Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acoustical Leak Detectors
Uploaded by
bingwazzup0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views2 pagesLeak detectors are used to detect the increased noise created by a leaking pipe. Leaks from a pressurized pipe will make a whoosh or hiss as it leaves a pipe orifice. The intensity of the leak will be proportional to the pressure in the pipe.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLeak detectors are used to detect the increased noise created by a leaking pipe. Leaks from a pressurized pipe will make a whoosh or hiss as it leaves a pipe orifice. The intensity of the leak will be proportional to the pressure in the pipe.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views2 pagesAcoustical Leak Detectors
Uploaded by
bingwazzupLeak detectors are used to detect the increased noise created by a leaking pipe. Leaks from a pressurized pipe will make a whoosh or hiss as it leaves a pipe orifice. The intensity of the leak will be proportional to the pressure in the pipe.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
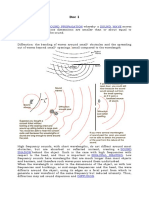
Acoustical Leak Detectors
When liquids are leaking from a pipe or other carrying medium that are
buried underground, they emit an audible noise when leaving the pipe
through a hole. Acoustic leak detectors are used to detect the
increased noise created by a leaking pipe in order to identify the
location of a leak to subsequently fix without having to waste money
on widespread exploration and investigation to find the source of a
leak.
Why Do Water Leaks Make Noise?
The sound of a leak from a pressurized pipe will make a number of
noises. The leak will produce a whoosh or hiss as it leaves a pipe orifice
and a slashing sound when flowing around a pipe. If the pressure of a
leaking pipe is more than 30 psi, it will produce an audible “hissing”
noise. Other sounds may or may not be produced by a leaking pipe
depending on the type of fluid and pressure that the pie is under.
What Factors Affect the Noise from a Leaking
Pipe?
Acoustic leak detectors take advantage of several factors that are
common amongst leaking pipes. These include the soil type and
compaction that the pipe is buried under, the pressure in the pipe,
depth of soil covering the pipe, pipe diameter and mater, and the
surface cover over top the pipe (asphalt, concrete, dirt, or grass). The
intensity of the leak will be proportional to the pressure the pipe in
under and the top cover and depth over the top of the pipe. Acoustic
leak detectors will have issues finding leaks in pipes buried deeper
than seven or eight feet that are not considered large leaks.
How Do Pipes Convey Sound?
Metal, copper, and steel pipes will convey the sound of leaks for
hundreds of feed in all directions. Pipes that are made of PVC or
asbestos-cement will not transmit sound as far with detectable ranges
being from 50 to 200 feet.
How Do Acoustic Leak Detectors Work?
Acoustic leak detectors are used to localize the location of potential
leaks for underground pipes. A monitoring system is used by a person
assigned to survey a potential leak area moving three to four feet at a
time with an acoustic listening device that uses a microphone set to a
constant volume to make measurements of the sounds detected from
the ground and displays results on a visual display to mark the
difference in sound output as the survey is conducted. If the loudness
significantly increases as any single point or points along the survey
route, then that location is identified as a spot to dig to verify the
existence of a leak on the pipe.
Source: http://www.tech-faq.com/acoustical-leak-detectors.html
You might also like
- Puma Diesel Engine Camshaft Removal & Installation GuideDocument9 pagesPuma Diesel Engine Camshaft Removal & Installation GuideJam Bab100% (1)
- The Radio Armateur Microwave Communications HandbookDocument192 pagesThe Radio Armateur Microwave Communications HandbookRapee Dev100% (1)
- A Brief Guide To The Pipe OrganDocument6 pagesA Brief Guide To The Pipe OrganAdeboye Adekola ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Directed Energy WeaponsDocument368 pagesDirected Energy WeaponsPete Santilli100% (1)
- 2012 Toyota Prius C WMGDocument58 pages2012 Toyota Prius C WMGbuddhikasatNo ratings yet
- Behavioral and Cognitive Effects of Microwave ExposureDocument24 pagesBehavioral and Cognitive Effects of Microwave Exposurebingwazzup100% (1)
- Acoustics PDFDocument15 pagesAcoustics PDFAllen YumangNo ratings yet
- RA The Book Vol 3: The Recording Architecture Book of Studio DesignFrom EverandRA The Book Vol 3: The Recording Architecture Book of Studio DesignNo ratings yet
- The Invisible Third World War by W. H. Bowart and Richard SuttonDocument35 pagesThe Invisible Third World War by W. H. Bowart and Richard Suttonhisroyalslynessone2funkNo ratings yet
- RA The Book Vol 2: The Recording Architecture Book of Studio DesignFrom EverandRA The Book Vol 2: The Recording Architecture Book of Studio DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- DST-PC, 02 PossibilitiesDocument35 pagesDST-PC, 02 PossibilitiestrutleptNo ratings yet
- Flute LabDocument8 pagesFlute Lablexard1No ratings yet
- TGT - Spectral Noise LoggingDocument5 pagesTGT - Spectral Noise LoggingrnoordinNo ratings yet
- Infra SoundDocument7 pagesInfra Soundbingwazzup100% (1)
- Dfe 29 JGDocument91 pagesDfe 29 JGKale ArbroughNo ratings yet
- POMI BoQ Pkg-4Document1,020 pagesPOMI BoQ Pkg-4Nicholas SmithNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Sound in An Enclosed SpaceDocument14 pagesBehaviour of Sound in An Enclosed Spacesanchit gupta100% (1)
- Acoustic Liquid Level Measurement Fundamentals GuideDocument33 pagesAcoustic Liquid Level Measurement Fundamentals GuideLuis Enrique Muñoz SeguraNo ratings yet
- Scada Ems PDFDocument35 pagesScada Ems PDFGaliousNo ratings yet
- DEW Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument3 pagesDEW Electromagnetic SpectrumbingwazzupNo ratings yet
- All About SOUND WAVESDocument5 pagesAll About SOUND WAVESAsuncion TheaNo ratings yet
- History of Acoustics MilestonesDocument13 pagesHistory of Acoustics Milestonessadhana illaNo ratings yet
- HP LP Bypass System (Turbine)Document9 pagesHP LP Bypass System (Turbine)Debasish Dewan67% (3)
- SoundDocument7 pagesSoundTatenda ChirobeNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves Lecture PPT (Wave Motion Part 2)Document37 pagesSound Waves Lecture PPT (Wave Motion Part 2)Leilani Manalaysay100% (1)
- Acoustics and LightingDocument16 pagesAcoustics and LightingDaryl Gomez TimatimNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Definations and DefectsDocument12 pagesAcoustic Definations and Defectstejaswini C gaur100% (2)
- Ultrasonic FlowmeterDocument24 pagesUltrasonic FlowmeterSaitej Tst100% (1)
- Character of SoundDocument35 pagesCharacter of SoundVinayak DodagoudarNo ratings yet
- Common Types of Pipe Defects PDFDocument7 pagesCommon Types of Pipe Defects PDFMichael LauNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.7Document8 pagesLesson 6.7pkrajenpillaiNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Acoustics (12 Hours) : Characteristics of SoundDocument12 pagesUnit I Introduction To Acoustics (12 Hours) : Characteristics of SoundRupa RajNo ratings yet
- Sound - Grade 6Document3 pagesSound - Grade 6Rathika SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 23 PHY STANDING WAVE SssDocument2 pages23 PHY STANDING WAVE SssDerpy 1028 (Cheah Wei Jian)No ratings yet
- Acoustic Wave Attenuation Through Buried Water MainsDocument8 pagesAcoustic Wave Attenuation Through Buried Water MainsPablo Cesar TrejoNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic: SoundDocument16 pagesPhysics Topic: SoundMariyam WaheedNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument28 pagesAcousticsKanika Maheshwari100% (1)
- Auditorium Acoustics 101: by Arthur NoxonDocument4 pagesAuditorium Acoustics 101: by Arthur NoxonMani MuruganNo ratings yet
- Elson, Arthur. Architectural AcousticsDocument15 pagesElson, Arthur. Architectural AcousticsTomas BarbagliaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshoot Rod Pumped Wells With Tubing Fluid Shots SWPSC 2014Document10 pagesTroubleshoot Rod Pumped Wells With Tubing Fluid Shots SWPSC 2014point blankNo ratings yet
- Compression Wave. What That Means Is That Sound: Problem: Make An Instrument Out of PVC PipeDocument3 pagesCompression Wave. What That Means Is That Sound: Problem: Make An Instrument Out of PVC PipeAlex RojasNo ratings yet
- Sound AttenuationDocument6 pagesSound AttenuationVictor Javier PerniaNo ratings yet
- Bored Pile - Integrity TestDocument2 pagesBored Pile - Integrity TestvisvisvisvisNo ratings yet
- A Way To Reduce Traffic Noise PollutionDocument16 pagesA Way To Reduce Traffic Noise Pollutionbu03haizul100% (1)
- Acoustics 01Document15 pagesAcoustics 01Ybette Anorico VillamarinNo ratings yet
- 2-Drainage PipingDocument3 pages2-Drainage PipingEugene MicarandayoNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument5 pagesSoundShubhamSoodNo ratings yet
- Reflection of SoundDocument12 pagesReflection of SoundAman LilaniNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument5 pagesSoundbritsomaxmillianNo ratings yet
- Sound: Aakanksha Sharma Ix-FDocument16 pagesSound: Aakanksha Sharma Ix-FAnnam JohnNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Done by Teacher::: Misckha Babwah & Rihana Seepersad Mr. GonzalesDocument3 pagesPhysics Project Done by Teacher::: Misckha Babwah & Rihana Seepersad Mr. GonzalesMisckha BabwahNo ratings yet
- Sound Recording LabDocument6 pagesSound Recording Labapi-458265595No ratings yet
- Acoustics: Acoustics of Building IncludeDocument16 pagesAcoustics: Acoustics of Building IncludeRohith ReddyNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument4 pagesResearchmiaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics FirstDocument80 pagesAcoustics FirstRekha SNo ratings yet
- Science of Sound Dealing With Wanted and Unwanted Sounds, Assures Optimum Conditions For Producing and Listing To Speech, Music .Document37 pagesScience of Sound Dealing With Wanted and Unwanted Sounds, Assures Optimum Conditions For Producing and Listing To Speech, Music .Satyajit MalNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument47 pagesAcousticsnidhimagoonNo ratings yet
- How sound waves are used in everyday lifeDocument10 pagesHow sound waves are used in everyday lifeSj Miasco-MejongNo ratings yet
- How Sound is Produced and PropagatedDocument5 pagesHow Sound is Produced and PropagatedNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- V. Vidal Et Al - Acoustic Signal Associated With The Bursting of A Soap Film Which Initially Closes An Overpressurized Cavity: Experiment and TheoryDocument19 pagesV. Vidal Et Al - Acoustic Signal Associated With The Bursting of A Soap Film Which Initially Closes An Overpressurized Cavity: Experiment and TheoryYamveaNo ratings yet
- STPM Physic CourworkDocument6 pagesSTPM Physic CourworkdurianganNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Theory of SoundDocument20 pagesIntroduction and Theory of SoundAditha Varma RajaNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument1 pageWave琬惠No ratings yet
- Acoustic For Civil EnggDocument4 pagesAcoustic For Civil EnggBRGRNo ratings yet
- Sound Propagation Sound Wave Wavelength: DiffractionDocument8 pagesSound Propagation Sound Wave Wavelength: DiffractionAUTO CADDYNo ratings yet
- BLDG - Utilities3 RSW#1 - Ferrer - Zildjian - M.Document25 pagesBLDG - Utilities3 RSW#1 - Ferrer - Zildjian - M.Zj FerrerNo ratings yet
- Reveiw Arch-2010 Acoustics and LightingDocument15 pagesReveiw Arch-2010 Acoustics and LightingiloilocityNo ratings yet
- Ch15 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science NotesDocument8 pagesCh15 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science NotesONE CLICK COMPUTERNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. SoundDocument4 pagesUnit 4. SoundGine LópezNo ratings yet
- Csat 11Document52 pagesCsat 11Mossad NewsNo ratings yet
- Non-Lethal Weaponry: Applications To Ac-130 GunshipsDocument36 pagesNon-Lethal Weaponry: Applications To Ac-130 Gunshipsbingwazzup100% (1)
- Nonlethal Weapons and CapabilitiesDocument74 pagesNonlethal Weapons and Capabilitiesbingwazzup100% (2)
- Auditory Response To Pulsed Radiofrequency EnergyDocument12 pagesAuditory Response To Pulsed Radiofrequency Energybingwazzup100% (1)
- Implementing A Digital Tracker For Monopulse Radar Using The TMS320C40 DSPDocument26 pagesImplementing A Digital Tracker For Monopulse Radar Using The TMS320C40 DSPbingwazzupNo ratings yet
- Remote Mobile Monitoring and Communications Systems (US Patent # 5870029)Document7 pagesRemote Mobile Monitoring and Communications Systems (US Patent # 5870029)bingwazzup100% (1)
- The Use of RFID For Human Identification A DRAFT REPORT From DHS Emerging Applications and Technology SubcommitteeDocument14 pagesThe Use of RFID For Human Identification A DRAFT REPORT From DHS Emerging Applications and Technology SubcommitteespectabearNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Interrogating System and Exciter-Detector Circuit ThereforDocument12 pagesUltrasonic Interrogating System and Exciter-Detector Circuit ThereforbingwazzupNo ratings yet
- Ip Multicast Part1Document18 pagesIp Multicast Part1Pallab PalNo ratings yet
- An Investigation On The Physiological and Psychological Effects of Infrasound On PersonsDocument6 pagesAn Investigation On The Physiological and Psychological Effects of Infrasound On Personsbingwazzup100% (1)
- A Low-Cost Approach To FMCW Radar: Through-Wall Microwatt RadarDocument28 pagesA Low-Cost Approach To FMCW Radar: Through-Wall Microwatt Radarbingwazzup100% (1)
- Model of A Monopulse Radar Tracking System For Student LaboratoryDocument6 pagesModel of A Monopulse Radar Tracking System For Student Laboratorybingwazzup100% (1)
- Model of A Monopulse Radar Tracking System For Student LaboratoryDocument6 pagesModel of A Monopulse Radar Tracking System For Student Laboratorybingwazzup100% (1)
- Apparatus and Methods Using Acoustic Telemetry For Intrabody CommunicationsDocument18 pagesApparatus and Methods Using Acoustic Telemetry For Intrabody CommunicationsbingwazzupNo ratings yet
- Random Noise Monopulse Radar System For Covert Tracking of TargetsDocument10 pagesRandom Noise Monopulse Radar System For Covert Tracking of TargetsbingwazzupNo ratings yet
- Frequency Choice For Radio Telemetry: HF-vs-VHF-ConundrumDocument7 pagesFrequency Choice For Radio Telemetry: HF-vs-VHF-Conundrumbingwazzup100% (1)
- An Overview of Acoustic TelemetryDocument11 pagesAn Overview of Acoustic TelemetrybingwazzupNo ratings yet
- Apparatus and Methods Using Acoustic Telemetry For Intrabody CommunicationsDocument18 pagesApparatus and Methods Using Acoustic Telemetry For Intrabody CommunicationsbingwazzupNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Digital Tracker For Monopulse Radar Using The TMS320C40 DSPDocument26 pagesImplementing A Digital Tracker For Monopulse Radar Using The TMS320C40 DSPbingwazzupNo ratings yet
- Radio Direction FinderDocument78 pagesRadio Direction Finderbingwazzup100% (1)
- An Investigation On The Physiological and Psychological Effects of Infrasound On PersonsDocument6 pagesAn Investigation On The Physiological and Psychological Effects of Infrasound On Personsbingwazzup100% (1)
- Aerial Laser ScanningDocument244 pagesAerial Laser Scanningbingwazzup100% (1)
- An Overview of Acoustic TelemetryDocument11 pagesAn Overview of Acoustic TelemetrybingwazzupNo ratings yet
- Random Noise Monopulse Radar System For Covert Tracking of TargetsDocument10 pagesRandom Noise Monopulse Radar System For Covert Tracking of TargetsbingwazzupNo ratings yet
- 4TEC3F60B1000ADocument21 pages4TEC3F60B1000ABlackdragon86No ratings yet
- Susol-UL-ACB E 1903 10Document100 pagesSusol-UL-ACB E 1903 10miguelpaltinoNo ratings yet
- Rotary Actuators-Sept 05Document8 pagesRotary Actuators-Sept 05Eng-Mohammed SalemNo ratings yet
- PRIORITY SECTOR LENDING CATEGORIESDocument23 pagesPRIORITY SECTOR LENDING CATEGORIESSONALI HIREKHANNo ratings yet
- TeSys Deca Contactors - LC1D326SDDocument4 pagesTeSys Deca Contactors - LC1D326SDaligamers70No ratings yet
- Narayana GT 5 QPDocument17 pagesNarayana GT 5 QPGowri Shankar100% (1)
- Flowserve Series 59Document4 pagesFlowserve Series 59Sidney RiveraNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Performance Analysis Matlab CodeDocument10 pagesWind Turbine Performance Analysis Matlab CodeChua Kah LiangNo ratings yet
- Warehouse and StorageDocument3 pagesWarehouse and StorageAnonymous mO72yqNcNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics Question PaperDocument27 pagesBusiness Ethics Question PaperPoonamlims100% (1)
- Feedback Control, History of TechnologyDocument16 pagesFeedback Control, History of TechnologyToni CamponiNo ratings yet
- Trane S9V2 Installer Guide ManualDocument104 pagesTrane S9V2 Installer Guide Manualed wNo ratings yet
- List of Approved Makes of Products by HQ CE CC (2020-21)Document32 pagesList of Approved Makes of Products by HQ CE CC (2020-21)GNV Engg ServicesNo ratings yet
- CT PDFDocument3 pagesCT PDFMr PahleviNo ratings yet
- Electric BrewingDocument5 pagesElectric BrewingxmacabaNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet H7..N: Type OverviewDocument4 pagesTechnical Data Sheet H7..N: Type OverviewEmir SabicNo ratings yet
- Proposed Medium-Rise Apartment Building Design AssessmentDocument17 pagesProposed Medium-Rise Apartment Building Design AssessmentRaynier LigayaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On Air Conditioning SystemDocument1 pagePractice Problems On Air Conditioning Systemsushil.vgiNo ratings yet
- Uzma - TB Press Release - Nza FinalDocument3 pagesUzma - TB Press Release - Nza Finalredevils86No ratings yet
- 2012Ch1 Supple NotesDocument12 pages2012Ch1 Supple Notesskywalker_handsomeNo ratings yet
- Colorful Convection CurrentsDocument2 pagesColorful Convection CurrentsJustin LoredoNo ratings yet
- EE 152 Chapter 3Document53 pagesEE 152 Chapter 3Gideon AdomNo ratings yet
- An Active-Clamp Push-Pull Converter For Battery Sourcing ApplicationsDocument9 pagesAn Active-Clamp Push-Pull Converter For Battery Sourcing ApplicationsYury KrivtsovNo ratings yet