Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Legal Obligations in Business: Dr. Sairam Bhat
Uploaded by
Craypal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views21 pagesThis document provides an overview of various areas of business law including tort law, criminal law, contract law, and consumer protection law. It discusses key principles and cases related to negligence, strict liability, product liability, criminal offenses, contract essentials and defenses, bailment, sale of goods, remedies for breach, and e-contracts. The document is intended as a comprehensive reference on legal obligations and principles relevant to business operations and activities.
Original Description:
LAw-2015
Original Title
PGD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of various areas of business law including tort law, criminal law, contract law, and consumer protection law. It discusses key principles and cases related to negligence, strict liability, product liability, criminal offenses, contract essentials and defenses, bailment, sale of goods, remedies for breach, and e-contracts. The document is intended as a comprehensive reference on legal obligations and principles relevant to business operations and activities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views21 pagesLegal Obligations in Business: Dr. Sairam Bhat
Uploaded by
CraypalThis document provides an overview of various areas of business law including tort law, criminal law, contract law, and consumer protection law. It discusses key principles and cases related to negligence, strict liability, product liability, criminal offenses, contract essentials and defenses, bailment, sale of goods, remedies for breach, and e-contracts. The document is intended as a comprehensive reference on legal obligations and principles relevant to business operations and activities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
Legal Obligations in Business
Dr. Sairam Bhat
Civil Obligations
• Tort Law: ‘ubi jus ubi remedium’
– where there is right there is remedy.
• Types of Tort:
– Defamation, Tresspass, Nuisance, Negligence
Tort Law
• Principles in tort law:
– Product liability: Donoghue v Stevenson
– Privity: Spring Meadows Hospital v S S Aluwalia
– Strict liability [Rylands v Fletcher 1868]
– Bhopal Disaster and Liability of MNC
– Absolute Liability M C Mehta v UOI [1987: J Bhagwati]
– Upahaar Cinema tragedy [Rs.20 crore exemplary
damages]
– BP Oil disaster: Shareholder claiming reckless
negligence on part of the management.
– Vicarious liability:
• Master-Servant: During the course of employment
• Principal-Agent: Within the scope of authority
• Independent contractor
General Defence
– Defamation: Fair criticism/truth
– Tresspass: Licensee/authorized
– Nuisance: Who came first rule: minor
discomfort
– Negligence: Volenti non fit injuria/ Contributor
negligence
– Strict liability: Act of God/third party
Criminal Law
• General Exception
– Under 7 years of age
– Unsound mind: Sec. 84
– Intoxication
• Drunken driving: Salman Khan and Sanjiv Nanda [BMW] case
– Good faith-duty of law
• Extra territorial application of criminal Law: Right of hot pursuit, territorial
waters
• Of Private Defence
• Abetment of offence
• Unlawful assembly
• Giving false evidence
• Offences affecting the human body
– Murder v/s culpable homicide
– Negligently causing death: Sec. 304 IPC
– Causing miscarriage: Right of unborn
– Dowry death
– Attempt to suicide
– Wrongful confinement
– Kidnapping-theft-extortion-robbery
– Criminal tresspass
Criminal procedure and Justice
delivery system
• Adversarial v/s Inquisitorial
• Complaint-FIR-Investigation-Charge sheet-trail-
appeal
• Bailable and non bailable
• Cognizable: can arrest without warrant [more 3
yr imprisonment. generally non bailable as well]
• Sec. 133, 144 Cr. P C
• Juvenile Justice Act 2000: special law
• Plea bargaining
• What is required: Wittness protection and victim
compensation
• Abolition of death penalty? ‘Rarest of rare’ test
Evidence Law
• Proof beyond reasonable doubt
• Selvi v State of Karnataka: Narco analysis,
brain mapping, polygraph test without the
consent of the accused is violation of right
to privacy and inadmissible as evidence.
• Forensic evidence
Contract Law
• Law of obligations
• Essentials of a valid Contract: Offer-Acceptance-
Consideration
• Intention to create Legal Relations: Balfour v Balfour
• Privity of contracts
• Capacity to contract
• Free Consent
• Void agreements: Against public policy
• Government Contracts: M P Sugar Mills case
• Remedies
– Injunction
– Damages [LD]
– Specific performance
International law
• Public International law and Private International
Law
• Hard law or soft law?
• State Responsibility
• Nationality-Refugee-Convention on Diplomatic
immunity-asylum
• United Nations [ICJ] [ICC] v/s WTO [Appellate
Body]-Shrimp turtle case
• International law and ratification in India:
Legislative
• International Law and Judiciary:
Vishaka/Parmanand Khatar
Free Consent
– Coercion
– Economic Duress: Hawker Pacific helicopter case
– Undue influence: Tate v Williamson
– Misrepresentation
– Fraud: Ward v Hobbs
– Spice Girls v Aprilia World Service 2002
– Whether Silence amounts to Fraud: uberrimae fidei
i.e utmost good faith
– Mistake: Phillips v Brooks, Lewis v Avery
Void Agreement
• Against Public Policy
• Forbidden by Law
• Agreements in Restraint of legal proceedings
– Arbitration
• Agreements in Restraint of Marriage
• Restraint of Trade
– Absolute restraint and partial restraint
– Exceptions: Nordenfelt Guns case
– Gujarat Bottling case
– Brojonath Ganguly v State of WB
• Quasi Contract: finder of lost goods: Sec. 71
Bailment and Pledge
• Gratuitous Bailment and Bailment for
reward
• Duty of care
• Pledge: Bailment for a loan advanced
• Pledge an Hypothecation
Indemnity and Guarantee
• Role of Surety: Rule of Subrogation
Principal-Agent Contract
• Agent v/s Independent Contractor
• Types of Agents
– Del credere agent, auctioneer, broker, parnters
– Direct Sale Agent
• Type of Authority
• Personal Liability of an Agent: Respondent
superior
• for example: trademark infringement,
misappropriation of trade secrets, copyright
infringement, unfair competition and antitrust,
and fraudulent misrepresentation
Sale of Goods Act, 1930
• Distinction between Sale and Agreement to Sell
• Definition of Goods: Gannon Dunkerley case
[works contract]
• Transfer of Ownership: risks
• Conditions and warranties
• Caveat emptor ----caveat venditor
• Unpaid seller rights
– Right of lien
– Right to stop goods in transit
– Right of sale
Remedies for Breach
• Anticipatory Breach
• Specific Performance
– Contract of personal service
– When damages are adequate remedy
– When court would have to monitor compliance
• Injunction
– Temporary
– Perpetual
– Mandatory
• Damages
– Nominal
– Liquidated
– Exemplary
Consumer Protection Act, 1986
• Sale of Goods Act, 1930
• Who is a Consumer ? ‘hire’
• Defect in ‘goods’ Deficiency in ‘Services’
• Validity of Liability excluding clause
• Consumer Forums [20 lakh]-State [20 lakh
to 1 crore] and National Commission
• Ex: Coke contamination controversy
Product Liability
• The Foods Adulteration Act, 1954
• The Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006
• The Drug & Cosmetics Act, 1940
• The Indian Penal Code, 1860
• The Standards of Weights and Measures Act, 1956
• The Agricultural Produce (Grading and Marking) Act, 1937 for marking and
grading of commodities like vegetables, butter, etc.
• The Indian Standards Institution (Certification Marks) Act , 1952 to formulate
a number of standards for different products by ISI
• The Bureau of Indian Standards Act , 1986
• All the above laws have civil as well as criminal liability
• Smt. Uma Deepak v. Maruti Udyog Ltd Ors (2003) CPJ 90(MRTP) the
Complainant alleged that the car sold by the opposite party was not only
accidental but the price, for the same, was also overcharged. The Court, in
response to the allegations made by the complainant, directed arrest of the
Directors as well as the manager of the dealers/agents who sold the said
defective car to the complainant and remanded them to judicial custody.
Subsequent thereto, the said officers of the opposite party were released on
bail and were directed to replace the disputed car with a new car.
Product Liability: New initiatives
• ISO standards for processes and Products
• Extend Producers Responsibility: Right to
recall a product
E-Contract
• IT Act 2000: Sec. 11-13
• Shrink warp: ProCD Inc. v. Zeidenberg
• Click warp
• Avinash Bajaj case 2002
• TCS v State of AP
• P R Transport Agency v UOI -2005: Where
contract is concluded
• Unresolved issue: California Software Inc v
Reliability Research Inc
New forms of Contracts
• PPP
• JV Agreements
• IPR Licensing
You might also like
- Legal Obligations in BusinessDocument18 pagesLegal Obligations in BusinessVinay KalalNo ratings yet
- Difference between Law of Torts and ContractDocument9 pagesDifference between Law of Torts and Contractanon_50486533No ratings yet
- Torts Modules CompiledDocument191 pagesTorts Modules CompiledAryan DashNo ratings yet
- BL PreliminaryDocument19 pagesBL PreliminaryMohammad ShahwazNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 JurisprudenceDocument33 pagesUnit 6 JurisprudenceRahulNo ratings yet
- @CPC IntroductionDocument20 pages@CPC Introductionsheetal rajputNo ratings yet
- BL Notes - DigitalDocument32 pagesBL Notes - DigitalRaaj Nishanth SNo ratings yet
- Law of TortDocument61 pagesLaw of TortNikhilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Legal Environment of BusinessDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Legal Environment of BusinessAnkita SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Labor Laws, Contracts, Torts and Consumer ProtectionDocument7 pagesLabor Laws, Contracts, Torts and Consumer ProtectionLFC FanNo ratings yet
- Law LLM Coqp14Document15 pagesLaw LLM Coqp14Aryan ksNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Contract LawDocument8 pagesEssential Elements of Contract LawshwetagurnaniNo ratings yet
- LAB 6 - Consumer LawDocument28 pagesLAB 6 - Consumer Lawelizabeth shrutiNo ratings yet
- Torts Law ExplainedDocument35 pagesTorts Law ExplainedRishabh Nayyar100% (1)
- Introduction To LawsDocument37 pagesIntroduction To LawsChristine Joy LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 15Document36 pagesSyllabus 15Rajesh KatareNo ratings yet
- LLB First Sem Syllabus WordDocument58 pagesLLB First Sem Syllabus WordShyamsundar PatilNo ratings yet
- Legal Maxims 1 - 10Document45 pagesLegal Maxims 1 - 10Shalu MandiyaNo ratings yet
- Contract LawDocument86 pagesContract LawAman SaxenaNo ratings yet
- C05 (Autosaved)Document59 pagesC05 (Autosaved)Mir Fida NadeemNo ratings yet
- Business Law and Corporate LawDocument123 pagesBusiness Law and Corporate LawSYED ALIZARNo ratings yet
- Business Law 2023Document278 pagesBusiness Law 2023Midhul MineeshNo ratings yet
- 1075 - Unit - I - Law of Tort BALLB III SEMDocument49 pages1075 - Unit - I - Law of Tort BALLB III SEMpravin awalkondeNo ratings yet
- Ahmchapter 07Document27 pagesAhmchapter 07api-209542414No ratings yet
- Business & Corporate Law: An IntroductionDocument42 pagesBusiness & Corporate Law: An Introductioninaya khanNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Civil LawDocument14 pagesWeek 10 - Civil LawBerke NarNo ratings yet
- Unit II - BL-1Document51 pagesUnit II - BL-1sneha002503No ratings yet
- Business Law Chapter 1-12 SummaryDocument3 pagesBusiness Law Chapter 1-12 Summaryapi-336313643No ratings yet
- Limitations to Freedom of Contract: Types of Agreements and Legality of ObjectDocument55 pagesLimitations to Freedom of Contract: Types of Agreements and Legality of ObjectAadhitya NarayananNo ratings yet
- RemediesDocument17 pagesRemediesSunil beniwalNo ratings yet
- 2.1personal Capacity and Vicarious LiabilityDocument44 pages2.1personal Capacity and Vicarious LiabilityAnshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Law of Torts 1 Lecture NotesDocument78 pagesLaw of Torts 1 Lecture Notesmarie100% (3)
- SyllabusDocument17 pagesSyllabuskomalNo ratings yet
- 1 A Indian Contract Act 1872Document36 pages1 A Indian Contract Act 1872Ayesha GuptaNo ratings yet
- CLRA For IICM HR ExecutivesDocument34 pagesCLRA For IICM HR ExecutivesKaushik ChopraNo ratings yet
- EcelawsDocument21 pagesEcelawsShiela Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Divisions of LawDocument16 pagesDivisions of LawSakshi JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Law Is Difficult To Arrive At. The Term Law IsDocument14 pagesLaw Is Difficult To Arrive At. The Term Law IssurbhiscribdNo ratings yet
- MI - UNIT 2 Law, Contracts, CompensationDocument30 pagesMI - UNIT 2 Law, Contracts, CompensationjNo ratings yet
- Delict B 3rd TermDocument52 pagesDelict B 3rd TermAllan Sabz NcubeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Auditor's Legal LiabilityDocument16 pagesChapter 4 - Auditor's Legal LiabilityViolla OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Tort and CrimeDocument43 pagesTort and CrimeMEDICAL FEILDNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title: Your Company InformationDocument53 pagesPresentation Title: Your Company InformationRap HaelNo ratings yet
- Notes On Business LawDocument27 pagesNotes On Business LawSharrme ChandranNo ratings yet
- Roles of Men and Necessity of Law in SocietyDocument40 pagesRoles of Men and Necessity of Law in Societydeepika vettikuntlaNo ratings yet
- LLM SYLLABUS ENTRANCE-mergedDocument22 pagesLLM SYLLABUS ENTRANCE-mergedShivam MishraNo ratings yet
- Reva - PPT Template B LDocument57 pagesReva - PPT Template B LPurushottam KumarNo ratings yet
- HSE Background and Law - Unit 1 Session 1Document27 pagesHSE Background and Law - Unit 1 Session 1Parashuram PatilNo ratings yet
- LAB Semester 1Document77 pagesLAB Semester 1Shubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Elements of Torts ExplainedDocument28 pagesElements of Torts ExplainedServer OneNo ratings yet
- Duties of An AdvocateDocument129 pagesDuties of An AdvocatemasaabatNo ratings yet
- Law of Torts Unit IDocument32 pagesLaw of Torts Unit ISana RiyasNo ratings yet
- Legal Language Concepts, Legis & Juris MaterialDocument9 pagesLegal Language Concepts, Legis & Juris MaterialRoshniNo ratings yet
- The Self-Help Guide to the Law: Contracts, Landlord-Tenant Relations, Marriage, Divorce, Personal Injury, Negligence, Constitutional Rights and Criminal Law for Non-Law: Guide for Non-Lawyers, #3From EverandThe Self-Help Guide to the Law: Contracts, Landlord-Tenant Relations, Marriage, Divorce, Personal Injury, Negligence, Constitutional Rights and Criminal Law for Non-Law: Guide for Non-Lawyers, #3No ratings yet
- The Self-Help Guide to the Law: Contracts and Sales Agreements for Non-Lawyers: Guide for Non-Lawyers, #5From EverandThe Self-Help Guide to the Law: Contracts and Sales Agreements for Non-Lawyers: Guide for Non-Lawyers, #5No ratings yet
- Consumer Protection in India: A brief Guide on the Subject along with the Specimen form of a ComplaintFrom EverandConsumer Protection in India: A brief Guide on the Subject along with the Specimen form of a ComplaintNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Law and Legal System: N.L.S I.UDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Law and Legal System: N.L.S I.UCraypalNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course (2) Jan15 2Document15 pagesBridge Course (2) Jan15 2CraypalNo ratings yet
- NFHS-3 India 2005-06 Contract Law Offer AcceptanceDocument9 pagesNFHS-3 India 2005-06 Contract Law Offer AcceptanceCraypalNo ratings yet
- PGD CP P1 Oct14 - 2 PDFDocument2 pagesPGD CP P1 Oct14 - 2 PDFCraypalNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course (1) Jan15 - 2 PDFDocument11 pagesBridge Course (1) Jan15 - 2 PDFCraypalNo ratings yet
- Indian Legal System OverviewDocument4 pagesIndian Legal System OverviewCraypalNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course (1) Jan15 - 2 PDFDocument11 pagesBridge Course (1) Jan15 - 2 PDFCraypalNo ratings yet
- XAPAX SecurityDocument212 pagesXAPAX SecurityCraypalNo ratings yet
- XAPAX SecurityDocument212 pagesXAPAX SecurityCraypalNo ratings yet
- OSCPNotesDocument1 pageOSCPNotesCraypalNo ratings yet
- Bank Guarantee FormatDocument4 pagesBank Guarantee FormatYogesh Bajaj100% (1)
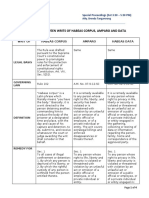
- Distinguishing Habeas Corpus, Amparo, and Habeas Data WritsDocument4 pagesDistinguishing Habeas Corpus, Amparo, and Habeas Data WritsPring SumNo ratings yet
- IPHR Exam 2018 ABDocument3 pagesIPHR Exam 2018 ABNabeel AnwerNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Guaring Vs CA (1997)Document5 pagesHeirs of Guaring Vs CA (1997)Jon JamoraNo ratings yet
- Sample questions on obligations and contractsDocument16 pagesSample questions on obligations and contractsDante Jr. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Copyright Transfer Nursing JournalDocument1 pageCopyright Transfer Nursing JournalMoh heri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Respondents' Joint Counter-Affidavit ReplyDocument10 pagesRespondents' Joint Counter-Affidavit ReplyMarianoFloresNo ratings yet
- 4case Digest Tanguilig Vs Court of Appeals GR No 117190Document2 pages4case Digest Tanguilig Vs Court of Appeals GR No 117190James ScoldNo ratings yet
- Natangwe I Ngatjizeko and The StateDocument12 pagesNatangwe I Ngatjizeko and The StateAndré Le RouxNo ratings yet
- Rosicki Opposition To Motion To DismissDocument44 pagesRosicki Opposition To Motion To DismissDinSFLA100% (1)
- Sheker vs. Estate of Alice O. Sheker PDFDocument15 pagesSheker vs. Estate of Alice O. Sheker PDFMark BNo ratings yet
- The Oecd Principles of Corporate GovernanceDocument8 pagesThe Oecd Principles of Corporate GovernanceNazifaNo ratings yet
- Crimlaw 1 Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesCrimlaw 1 Midterm ExamAyi AbeloNo ratings yet
- Revised rules on evidenceDocument17 pagesRevised rules on evidenceMaria VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Capitol Insurance V Del Monte MotorsDocument2 pagesCapitol Insurance V Del Monte MotorsMark Evan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Layman'sDocument1 pageLayman'sdurablebradNo ratings yet
- Under The Guidence Of: Mrs. Akansha Gupta: Speaking Orders or Reasoned DecisionsDocument8 pagesUnder The Guidence Of: Mrs. Akansha Gupta: Speaking Orders or Reasoned DecisionsRobin Singh100% (1)
- Wildlife Protection ActDocument10 pagesWildlife Protection ActGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Reorganizing Barangay Emergency TeamDocument2 pagesReorganizing Barangay Emergency TeamCA T He96% (24)
- Consumer Protection Act 1986Document10 pagesConsumer Protection Act 1986Anoop DwarakaNo ratings yet
- Bernina Distributors, Inc. v. Bernina Sewing MacHine Co., Inc., 689 F.2d 903, 10th Cir. (1981)Document2 pagesBernina Distributors, Inc. v. Bernina Sewing MacHine Co., Inc., 689 F.2d 903, 10th Cir. (1981)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Art. 946-959Document7 pagesArt. 946-959ChaNo ratings yet
- Rough Draft of Law of TortsDocument5 pagesRough Draft of Law of TortsSundram GauravNo ratings yet
- Sample Brief For Appellant-RapeDocument11 pagesSample Brief For Appellant-RapeAngelNavalle100% (2)
- George Mercier Introduces Invisible ContractsDocument136 pagesGeorge Mercier Introduces Invisible ContractsregalNo ratings yet
- 2012 Capital Crimes Annual ReportDocument357 pages2012 Capital Crimes Annual ReportMike DeWineNo ratings yet
- Acebedo Optical Company vs. CADocument3 pagesAcebedo Optical Company vs. CAElyn ApiadoNo ratings yet
- 07-16226 MERS OpinionDocument15 pages07-16226 MERS Opinionindio007No ratings yet
- Lammers Charges Filed 7/30/09Document1 pageLammers Charges Filed 7/30/09thereadingshelfNo ratings yet
- Mituniewicz v. Clark - Document No. 5Document2 pagesMituniewicz v. Clark - Document No. 5Justia.comNo ratings yet