Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biodiversity Terms
Uploaded by
melloroqr12620 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views2 pagesThe Biodiversity Branch is one of the branches in the Conservation and protection Division, The National Environment and Planning Agency. "Protecting Jamaica's land, wood and water" is the mission of the NEPA. Afforestation is the process of establishing forest cover where none existed before and also the restoration of deforested areas. Biological resources are components of biodiversity that are either used by humans or have potential use in the production of food, medicines or other essential products.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Biodiversity Branch is one of the branches in the Conservation and protection Division, The National Environment and Planning Agency. "Protecting Jamaica's land, wood and water" is the mission of the NEPA. Afforestation is the process of establishing forest cover where none existed before and also the restoration of deforested areas. Biological resources are components of biodiversity that are either used by humans or have potential use in the production of food, medicines or other essential products.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views2 pagesBiodiversity Terms
Uploaded by
melloroqr1262The Biodiversity Branch is one of the branches in the Conservation and protection Division, The National Environment and Planning Agency. "Protecting Jamaica's land, wood and water" is the mission of the NEPA. Afforestation is the process of establishing forest cover where none existed before and also the restoration of deforested areas. Biological resources are components of biodiversity that are either used by humans or have potential use in the production of food, medicines or other essential products.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
The Biodiversity Branch is
National Environment and Planning one of the branches in the Conservation
and Protection Division,
Agency The National Environment
and Planning Agency.
Vision
For additional information contact:
That Jamaica’s natural resources are being The National Environment and Planning Agency
used in a sustainable way and that there is (NEPA)
broad understanding of environment, 10 & 11 Caledonia Avenue, Kingston 5
planning and development issues, with Telephone:
extensive participation amongst citizens and 754-7540
a high level of compliance with relevant
Fax:
legislation.
754-7595/6
Email: pubed@nepa.gov.jm
Mission
Hotline: 1-888-991-5005
To promote Sustainable Development by
ensuring protection of the environment and Website:
orderly development in Jamaica through http//www.nepa.gov.jm
highly motivated staff performing at the
highest standard.
Produced by the Public Education and
Corporate Communication Branch in
collaboration with the
Managing & Protecting Jamaica’s Land, Biodiversity Branch of NEPA
“Protecting Jamaica’s land, wood and water”
Wood and Water
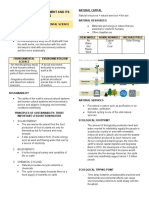
Afforestation All the processes involved in the es- Endangered Species An organism (plant or animal) M a r i n e Relating to salt water
tablishment of forest cover where none existed before and whose numbers are so low, that it is in danger of dying out,
also the restoration of deforested areas (usually termed that is, becoming extinct, for example, the Jamaican Iguana,
reafforestation). This usually involves replanting . seen below P o l l u t i o n Introduction of
elements, compounds or
any matter, into places, re-
Biological Diversity sulting in living organisms
(Biodiversity): being harmed
“Life on earth”; the variety of Air pollution
all plants, animals and micro- P r o t e c t e d A r e a An area of land or water that is
managed for the protection and maintenance of its eco-
organisms logical systems, biodiversity and/or specific natural,
cultural or aesthetic resources (e.g. Blue and John
The Jamaican Iguana Crow Mountains National Park and Montego Bay Ma-
rine Park)
Biological resources The components of biodiversity Endemic Species or race native to a particular place or
that are either used by humans or have potential for use found only there ( e.g. the Giant Swallowtail Butterfly)
in the production of food, medicines, manufactured goods Species Basic unit of classification consisting of
or other essential products, e.g. the Periwinkle, which is Extinct Term used to describe a species or population that population or series of populations of closely re-
used as a source of cancer medication has been lost lated or similar organism s
Fauna The animal life occurring in an area Terrestrial Living on land
Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
Flora The plant life occurring in an area Threatened Species Species of flora or fauna likely to
United Nations (UN) agreement setting out commitment
become endangered in the foreseeable future
for maintaining the world's ecology. Establishes three
main goals: Habitat An area that supports the life and provides the
• Conserve biological diversity food, shelter, light etc., of animals or plants. Plants and ani- Wildlife Animals and plants which exist in a relatively
• Sustainable use of its components mals occur in large numbers in such areas untouched state; usually considered a natural resource of
economic, scientific or cultural value
• Fair and equitable sharing of the benefits from the
use of genetic resources
Invasive species An alien species that colonises natural Wetland Area of land subject to flooding (inundation)
or semi-natural ecosystems, is an agent of change and and dominated by hydrophytic (adapted to life in water or
Ecosystem A com-
munity of living organ- threaten native biological diversity water-logged soils) vegetation. The inundation may be
isms, the region that tidal, seasonal or more permanent and may be saline,
brackish or freshwater. If the vegetation consists of trees,
they occupy their inter- Mangroves Salt loving plants, (halophytes), with extensive
actions with each other, the wetland is a swamp; if it is with herbaceous plants
root systems, which grow in swampy areas of sheltered ( e.g. reeds and grasses) it is a marsh
with the physical envi- tropical and sub-tropical shores. They are considered one of
ronment and the flow of the most productive ecosystems in the world and serve a The Giant Swallowtail
energy and matter variety of functions. These functions include providing a Butterfly, which is en-
through the system demic to Jamaica, is a
habitat for wildlife, nursery grounds for fish and shell- threatened species
fish and protecting coastal and inland areas from
A marine ecosystem waves and storms
You might also like
- SB24403 Ecology - Anthropogenic Influences Vs ConservationDocument15 pagesSB24403 Ecology - Anthropogenic Influences Vs ConservationMammoth CoffeeNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument30 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationPratik VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Importance of BiodiversityDocument46 pagesImportance of BiodiversityDaman Deep SinghNo ratings yet
- 4th Philippine National Report To The Convention On Biological DiversityDocument32 pages4th Philippine National Report To The Convention On Biological DiversityJaime Mari AguilarNo ratings yet
- BDR02Document16 pagesBDR02Ajay KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 8 BiodiversityDocument2 pagesModule 8 BiodiversityAryanna Kate De LunaNo ratings yet
- "Inventory of Terrestrial Arthropods in The Vicinity of Dila Falls, Brgy. Impalutao, Impasug-Ong Bukidnon" - Medura, MMMDocument14 pages"Inventory of Terrestrial Arthropods in The Vicinity of Dila Falls, Brgy. Impalutao, Impasug-Ong Bukidnon" - Medura, MMMs.medura.mamarielleNo ratings yet
- In Situ Conservation: ES - Biodiversity and Wildlife ConservationDocument38 pagesIn Situ Conservation: ES - Biodiversity and Wildlife ConservationJaffy BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Group-7-Biodiversity NewDocument2 pagesGroup-7-Biodiversity NewGina PiñeroNo ratings yet
- 'Mystery Dinner Snake' Found in Belly of Another Snake Finally IdentifiedDocument2 pages'Mystery Dinner Snake' Found in Belly of Another Snake Finally IdentifiedGina PiñeroNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument1 pageEcologyrashibaisoya.123No ratings yet
- E-Folio Grp3 BookkeepingDocument14 pagesE-Folio Grp3 BookkeepingElisha JuanilloNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity & Healthy SocietyDocument24 pagesBiodiversity & Healthy SocietyDickston AlojadoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Resources Group 1Document20 pagesEnvironmental Resources Group 1Joycel Ann GimenezNo ratings yet
- (Hamish) Kimmins 2011 Biodiversity and Its Relationship To Ecosystem Health and IntegrityDocument4 pages(Hamish) Kimmins 2011 Biodiversity and Its Relationship To Ecosystem Health and Integritymuhebullah motmaenNo ratings yet
- Report BiodiversityDocument57 pagesReport Biodiversityrodel zafraNo ratings yet
- Secsem Worksheet 2 EnviscieDocument7 pagesSecsem Worksheet 2 EnviscieSpearBNo ratings yet
- Ajol File Journals - 340 - Articles - 237126 - Submission - Proof - 237126 4057 572693 1 10 20221125Document9 pagesAjol File Journals - 340 - Articles - 237126 - Submission - Proof - 237126 4057 572693 1 10 20221125Ebinabo EriakumaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity, Classification and Conservation: BiologyDocument41 pagesBiodiversity, Classification and Conservation: BiologyAnggraeni Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Environment Programme, Biodiversity Typically Measures Variation at The Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem LevelDocument10 pagesEnvironment Programme, Biodiversity Typically Measures Variation at The Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem LevelCherry Ann JuitNo ratings yet
- G9-Pocket Lesson Saving Biodiversity - Attachment For LE Week 6 PRINTEDDocument2 pagesG9-Pocket Lesson Saving Biodiversity - Attachment For LE Week 6 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- STS Chap 3Document7 pagesSTS Chap 3Banan, Marvin B.No ratings yet
- Conservation Awareness and Techniques in Buluan Lake, Maguindanao, BARMMDocument9 pagesConservation Awareness and Techniques in Buluan Lake, Maguindanao, BARMMPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Wild Life LPM 1 PDFDocument87 pagesWild Life LPM 1 PDFNagesh N50% (2)
- Biology Revision Sankalp Bharat TeamnjrDocument255 pagesBiology Revision Sankalp Bharat TeamnjrShadab AliNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Laws Protect Species and HabitatsDocument4 pagesBiodiversity Laws Protect Species and HabitatsChristine RepuldaNo ratings yet
- Chapter III - Lesson 3 - Biodiversity LossDocument6 pagesChapter III - Lesson 3 - Biodiversity LossJhon Lloyd Zarco BantigueNo ratings yet
- Topics in The Chapter: Class-X Chapter-2 Geography Forest and Wildlife ResourcesDocument1 pageTopics in The Chapter: Class-X Chapter-2 Geography Forest and Wildlife ResourcesGranlolaNo ratings yet
- Science - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Document18 pagesScience - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Gan Wei ShengNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Healthy Society: Impacts of GMOsDocument10 pagesBiodiversity and Healthy Society: Impacts of GMOsJules Alvarado100% (1)
- Sustainability Development Goal Life On LandDocument2 pagesSustainability Development Goal Life On Landapi-359808400No ratings yet
- Biodiversity Loss in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesBiodiversity Loss in The PhilippineskiraNo ratings yet
- 1 BiodiversityDocument10 pages1 Biodiversityxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Green Olive Minimalis Modern Trip Promotion Trifold Brochure (Trifolds)Document2 pagesGreen Olive Minimalis Modern Trip Promotion Trifold Brochure (Trifolds)jovanie baliliNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document13 pagesModule 5Katrin Rose Cabag-iranNo ratings yet
- Philippine Biodiversity: Issues, Challenges, and InitiativesDocument64 pagesPhilippine Biodiversity: Issues, Challenges, and InitiativesRonnelMananganCorpuz100% (2)
- Rapid Biodiversity Assessment in The Buffer Zone of Bataan National Park, Luzon Island, PhilippinesDocument11 pagesRapid Biodiversity Assessment in The Buffer Zone of Bataan National Park, Luzon Island, PhilippinesHeza LeighNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Loss Causes and Solutions: HIPPO Factors, Laws, StrategiesDocument17 pagesBiodiversity Loss Causes and Solutions: HIPPO Factors, Laws, StrategiesOthoMirandaNo ratings yet
- LeaP-Science-G10-Week 7-Q3Document4 pagesLeaP-Science-G10-Week 7-Q3Eunice Kathleen M. JavelosaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Sts Chapter 9Document4 pagesReviewer For Sts Chapter 9Belle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity - Concept - Threats and Conservation - 2015Document10 pagesBiodiversity - Concept - Threats and Conservation - 2015Miguel Antonio CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Final ChaptersDocument55 pagesFinal ChaptersLlanie Mae DaigNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Healthy SocietyDocument2 pagesBiodiversity and Healthy SocietyYumi koshaNo ratings yet
- Conserve BiodiversityDocument1 pageConserve BiodiversityRaghuvir SinghNo ratings yet
- Es NotesDocument25 pagesEs NotesKESOCAKENo ratings yet
- BSESDocument55 pagesBSESRacel DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Why Mangroves Matter: Ecological and Socio-Economic AspectsDocument23 pagesWhy Mangroves Matter: Ecological and Socio-Economic AspectsNguwruw Chungpha MoyonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 - Bio-DiversityDocument12 pagesLesson 12 - Bio-DiversitySwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- ClassWork BiologyDocument1 pageClassWork BiologyVale R.No ratings yet
- APES Cheat Sheet Units 1 Through 7 OnlyDocument54 pagesAPES Cheat Sheet Units 1 Through 7 OnlyMarlon MccarthyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Ecosystem and BiodiversityDocument36 pagesChapter 3 - Ecosystem and BiodiversityRohan PolNo ratings yet
- Hope For Threatened Tropical Biodiversity: Lessons From The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesHope For Threatened Tropical Biodiversity: Lessons From The Philippinesarjay peloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9-Biodiversity and The Healthy SocietyDocument15 pagesLesson 9-Biodiversity and The Healthy SocietyApril HibitNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity LectureDocument40 pagesBiodiversity Lecturejuju on the beatNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity ProjectDocument19 pagesBiodiversity ProjectMadhurima khan92% (12)
- Earth's Systems Food Resources MISRA's Report Natural ResourcesDocument4 pagesEarth's Systems Food Resources MISRA's Report Natural ResourceskyscribdNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Module 4Document1 pageUnit 3 Module 4heideNo ratings yet
- Trees of Papua New Guinea: Volume 1: Introduction and Gnetales to FabalesFrom EverandTrees of Papua New Guinea: Volume 1: Introduction and Gnetales to FabalesNo ratings yet
- Uncharted Eden: Preserving Life's Gems within Earth's Natural SanctuariesFrom EverandUncharted Eden: Preserving Life's Gems within Earth's Natural SanctuariesNo ratings yet
- Gases-Thermochemistry Tutorial #1Document1 pageGases-Thermochemistry Tutorial #1melloroqr1262No ratings yet
- 40DaysofProsperity GeorgePearsonsDocument104 pages40DaysofProsperity GeorgePearsonsmelloroqr1262No ratings yet
- 1.1 Exercise 4 - Ionisation EnergiesDocument1 page1.1 Exercise 4 - Ionisation Energiesfags786No ratings yet
- Gases-Thermochemistry Tutorial #1Document1 pageGases-Thermochemistry Tutorial #1melloroqr1262No ratings yet
- Overview of FishDocument20 pagesOverview of FishCHAN KIMSYNo ratings yet
- Batty L C Halleberg K B Ecology of Industrial PollutionDocument372 pagesBatty L C Halleberg K B Ecology of Industrial PollutionAlmaz KassNo ratings yet
- Statment of PurposeDocument2 pagesStatment of PurposewaqasNo ratings yet
- (Haddad, 2003) Corridor Use by Diverse Taxa PDFDocument7 pages(Haddad, 2003) Corridor Use by Diverse Taxa PDFOscar Leonardo Aaron Arizpe VicencioNo ratings yet
- Migratory Birds: Tracing Their Flight: English PT-1 Activity 2019-2020Document17 pagesMigratory Birds: Tracing Their Flight: English PT-1 Activity 2019-2020Garvit Agarwal67% (6)
- Synopsis Ignou Pts5 KanpurDocument7 pagesSynopsis Ignou Pts5 KanpurAnjnaKandari100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument21 pagesIntroductionsachinagsNo ratings yet
- How People Destroy Natural ResourcesDocument2 pagesHow People Destroy Natural ResourcesLeomille C Tubac83% (6)
- RA 11038 Expanded NIPAS ActDocument26 pagesRA 11038 Expanded NIPAS ActRiver Mia RomeroNo ratings yet
- Wetland ManualDocument118 pagesWetland Manualqwertyuiop123mnb100% (1)
- Lesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsDocument3 pagesLesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsMaricel Cebrero Santiago100% (4)
- What is Biodiversity & its TypesDocument3 pagesWhat is Biodiversity & its TypesJulie marie PalmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Ecology in Aquatic Systems An Introduction PDFDocument301 pagesChemical Ecology in Aquatic Systems An Introduction PDFmoshroom914100% (1)
- Conceptual Inventory Population Dynamics Sept 2013Document18 pagesConceptual Inventory Population Dynamics Sept 2013Abdelaziz Abdelghany0% (1)
- Habitat Niche and SelectionDocument5 pagesHabitat Niche and SelectionSavannah Simone PetrachenkoNo ratings yet
- Adaptations Help Animals SurviveDocument8 pagesAdaptations Help Animals SurviveBhawna Kapoor100% (1)
- Orchids of Vejalnica and KRČ (Medvednica)Document9 pagesOrchids of Vejalnica and KRČ (Medvednica)keeesaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Notes PowerpointDocument24 pagesEcosystem Notes PowerpointVic Simangan FavilaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Integrating Wildfire Into Strategic Planning For Sierra Nevada ForestsDocument8 pages2 - Integrating Wildfire Into Strategic Planning For Sierra Nevada ForestsOtavio ItaloNo ratings yet
- Extinction Vortex Tutorial 3rd YearsDocument3 pagesExtinction Vortex Tutorial 3rd YearsDavid CrowhurstNo ratings yet
- Ecological Succession Cards To OrderDocument4 pagesEcological Succession Cards To OrderNermine AbedNo ratings yet
- Agroforestry Systems ExplainedDocument3 pagesAgroforestry Systems ExplainedVirendra PratapNo ratings yet
- Ecology and Evolution of InvasiveDocument295 pagesEcology and Evolution of InvasivevictoriaNo ratings yet
- enviroWORKS Vol 1 07 Feb 2007 1332007131850 465Document32 pagesenviroWORKS Vol 1 07 Feb 2007 1332007131850 465winstonNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem - Meaning and StructureDocument11 pagesEcosystem - Meaning and StructureParveenNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Environment StudiesDocument19 pagesLec 1 - Environment StudiesAjay DSNo ratings yet
- Fmars 07 581945Document8 pagesFmars 07 581945calvin cheungNo ratings yet
- Prac 3 Ex Situ ConservationDocument2 pagesPrac 3 Ex Situ Conservationytengku100% (1)
- South Africa'S National Biodiversity Strategy and Action PlanDocument108 pagesSouth Africa'S National Biodiversity Strategy and Action PlanPlandeAccionPNBNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Revision NotesDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Revision NotesSubhodeep GhoshNo ratings yet