Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 - Handout 131
Uploaded by
athenalavega0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views3 pagesOriginal Title
3- Handout 131
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views3 pages3 - Handout 131
Uploaded by
athenalavegaCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OBJECTIVES
A control system is dynamic: it responds to an input by undergoing a transient
response before reaching a steady-state response that generally resembles the
input
3 major objectives of systems analysis and design:
1. Producing the desired transient response
2. Reducing the steady-state error
3. Achieve stability
*also address some other design concerns such as cost and the sensitivity of
system performance to changes in parameters
Examples: Elevator, RW of computers disk storage
STABILITY
Control systems must be designed to be stable; that is their natural response
must decay to zero as time approaches infinity, or oscillate
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS:
Hardware selection- motor sizing, choice of sensors, etc
Finances- budget allocations and competitive pricing
Robust design- engineer wants to create a robust design so that the
system will not be sensitive to parameter changes
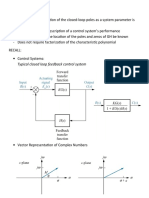
EXAMPLE OF A FEEDBACK CONTROL SYSTEM:
Antenna Azimuth: Position Control Systems
SUMMARY: design objectives and system performance revolves around the
transient response, steady-state error and stability; now that we have stated
our objectives and some methods available to meet those objectives, we
describe the orderly progression that leads us to the final system design
DESIGN PROCESS
You might also like
- Group No 2 ControlDocument16 pagesGroup No 2 ControlCrescent MnyamaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - IntroductionDocument57 pagesLesson 1 - IntroductionKobe YambiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Controls: ME211 Control System EngineeringMuhammad Junaid JahangirNo ratings yet
- Sigmetrics08 Control PDFDocument31 pagesSigmetrics08 Control PDFyalllikNo ratings yet
- Control System RequirementsAn ideal control system would:- Be stable- Provide absolute accuracy (maintain zero error) - Respond instantaneouslyDocument32 pagesControl System RequirementsAn ideal control system would:- Be stable- Provide absolute accuracy (maintain zero error) - Respond instantaneouslySudipta PaulNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics & Control: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument32 pagesProcess Dynamics & Control: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- 1200 Buildings Program BMS Seminar 2Document39 pages1200 Buildings Program BMS Seminar 2HayanJanakat71% (7)
- Chapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisJoy Rizki Pangestu DjuansjahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisJoy Rizki Pangestu DjuansjahNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.0 Design of Feedback Control Systems TCE5102Document30 pagesTopic 1.0 Design of Feedback Control Systems TCE5102Courage ChigerweNo ratings yet
- ISE Not 1Document13 pagesISE Not 1Deniz DemirNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument27 pagesControl SystemskakiksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument68 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionNtiyisoColbertNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Design of Feedback Controllerstce5102Document11 pagesTopic 1 Design of Feedback Controllerstce5102Fadzai FunguraNo ratings yet
- Key Elements of MechatronicsDocument14 pagesKey Elements of Mechatronicsmatininamdar50% (2)
- ME-314 Control SystemsDocument16 pagesME-314 Control SystemsFaysal Qadeer KhanNo ratings yet
- Am Unit - 7 PDFDocument6 pagesAm Unit - 7 PDFSravanth KondetiNo ratings yet
- 1200 Buildings Program BMS Seminar 1Document37 pages1200 Buildings Program BMS Seminar 1HayanJanakatNo ratings yet
- Reliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?Document16 pagesReliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?Jayson SoguilonNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components Consulting Services Inc. Reliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How They Benefit DesignDocument16 pagesElectronic Components Consulting Services Inc. Reliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How They Benefit DesignPatel MswaziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Industrial Control SystemsDocument31 pagesChapter 5 - Industrial Control SystemsAvik MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document21 pagesPart 1TwinkelsNo ratings yet
- Control Systems FundamentalsDocument30 pagesControl Systems Fundamentalskhaled jNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control SystemsDocument25 pagesIndustrial Control SystemsweilingkwayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Embedded SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Embedded SystemStephanie CalabungNo ratings yet
- ASS Control EngiDocument2 pagesASS Control Engipogikian.pascoNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control System: Output - Desired OutputDocument13 pagesFeedback Control System: Output - Desired OutputApril BalceNo ratings yet
- Controller TuningDocument54 pagesController TuningNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- System EngagementsDocument51 pagesSystem EngagementsSyrell NaborNo ratings yet
- What can be said about the controllability and observability conditions if the transfer function has poleDocument6 pagesWhat can be said about the controllability and observability conditions if the transfer function has poleMengistu BirukeNo ratings yet
- EIE325 Course on Engineering Software PackagesDocument11 pagesEIE325 Course on Engineering Software PackagesnyenookeNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering Chapter 1: Introduction: Dr.-Ing. Witthawas PongyartDocument51 pagesControl Systems Engineering Chapter 1: Introduction: Dr.-Ing. Witthawas PongyartAphichaya thanchaiNo ratings yet
- Reliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?Document16 pagesReliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?Oussama AbderrahimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document19 pagesLecture 6Philani XabaNo ratings yet
- Reliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?Document13 pagesReliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?augur886No ratings yet
- Bontoy ReportingDocument19 pagesBontoy ReportingKEZIA MAE JALANDONINo ratings yet
- Methods to Improve Verification QualityDocument17 pagesMethods to Improve Verification QualityMohammad Seemab AslamNo ratings yet
- CoE Unit1 Ch1 (Introduction)Document25 pagesCoE Unit1 Ch1 (Introduction)All_regNo ratings yet
- 5 Computer Organization Concept and Memory: 1.6 The Embedded System Design ProcessDocument3 pages5 Computer Organization Concept and Memory: 1.6 The Embedded System Design ProcessqNo ratings yet
- ControlDocument43 pagesControlaramNo ratings yet
- Finish Reading Before Answering Questions., 11 Design Problems Are Assigned, Submit A Word Document With Your Solution OnlyDocument50 pagesFinish Reading Before Answering Questions., 11 Design Problems Are Assigned, Submit A Word Document With Your Solution Onlyazeem sheikhNo ratings yet
- CST 04Document95 pagesCST 04Sourav ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- B Lecture1 Introduction Automatic Control SystemDocument29 pagesB Lecture1 Introduction Automatic Control SystemAbaziz Mousa OutlawZzNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Control SystemsDocument26 pagesIntroduction to Control SystemsNicole HyominNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ControlDocument29 pagesAdaptive Controlsam0025No ratings yet
- Free Study Materials & Career Guidance for Engineers, Doctors & MoreDocument124 pagesFree Study Materials & Career Guidance for Engineers, Doctors & MoreaduveyNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To Control SystemsDocument14 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To Control SystemsHane MinasalbasNo ratings yet
- Architectural Analysis and ATAM MethodDocument23 pagesArchitectural Analysis and ATAM MethodAhmed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01-Intro. Cont.Document20 pagesLecture 01-Intro. Cont.Reagan TorbiNo ratings yet
- RCM XXXDocument11 pagesRCM XXXOmar KhaledNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Quality Attributes of Embedded SystemsDocument29 pagesCharacteristics and Quality Attributes of Embedded SystemsRonny Fae FabonNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document11 pagesModule 2suresh mariappanNo ratings yet
- Reliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?Document16 pagesReliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?b_shadid8399100% (1)
- Practical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneFrom EverandPractical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneNo ratings yet
- Digital Control Engineering: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandDigital Control Engineering: Analysis and DesignRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Low-Current Systems Engineer’S Technical Handbook: A Guide to Design and SupervisionFrom EverandLow-Current Systems Engineer’S Technical Handbook: A Guide to Design and SupervisionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ee 170 Final GradesDocument2 pagesEe 170 Final GradesathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Postfinal 170Document1 pagePostfinal 170athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 9-Steady State SpecificationsDocument3 pages9-Steady State SpecificationsathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Signal Flow AdditionalDocument2 pages8 - Signal Flow AdditionalathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Ee 170 Final GradesDocument1 pageEe 170 Final GradesathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Signal Flow GraphsDocument3 pages8 - Signal Flow Graphsathenalavega100% (1)
- 12 Refining The SketchDocument2 pages12 Refining The SketchathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Ee 170 Final GradesDocument1 pageEe 170 Final GradesathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Ee 170 Final GradesDocument1 pageEe 170 Final GradesathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 11 Root Locus 1Document6 pages11 Root Locus 1athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 9-Steady State ErrorDocument4 pages9-Steady State ErrorathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 9 - Steady State 2Document7 pages9 - Steady State 2athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 7-Block Diagram Reduction Notes2Document6 pages7-Block Diagram Reduction Notes2athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Ee 131 Problem SetDocument3 pagesEe 131 Problem SetathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 6 Stability HandoutDocument3 pages6 Stability HandoutathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 6 Stability Routh Hurwitz BasicDocument2 pages6 Stability Routh Hurwitz BasicathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- EE 170 Problem Set 1 AY 2010-2011 2 SemDocument1 pageEE 170 Problem Set 1 AY 2010-2011 2 SemathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 6-Stability Routh Hurwitz SPECIALDocument1 page6-Stability Routh Hurwitz SPECIALathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Handout 131Document3 pages5 - Handout 131athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument2 pagesControl SystemsathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Simplest Form of A Block DiagramDocument7 pagesSimplest Form of A Block DiagramathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Handout 131Document4 pages4 - Handout 131athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline 131Document3 pagesCourse Outline 131athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Handout 131Document4 pages4 - Handout 131athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Introduction HandoutDocument3 pagesIntroduction Handoutathenalavega100% (1)
- Set Elements: Lecture Notes A. Set DefinitionsDocument4 pagesSet Elements: Lecture Notes A. Set DefinitionsathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Simplest Form of A Block DiagramDocument7 pagesSimplest Form of A Block DiagramathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- EE170-Problem Set 3Document1 pageEE170-Problem Set 3athenalavega100% (1)
- EE170-Problem Set 3Document1 pageEE170-Problem Set 3athenalavega100% (1)