<
2 −1 +2
1 1
− <0
2 −1 +2
1( + 2) − 1(2 − 1)
<0
(2 − 1)( + 2)
+2−2 +1
<0
(2 − 1)( + 2)
− +3
<0
(2 − 1)( + 2)
− +3=0 2 −1=0 +2=0
=3 = = −2
1 1
(−∞, −2) −2, ,3 (3, ∞)
2 2
− +3 + + + -
2 −1 - - + +
+2 - + + +
− +3
(2 − 1)( + 2)
+ - + -
1
∴ ℎ −2, ∪ (3, ∞)
2
Chow Choon Wooi Page 5
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
3. Given + 2, − 4, − 7 are the first three terms of a geometric series. Determine the
value of . Hence, find the sum to infinity of the series.
SOLUTION
+ 2, − 4, − 7 …
−4 −7
=
+2 −4
( − 4)( − 4) = ( − 7)( + 2)
− 4 − 4 + 16 = + 2 − 7 − 14
− 8 + 16 = − 5 − 14
16 + 14 = −5 + 8
3 = 30
= 10
When = 10 , the sequence is
10 + 2, 10 − 4, 10 − 7 …
12, 6, 3 …
= 12, = =
=
1−
12
=
1
1− 2
12
=
1
2
= 24
Chow Choon Wooi Page 6
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
4. Given a complex number = 1 − √3 . Determine the value of if = ̅
.
SOLUTION
= 1 − √3 ̅ = 1 + √3
1
=
̅
1
1 − √3 =
1 + √3
1 − √3 1 − √3 =
1 + √3
1 − 2√3 + 3 =
1 + √3
1 − 2√3 + 3(−1) =
1 + √3
1 − 2√3 − 3 =
1 + √3
−2 − 2√3 =
1 + √3
−2 + 2√3 =
1 + √3
= −2 + 2√3 1 + √3
= −2 − 2√3 + 2√3 + 6
= −2 + 6(−1)
= −8
Chow Choon Wooi Page 7
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
3 −1
5. (a) Matrix is given as . Show that =7 − 8 , where is the 2 x 2
−4 4
identity matrix. Deduce that = − .
+1 −1 1
(b) Given matrix = 3 2 4 and | | = 27. Find the value of , where
−1 0 +2
is an integer.
SOLUTION
5(a)
3 −1
=
−4 4
3 −1 3 −1
=
−4 4 −4 4
9+4 −3 − 4
=
−12 − 16 4 + 16
13 −7
=
−28 20
3 −1 1 0
7 −8 = 7 −8
−4 4 0 1
21 −7 8 0
7 −8 = −
−28 28 0 8
13 −7
7 −8 =
−28 20
∴ =7 −8
=7 −8
−7 = −8
( − 7 ) = −8
1
=− ( −7 )
8
1 7
=− +
8 8
7 1
= −
8 8
Chow Choon Wooi Page 8
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
5(b)
+ 1 −1 1
= 3 2 4
−1 0 +2
| | = 27
2 4 3 4 3 2
| | = +( + 1) − (−1) + (1)
0 +2 −1 +2 −1 0
| | = +( + 1)[(2 + 4) − (0)] + [(3 + 6) − (−4)] + [(0) − (−2)]
| | = ( + 1)(2 + 4) + (3 + 6 + 4) + 2
| |=2 +4 +2 +4+3 +6+4+2
| |=2 + 9 + 16
2 + 9 + 16 = 27
2 + 9 − 11 = 0
(2 + 11)( − 1) = 0
=− =1
Since is an integer, ∴ =1
Chow Choon Wooi Page 9
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
6. The functions and are defined as ( ) = , ≠ 2 and ( ) = 3 − .
(a) Find ( ) and ( ).
(b) Evaluate ( ⃘ )(3).
(c) If ( ⃘ )( ) = , find the value of .
SOLUTION
6(a)
3 +4 ( )=3−
( )=
−2
=3−
3 +4
=
−2 =3−
( − 2) = 3 + 4 ( )=3−
−2 =3 +4
−3 =4+2
( − 3) = 4 + 2
4+2
=
−3
4+2
( )=
−3
6(b)
( )= ( )=
( )=3− ( )=3−
( ⃘ )( ) = [ ( )]
= [3 − ]
3(3 − ) + 4
=
(3 − ) − 2
Chow Choon Wooi Page 10
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
9−3 +4
=
3− −2
13 − 3
=
1−
13 − 3(3)
( ⃘ )(3) =
1 − (3)
13 − 9
( ⃘ )(3) =
−2
( ⃘ )(3) = −2
6(c)
( )= ( )=
( )=3− ( )=3−
2
( ⃘ )( ) =
3
( ⃘ )( ) = [ ( )]
4+2
=
−3
4+2
=3−
−3
4+2 2
3− =
−3 3
4+2 2
=3−
−3 3
4+2 7
=
−3 3
3(4 + 2 ) = 7( − 3)
12 + 6 = 7 − 21
= 33
Chow Choon Wooi Page 11
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
7. (a) Solve | − − 3| = 3.
(b) Find the solution set of the inequality < 4.
SOLUTION
7(a)
| − − 3| = 3
− −3 = 3 or − − 3 = −3
− −6 = 0 or − =0
( − 3)( + 2) = 0 or ( − 1) = 0
=3 = −2 or =0 =1
7(b)
2 +9 −4
<4
+2
2 +9 −4
−4<0
+2
(2 + 9 − 4) − 4( + 2)
<0
+2
2 +9 −4−4 −8
<0
+2
2 + 5 − 12
<0
+2
(2 − 3)( + 4)
<0
+2
2 −3=0 +4=0 +2=0
= = −4 = −2
Chow Choon Wooi Page 12
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
3 3
(−∞, −4) (−4, −2) −2, ,∞
2 2
2 −3 - - - +
+4 - + + +
+2 - - + +
(2 − 3)( + 4)
- + - +
+2
3
∴ ℎ solution set : < −4 ∪ −2 < <
2
Chow Choon Wooi Page 13
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
8. The first four terms of a binomial expansion (1 + ) is
1
1+ − + +⋯
2
Find
(a) the values of a and n where ≠ 0.
(b) the value of p Hence, by substituting = , show that is approximately
equal to .
SOLUTION
8(a)
Given that
1
(1 + ) =1+ − + +⋯
2
From binomial expansion
( − 1) ( − 1)( − 2)
(1 + ) = 1 + ( )( ) + ( ) + ( ) +⋯
2! 3!
( − 1) ( − 1)( − 2)
(1 + ) =1+ + + +⋯
2 6
1 ( − 1) ( − 1)( − 2)
1+ − + +⋯=1+ + + +⋯
2 2 6
Coefficient of :
= 1 ...................... (1)
Coefficient of :
( − 1) 1 =1
=−
2 2
( − 1) = −1
( − 1) = −1
( − 1) = −1 ................(2)
( ) ( )
=
( )
( − 1)
= −1
−1=−
2 =1
Chow Choon Wooi Page 14
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
1
=
2
From (1)
=1
1
=1
2
=2
8(b)
Compare coefficient of :
( − 1)( − 2)
=
6
1 1 1
2 2 − 1 2 − 2 (2) =
6
1 1 3
2 − 2 − 2 (8)
=
6
24
=6
8
6 =3
1
=
2
1 1
(1 + 2 ) = 1 + − + +⋯
2 2
When =
1 1 1 1 1 1
1+2 =1+ − + +⋯
4 4 2 4 2 4
1 1 1 1 1 1
1+ =1+ − + +⋯
2 4 2 16 2 64
3 1 1 1
≈1+ − +
2 4 32 128
Chow Choon Wooi Page 15
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
3 1(128) + 1(32) − 1(4) + 1
≈
2 128
3 157
≈
2 128
3 157
≈
2 128
Chow Choon Wooi Page 16
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
9. Given ( ) = ln(2 + 3) and ( ) = .
(a) Show that ( ) is a one-to-one function algebraically.
(b) Find ( ⃘ )( ) and ( ⃘ )( ). Hence, state the conclusion about the results.
(c) Sketch the graphs of ( ) and ( ) on the same axes. Hence, state the
domain and range of ( ).
SOLUTION
9(a)
( ) = ln(2 + 3)
( ) = ln(2 + 3)
( ) = ln(2 + 3)
Let ( ) = ( )
ln(2 + 3) = ln(2 + 3)
2 +3=2 +3
2 =2
Since = , therefore ( ) is a one-to-one function.
9(b)
( ) = ln(2 + 3), ( )=
( ⃘ )( ) = [ ( )]
−3
=
2
−3
= ln 2 +3
2
= ln[ − 3 + 3]
Chow Choon Wooi Page 17
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
= ln[ ]
( ⃘ )( ) = [ ( )] =
( )
=2 +3
= [ (2 + 3)]
( )
−3
=
2
(2 + 3) − 3
=
2
Conclusion
Since ( ) = ( ) = , therefore ( ) = ( ) and ( ) = ( ).
9(c)
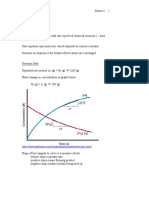
3 y
=−
2
( )
( )
3
=−
2
− ,∞ (−∞, ∞)
Chow Choon Wooi Page 18
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
10. Given
2 2 3
= 1 5 4
3 1 4
(a) Find the determinant of matrix .
(b) Find the minor, cofactor and adjoint of matrix .
(c) Given ( ( )) = | | where is 3 x 3 identity matrix, show that
=| ( ). Hence, find .
|
(d) By using in part ( ), solve the following simultaneous equations.
2 + 2 + 3 = 49
+ 5 + 4 = 74
3 + + 4 = 49
SOLUTION
10(a)
2 2 3
= 1 5 4
3 1 4
| | = (2) 5 4 1 4 1 5
− (2) + (3)
1 4 3 4 3 1
= (2)(20 − 4) − (2)(4 − 12) + (3)(1 − 15)
= (2)(16) − (2)(−8) + (3)(−14)
= 32 + 16 − 42
=6
10(b)
5 4 1 4 1 5
⎡1 4 3 4 3 1⎤
⎢2 3 2 3 2 2 ⎥⎥
, =⎢
⎢1 4 3 4 3 1⎥
⎢2 3 2 3 2 2⎥
⎣5 4 1 4 1 5⎦
(20 − 4) (4 − 12) (1 − 15)
= (8 − 3) (8 − 9) (2 − 6)
(8 − 15) (8 − 3) (10 − 2)
Chow Choon Wooi Page 19
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
16 −8 −14
= 5 −1 −4
−7 5 8
+ − +
, = − + −
+ − +
+(16) −(−8) +(−14)
= −(5) +(−1) −(−4)
+(−7) −(5) +(8)
16 8 −14
= −5 −1 4
−7 −5 8
, =
16 8 −14
= −5 −1 4
−7 −5 8
16 −5 −7
= 8 −1 −5
−14 4 8
10(c)
( =
( )) = | |
( ( )) = | |
( ( )) = | |
( ( )) = | |
| |=( ( ))
1
= ( ( ))
| |
1 16 −5 −7
= 8 −1 −5
6
−14 4 8
Chow Choon Wooi Page 20
PSPM 1 QS 015/1 Session 2012/2013
16 −5 −7
⎡ ⎤
⎢ 6 6 6⎥
8 −1 −5⎥
=⎢
⎢ 6 6 6⎥
⎢−14 4 8⎥
⎣ 6 6 6⎦
8 −5 −7
⎡ ⎤
⎢3 6 6⎥
4 −1 −5⎥
=⎢
⎢3 6 6⎥
⎢−7 2 4⎥
⎣3 3 3⎦
10(d)
=
2 + 2 + 3 = 49 =
+ 5 + 4 = 74
3 + + 4 = 49 =
2 2 3 49 =
1 5 4 = 74
3 1 4 49
8 −5 −7 8 −5 −7
⎡ ⎤ ⎡ ⎤
⎢3 6 6⎥
2 2 3 ⎢3 6 6⎥
⎢ 4 −1 −5⎥ 1 5 4 4 −1 −5⎥ 49
=⎢ 74
⎢3 6 6⎥ 3 1 4 ⎢3 6 6 ⎥ 49
⎢−7 2 4⎥ ⎢−7 2 4⎥
⎣3 3 3⎦ ⎣3 3 3⎦
8 −5 −7
⎡ ⎤
⎢3 6 6⎥
4 −1 −5⎥ 49
=⎢ 74
⎢3 6 6 ⎥ 49
⎢−7 2 4⎥
⎣3 3 3⎦
71
6
73
=
6
1
3
∴ = , = , =
Chow Choon Wooi Page 21
You might also like
- Measurements and Instrumentation Unit 1Document62 pagesMeasurements and Instrumentation Unit 1R. Jhansirani83% (6)
- CSEC ADD Maths SPECIMEN PAPER 1 PDFDocument26 pagesCSEC ADD Maths SPECIMEN PAPER 1 PDFreeta ram100% (1)
- Fundamentals of INdustrial ControlDocument5 pagesFundamentals of INdustrial ControlKirtikumarNo ratings yet
- DNV Bolts Failure Analisys Marine ApplicationDocument34 pagesDNV Bolts Failure Analisys Marine ApplicationBrian Chmeisse100% (2)
- Mathematics Paper I: Question-Answer BookDocument11 pagesMathematics Paper I: Question-Answer BookTO ChauNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Supercritical PlantDocument71 pagesSupercritical PlantNitish KumarNo ratings yet
- 1962 Fallout Shelter DesignDocument218 pages1962 Fallout Shelter DesignLouie_popwhatski100% (1)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Distance and Midpoint FormulaDocument18 pagesDistance and Midpoint FormulaWrath100% (1)
- Mathematical Induction and Binomial TheoremDocument4 pagesMathematical Induction and Binomial TheoremClain ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument4 pagesThin Layer Chromatographynaveenbimal2005No ratings yet
- List of Least Learned Competencies With Interventions ConductedDocument2 pagesList of Least Learned Competencies With Interventions ConductedGerry Chel-Nunez Awa-Laurente Aga100% (1)
- Chapter3 PDFDocument57 pagesChapter3 PDFAmilvia Vega OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 PDFDocument57 pagesChapter3 PDFAmilvia Vega OrozcoNo ratings yet
- UACE MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 2014 Marking GuideDocument14 pagesUACE MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 2014 Marking GuideSamuel HarvNo ratings yet
- Buting Senior High School Media and Information Literacy Unit TestDocument2 pagesButing Senior High School Media and Information Literacy Unit TestGina BundaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Overview of The FEMDocument60 pagesLecture 1 Overview of The FEMMarcoFranchinottiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Separation of Oil and WaterDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Separation of Oil and Waterodracir091865100% (1)
- MathsDocument5 pagesMathsThorNo ratings yet
- BYJU'S Home Learning Program: Daily Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesBYJU'S Home Learning Program: Daily Practice ProblemsSomesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument5 pagesMathsThorNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics 1: Quadrati CSDocument11 pagesPure Mathematics 1: Quadrati CSTest BigbenNo ratings yet
- Topical Guidance of SPM MathematicsDocument39 pagesTopical Guidance of SPM MathematicsSEOW INN LEENo ratings yet
- 0910 Solution UPS QM016Document10 pages0910 Solution UPS QM016OMAR BIN ALI -No ratings yet
- IX - Oly - 12 - 3 - 23 (Solution)Document8 pagesIX - Oly - 12 - 3 - 23 (Solution)Mihir DhankarNo ratings yet
- S5 Mathematics End of Term III Paper 1 KINGS COLLEGE BUDODocument3 pagesS5 Mathematics End of Term III Paper 1 KINGS COLLEGE BUDOvanessablessed999No ratings yet
- Quiz3 SolutionDocument3 pagesQuiz3 Solution張育安No ratings yet
- MatrixDocument1 pageMatrixbrendonnyirenda123No ratings yet
- Matematik Tambahan: Modul Mas (Minimum Adequate Syllabus) SPM 2019Document37 pagesMatematik Tambahan: Modul Mas (Minimum Adequate Syllabus) SPM 2019Jinny NeutrollNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 4 (Online) - With AnswersDocument4 pagesExercise No 4 (Online) - With AnswersRabiahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Solutions - Algebra, Equations and Inequalities - 2020-2Document9 pagesWorksheet Solutions - Algebra, Equations and Inequalities - 2020-2Shinyi GohNo ratings yet
- Bed (FT) 17-18 Assignment 1: (I) (Ii) (Iii)Document2 pagesBed (FT) 17-18 Assignment 1: (I) (Ii) (Iii)Treep DiaNo ratings yet
- (8th) James Stewart - Student Solutions Manual 2Document2 pages(8th) James Stewart - Student Solutions Manual 254rlatkddnjsNo ratings yet
- Jika Vector ADocument6 pagesJika Vector AAhmad RaihanNo ratings yet
- Monthly Class Test 01: Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Document1 pageMonthly Class Test 01: Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- Sol Adv Pure 2011 PDFDocument14 pagesSol Adv Pure 2011 PDFMargaretNo ratings yet
- AK - Mathematics - Class 11 - UT1 - 2022-23Document5 pagesAK - Mathematics - Class 11 - UT1 - 2022-23Aditya jainNo ratings yet
- AK - Mathematics - Class 11 - UT1 - 2022-23Document5 pagesAK - Mathematics - Class 11 - UT1 - 2022-23Aditya jainNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document59 pagesProblem Set 1Joash Normie DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- STA100 All Paper Mid TermDocument7 pagesSTA100 All Paper Mid TermMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- கல்வி வேலைவாய்ப்பு தகவல்கள் 27 07 22Document2 pagesகல்வி வேலைவாய்ப்பு தகவல்கள் 27 07 22Jagadeesh kumarNo ratings yet
- 1112 Solution UPS QS025Document10 pages1112 Solution UPS QS025James DabNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 JOHOR SMKTinggiKluang Maths QADocument8 pages2014 2 JOHOR SMKTinggiKluang Maths QASK100% (2)
- QS 015/2 Matriculation Programme Examination Semester 1 Session 2012/2013Document23 pagesQS 015/2 Matriculation Programme Examination Semester 1 Session 2012/2013Attika zahiraNo ratings yet
- Skema Add Math Melaka K2 2023Document9 pagesSkema Add Math Melaka K2 2023HASWIN EDU HUBNo ratings yet
- SeriesDocument16 pagesSeriesMav CastilloNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For Calculus 4th Edition Jon Rogawski Colin Adams Robert Franzosa PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Calculus 4th Edition Jon Rogawski Colin Adams Robert Franzosa PDF Full Chaptersquamulecytulab9z7100% (17)
- Solution Manual For Calculus 4th Edition Jon Rogawski Colin Adams Robert FranzosaDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Calculus 4th Edition Jon Rogawski Colin Adams Robert Franzosastree.brooklet1wue7u100% (46)
- Answers-Chaks Pure Maths P2 Ex 1 Pure Mathematics0001Document13 pagesAnswers-Chaks Pure Maths P2 Ex 1 Pure Mathematics0001Michael MyamboNo ratings yet
- IndiceDocument19 pagesIndiceNalweyiso JoyceNo ratings yet
- 1819F4T2M1MSDocument15 pages1819F4T2M1MSLUI ansonNo ratings yet
- Destacamento Jake - Problem Set 3Document5 pagesDestacamento Jake - Problem Set 3Generose PurolNo ratings yet
- Latihan Transformasi LaplaceDocument9 pagesLatihan Transformasi LaplaceDhimas Agil UmariNo ratings yet
- SMK Anderson (A)Document8 pagesSMK Anderson (A)ルーエデッドNo ratings yet
- Prayas JEE (2024) : Basic Math & LogarithmDocument3 pagesPrayas JEE (2024) : Basic Math & Logarithmaegffdfd vfdfdfgdfffcNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Tools S1 Worksheet April 13Document5 pagesMathematical Tools S1 Worksheet April 13Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Homework 2-MAT319/320: 1 Section 1.3Document3 pagesSolutions To Homework 2-MAT319/320: 1 Section 1.3Manahil SabirNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Homework 2-MAT319/320: 1 Section 1.3Document3 pagesSolutions To Homework 2-MAT319/320: 1 Section 1.3M ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry (Solutions)Document8 pagesAnalytic Geometry (Solutions)Karumon UtsumiNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 KalkulusDocument5 pagesTugas 1 KalkulusRini PurwantiNo ratings yet
- Pure Maths Exercise 2Document1 pagePure Maths Exercise 2Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- Y11 2U Algebra QuizDocument9 pagesY11 2U Algebra QuizmisoandcheeseNo ratings yet
- Sec 2 Mock Exam WA2 2022Document6 pagesSec 2 Mock Exam WA2 2022qisyatay21No ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section.: Strictly Confidential/954/1 2021-1-PE-JIT SIN Section A (45 Marks)Document7 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section.: Strictly Confidential/954/1 2021-1-PE-JIT SIN Section A (45 Marks)Nicholas TanNo ratings yet
- 1718 QS015 - 2 SolutionDocument22 pages1718 QS015 - 2 SolutionVeshal RameshNo ratings yet
- SetsDocument3 pagesSetsRahul PandeyNo ratings yet
- Math 803Document3 pagesMath 803Ishak IshakNo ratings yet
- (Cikgujep - Com) MS Melaka P2 2021Document10 pages(Cikgujep - Com) MS Melaka P2 2021gigi_panNo ratings yet
- Class XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With SolutionDocument128 pagesClass XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With Solutionanushkabisht2006No ratings yet
- Sec 3 A Math WA1 Mock Exam 2023Document5 pagesSec 3 A Math WA1 Mock Exam 2023KaRen OnGNo ratings yet
- Colloid, Surface Chemistry and CatalysisDocument58 pagesColloid, Surface Chemistry and CatalysisViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Instruction I: Stem Cell and YouDocument2 pagesInstruction I: Stem Cell and YouViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Kaedah Tatatertib Pelajar 1999 EnglishDocument23 pagesKaedah Tatatertib Pelajar 1999 EnglishViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Branch Appointment: This Appointment Confirmation Is Computer Generated and No Signature Is RequiredDocument1 pageBranch Appointment: This Appointment Confirmation Is Computer Generated and No Signature Is RequirederaaimanNo ratings yet
- My-Visual 56721282Document1 pageMy-Visual 56721282Viknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Figure 1a - Conceptualising The Caries ProcessDocument1 pageFigure 1a - Conceptualising The Caries ProcessViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis / Detection Techniques: Nurin Syasya Binti Mohamad ZukhiDocument9 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis / Detection Techniques: Nurin Syasya Binti Mohamad ZukhiViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum ChemistryDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Quantum ChemistryViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- M2L4 Handout - Saliva & Dental CariesDocument31 pagesM2L4 Handout - Saliva & Dental CariesViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- ChE 31 Lec 1 PDFDocument24 pagesChE 31 Lec 1 PDFLester Jason T. ChengNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Mass Balance Part 2 Baru 2021Document36 pagesFundamentals of Mass Balance Part 2 Baru 2021Viknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- M2L6 XylitolDocument5 pagesM2L6 XylitolViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Fejerskov-1997-Community Dentistry and Oral EpidemiologyDocument9 pagesFejerskov-1997-Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiologylarissa costaNo ratings yet
- M2L3 Handout - Fluoride & Dental CariesDocument43 pagesM2L3 Handout - Fluoride & Dental CariesViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- M2L3 Fluoride MOADocument7 pagesM2L3 Fluoride MOAViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Alkaline PhosphataseDocument4 pagesAlkaline PhosphataseViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Genetics Inheritance: PatternDocument2 pagesGenetics Inheritance: PatternViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Mediastinum Great VesselsDocument31 pagesMediastinum Great VesselsViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Relevance in DentistryDocument4 pagesRelevance in DentistryViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- CLINICAL MANAGEMENT - Conclusion BiochemDocument6 pagesCLINICAL MANAGEMENT - Conclusion BiochemViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Mediastinum Great VesselsDocument31 pagesMediastinum Great VesselsViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- FIn ProblemsDocument8 pagesFIn ProblemsThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 DDocument44 pagesChapter 7 Dali_bohahaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Oral Mucosa-Part1Document20 pagesTutorial Oral Mucosa-Part1Viknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- AxillaDocument23 pagesAxillaViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue MusclesDocument21 pagesConnective Tissue MusclesViknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Kinetics 2014Document23 pagesKinetics 2014Viknish ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Steady Conduction Heat TransferDocument14 pagesSteady Conduction Heat TransferAmirNo ratings yet
- Life in Zero-G: Physiological EffectsDocument2 pagesLife in Zero-G: Physiological Effectsansweringthecal100% (1)
- Geotechnical Variation of London Clay Across Central LondonDocument12 pagesGeotechnical Variation of London Clay Across Central LondonChiaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-Propertiesoffluids Semakan2.1Document35 pagesChapter1-Propertiesoffluids Semakan2.1sufi 3393No ratings yet
- QMOTheoryDocument16 pagesQMOTheoryShubhamNandiNo ratings yet
- ML12142A123Document58 pagesML12142A123Mohammed RiyaazNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Sabuk Ties TC Potain MCR 225ADocument15 pagesPerhitungan Sabuk Ties TC Potain MCR 225AsuryaNo ratings yet
- C184 E037bDocument48 pagesC184 E037bNeyda Flores VasquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 Introduction To Power Generation and Electrical Power SystemsDocument28 pagesLecture-1 Introduction To Power Generation and Electrical Power SystemsHassanAhmed124No ratings yet
- Identification of Transport Mechanism in Adsorbent Micropores From Column DynamicsDocument9 pagesIdentification of Transport Mechanism in Adsorbent Micropores From Column DynamicsFernando AmoresNo ratings yet
- Gestión de Formación Profesional Integral Procedimiento Desarrollo Curricular Guía de Aprendizaje 1. Identificación de La Guia de AprenizajeDocument9 pagesGestión de Formación Profesional Integral Procedimiento Desarrollo Curricular Guía de Aprendizaje 1. Identificación de La Guia de AprenizajeMilena Sánchez LópezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank For JEE Advance Part 1Document55 pagesChemistry Question Bank For JEE Advance Part 1gfffdssseNo ratings yet
- Moisture Content in PET PreformsDocument3 pagesMoisture Content in PET PreformsGeorge MarkasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields: Lecture 3: The Electric FieldDocument24 pagesElectromagnetic Fields: Lecture 3: The Electric FieldNazar AzizNo ratings yet
- Ak-Cc 460Document30 pagesAk-Cc 460Øyvind SkulstadNo ratings yet
- NEXAFS Tutorial Review ArticleDocument12 pagesNEXAFS Tutorial Review ArticleAngelique LusuanNo ratings yet
- Terms Detail No - of GB Test NameDocument80 pagesTerms Detail No - of GB Test NameTarek FennicheNo ratings yet
- Advanced Som SyllabusDocument1 pageAdvanced Som SyllabusRaj Kumar0% (1)
- ALLMENDINGER (1999) Introduction To Structural GeologyDocument290 pagesALLMENDINGER (1999) Introduction To Structural GeologyeliasNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument2 pagesMathsAditya Singh PatelNo ratings yet