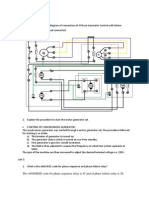
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ejemplo Calculo Nec
Uploaded by
jonatanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ejemplo Calculo Nec
Uploaded by
jonatanCopyright:
Available Formats
Schedule of load preparation is essential and a basic calculation for electrical
engineers. In this process the proper sizing of conductors, overload protection and
conduits are determined.
While there are different methods doing an electrical design but there is only one
thing that cannot be altered --- code requirements must be followed.
This example emphasized the procedure rather than mimicking the actual
loads of a residential unit.
In this example the voltage drop and short circuit calculation is not included.
The system voltage of this example is 220 VAC, 60 Hz.
Schedule of Loads
Ckt Loa Ph Rating No. VA Volt Amp Wire CB Con
d Per of s s d.
outlet Outle
ts
1 L.O. 1 100 12 1,200 220 5.45 #14 TW 15 AT, ½”
VA 1P dia.
plug-in
2 L.O. 1 100 9 900 220 4.09 #14 TW 15 AT, ½”
VA 1P dia.
plug-in
3 L.O. 1 100 6 600 220 2.73 #14 TW 15 AT, ½”
VA 1P dia.
plug-in
4 C.O 1 180 10 1,800 220 8.18 #12 TW 20 AT, ¾”
VA 1P dia.
plug-in
5 C.O 1 180 12 2,160 220 9.82 #12 TW 30 AT, ¾”
VA 1P dia.
plug-in
6 AC 1 2.5 HP 1 2331 220 10.6 #10 TW 30 AT, ¾”
U 0 1P dia.
plug-in
7 AC 1 2.5 HP 1 2331 220 10.6 #10 TW 30 AT, ¾”
U 0 1P dia.
plug-in
8 AC 1 2.5 HP 1 2331 220 10.6 #10 TW 30 AT, ¾”
U 0 1P dia.
plug-in
9 Ran 1 5000 1 5000 220 22.7 # 8 TW 80 AT, 1.0”
ge W 1 1P dia.
Loa plug-in
d
Schedule of Loads
Schedule of loads are just a summary of data to easily identify and facilitate the
necessary values and equipment rating to be used in any electrical installation. Any
data given in the schedule of loads were backed by calculation based on a well
settled electrical principles and code requirements.
Computations
Circuit 1:
I = 1,200 VA/ 220 V = 5.45 Ampere
Wire = 5.45 / 80% = 6.82 Amperes , Use 2.0 sqmm TW wire or #14 AWG [1]
Circuit Breaker = Use 15 A Circuit Breaker
Conduit = Use 1/2" diameter PVC conduit.
Circuit 2:
I = 900 VA/ 220 V = 4.09 Ampere
Wire = 4.09/ 80%= 5.11 Amperes , Use 2.0 sqmm TW wire or #14 AWG
Circuit Breaker = Use 15 A Circuit Breaker
Conduit = Use 1/2" diameter PVC conduit.
Circuit 3:
I = 600 VA/ 220 V = 2.72 Ampere
Wire = 2.72/ 80%= 3.41 Amperes , Use 2.0 sqmm TW wire or #14 AWG
Circuit Breaker = 6.82 Amperes, Use 15 A Circuit Breaker
Conduit = Use 1/2" diameter PVC conduit.
Circuit 4:
I = 1,800 VA/ 220 V = 8.18 Ampere
Wire = 8.18/ 80%= 10.23 Amperes , Use 3.5 sqmm TW wire or #12 AWG
Circuit Breaker = Use 20 A CB
Conduit = Use 3/4" diameter PVC conduit.
Circuit 5:
I = 2,160 VA/ 220 V = 9.82 Ampere
Wire = 9.82/ 80% = 12.27 Amperes , Use 3.5 sqmm TW wire or #12 AWG
Circuit Breaker = Use 20 A CB
Conduit = Use 3/4" diameter PVC conduit.
Circuit 6-8:
VA = [ 2.5 HP x ( 746 Watts/ HP ) ] / 0.8 pf (assume 0.8 pf)
VA = 2331 VA
I = 2,331 VA/ 220 V = 10.60 Ampere
Wire = 10.60 x 125% = 13.24 Amperes , Use 3.5 sqmm TW wire or #12 AWG [2]
Circuit Breaker = 5.45 x 250% = 26.5 Amperes, Use 30 A Circuit Breaker [3]
Conduit = Use 3/4" diameter PVC conduit.
Note: since the breaker is 30 Ampere, we could increase the cable size to 5.5
sqmm (rated 30 amps by NEC ) to maintain the coordination of cable and the
circuit breaker.
Circuit 9:
VA = 5000 W / 1.0 pf (heating load is a resistive load w/ 100% pf)
VA = 5,000 VA
I = 5, 000 VA/ 220 V = 22.72 Ampere
Wire = 22.71 / 80% = 28.41 Amperes , Use 8.0 sqmm TW wire or #8 AWG
Circuit Breaker = Use 40 A Circuit Breaker
Conduit = Use 1.0" diameter PVC conduit.
Main Feeder
By inspection:
Continuous loads = 9,963 VA or 45.29 A @ 220V (lighting loads and ACU)
Non- Continuous = 8, 960 VA or 40.72 @ 220V (conv. outlet & range load)
Total Loads = 19, 923 VA
Main Feeder Current = (45.29 x 100% ) + (40.72 x 125%) = 96.19 Amperes [4]
Use 50 sqmm TW cable as main feeder or service entrance wire
Use 100 Ampere MCCB, 1 pole - 10 kAIC*
note: 10 kAIC is just an assumed value, we need short circuit calculation to
determine the right specs of the OCPD to be used in this example
Rules Applied:
1. NEC 210-9a - Maximum to be served by branch circuit must not be less than
80% of the ampacity of the condutor
2. NEC 430 -22 = The size of the wire supplying motorized load shall not be less
than 125% of the rated full load current of the motor.
3. NEC 430- 52 = The size of the branch circuit protection for motor loads shall not
be greater than 250% of motor full load current for CB and 300% for non-time
delay fuses on full voltage starting.
4. NEC 210-22(C) = Over-Current Protection Device shall be calculated as 100%
of non-continuous load + 125% of the continuous load.
References:
1. National Electrical Code 2011 (Handbook)
2. General Electric Circuit Breaker Catalogue
Any comments for this article are welcome....
You might also like
- AAA-SKM-Overcurrent Coordination Basic TransformerDocument5 pagesAAA-SKM-Overcurrent Coordination Basic TransformerJOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation Specification TableDocument1 pageElectrical Installation Specification TableEmil D. PadullonNo ratings yet
- EIM 6 Lesson 1Document19 pagesEIM 6 Lesson 1Criselva Eupeña PabrigalNo ratings yet
- The ANSI/IEEE Code For Phase Sequence Relay Is 47 and of Phase Failure Relay Is 58Document9 pagesThe ANSI/IEEE Code For Phase Sequence Relay Is 47 and of Phase Failure Relay Is 58ax33m144No ratings yet
- CPA-Arc Flash Protection-ASTM 1506-NFPA 70EDocument16 pagesCPA-Arc Flash Protection-ASTM 1506-NFPA 70EJOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Simplecircuitusing 3 Way Switch (S3W) Schematic Diagram PictorialdrawingDocument15 pagesSimplecircuitusing 3 Way Switch (S3W) Schematic Diagram PictorialdrawingMa Cecelia BorjaNo ratings yet
- Power Quality at The PanelDocument5 pagesPower Quality at The PanelDomingo RuizNo ratings yet
- Lennox-VRF EHB VRF Three-PhaseDocument187 pagesLennox-VRF EHB VRF Three-PhaseLouie Derek OrtizNo ratings yet
- Inspection Checklist Guide For PV Systems in One-And Two - Family DwellingsDocument7 pagesInspection Checklist Guide For PV Systems in One-And Two - Family DwellingsElectricité & Instrumentation Gassi TouilNo ratings yet
- CEA Inspection Compliance Report SummaryDocument4 pagesCEA Inspection Compliance Report Summarykalyan ReddyNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Electrical Learning Module Sabella 2Document172 pagesK To 12 Electrical Learning Module Sabella 2bhadz SabellaNo ratings yet
- Module 01 Student Assignment Booklet - Electrician Module 1Document35 pagesModule 01 Student Assignment Booklet - Electrician Module 1imabacchus23No ratings yet
- Prime Continuous Power vs. Standby Backup PowerDocument5 pagesPrime Continuous Power vs. Standby Backup PowerOsama ShalabyNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Installation RequirementsDocument48 pagesFire Pump Installation Requirementsczds6594No ratings yet
- Supplying Power For Electric Fire Pumps-Pacuku-CEEDocument5 pagesSupplying Power For Electric Fire Pumps-Pacuku-CEEJOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Fmm-1 Manual FZMDocument5 pagesFmm-1 Manual FZMCarolina Salem RomoNo ratings yet
- Ekor - RPS: Multifunctional Protection Unit Volume 1 of 3Document144 pagesEkor - RPS: Multifunctional Protection Unit Volume 1 of 3Mayrita M Rojas100% (1)
- CocDocument3 pagesCoctapera_mangeziNo ratings yet
- Indoor RMU ManualDocument20 pagesIndoor RMU Manualhardeepsingh_08No ratings yet
- Classifications of Low Voltage Panel SeparationDocument8 pagesClassifications of Low Voltage Panel SeparationUNNI VENUGOPAL100% (1)
- 200 Item Answer SheetDocument4 pages200 Item Answer SheetFroilan EspinosaNo ratings yet
- User Manual Type HD8967 / HD8968 / HD8969: Read Carefully Before Using The MachineDocument116 pagesUser Manual Type HD8967 / HD8968 / HD8969: Read Carefully Before Using The Machineeddystoel2653No ratings yet
- NEC Code Change: For Health Care FacilitiesDocument12 pagesNEC Code Change: For Health Care FacilitiesJorge Buitrago100% (1)
- MRP Mar 2013Document71 pagesMRP Mar 2013wasinchaiNo ratings yet
- 13 Transformer ContDocument12 pages13 Transformer ContHusseinZyoudNo ratings yet
- CBLM Electric Fan, (Revised)Document73 pagesCBLM Electric Fan, (Revised)sorcererpcNo ratings yet
- Power Supply and Security Alarm ProjectDocument29 pagesPower Supply and Security Alarm ProjectDhruv Gupta100% (1)
- Renewable Energy Central America 2011Document231 pagesRenewable Energy Central America 2011Anne MarieNo ratings yet
- Wire Basics of Ampacity or Copper Wire Current Carrying Capacity Carrying CapacitiesDocument3 pagesWire Basics of Ampacity or Copper Wire Current Carrying Capacity Carrying CapacitiesarifardentNo ratings yet
- 0613CT0001 PDFDocument180 pages0613CT0001 PDFhimanshu yadavNo ratings yet
- Electrician Hydro Draft FinalizedDocument57 pagesElectrician Hydro Draft Finalizedsherub wangdi100% (1)
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration: Safely Installing, Maintaining and Inspecting Cable TraysDocument14 pagesOccupational Safety and Health Administration: Safely Installing, Maintaining and Inspecting Cable TrayselmerNo ratings yet
- Development of An Electrical Wiring Installation TrainerDocument4 pagesDevelopment of An Electrical Wiring Installation TrainerJeff PereyrasNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Installation, Operation and Maintenance of Magnum SB Insulated Case Low Voltage Power Circuit BreakersDocument70 pagesInstructions For Installation, Operation and Maintenance of Magnum SB Insulated Case Low Voltage Power Circuit BreakersedgarNo ratings yet
- Iom 1202 082013Document137 pagesIom 1202 082013Bianca L. Foliaco100% (1)
- Relay Applications PDFDocument52 pagesRelay Applications PDFRM HaroonNo ratings yet
- Meter HXE34K DataSheetDocument5 pagesMeter HXE34K DataSheetAntonio Jimenez0% (1)
- Aurora Commercial Outdoor Lighting V1Document320 pagesAurora Commercial Outdoor Lighting V1Aurora LightingNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION 314 EXPERIMENTS MANUALDocument11 pagesINDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION 314 EXPERIMENTS MANUALkatjinomasa kavetuNo ratings yet
- FCC Accessories PDFDocument40 pagesFCC Accessories PDFSorcerer NANo ratings yet
- Transformer - Best Practice ManualDocument52 pagesTransformer - Best Practice ManualkrcdewanewNo ratings yet
- KEB F4 - 00f4c0bk110 - GBDocument28 pagesKEB F4 - 00f4c0bk110 - GBOleksQ100% (1)
- As 60947.4.1-2004 Low-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear Contactors and Motor-Starters - Electromechanical CoDocument12 pagesAs 60947.4.1-2004 Low-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear Contactors and Motor-Starters - Electromechanical CoSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Inventory Training ResourcesDocument3 pagesInventory Training ResourcesEmil D. PadullonNo ratings yet
- 10A.10.11.13 Xcel Energy Outdoor Lighting ManualDocument209 pages10A.10.11.13 Xcel Energy Outdoor Lighting ManualCharlesNo ratings yet
- L&T's Air Circuit BreakersDocument31 pagesL&T's Air Circuit BreakersNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Gamewell 7100 Manual PDFDocument50 pagesGamewell 7100 Manual PDFHenrySiviraNo ratings yet
- FCS Capacitor SwitchDocument7 pagesFCS Capacitor SwitchJoe ChuengNo ratings yet
- GreenleeDocument49 pagesGreenleeBrianHaze100% (1)
- Heating and Cooling With Heat PumpDocument33 pagesHeating and Cooling With Heat Pumpget2anushNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument16 pagesProjectKiran TkNo ratings yet
- 24-47GHz Mixer Experiments by Wolfgang DD8BDDocument27 pages24-47GHz Mixer Experiments by Wolfgang DD8BDognianov100% (1)
- PCRPH1537 - Multi-Split Air Conditioners with DC Inverter ControlDocument21 pagesPCRPH1537 - Multi-Split Air Conditioners with DC Inverter Controlcolleen bergancia100% (1)
- Soft Starters.Document67 pagesSoft Starters.Shijumon KpNo ratings yet
- Install LG Room Air Conditioner EasilyDocument55 pagesInstall LG Room Air Conditioner EasilyOscar PiñerosNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Load PreparationDocument3 pagesSchedule of Load PreparationTeodoro Quintana100% (1)
- Schedule of Electrical Loads SummaryDocument3 pagesSchedule of Electrical Loads SummaryCab VicNo ratings yet
- Schedule of load preparation is essential for electrical engineersDocument5 pagesSchedule of load preparation is essential for electrical engineersEric MendozaNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare Schedule of LoadsDocument6 pagesHow To Prepare Schedule of LoadsFlorencio Jolongbayan0% (1)
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- DetectordecircuitoselectricosDocument72 pagesDetectordecircuitoselectricosjonatanNo ratings yet
- Inv Current Busbar 1.2 - Main /1.25or Inv Current Busbar 1.2 - Main 0.8note: 0.8 1/1.25Document1 pageInv Current Busbar 1.2 - Main /1.25or Inv Current Busbar 1.2 - Main 0.8note: 0.8 1/1.25jonatanNo ratings yet
- Neca 101 Ansi Review DraftDocument45 pagesNeca 101 Ansi Review DraftjonatanNo ratings yet
- Preface: 38740 - 00 - FM - Pi-X.indd IIIDocument2 pagesPreface: 38740 - 00 - FM - Pi-X.indd IIIjonatanNo ratings yet
- WEG Sca06 Modbus Rtu Manual 10001625775 Manual EnglishDocument25 pagesWEG Sca06 Modbus Rtu Manual 10001625775 Manual EnglishjonatanNo ratings yet
- WEG Sca06 Profibus DP Manual 10001227142 Manual EnglishDocument31 pagesWEG Sca06 Profibus DP Manual 10001227142 Manual EnglishjonatanNo ratings yet
- Electric Cables Handbook 3rd Ed - C. Moore Black Well, 1997) WWDocument1,101 pagesElectric Cables Handbook 3rd Ed - C. Moore Black Well, 1997) WWSDumas100% (16)
- Applications & Tools: Connecting A SINAMICS G120 Drive To An S7-300/400 CPU in TIA Portal V11Document56 pagesApplications & Tools: Connecting A SINAMICS G120 Drive To An S7-300/400 CPU in TIA Portal V11jonatanNo ratings yet
- NEC Article 250Document42 pagesNEC Article 250unknown_3100% (1)
- Common Power Quality Factors Affecting Transformers: Application NoteDocument6 pagesCommon Power Quality Factors Affecting Transformers: Application NotejonatanNo ratings yet
- SFD Electrical Vehicle Charger Service Load Calculation Form in Form 00Document1 pageSFD Electrical Vehicle Charger Service Load Calculation Form in Form 00Michael SharpeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Layout and Estimate Second Edition GuideDocument349 pagesElectrical Layout and Estimate Second Edition GuideArlie Lobrigo93% (136)
- Advances in Communications Based Train Control Systems by F. Richard YuDocument273 pagesAdvances in Communications Based Train Control Systems by F. Richard Yujonatan100% (4)
- NEC Grounding MREC2010Document3 pagesNEC Grounding MREC2010jonatanNo ratings yet
- 17NCDVD2 1568 SampleDocument12 pages17NCDVD2 1568 SampleIrving GuatemalaNo ratings yet
- 17NCDVD2 1568 SampleDocument12 pages17NCDVD2 1568 SampleIrving GuatemalaNo ratings yet
- 17NCDVD2 1568 SampleDocument12 pages17NCDVD2 1568 SampleIrving GuatemalaNo ratings yet
- Tracking sports training efficiency with surface EMGDocument8 pagesTracking sports training efficiency with surface EMGsdjuknicNo ratings yet
- Manoeuvrability Final EditedDocument12 pagesManoeuvrability Final EditedSaptarshi BasuNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214860417301148 Main PDFDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S2214860417301148 Main PDFQuy Hoang KimNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Assignment - CompletedDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Assignment - CompletedSu GarrawayNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument1 pageTramadol Drug Studymilkv82% (11)
- MR-JE - A SERVO AMPLIFIER INSTRUCTION MANUAL (Modbus RTU Protocol)Document114 pagesMR-JE - A SERVO AMPLIFIER INSTRUCTION MANUAL (Modbus RTU Protocol)Aung Naing OoNo ratings yet
- Inkontinensia Urin: Dr. Adhi Permana, SPPDDocument35 pagesInkontinensia Urin: Dr. Adhi Permana, SPPDTiara KhairinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (CHM 127)Document105 pagesChapter 3 (CHM 127)FiqajasmeNo ratings yet
- F588 PDFDocument8 pagesF588 PDFOscar Gutiérrez-JuncoNo ratings yet
- Deam Edan M8 Monitor - User ManualDocument248 pagesDeam Edan M8 Monitor - User Manualvelasquez diazNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Safe - One Pager - Version 1.0 - Oct 20Document2 pagesDiabetic Safe - One Pager - Version 1.0 - Oct 20naval730107No ratings yet
- Introducing Inspira's: Managed Noc & Itoc ServicesDocument2 pagesIntroducing Inspira's: Managed Noc & Itoc ServicesmahimaNo ratings yet
- Orrick PostedbyrequestDocument4 pagesOrrick PostedbyrequestmungagungadinNo ratings yet
- Mycotoxin Test ProcedureDocument3 pagesMycotoxin Test ProcedureKishenthi KerisnanNo ratings yet
- Paradise Pools Flyer With Price ListDocument5 pagesParadise Pools Flyer With Price ListKhuzaima HussainNo ratings yet
- Tween 80Document11 pagesTween 80fvdxrgNo ratings yet
- Great Gatsby Study NotesDocument69 pagesGreat Gatsby Study NotesLara Westwood100% (2)
- S10 Electric Power PackDocument12 pagesS10 Electric Power PackrolandNo ratings yet
- Chemical reactions and structuresDocument22 pagesChemical reactions and structuresStormy StudiosNo ratings yet
- INChO 2008 Question PaperDocument23 pagesINChO 2008 Question PaperChaitanya GaurNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Elevator Manual Helmon 2000 InstructionDocument27 pagesHyundai Elevator Manual Helmon 2000 InstructionReynold Suarez100% (1)
- Purification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneityDocument9 pagesPurification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneitySinaí GutierrezNo ratings yet
- PCS PADDLE SHIFTER INSTALL GUIDEDocument21 pagesPCS PADDLE SHIFTER INSTALL GUIDEAndreas T P ManurungNo ratings yet
- EAGLE TUGS - Parts Service ManualDocument72 pagesEAGLE TUGS - Parts Service ManualDave MilnerNo ratings yet
- Paguro 06000 Spare Parts Catalogue PDFDocument88 pagesPaguro 06000 Spare Parts Catalogue PDFBoris Sitorus100% (2)
- HistorydylaneditDocument6 pagesHistorydylaneditapi-19858424No ratings yet
- Limbah PabrikDocument2 pagesLimbah Pabrikindar dewaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 PDFDocument54 pagesCh1 PDFChristian Jegues100% (2)
- PDPM Iiitdm Jabalpur: LASER Beam Machining AdvancementsDocument12 pagesPDPM Iiitdm Jabalpur: LASER Beam Machining AdvancementsDeva RajNo ratings yet
- MACRO-ETCHING SOLUTIONS FOR ALUMINIUM ALLOYSDocument1 pageMACRO-ETCHING SOLUTIONS FOR ALUMINIUM ALLOYSsensoham03No ratings yet