Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parts of Speech Handout2
Uploaded by
Christopher JohnCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parts of Speech Handout2
Uploaded by
Christopher JohnCopyright:
Available Formats
The College of Saint Rose Writing Center, 2008
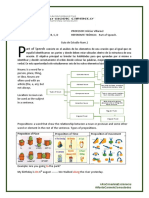
Parts of Speech
What are parts of speech?
They are eight categories of words defined in terms of their purpose, place, meaning, and use within
sentences. The categories are: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions,
and interjections.
Part of Speech Definition Examples
Nouns Names persons, places, things, teacher, Albany, basketball, proposal,
ideas, or qualities. pride
Pronouns Words that replace a noun that I, you, him, her, me, this, that, they,
has already been mentioned. which, she, he
Verbs Words that convey action, a state walk, go, sing, are, seem, sleep
of being, or existence.
Adjectives Words that describe nouns and beautiful, green, angry, necessary
pronouns.
Adverbs Words that modify verbs, gracefully, very, too, loudly, finally
adjectives, or other adverbs.
They answer the questions:
“When?”, “Where?”, “Why?”,
“How?”, “How much?”, and “In
what way?”
Prepositions Words that link nouns or on, in, over, under, within
pronouns to other words within a
sentence
Conjunctions Words that link other words,
phrases, or clauses in a sentence.
a. Coordinating Words that link independent for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so
Conjunctions clauses.
b. Subordinating Words that link dependent clauses although, because, whether, while
Conjunctions with independent clauses.
Interjections Words that are used as Hey! Oh! Darn! Wow!
exclamations or to express
feeling.
The College of Saint Rose Writing Center, 2008
Parts of Sentences
What are the parts of sentences?
They are categories of words or groups of words that make up a sentence. These categories are:
subjects, predicates, objects, complements, phrases, and clauses.
Part of Sentence Definition Examples
Subject Word or word group in a The teacher grades fairly.
sentence that performs the action
expressed in the predicate.
Predicate Word or word group that The students worked very hard
expresses a certain action or state on their papers.
of being.
Object Nouns or pronouns that receive
the action or complete the
meaning of a verb.
a. Direct Objects Receive the action or complete The professor wrote a book
the meaning of a verb and answer about the Civil War.
the questions: “What?” or
“Whom?” (i.e. wrote what? Wrote a
book).
b. Indirect Objects Words that follow transitive The tutor gave me feedback
verbs and come before direct that was helpful.
objects. They answer the
questions: “To what?”, “For (i.e. gave feedback to whom?
whom?”, or “To whom?” Gave me feedback).
c. Object of Prepositions Nouns or pronouns that follow The young boy ran in the hall.
the preposition.
(in is the preposition)
Complements Word or word group that
completes the meaning of a
subject, object, or verb.
a. Subject Complements Subject modifiers that follow She is an engineer. (predicate
linking verbs. As nouns, they are noun)
known as predicate nouns. As
adjectives, they are known as He was discouraged. (predicate
predicate adjectives. adjective)
b. Object Complements Modify or refer to the direct The town pronounced John a
object. hero.
c. Verb Complements The direct or indirect objects of a Tutoring gives students time to
verb. reflect on their own work.
(Students is the indirect object
and time is the direct object of
the verb “gives.”)
The College of Saint Rose Writing Center, 2008
Phrases Group of related words without
subjects or predicates.
a. Prepositional Phrases This consists of a preposition and The animals slept in the barn.
an object, and is usually a
modifier.
b. Verb Phrases Phrases that consist of a verb and Joan and Ken adopted a baby
other words in the predicate of a from Russia.
sentence.
c. Verbal Phrases Phrases formed from a verbal (a
word originating from a verb).
i. Infinitive phrases Phrases consisting of infinitives She seemed to enjoy the movie
and objects, plus their modifiers. the teacher played in class.
(to enjoy is the infinitive)
ii. Participle phrases Phrases consisting of participles, I noticed the students
their objects, and modifiers. The pretending to do their
phrases act as adjectives. homework were all in Mr.
Smith’s class.
(pretending is the participle)
iii. Gerund phrases Phrases consisting of gerunds, Biking on a busy street can be
their objects, and modifiers. The dangerous.
phrases act as nouns.
(Biking is the gerund)
Clauses Related words containing
subjects and predicates that are
either sentences or parts of
sentences.
a. Main (independent) Clauses that are able to stand The student completed his
clauses alone in a sentence. paper on time.
b. Subordinate (dependent) Clauses that can’t stand alone in The student completed his
clauses a sentence. paper on time because he
started it early.
The following resources were consulted in the design of this handout:
Cogdill, Sharon and Judith Kilborn. “Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence.” Literacy Education Online. October 5, 1999.
The Write Place, St. Cloud State University. 17 October 2000.
http://leo.stcloudstate.edu/grammar/grammarcondensed.html .
Harris, Muriel. Prentice Hall Reference Guide to Grammar and Usage. 6th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2006.
***************************************************************************************************
Permission is granted to duplicate and distribute this handout, providing that the following information remain intact:
This page is located at: www.strose.edu/writingcenter The College of Saint Rose Writing Center, 2008
Designed by Emily Vachula
You might also like
- English Study Pack 1Document16 pagesEnglish Study Pack 1sajiniNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of SpeechDocument2 pages8 Parts of SpeechJuan Diego Ramos CabralNo ratings yet
- T&AG 1hjjkkkDocument139 pagesT&AG 1hjjkkkRachidNo ratings yet
- Lesson Three - Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesLesson Three - Parts of Speechsathvik.guduguntlaNo ratings yet
- Writing Guide: Essential Skills for MOE ExamsDocument86 pagesWriting Guide: Essential Skills for MOE ExamsSedra Mousa Al Samara mousa almokdad Almokdad al samaraNo ratings yet
- Eed 111 (Lesson 3 Structure of Predication)Document25 pagesEed 111 (Lesson 3 Structure of Predication)Andal Bianzon Leslie AnnNo ratings yet
- Escrita II ResumenDocument13 pagesEscrita II ResumenBárbara AvilaNo ratings yet
- The Young Boy: AlthoughDocument4 pagesThe Young Boy: AlthoughZARANo ratings yet
- Studying For ToeflDocument41 pagesStudying For ToeflFernanda FuentesNo ratings yet
- HNJDocument17 pagesHNJwafaNo ratings yet
- Structure of EnglishDocument9 pagesStructure of EnglishCherry Mae PalilioNo ratings yet
- English 10 Parts of Speech Flashcards - Quizlet PDFDocument6 pagesEnglish 10 Parts of Speech Flashcards - Quizlet PDFJustice MervilleNo ratings yet
- English 7 Lesson 3 Active and Passive VoicesDocument46 pagesEnglish 7 Lesson 3 Active and Passive VoicesSEh-sEh Mae RepompoNo ratings yet
- Subject Pronouns and Possessive AdjectivesDocument13 pagesSubject Pronouns and Possessive AdjectivesAlexa OnofreNo ratings yet
- Oral Test Course Outline Reviewer English 7Document4 pagesOral Test Course Outline Reviewer English 7Victoria DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument47 pagesParts of SpeechApril RiceNo ratings yet
- Grammar BookDocument35 pagesGrammar BookHunwind FirelightNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument1 pageParts of SpeechMichaela San BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8. Lexical Categories Introduction DiscussionDocument6 pagesLesson 8. Lexical Categories Introduction DiscussionColleen CastueraNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speec1Document1 pageParts of Speec1jasminespalmadobcc26No ratings yet
- EL108 LessonPlan VerbDocument8 pagesEL108 LessonPlan VerbFranchesca Alon-alonNo ratings yet
- Sentence Pattern Project: Terms Example IllustrationDocument2 pagesSentence Pattern Project: Terms Example IllustrationNithya SekarNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 6 (Fisika A 2019) PronounDocument10 pagesKelompok 6 (Fisika A 2019) Pronounsalsabilla alifiaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - For EditDocument44 pagesStudy Guide - For EditDe AlaipNo ratings yet
- Engl111 (Week 11)Document28 pagesEngl111 (Week 11)matusjosealfonsoNo ratings yet
- 3 Yellow Red Playful Illustration Class Syllabus Education PresentationDocument70 pages3 Yellow Red Playful Illustration Class Syllabus Education PresentationCristine CruzNo ratings yet
- PartsofSpeechTheory 1Document18 pagesPartsofSpeechTheory 1anaclara.favuzzaNo ratings yet
- ComplementsDocument29 pagesComplementsGohar Ali0% (1)
- Lee Esto Primero... !Document13 pagesLee Esto Primero... !Orlando Chandía OchoaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Academic English PDFDocument8 pagesModule 1 - Academic English PDFRizal MuharamNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesParts of SpeechТетяна ДармограйNo ratings yet
- Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences - Grammar - Academic Guides at Walden UniversityDocument1 pageSentence Structure and Types of Sentences - Grammar - Academic Guides at Walden Universityphia mrtnNo ratings yet
- Eight Parts of Speech Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesEight Parts of Speech Lesson PlanRogelyn RendoqueNo ratings yet
- Grammar Rules:: Parts of SpeechDocument7 pagesGrammar Rules:: Parts of SpeechRopaNo ratings yet
- Grammar HandbookDocument24 pagesGrammar Handbookgt211No ratings yet
- PronounsDocument5 pagesPronounsABELLANO, SHEENA MAE A.No ratings yet
- VERBS Review 2015 2016 1zxiadhDocument17 pagesVERBS Review 2015 2016 1zxiadhHeinz L. FangonilNo ratings yet
- Quizlet 8Document7 pagesQuizlet 8Angelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech GuideDocument16 pagesParts of Speech GuideSupernisahNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Content (Open Class) Function (Closed Class)Document4 pagesEnglish Grammar: Content (Open Class) Function (Closed Class)MarienNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 2023Document1 pageParts of Speech 2023Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Ansari MD Imran - 18 - Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument24 pagesAnsari MD Imran - 18 - Parts of Speech in EnglishA.M. College100% (1)
- Grammar 2Document8 pagesGrammar 2الشيخة جمانةNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument10 pagesPart of Speechชนิกานต์No ratings yet
- WDocument2 pagesWhihiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Phrases and SentencesDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Phrases and SentencesVerlandi PutraNo ratings yet
- Grammar2 6 17Document2 pagesGrammar2 6 17api-328344919No ratings yet
- Verbs - Structured Notes TakenDocument10 pagesVerbs - Structured Notes Takenzp9nygy7tqNo ratings yet
- Written Report in Teaching EnglishDocument5 pagesWritten Report in Teaching Englishhazel ann canejaNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech Guide Analyzes Elements of SentencesDocument4 pagesPart of Speech Guide Analyzes Elements of SentencesRamon Franco IINo ratings yet
- Parts of speech guide for basic communication skillsDocument28 pagesParts of speech guide for basic communication skillsAnn Kristel EstebanNo ratings yet
- Super HandoutsDocument22 pagesSuper HandoutsShinki MirikaNo ratings yet
- The Eigth Parts of Speech-Tatiana RDocument14 pagesThe Eigth Parts of Speech-Tatiana RTATIANA RNo ratings yet
- Education Verb TypesDocument8 pagesEducation Verb TypesNovi IndrianiNo ratings yet
- The Preposition - 24626468 - 2023 - 10 - 27 - 10 - 36Document3 pagesThe Preposition - 24626468 - 2023 - 10 - 27 - 10 - 36gandhi paramasivamNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument51 pages8 Parts of Speech in EnglisharmanoticNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Parts of SpeechAhmad SaifiNo ratings yet
- New Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetFrom EverandNew Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in English (Grade 7)Document2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in English (Grade 7)Mariya100% (2)
- Headway5thEd Pre Intermediate TeachersGuideDocument150 pagesHeadway5thEd Pre Intermediate TeachersGuideAmbra FerrarottoNo ratings yet
- Prepositional PhrasesDocument5 pagesPrepositional PhrasesNoor Hazwani Mansor100% (1)
- Discriptive Approach To Establishing Word ClassesDocument1 pageDiscriptive Approach To Establishing Word ClassesЮлия ПолетаеваNo ratings yet
- Q1 Writing AssignmentDocument1 pageQ1 Writing Assignmentapi-3828651No ratings yet
- Prepare For Exam Success: C1 Advanced Self-Access LearningDocument7 pagesPrepare For Exam Success: C1 Advanced Self-Access LearningACRNo ratings yet
- ENGL 157 - Lecture 4Document17 pagesENGL 157 - Lecture 4Abede Saviour DelaliNo ratings yet
- Diploma Thesis-P AdamecDocument82 pagesDiploma Thesis-P AdamecKristine Guia CastilloNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EappDocument18 pagesModule 1 EappMelerose Dela SernaNo ratings yet
- World Dictionary of Foreign Expressions PDFDocument444 pagesWorld Dictionary of Foreign Expressions PDFCarmen Nel100% (1)
- Language Hub Pre Intermediate Student S Book Scope and SequenceDocument4 pagesLanguage Hub Pre Intermediate Student S Book Scope and Sequenceباسل الغامدي0% (2)
- Barriers of CommunicationDocument37 pagesBarriers of CommunicationJustin SolanoNo ratings yet
- Free and Bound MorphemesDocument9 pagesFree and Bound MorphemesRaghadNo ratings yet
- Week 6 PRESENTATIONDocument10 pagesWeek 6 PRESENTATIONMichalcova Realisan JezzaNo ratings yet
- 4000 Essential English Words 3 PDF - 2nd Edition (WWW - Languagecentre.ir)Document197 pages4000 Essential English Words 3 PDF - 2nd Edition (WWW - Languagecentre.ir)azadeNo ratings yet
- Theory and Social Research - Neuman - Chapter2Document24 pagesTheory and Social Research - Neuman - Chapter2Madie Chua0% (1)
- Class XI Social Studies Cause and EffectDocument8 pagesClass XI Social Studies Cause and EffectKiaraNo ratings yet
- Texas Pre-K Guidelines: At-A-GlanceDocument12 pagesTexas Pre-K Guidelines: At-A-Glanceapi-573880054No ratings yet
- Editorial Assignment Grading RubricDocument2 pagesEditorial Assignment Grading RubricRichmond Jake AlmazanNo ratings yet
- How to Communicate EffectivelyDocument49 pagesHow to Communicate EffectivelyAllana RayosNo ratings yet
- Teaching Holiday Vocab to Young LearnersDocument38 pagesTeaching Holiday Vocab to Young LearnersselvychrisnadwiNo ratings yet
- Understanding key linguistic concepts like homonymy, synonymy and antonymyDocument19 pagesUnderstanding key linguistic concepts like homonymy, synonymy and antonymyÁlvaro Sánchez AbadNo ratings yet
- Great Conductor ReportDocument5 pagesGreat Conductor ReportFreddieNo ratings yet
- Sentiment Analysis: Understanding the Challenges of NLPDocument32 pagesSentiment Analysis: Understanding the Challenges of NLPJaiswal Technical MentorNo ratings yet
- English Topics RBEC & K-12Document23 pagesEnglish Topics RBEC & K-12Zee Na0% (1)
- Grade 7 English: Appreciating Literature and LanguageDocument5 pagesGrade 7 English: Appreciating Literature and LanguageMonaliza PawilanNo ratings yet
- Words and Sentences Analysis of Robert Frost's DesignDocument10 pagesWords and Sentences Analysis of Robert Frost's Designiamream26No ratings yet
- Language Ambiguity in TranslationDocument29 pagesLanguage Ambiguity in TranslationAmmar Mustafa Mahadi AlzeinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Business Communication: Student Slides Business Communication Krizan, Merrier, Logan, & Williams CH 4 - 1Document11 pagesPrinciples of Business Communication: Student Slides Business Communication Krizan, Merrier, Logan, & Williams CH 4 - 1Ajay GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Chapter Ii - Lesson 1 - Understanding The Value of Philippine LiteratureDocument14 pages1 - Chapter Ii - Lesson 1 - Understanding The Value of Philippine LiteratureChristine Joyce Navarro100% (1)