Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ifm WS 1
Uploaded by
singhai_sud3138Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ifm WS 1
Uploaded by
singhai_sud3138Copyright:
Available Formats
QUEENS’ COLLEGE, INDORE
INTRO. TO FIN. MARKET WORKSHEET – 1 (No. of Pages – 6)
CLASS – XI – TYPES OF MARKET
The term "finance" in our simple understanding it is perceived as equivalent to 'Money'. We read
about Money and banking in Economics, about Monetary Theory and Practice and about "Public
Finance". But finance exactly is not money, it is the source of providing funds for a particular
activity. Thus public finance does not mean the money with the Government, but it refers to
sources of raising revenue for the activities and functions of a Government. Here some of the
definitions of the word 'finance', both as a source and as an activity i.e. as a noun and a verb.
The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition defines the term as
under-
1:"The science of the management of money and other assets.";
2: "The management of money, banking, investments, and credit. ";
INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM
The economic development of a nation is reflected by the progress of the various economic units,
broadly classified into corporate sector, government and household sector. While performing
their activities these units will be placed in a surplus/deficit/balanced budgetary situations.
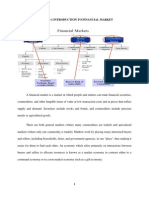
There are areas or people with surplus funds and there are those with a deficit. A financial system
or financial sector functions as an intermediary and facilitates the flow of funds from the areas of
surplus to the areas of deficit. A Financial System is a composition of various institutions,
markets, regulations and laws, practices, money manager, analysts, transactions and claims and
liabilities.
Financial System
The word "system", in the term "financial system", implies a set of complex and closely
connected or interlined institutions, agents, practices, markets, transactions, claims, and liabilities
in the economy. The financial system is concerned about money, credit and finance-the three
terms are intimately related yet are somewhat different from each other. Indian financial system
consists of financial market, financial instruments and financial intermediation. These are briefly
discussed below;
FINANCIAL MARKETS
A Financial Market can be defined as the market in which financial assets are created or
transferred. As against a real transaction that involves exchange of money for real goods or
services, a financial transaction involves creation or transfer of a financial asset. Financial Assets
or Financial Instruments represents a claim to the payment of a sum of money sometime in the
future and /or periodic payment in the form of interest or dividend.
Prepared by – SUDHIR SINGHAI 1
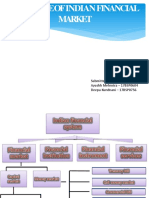
Types of Financial Market
(1) Money Market
(2) Capital Market
(a) Securities Market
(i) Primary Market
(ii) Secondary Market
a) Spot Market
b) Forward Market
i) Future Market
ii) Options Market
1) Put option
2) Call option
(b) Non Securities Market
MONEY MARKET
The money market is a wholesale debt market for low-risk, highly-liquid, short-term instrument.
Funds are available in this market for periods ranging from a single day up to a year. This market
is dominated mostly by government, banks and financial institutions.
The money market can be defined as a market for short-term money and financial assets that are
near substitutes for money. The term short-term means generally a period upto one year and near
substitutes to money is used to denote any financial asset which can be quickly converted into
money with minimum transaction cost.
Some of the important money market instruments are briefly discussed below;
1. Call/Notice Money
2. Treasury Bills
3. Term Money
4. Certificate of Deposit
5. Commercial Papers
CAPITAL MARKET
It is market for long-term financial assets. Corporate issues these securities in the capital market
and investors can subscribe purchase or resell these in the capital market. Apart from these
securities derivatives are also traded in this market.
It is again classified into two types:
(i) Securities Market
(ii) Non Securities Market
DIFFERENCE : MONEY MARKET & CAPITAL MARKET
Basis MONEY MARKET CAPITAL MARKET
1. Subject matter Short-term financial instruments Long-term financial instruments
having maturity of less than one having maturity of more than one year.
year.
2. Participants It is wholesale market and Even a small individual investor can
Participants are large institutional deal by sale or purchase of shares,
investors, commercial banks and debentures etc.
mutual funds.
3. Subdivision No sub division is there. Divided into two common segments
primary and secondary.
4.Volume Total volume is many fold as Volume is less as compared to Money
compared of Capital markets market.
5. Instruments Treasury bill, Commercial paper, Shares, Debentures, Public Sector
cash deposit, call money Bonds and Units of Mutual Funds.
commercial bills.
Prepared by – SUDHIR SINGHAI 2
NON SECURITIES MARKET
It deals with Mutual Funds, Fixed Deposits, Bank Deposits, Provident Fund, Small Savings,
Insurance etc.
SECURITIES MARKET
Securities market however refers to the markets for those financial instruments / claims /
obligations that are commonly and readily transferable by sale.
It is divided into two interdependent and inseparable segments, the new issues (primary) market
and the stock (secondary) market.
PRIMARY MARKET
It provides channel for sale of new securities. It is the channel through which industry raise funds
by issuing different types of securities to meet their financial requirements for modernization,
expansion and diversification programmes. The Primary market discharges the important function
of transfer of savings from surplus sector to government and corporate sector.
SECONDARY MARKET
It refers to the network for the subsequent sale and purchase of securities. In other words
secondary market deals in securities previously issued. They are represented by Stock Exchanges
in any capital market.
Secondary Market has further two components –
SPOT MARKET
Here securities are traded for immediate delivery and payment.
The spot market or cash market is a market where securities are sold for cash and delivered
immediately. Contracts bought and sold on these markets are immediately effective.
FORWARD MARKET
Here securities are traded for future delivery and payment.
Forward contracts are personalized between parties and therefore not frequently traded on
exchanges. The forward market is a general term used to refer to the informal market in which
these contracts are entered and exited.
Forward contracts are personalized between parties and therefore not frequently traded on
exchanges. The forward market is a general term used to refer to the informal market in which
these contracts are entered and exited.
Forward Market has further two components –
FUTURE
Standardized forward contracts are called futures contracts and traded on a futures exchange.
A future contract, or simply called futures, is a contract to buy or sell a stated quantity of a
commodity or a financial claim at a specified price at a future specified date.
Futures are traded on the exchanges and the terms of the futures contracts are standardized by the
exchange with reference to quantity, date ,units of price quotation, minimum change in price etc.
DIFFERENCE : FUTURES & FORWARDS
BASIS FORWARDS FUTURES
1. Type of Contract They are customized market. They are standardized contract.
2. Relationship All forwards are not futures. All futures are forwards.
3. Trading through Not traded through Stock Traded through Stock Exchange.
stock exchange Exchange.
4. Centralised Lack of Centralisation of trading. It is Centralised market.
trading It is decentralized market.
5. Default There is chance of default by There are no chances of default by
party. counter party.
Prepared by – SUDHIR SINGHAI 3
OPTION
Options are contracts which provide the holder the right to sell or buy a specified quantity of an
underlying asset at a fixed price on or before the expiration of the option date.
In option contracts, the writer of the options grants the buyer of the options a right but not the
obligation, to buy or sell to the writer, some asset at the specified price on the specified date. The
writer gets a price for granting this option. The person who acquires the right is known as option
holder or option buyer and the person who grants this right is known as option seller or option
writer. The price payable for this right is known as premium and depends upon the underlying
assets or securities.
Options can be classified into two types –
CALL OPTIONS –
It provides to the holder a right to buy specified assets at specified price on or before a specified
date.
PUT OPTIONS –
It provides to the holder a right to sell specified assets at specified price on or before a specified
date.
Example – Amit enters into a contract with Sumit whereby Amit has the right to buy 100 shares
of RPL @ Rs.90 each on or before a specified date. This is a call option. In the same case if Amit
has the right to sell instead of buying, it is called put option. It is not necessary to
Amit to buy or sell the shares, it is only option available to him. If he does not exercises his right
on or before specified date option will lapse. In order to acquire this right Amit has to pay a price
to Sumit called premium.
DIFFERENCE : FUTURES & OPTIONS
FUTURES OPTIONS
1. Futures involves obligation. It must be 1. Options involves right. Options holder has
fulfilled by both parties. right to exercise his option or not.
2. There is no premium payable to buy 2. Premium is payable by the optionholder.
futures.
3. Profit or Loss of both parties depend upon 3. Profit of option writer is limited to the
the specified price and actual price on premium received but he is exposed to
settlement day. So both the parties are unlimited risk, and the loss of option holder
exposed to unlimited profit or loss. is limited to the premium paid but his gains
are unlimited.
FOREX MARKET
The Forex market deals with the multicurrency requirements, which are met by the exchange of
currencies. Depending on the exchange rate that is applicable, the transfer of funds takes place in
this market. This is one of the most developed and integrated market across the globe.
CREDIT MARKET
Credit market is a place where banks, FIs and NBFCs purvey short, medium and long-term loans
to corporate and individuals.
DEBT MARKET
For a developing economy like India, debt markets are a crucial source of funds. The debt market
in India is amongst the largest in Asia. It includes government securities – the largest component -
and bonds issued by public sector undertakings, other government bodies, financial institutions,
banks and companies. Debt markets are now considered an alternative route to banking channels
for finance.
Prepared by – SUDHIR SINGHAI 4
CROSS WORD
ACROSS
2. ________ Market is where subsequent sale and purchase of securities takes place.(9)
4. ________ Market can be defined as a market for short-term money and financial assets that are
near substitutes for money. (5)
6. contracts are personalized between parties and therefore not frequently traded on exchanges. (7)
9. Contracts bought and sold on these markets are immediately effective. (4)
12. NCDEX _________ is an example of ____________ Market. (11)
13. ________ Market provides channel for sale of new securities.(7)
15. Minimum seven members are required to form such company. (6)
16. __________ option provides to the holder a right to buy specified assets at specified price on
or before a specified date. (4)
17. __________ value is derived from one or more basic variable, called bases. (11)
DOWN
1. First Stock Exchange of India (19)
3. ________ are traded on Stock Exchange. (10)
5. ________ Companies are not registered in India but doing business in India. (6)
Prepared by – SUDHIR SINGHAI 5
7. _______ Markets includes government securities – the largest component - and bonds issued
by public sector undertakings, other government bodies, financial institutions, banks and
companies. (4)
8. _______ is the third largest Stock Exchange of World (3)
10. _________ are contracts which provide the holder the right to sell or buy a specified quantity
of an underlying asset at a fixed price on or before the expiration of the option date. (7)
11. Standardized forward contracts are called __________ contracts. (7)
14. _______ options provides to the holder a right to sell specified assets at specified price on or
before a specified date. (3)
Write the correct word and explain it in one or two sentences.
(a) ITOPSON
(b) STOP EAKMTR
(c) ITIDRSEAVVE
(d) SEN
(e) CLLA
(f) ERGFON NAYOCMP
(g) BABMYO OTCSK GENACEHX
(h) RAMIPYR AKRTEM
(i) OADERCSNY KRMATE
(j) LCPUBI PYCMAON
(k) EEICTRSUIS RATEKM
(l) AIEPRTV MONCYAP
(m) TFSUUER
(n) TPU
(o) WFRAORD KEATMR
(p) NOYEM KTMERA
(q) IOITMOEMCSD MKRTAE
(r) BEDT AKMERT
QUESTIONS
1. Diagrammatically explain Indian Financial System.
2. What are the reforms made in financial markets in 1991 to improve the functioning?
3. How Stock market begin in India.
4. Write a short note on Style of operating in Stock Exchanges.
5. Explain the products and participants of Derivative Markets.
6. Name any five instruments of Debt market.
7. What are the functions of Derivative market.
8. Differentiate Commodity and Derivative market.
9. Differentiate Private and Public Company.
10. What are the steps in formation of a Public company and Private company.
Prepared by – SUDHIR SINGHAI 6
You might also like
- Equity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2From EverandEquity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Classification of Financial MarketsDocument12 pagesClassification of Financial Marketsvijaybhaskarreddymee67% (6)
- Bba Notes 6Document53 pagesBba Notes 6RAJATNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions - PART1Document75 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions - PART1shweta_46664100% (3)
- Raja Shekar ReddyDocument42 pagesRaja Shekar ReddypavithrajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Financial Markets and InstrumentsDocument61 pagesChapter Two Financial Markets and InstrumentsKume MezgebuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finacial Markets Final With Refence To CDSLDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Finacial Markets Final With Refence To CDSLShoumi Mahapatra100% (1)
- Final Blackbook by Sanju PDF VARSHADocument67 pagesFinal Blackbook by Sanju PDF VARSHAYukta SalviNo ratings yet
- Financial/ Securities Markets Notes: For Sebi Grade A & Rbi Grade BDocument10 pagesFinancial/ Securities Markets Notes: For Sebi Grade A & Rbi Grade BAadeesh JainNo ratings yet
- Amanpreet Singh - Financial Market AssignmentDocument8 pagesAmanpreet Singh - Financial Market AssignmentSiddharth JainNo ratings yet
- Investment NotesDocument30 pagesInvestment Notesshantanu100% (2)
- International Financial MarketDocument36 pagesInternational Financial MarketSmitaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Financial SystemsDocument62 pagesNotes On Financial SystemsamitNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutionschap 2Document8 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutionschap 2Ini IchiiiNo ratings yet
- GR12 Business Finance Module 3-4Document8 pagesGR12 Business Finance Module 3-4Jean Diane JoveloNo ratings yet
- Financial Market FinalDocument58 pagesFinancial Market FinalMUEKSH MANWANINo ratings yet
- Financial Markets Dba 302Document5 pagesFinancial Markets Dba 302mulenga lubembaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-Indian Capital MarketDocument70 pagesChapter-2-Indian Capital MarketGowtham SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document5 pagesTopic 2Jeffrey RiveraNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial Market: Rahul Kumar Department of Business AdminestrationDocument52 pagesIndian Financial Market: Rahul Kumar Department of Business AdminestrationDhruv MishraNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument78 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutionsamol_more37100% (1)
- Money Market Bond Market Derivatives MarketDocument19 pagesMoney Market Bond Market Derivatives MarketRamil Jr GaciasNo ratings yet
- BY: Osama Tariq. Sajawal. Adnan Shahzad. Shaikh Ahmed AliDocument36 pagesBY: Osama Tariq. Sajawal. Adnan Shahzad. Shaikh Ahmed Alishaikh ahmedNo ratings yet
- Module 04 Financial Markets and InstrumentsDocument13 pagesModule 04 Financial Markets and InstrumentsGovindNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument18 pagesFinancial MarketHusain BohraNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets - Module 4 - Week 4Document8 pagesCapital Markets - Module 4 - Week 4Jha Jha CaLvez100% (2)
- Portfolio InvestmentDocument129 pagesPortfolio Investmentanchal1987No ratings yet
- Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesQuestion and AnswersAshwin SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- An Overview OF Indian Financial SystemDocument16 pagesAn Overview OF Indian Financial SystemArthiKalisamyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Financial TheoryDocument12 pagesLecture 1-Financial TheoryNe PaNo ratings yet
- MGT of Financial MKT & Instu CH-3Document7 pagesMGT of Financial MKT & Instu CH-3fitsumNo ratings yet
- Copy of SS-BF-II-12 WEEK 3 Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesCopy of SS-BF-II-12 WEEK 3 Lecture NotesSheanne GuerreroNo ratings yet
- What Is The Money Market?Document12 pagesWhat Is The Money Market?Vishnu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- FMI NotesDocument93 pagesFMI Notesjain_ashish_19888651No ratings yet
- Big Picture in Focus: Ulob. Differentiate The Types of Financial MarketsDocument10 pagesBig Picture in Focus: Ulob. Differentiate The Types of Financial MarketsJohn Stephen PendonNo ratings yet
- Debt Instrument Project PDFDocument50 pagesDebt Instrument Project PDFRohit VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary MarketsDocument19 pagesPrimary and Secondary MarketsyanaNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument13 pagesFinancial MarketRajeswari KuttimaluNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions: Required Reading: Mishkin, Chapter 1 andDocument43 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions: Required Reading: Mishkin, Chapter 1 andrudraarjunNo ratings yet
- Final Project of Bba 1 1Document50 pagesFinal Project of Bba 1 1Om PatelNo ratings yet
- 8526 1uniDocument18 pages8526 1uniMs AimaNo ratings yet
- 1-Bond MarketDocument85 pages1-Bond Marketdharmtamanna80% (5)
- Types of Financial Markets Wihtin The Financial SystemDocument2 pagesTypes of Financial Markets Wihtin The Financial SystemRod'z Tan LongaresNo ratings yet
- Financial Market and InstitutionsDocument43 pagesFinancial Market and Institutionsdhiviraj100% (3)
- Some of The Features of The Financial Market Are As FollowsDocument4 pagesSome of The Features of The Financial Market Are As FollowsabcdNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument5 pagesFinancial MarketRoxanne Jhoy Calangi VillaNo ratings yet
- Capital Market and Money MarketDocument17 pagesCapital Market and Money MarketSwastika Singh100% (1)
- Money Market InstumentsDocument39 pagesMoney Market InstumentsDilshaad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial MarketDocument20 pagesIndian Financial MarketRahulJainNo ratings yet
- Financial Market TopicDocument31 pagesFinancial Market TopicGautam MahtoNo ratings yet
- Financial Market FinalDocument327 pagesFinancial Market Finalvarshadumbre100% (3)
- Stock Market Investing for Beginners: The Best Book on Stock Investments To Help You Make Money In Less Than 1 Hour a DayFrom EverandStock Market Investing for Beginners: The Best Book on Stock Investments To Help You Make Money In Less Than 1 Hour a DayNo ratings yet
- Locked-In Range Analysis: Why Most Traders Must Lose Money in the Futures Market (Forex)From EverandLocked-In Range Analysis: Why Most Traders Must Lose Money in the Futures Market (Forex)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Investing For Beginners: How to Save, Invest and Grow Your Wealth Through the Stock Market, Real Estate, Index Funds, Precious Metals, and MoreFrom EverandInvesting For Beginners: How to Save, Invest and Grow Your Wealth Through the Stock Market, Real Estate, Index Funds, Precious Metals, and MoreRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- SEBIDocument6 pagesSEBISusan sophia.YNo ratings yet
- Features: Graham D Vinter, Project Finance, 3 Edition, 2006, Page No.1Document9 pagesFeatures: Graham D Vinter, Project Finance, 3 Edition, 2006, Page No.1ayush gattaniNo ratings yet
- Financial SystemDocument32 pagesFinancial Systemsaritasharma_sharmaNo ratings yet
- Harshad Mehta ScamDocument17 pagesHarshad Mehta ScamRupali Manpreet Rana0% (1)
- Capital Markets Q&ADocument14 pagesCapital Markets Q&AMachinimaC0dNo ratings yet
- Multinational Financial FunctionDocument20 pagesMultinational Financial FunctionVINITHANo ratings yet
- MVB Notes To: Capital Markets and Securities Laws For Cs-ExecutiveDocument50 pagesMVB Notes To: Capital Markets and Securities Laws For Cs-ExecutiveJagdishLimbachiyaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument5 pagesReviewerJeline E LansanganNo ratings yet
- Project On Indian Financial Market.Document45 pagesProject On Indian Financial Market.Sarvesh Mishra70% (23)
- NISM VII - SORM Short NotesDocument25 pagesNISM VII - SORM Short Notescomplaints.tradeNo ratings yet
- Sharekhan Internship ProjectDocument74 pagesSharekhan Internship Projectayush goyalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Commodity Market With Capital MarketDocument70 pagesAnalysis of Commodity Market With Capital MarketChandrashekar AkkiyavarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 The Bond MarketDocument7 pagesChapter 12 The Bond Marketlasha KachkachishviliNo ratings yet
- Equity 5.1. Overview of Financial Market: Function & Regulation 5.1.1. 5.1.1.1. Main Functions of The Financial MarketDocument76 pagesEquity 5.1. Overview of Financial Market: Function & Regulation 5.1.1. 5.1.1.1. Main Functions of The Financial MarketEvelyn YangNo ratings yet
- Native Migrations India Financial Services July To September PDFDocument41 pagesNative Migrations India Financial Services July To September PDFHariharan SNo ratings yet
- Unit I FM Introduction To FMDocument58 pagesUnit I FM Introduction To FMMufaddal SidsNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Liabilities Under Securities Law 28.11.2011Document51 pagesPresentation On Liabilities Under Securities Law 28.11.2011Vidya AdsuleNo ratings yet
- Global Securities OperationsDocument264 pagesGlobal Securities Operationsnishant hawelia100% (1)
- Project On Gold Loan J PDocument61 pagesProject On Gold Loan J PJai Praksah Sharma83% (12)
- Investors Preference Towards Equity Market.Document115 pagesInvestors Preference Towards Equity Market.amanjeet singhNo ratings yet
- G30 recommendation@CSD SSS PS CCPDocument143 pagesG30 recommendation@CSD SSS PS CCPRajesh PoudelNo ratings yet
- Study On Types of Financial Services Offered by Banking Industry With Reference To ICICI Bank (1) .DoDocument81 pagesStudy On Types of Financial Services Offered by Banking Industry With Reference To ICICI Bank (1) .Do20120 SANSKAR MEENANo ratings yet
- Business Finance PrelimDocument24 pagesBusiness Finance PrelimSandro SerdiñaNo ratings yet
- Pages 55 Capital Market Operation FinalDocument38 pagesPages 55 Capital Market Operation FinalAakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- EY Capital Markets Innovation and The FinTech Landscape Executive SummaryDocument9 pagesEY Capital Markets Innovation and The FinTech Landscape Executive SummaryCrowdfundInsider100% (1)
- ASNB MasterProspectus 2011Document169 pagesASNB MasterProspectus 2011David Ten Kao YuanNo ratings yet
- Role of Capital MarketDocument3 pagesRole of Capital Marketlnl2405100% (1)
- Ppteconomics 130428060347 Phpapp01Document18 pagesPpteconomics 130428060347 Phpapp01Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nism Series Ix Merchant Banking WorkbookDocument127 pagesNism Series Ix Merchant Banking Workbookalpha012550% (2)
- OnlyIAS Indian Economy UDAANDocument160 pagesOnlyIAS Indian Economy UDAANHUSSAIN B GNo ratings yet