Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Botanical Terms Etymological Meaning: +sperma (Seed)
Uploaded by
Katrina Mendiola0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesbotany
Original Title
Botanical Terms
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbotany
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesBotanical Terms Etymological Meaning: +sperma (Seed)
Uploaded by
Katrina Mendiolabotany
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
BOTANICAL TERMS ETYMOLOGICAL MEANING DEFINITION
1 Agamospermy agamos(unmarried)+ sperma(seed) Asexual reproduction methods
involving cells of only the ovule
to yield seeds and fruit
2 Angiosperm angeion(“case” or “casing”) Plants with seeds enclosed in
+sperma(seed) ovaries that mature into a fruit
3 Anthocyanin anthos(flower) Water soluble pigment located
the cell sap, which varies from
+ red to blue in color. Found in
flowers of most plants.
kuanos(blue)
4 Archegonium arkhe(chief) Female reproductive organ in
non-vascular plants like ferns
+ and mosses.
gonos(race)
5 Coenocytic koinós(“common”) Large cells containing myriad
nuclei. It is formed when the ce
+ nucleus divides multiple times
without the actual division of the
kýtos(box) cell
6 Collenchyma kolla(glue) Cells containing primary walls
thickened at the cells corners,
+ but thin elsewhere
enkhuma(infusion)
7 Dikaryotic di(two) Presence of two nuclei in a cell
+
karyon(nut)
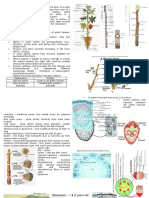
8 Endodermis endo(within) Single layer of specialized
parenchyma cells surrounding
+ the vascular tissues in the roots
and stems. It forms the inner
dermid(skin)
boundary of the cortex.
9 Gymnosperm gymnos(naked) Type of plants in which the
seeds are not enclosed in the
+ ovary during the development.
sperma(seed)
10 Hypha Huphe- (web) Threadlike like tubular
filaments found in fungi.
11 Internode Inter(between) Region between two nodes
+
Nodus(knot)
12 Isogamy Iso(equal) Sexual reproduction taking
+ place between gametes that
Gamos(marriage) are similar in size. Seen in
certain fungi and algae.
13 Jungle jāṅgala(rough and arid A dense growth of various
(terrain)) plants where many organism
can thrive. Forest is another
term used for a jungle.
14 Laticifer Latex, Latic(fluid) Specialized ducts or cells
+ that bear resemblance to
vessels. These form a
Fer(bearing) network of cells in the
phloem and other plant parts
that secrete latex.
15 Legume Legere (to pick)(L) > (L)legumen Dried fruits comprising seeds
>le^gume(French) adhering to their edges
which split along two seams
16 Lenticel lens, lent- ‘lentil’. Spongy cluster of cells
located in the bark of woody
plants, which allow gas
exchange between the
external atmosphere and
interior of a plant.
20 Lignin Ligni (of wood) Type of polymer
impregnating some cell
walls, like those of wood.
21 Lumen Lumen(light) Inner portion of cell
structures such as vacuole,
vesicle, resin duct or oil
chamber.
22 Megaphyll Mega(big) Present in all seed plants
+ and ferns. It is a leaf that has
Phyll(leaf) evolved from a branch
system and is characterized
by branching veins.
23 Mesocarp Mesos(middle) Central portion of the fruit
+ wall, which is sandwiched
Karpos(fruit) between the outer exocarp
and inner endocarp.
Monos(single) + oikos (house) Plants which
Monoecious
possess both
unisexual male and
female flowers or
cones on the same
plant.
Node Nodus(knot) Point of attachment
of the leaves
You might also like
- 13D-13.2 Tissues Systems in Plants Flow Chart SummaryDocument1 page13D-13.2 Tissues Systems in Plants Flow Chart SummaryAvena SinghNo ratings yet
- Sugar Glider Booklet 1Document18 pagesSugar Glider Booklet 1api-277965625No ratings yet
- BLW Graphic 100 FoodsDocument3 pagesBLW Graphic 100 FoodsTwoshanNo ratings yet
- Footprints Pupils Book 2 Unit 8Document8 pagesFootprints Pupils Book 2 Unit 8rotuc100% (2)
- OTR Shipper List UnusedDocument287 pagesOTR Shipper List Unusedscott.maison100% (1)
- Soft Food DietDocument4 pagesSoft Food DietPrathibha LankipalliNo ratings yet
- SMK Gajah Berang, Melaka: Sulit Science Paper 1 1 HourDocument11 pagesSMK Gajah Berang, Melaka: Sulit Science Paper 1 1 HourYanti FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissue OwnDocument43 pagesPlant and Animal Tissue Ownapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Tle DLLDocument6 pagesTle DLLAljo Palma CatedralNo ratings yet
- Botany Module 2.1Document11 pagesBotany Module 2.1Yaz VergaraNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell - Student'sDocument40 pagesPlant Cell - Student'sKayraine Mae Edillor CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues and Organs Plant Tissues: Tracheary Elements Tracheids TracheidsDocument2 pagesPlant Tissues and Organs Plant Tissues: Tracheary Elements Tracheids TracheidsNathaniel John AlcoranNo ratings yet
- Botlec The Stems 4Document10 pagesBotlec The Stems 4Jeff MarianoNo ratings yet
- Simple Permanent Tissues Three Major Types of Root SystemDocument4 pagesSimple Permanent Tissues Three Major Types of Root SystemAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- TISSUES (Prashant Kirad)Document9 pagesTISSUES (Prashant Kirad)abhijotsinghas83No ratings yet
- Core CH 19 BiodiversityDocument8 pagesCore CH 19 Biodiversitystudy.stkgNo ratings yet
- General Biology, Lesson 2.3Document43 pagesGeneral Biology, Lesson 2.3sansytheskeleton298No ratings yet
- Exercise No. 17Document9 pagesExercise No. 17Francis Jay MerencilloNo ratings yet
- 1 Botlec ReviewerDocument7 pages1 Botlec ReviewerKamille PobleteNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues Lateral Meristems Increase The Girth orDocument3 pagesPlant Tissues Lateral Meristems Increase The Girth orWennie Fe MartinezNo ratings yet
- Name: Michael A. Galiza Year & Section: BAT 3 - A: Crops Mode of Reproduction Seeds StructureDocument7 pagesName: Michael A. Galiza Year & Section: BAT 3 - A: Crops Mode of Reproduction Seeds StructureRONALD CRISTOBALNo ratings yet
- Meristematic Tissue: Cell Modifications and Specialization I. Plant Cells and TissuesDocument6 pagesMeristematic Tissue: Cell Modifications and Specialization I. Plant Cells and TissuesBigsmile PhotoboothNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 09 Feb 2024Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 09 Feb 2024shradhasharma2101No ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 05. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesII ME NRP B SS 05. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 Module 3 4 PDFDocument101 pagesBio 1 Module 3 4 PDFJoyvy KidoNo ratings yet
- 31 Biology 3-11-08 5a8c13a Plants 1Document38 pages31 Biology 3-11-08 5a8c13a Plants 1Via SiregarNo ratings yet
- Land Ho: Plants and Arthropods!Document58 pagesLand Ho: Plants and Arthropods!BarbNo ratings yet
- Biology Tissue Notes of Class 9thDocument12 pagesBiology Tissue Notes of Class 9thrishabhraj.adzNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument5 pagesPlant TissueClarenz100% (1)
- Types of Plant CellsDocument26 pagesTypes of Plant CellsJustin BiboNo ratings yet
- Biology Systems in Plants 3Document6 pagesBiology Systems in Plants 3Alyana Grace GuquibNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document13 pagesModule 4krlndrw26No ratings yet
- Work Sheet TutorDocument4 pagesWork Sheet TutorNuni Rismayanti NurQalbiNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Anatomy of Flowering Plants NotesDocument8 pagesClass 11 Anatomy of Flowering Plants NotesPriyansh PatelNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functiond of PlantsDocument5 pagesParts and Functiond of PlantsCjoy MañiboNo ratings yet
- Transport Water and SolutesDocument4 pagesTransport Water and SolutesAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Kebo 106Document8 pagesKebo 106Mohamed Fayaz Sheik DawoodNo ratings yet
- Notes Plant TissuesDocument7 pagesNotes Plant TissuesHariprasanthNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument17 pagesBotanyAbdelrhman AmrNo ratings yet
- Roots: Allium (Onion) Root Tip L.S (Mono)Document11 pagesRoots: Allium (Onion) Root Tip L.S (Mono)reeNo ratings yet
- Ground TissuesDocument17 pagesGround TissuesHelen Gail EmbudoNo ratings yet
- Botany Notes PDFDocument21 pagesBotany Notes PDFKrizel LagundiNo ratings yet
- Tissue 9 PDFDocument5 pagesTissue 9 PDFNilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- Plant Form and Function: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityDocument66 pagesPlant Form and Function: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityThu AnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDwight Luciano T MendezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cellular Reproduction and Plant TissuesDocument38 pagesLecture 3 - Cellular Reproduction and Plant TissuesJohn Zephyr TyskaNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology Chapter 4 and 5 QADocument6 pages11th Biology Chapter 4 and 5 QADushyantNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document6 pagesModule 5myshachaudhuri75No ratings yet
- CH - 2 - Reproduction in Flowering Plants - L-1Document23 pagesCH - 2 - Reproduction in Flowering Plants - L-1yashNo ratings yet
- Main Functions of Roots:: and Produces Branch Roots Called Lateral RootsDocument4 pagesMain Functions of Roots:: and Produces Branch Roots Called Lateral RootsAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter MeristemsDocument5 pagesChapter Meristemsyoura4203No ratings yet
- Differences Between Ground Tissue ParenchymaDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Ground Tissue Parenchymanurul taqinah ismailNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Work Sheet KeyDocument10 pagesAnatomy Work Sheet KeysriNo ratings yet
- 1696 FdoDocument6 pages1696 FdoNhlanhla HlátzNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Plant Reproduction and Development 1Document51 pagesLESSON 1 - Plant Reproduction and Development 1ejayxxrizzNo ratings yet
- 1 Biology CD Solutions-M2Document10 pages1 Biology CD Solutions-M2raseemsha2No ratings yet
- 2.3 Plant Cells and TissueDocument5 pages2.3 Plant Cells and TissueMumtaz BarhiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesChapter - 6 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsPriyansh PatelNo ratings yet
- Notes 9 Tissues New 2021Document9 pagesNotes 9 Tissues New 2021Arjun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 Organismal Body of PlantsDocument20 pagesLesson1 Organismal Body of PlantsKyle MantoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Advance Biology 4th QuarterDocument6 pagesReviewer in Advance Biology 4th QuarterTherese CuetoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument13 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantsaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Cbse Chapter-6 Plant TissuesDocument16 pagesGrade-9 Cbse Chapter-6 Plant Tissuesniranjana75% (4)
- Tissues: ClassDocument4 pagesTissues: ClassShail KumariNo ratings yet
- Word Problems + 10Document2 pagesWord Problems + 10jacwollongongNo ratings yet
- CoombeDocument7 pagesCoombemedpsplitNo ratings yet
- RelianceDocument19 pagesRelianceAanchal Vijh50% (2)
- CollegeCore Aptitude Test 2020Document22 pagesCollegeCore Aptitude Test 2020sahana duaNo ratings yet
- Mango VarietiesDocument2 pagesMango VarietiesMech LearningNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Grade 5Document10 pagesChapter 1 Grade 5Rawsht SdiqNo ratings yet
- National Horticulture Board: Year 2009-10Document231 pagesNational Horticulture Board: Year 2009-10Vipasha SanghaviNo ratings yet
- YarrowayFarm SowingCalendarDocument3 pagesYarrowayFarm SowingCalendarYasir MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Food Grocery List PDFDocument1 pageDiabetic Food Grocery List PDFdee.aira2955No ratings yet
- Book SG L1 Answers PDFDocument18 pagesBook SG L1 Answers PDFKadir ErgenNo ratings yet
- My Living World 3 - 2015Document20 pagesMy Living World 3 - 2015Nafisa AhmadNo ratings yet
- FDI Mapping With NIC CodeDocument53 pagesFDI Mapping With NIC CodeRajeev BhambriNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade Iii ScienceDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade Iii ScienceEvita Esguerra100% (2)
- English Book Level 1+2Document50 pagesEnglish Book Level 1+2Surya AcuyNo ratings yet
- Food Always in The Home (FAITH)Document36 pagesFood Always in The Home (FAITH)Judith T. AgpalzaNo ratings yet
- 15 Foods To Stop RefrigeratingDocument8 pages15 Foods To Stop RefrigeratingnaginatNo ratings yet
- Biji Dan Buah (Seeds and Fruit)Document27 pagesBiji Dan Buah (Seeds and Fruit)Syarif Hidayat AmrullahNo ratings yet
- KAU Avail - Plant MetDocument6 pagesKAU Avail - Plant MethusainppNo ratings yet
- Xamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument31 pagesXamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsShireen SuhailNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Fruits and Vegetables in UAE Market NewDocument51 pagesDistribution of Fruits and Vegetables in UAE Market NewASHITA ANN STEPHEN MBA19-21No ratings yet
- PlantsDocument44 pagesPlantsSanjeev ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningDocument11 pagesCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningMerce Tojino ManigosNo ratings yet
- T T 22915 British Food Fortnight Powerpoint Ver 3Document27 pagesT T 22915 British Food Fortnight Powerpoint Ver 3Mohamed ElhelalyNo ratings yet