Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Financial Systems
Uploaded by
Shipra Baxi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views2 pagesThe document provides an introduction to financial systems and the Indian financial system. It states that a financial system comprises financial institutions, markets, instruments, and services that help mobilize savings and allocate them to productive investments, fueling economic growth. It describes how the Indian financial system transformed after 1991 with the introduction of new economic policies, reducing the government's role in business and allowing private players to enter various sectors like banking, insurance, and mutual funds. Key developments included the privatization of institutions like IFCI, and the reorganization of the institutional structure to shift focus from development finance institutions to capital markets. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was given powers to regulate financial markets and protect investors.
Original Description:
Original Title
Introduction to Financial Systems
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an introduction to financial systems and the Indian financial system. It states that a financial system comprises financial institutions, markets, instruments, and services that help mobilize savings and allocate them to productive investments, fueling economic growth. It describes how the Indian financial system transformed after 1991 with the introduction of new economic policies, reducing the government's role in business and allowing private players to enter various sectors like banking, insurance, and mutual funds. Key developments included the privatization of institutions like IFCI, and the reorganization of the institutional structure to shift focus from development finance institutions to capital markets. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was given powers to regulate financial markets and protect investors.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views2 pagesIntroduction To Financial Systems
Uploaded by
Shipra BaxiThe document provides an introduction to financial systems and the Indian financial system. It states that a financial system comprises financial institutions, markets, instruments, and services that help mobilize savings and allocate them to productive investments, fueling economic growth. It describes how the Indian financial system transformed after 1991 with the introduction of new economic policies, reducing the government's role in business and allowing private players to enter various sectors like banking, insurance, and mutual funds. Key developments included the privatization of institutions like IFCI, and the reorganization of the institutional structure to shift focus from development finance institutions to capital markets. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was given powers to regulate financial markets and protect investors.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
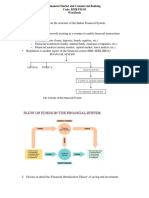
INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL SYSTEMS
Economic growth and development of any country depends upon a well-knit
financial system. Financial system comprises, a set of sub-systems of financial
institutions financial markets, financial instruments and services which help in the
formation of capital. Thus a financial system provides a mechanism by which
savings are transformed into investments and it can be said that financial system
play an significant role in economic growth of the country by mobilizing surplus
funds and utilizing them effectively for productive purpose.
The financial system is characterized by the presence of integrated, organized
and regulated financial markets, and institutions that meet the short term and
long term financial needs of both the household and corporate sector. Both
financial markets and financial institutions play an important role in the financial
system by rendering various financial services to the community. They operate in
close combination with each other.
INTRODUCTION TO INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM
The organizations of Indian Financial system witnessed transformation
after launching of new economic policy 1991. The development process
shifted from controlled economy to free market for these changes were
made in the economic policy. The role of government in business was
reduced the measure trust of the government should be on development
of infrastructure, public welfare and equity. The capital market an
important role in allocation of resources. The major development during
this phase are:-
1. Privatisation of Financial Institutions –
At this time many institutions were converted in to public company and
number of private players were allowed to enter in to various sectors:
a) Industrial Finance Corporation on India (IFCI): The pioneer
development finance institution was converted in to a public
company.
b) Industrial Development Bank of India & Industrial Finance
Corporation of India (IDBI & IFCI): IDBI & IFCI ltd offers their
equity capital to private investors.
c) Private Mutual Funds have been set up under the guidelines
prescribed by SEBI.
d) Number of private banks and foreign banks came up under the RBI
guidelines. Private institution companies emerged and work under
the guidelines of IRDA, 1999.
e) In this manner government monopoly over financial institutions
has been dismantled in phased manner. IT was done by converting
public financial institutions in joint stock companies and permitting
to sell equity capital to the government.
2. Reorganization of Institutional Structure –
The importance of development financial institutions decline with shift to
capital market for raising finance commercial banks were give more
funds to investment in capital market for this. SLR and CRR were
produced; SLR earlier @ 38.5% was reduced to 25% and CRR which
used to be 25% is at present 5%. Permission was also given to banks to
directly undertake leasing, hire-purchase and factoring business. There
was trust on development of primary market, secondary market and
money market.
3. Investors Protection –
SEBI is given power to regulate financial markets and the various
intermediaries in the financial markets.
You might also like
- Indian Financial SystemDocument106 pagesIndian Financial SystemKajal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System From 1950 To 1980 - : Shah Classes IFSDocument18 pagesIndian Financial System From 1950 To 1980 - : Shah Classes IFSNayan MaldeNo ratings yet
- Introduction:-: Financial Service Refer To Services Provided by The Finance Industry. The Finance IndustryDocument63 pagesIntroduction:-: Financial Service Refer To Services Provided by The Finance Industry. The Finance Industrypriyasen2433No ratings yet
- Fis-Balaji Mba College - KadapaDocument97 pagesFis-Balaji Mba College - KadapaBhuvana AnalapudiNo ratings yet
- Indian Capital MarketsDocument20 pagesIndian Capital MarketsHarshaNo ratings yet
- Mba Anna University PPT Material For MBFS 2012Document39 pagesMba Anna University PPT Material For MBFS 2012mail2nsathish67% (3)
- SBAA3010Document201 pagesSBAA3010Tushar PaygudeNo ratings yet
- Ma 0027Document17 pagesMa 0027sathishNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Indian Financial System Since 1991Document8 pagesChanges in The Indian Financial System Since 1991Samyra RathoreNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking and Financial Services Question PaperDocument248 pagesMerchant Banking and Financial Services Question Paperexecutivesenthilkumar100% (1)
- Unit 1Document83 pagesUnit 1Bothuka ShoheNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Indian Financial System: A Critical Review: Saraswathi Chandrashekhar DR Yogesh MaheshwariDocument12 pagesEvolution of Indian Financial System: A Critical Review: Saraswathi Chandrashekhar DR Yogesh Maheshwarividhyashekar93No ratings yet
- Introduction To FinanceDocument68 pagesIntroduction To FinancejohnnybondNo ratings yet
- Workbook FMCBDocument20 pagesWorkbook FMCBPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- Financial Sector Reforms in IndiaDocument14 pagesFinancial Sector Reforms in IndiaRimple Abhishek Delisha ViraajvirNo ratings yet
- FMO Module 1.........Document16 pagesFMO Module 1.........Sonia Dann KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Pre and Post Reforms in Indian Financial SystemDocument16 pagesPre and Post Reforms in Indian Financial SystemsunilNo ratings yet
- Fiancial Institutions Markets and Services Merged Merged Merged CompressedDocument97 pagesFiancial Institutions Markets and Services Merged Merged Merged Compressednitishtitu143No ratings yet
- Policy Measures and Initiatives: Capital Market ReformsDocument7 pagesPolicy Measures and Initiatives: Capital Market ReformsAshish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fis-1,2 - Units-1Document39 pagesFis-1,2 - Units-1SAI SUDHEER BARUNo ratings yet
- Non Banking Financial CompanyDocument39 pagesNon Banking Financial Companymanoj phadtareNo ratings yet
- $$ Final Indian Finanacial System 2$Document112 pages$$ Final Indian Finanacial System 2$Kumaran VelNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Financial System - 86385Document20 pagesEvolution of Financial System - 86385guptadev.1912No ratings yet
- Overview of IFSDocument21 pagesOverview of IFSMaiyakabetaNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument4 pagesIndian Financial SystemLbsim-akash100% (2)
- What Is The Role of The Financial System in Economic DevelopmentDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Role of The Financial System in Economic DevelopmentBasappaSarkarNo ratings yet
- Updates On JAIIB/CAIIB Papers Note:: Module ADocument15 pagesUpdates On JAIIB/CAIIB Papers Note:: Module ARamasundaram TNo ratings yet
- Role and Importance of Capital Market in IndiaDocument9 pagesRole and Importance of Capital Market in IndiaMukul Babbar50% (4)
- CPTL MKT ReformsDocument51 pagesCPTL MKT ReformsjustingosocialNo ratings yet
- Unit V FMDocument35 pagesUnit V FMHR HMA TECHNo ratings yet
- Correction ProDocument42 pagesCorrection ProJyothi RameshNo ratings yet
- Non-Banking Financial CompaniesDocument36 pagesNon-Banking Financial CompaniessarvaianNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument30 pagesBasic Conceptsjoslin12100% (1)
- Financial System in IndiaDocument53 pagesFinancial System in IndiaCharu SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Recent Trend of Financial ManagementDocument17 pagesRecent Trend of Financial ManagementShahbazHasanNo ratings yet
- Industrial FinanceDocument9 pagesIndustrial FinancelovleshrubyNo ratings yet
- Exm - 26842 Financial ManagementDocument20 pagesExm - 26842 Financial ManagementAbdul AshrafNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System Project 3sem (Priyank)Document35 pagesIndian Financial System Project 3sem (Priyank)priyank chourasiyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Indian Financial SystemDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Indian Financial SystemMohd asimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FinanceDocument69 pagesIntroduction To FinancejohnnybondNo ratings yet
- Vision 2020 For India The Financial Sector: Planning CommissionDocument22 pagesVision 2020 For India The Financial Sector: Planning Commissionarpitasharma_301No ratings yet
- A Critical Analysis of SebiDocument15 pagesA Critical Analysis of SebiVelivelli Naga Venkata Chandra sekhar 20BBA7031No ratings yet
- Financial Services Unit-1Document24 pagesFinancial Services Unit-1Feeroj PathanNo ratings yet
- Stock Market Modern Is at IonDocument9 pagesStock Market Modern Is at IonKulraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionDocument31 pagesFinancial InstitutionManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Fim Unit 1Document10 pagesFim Unit 1gadiyasiddhi0No ratings yet
- Indian Financial System - An OverviewDocument33 pagesIndian Financial System - An OverviewShilpiVaishkiyar0% (1)
- Dessertation Report On NBFCDocument65 pagesDessertation Report On NBFCHarsh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Role of Financialmarkets in The Economy: Features of Financial SystemDocument18 pagesUnit 1 The Role of Financialmarkets in The Economy: Features of Financial Systemsudhir.kochhar3530No ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument13 pagesIndian Financial SystemkajalNo ratings yet
- From-Nikunjkumar Sanghavi ROLL NO.140 Sybba C'Document18 pagesFrom-Nikunjkumar Sanghavi ROLL NO.140 Sybba C'Nik SanghviNo ratings yet
- JETIR1908831Document5 pagesJETIR1908831abhipt441No ratings yet
- Introduction To Indian Financial SystemDocument259 pagesIntroduction To Indian Financial SystemTera BoxNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector in IndiaDocument99 pagesBanking Sector in IndiaRajesh SaharanNo ratings yet
- T R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)From EverandT R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)No ratings yet
- Emerging Issues in Finance Sector Inclusion, Deepening, and Development in the People's Republic of ChinaFrom EverandEmerging Issues in Finance Sector Inclusion, Deepening, and Development in the People's Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingFrom EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNo ratings yet
- Securitization in India: Managing Capital Constraints and Creating Liquidity to Fund Infrastructure AssetsFrom EverandSecuritization in India: Managing Capital Constraints and Creating Liquidity to Fund Infrastructure AssetsNo ratings yet
- A Random Walk Down Wall Street Malkiel en 2834Document5 pagesA Random Walk Down Wall Street Malkiel en 2834Min Park100% (6)
- Heikin-Ashi Algorithms OptimizeDocument6 pagesHeikin-Ashi Algorithms Optimizerenger20150303No ratings yet
- Final Exam - Example 4Document12 pagesFinal Exam - Example 4萧霄No ratings yet
- Candlestick Charting and Technical Analysis (PDFDrive)Document39 pagesCandlestick Charting and Technical Analysis (PDFDrive)Rathod arvinNo ratings yet
- Investment Law Power PointDocument82 pagesInvestment Law Power PointMulugeta AkaluNo ratings yet
- Stock Trading Project GuidelinesDocument2 pagesStock Trading Project GuidelinesNeo4u44No ratings yet
- Final PPT of Balance SheetDocument23 pagesFinal PPT of Balance SheetShailesh SatarkarNo ratings yet
- Dodgy Transaction: Powers of SEBIDocument11 pagesDodgy Transaction: Powers of SEBIJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Jossette Naiken: South Ridge, Downtown Burj Khalifa, Dubai +971 50 845 3671Document1 pageJossette Naiken: South Ridge, Downtown Burj Khalifa, Dubai +971 50 845 3671ahadNo ratings yet
- Algo Trading Intro 2013 Steinki Session 3 PDFDocument15 pagesAlgo Trading Intro 2013 Steinki Session 3 PDFMichael ARKNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in BankDocument29 pagesRisk Management in BankKovida GunawardanaNo ratings yet
- Hedging Strategies Using OptionsDocument13 pagesHedging Strategies Using OptionsDushyant MudgalNo ratings yet
- NKLA Warrant AgreementDocument16 pagesNKLA Warrant AgreementksNo ratings yet
- MARKETPLACE LIVE SIMULATION REPORT - UpDocument4 pagesMARKETPLACE LIVE SIMULATION REPORT - UpLien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Thoughts On Valuation: Equity Research-AmericasDocument20 pagesThoughts On Valuation: Equity Research-AmericasIzumi Hiroshima100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Financial Management: (Theory and Practicals)Document15 pagesFundamentals of Financial Management: (Theory and Practicals)tawandaNo ratings yet
- Lee VeeDocument19 pagesLee VeeIve EspiaNo ratings yet
- As 20Document6 pagesAs 20Rajiv JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 AFAR 2 ProblemsDocument3 pagesChapter 10 AFAR 2 ProblemsMa Alyssa DelmiguezNo ratings yet
- Cbse Board Accountancy SyllabusDocument4 pagesCbse Board Accountancy Syllabusapi-139761950No ratings yet
- Performance As of October 31, 2020 Holdings by Company Size: Institutional ClassDocument1 pagePerformance As of October 31, 2020 Holdings by Company Size: Institutional ClassLjubisa MaticNo ratings yet
- New Book Oficial EnglishDocument97 pagesNew Book Oficial EnglishAbolaji MuazNo ratings yet
- Final Report StratmanDocument76 pagesFinal Report StratmanImmanuel RiyadiNo ratings yet
- FM 1 ProblemsDocument4 pagesFM 1 ProblemsRanjit SpNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Cash Flow StatementDocument1 pageProblem 1: Cash Flow StatementNafisaRafaNo ratings yet
- ch9 1Document33 pagesch9 1Sai Karthik BaggamNo ratings yet
- Ex.C.BudgetDocument3 pagesEx.C.BudgetGeethika NayanaprabhaNo ratings yet
- Set - B - SolutionDocument2 pagesSet - B - Solutionyh9bzwtzwmNo ratings yet
- MOJO Stock SmallcapDocument3 pagesMOJO Stock SmallcapAnonymous Clm40C1No ratings yet
- Annamalai University: Accounting For Managerial DecisionsDocument307 pagesAnnamalai University: Accounting For Managerial DecisionsMALU_BOBBYNo ratings yet