Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OR
Uploaded by
samadonyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
OR
Uploaded by
samadonyCopyright:
Available Formats
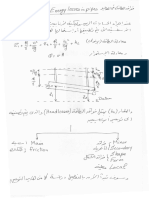
CFD ASSESSMENT OF OPERATING ROOM
HVAC SYSTEMS DESIGN
Mahmoud Fouad* and M. Osama El samadony**
* Professor ** Graduate research student
Mechanical Power Engineering Department, Cairo University, Egypt
Faculty of Engineering, Cairo University, El-Gamma Avenue, Giza, Egypt
ABSTRACT
In this paper computational fluid dynamics (CFD) techniques are used to evaluate the
efficiency of operating room HVAC systems in minimizing the risk of postoperative infection.
Seven different design configurations of operating room HVAC systems have been compared
numerically to assess their agreement with international standards of operating room
ventilation and airflow pattern requirements. The ventilation systems designs considered are
built-in using different air outlet devices, usual, laminar, non-aspirating, and slot diffuser
types. The airflow pattern of each configuration has been analyzed in terms of airflow
vectors, velocities, and turbulent intensity, and pollutant concentration distribution. It was
concluded that all the systems except for the non laminar flow one fulfilled well the
requirements of operating room ventilation, but, that unidirectional airflow with curtain and
zoned exponential unidirectional airflow configurations are the most versatile and energy
efficient.
Keywords: CFD, HVAC, operating room, anesthetic gases, Nitrous Oxide.
INTRODUCTION
Operating room is a complex environment that Lidewell2 and Whyte et al. intensively studied
requires ventilation for comfort and to control the transmission of airborne germs in operating
hazardous emissions for patients, and surgical rooms. These investigations resulted in the
staff. Indoor air quality is more critical in health finding that hygienic safety was definitely
care facilities than in most other indoor achieved if less than 10 CFU*/m3 air was
environments due to many dangerous microbial detected in the operating area.
and chemical agents present and due to the Several factors can affect postoperative
increased susceptibility of the patients, infection, including patient factors (e.g.,
especially immunosuppressed persons. susceptibility to infection), surgical field factors
(e.g., the thermal plume from the site), room
The contamination of operating room air with factors (e.g., cleanliness of the operating room),
microbes and viruses is considered as a major and HVAC factors (e.g., air change rate [ACH]
risk factor for surgical site infection (SSI). It and direction of airflow).
was been reported that 80-90% of bacterial Healthcare personnel can also react negatively
contamination found in an open wound comes to cleaning materials, sterilants, disinfectants,
from ambient air1. Operating room air may and anesthetic gases.
contain microbial-laden dust, lint, skin squames, The anesthetic gas and vapors that leak out and
or respiratory droplets. into the surrounding room during medical
* CFU - Colony Forming Unit
1 1st. National conference on “Human performance in health and disability”, Egyptian Society of Fitness, Disability & Environmental Health
(ESFDEH), March 10-11, 2004, Cairo.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Effect of EMF On Human BeingDocument37 pagesEffect of EMF On Human BeingsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On StaticsDocument121 pagesLecture Notes On StaticsМарко Шилобод75% (4)
- Radiation Protection 2018Document213 pagesRadiation Protection 2018Ricardo EdanoNo ratings yet
- The Holy Grail of Curing DPDRDocument12 pagesThe Holy Grail of Curing DPDRDany Mojica100% (1)
- Part B - System of Equations For Pipe NetworkDocument137 pagesPart B - System of Equations For Pipe Networksamadony100% (2)
- Dr. LakshmayyaDocument5 pagesDr. LakshmayyanikhilbNo ratings yet
- Audits, Gap Assessments, CAPA - 0Document230 pagesAudits, Gap Assessments, CAPA - 0mgvtertv100% (3)
- Basic Principles of Cross-Examination: Claire F. RushDocument14 pagesBasic Principles of Cross-Examination: Claire F. RushSellappan RathinamNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Precision Performance of Quantitative Measurement Methods Approved Guideline-Second EditionDocument56 pagesEvaluation of Precision Performance of Quantitative Measurement Methods Approved Guideline-Second EditionHassab Saeed100% (1)
- Pipeline Lec01Document92 pagesPipeline Lec01samadonyNo ratings yet
- Static C/cs of MeasurementsDocument3 pagesStatic C/cs of MeasurementssamadonyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Pressure MeasurementsDocument65 pagesChapter 5 Pressure MeasurementssamadonyNo ratings yet
- Simulation of a hybrid solar dryerDocument5 pagesSimulation of a hybrid solar dryersamadonyNo ratings yet
- Schematic HRSG 65Document17 pagesSchematic HRSG 65aquilesanchezNo ratings yet
- Multi pressure vapor compression refrigerationDocument14 pagesMulti pressure vapor compression refrigerationsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Part A - Pipe FlowDocument268 pagesPart A - Pipe FlowsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Schematic HRSG 65Document17 pagesSchematic HRSG 65aquilesanchezNo ratings yet
- Lab NotesDocument107 pagesLab NotessamadonyNo ratings yet
- Condensation & Evaporation Processes in MicropipesDocument8 pagesCondensation & Evaporation Processes in MicropipessamadonyNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump ExperimentsDocument18 pagesCentrifugal Pump ExperimentssamadonyNo ratings yet
- Lectures On Pipe FlowDocument48 pagesLectures On Pipe FlowsamadonyNo ratings yet
- AC-Training II.2 Cooling DistributionDocument94 pagesAC-Training II.2 Cooling DistributionsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Rankine ThaiDocument40 pagesSteam Power Rankine ThaisamadonyNo ratings yet
- HartungDocument5 pagesHartungsamadonyNo ratings yet
- AirpreheaterDocument7 pagesAirpreheatersamadonyNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Health Air FlowDocument3 pagesVentilation Health Air FlowsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Indoor Air PollutionDocument4 pagesIndoor Air PollutionsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Ventricle Assist Devices - ReviewDocument39 pagesVentricle Assist Devices - ReviewsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow ReviewDocument12 pagesPipe Flow ReviewsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Rectangular FinsDocument119 pagesRectangular FinssamadonyNo ratings yet
- SBSDocument108 pagesSBSsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Trusses and FramesDocument12 pagesTrusses and FramessamadonyNo ratings yet
- TrussesDocument59 pagesTrussessamadony100% (1)
- TrussesDocument49 pagesTrussessamadony100% (2)
- System of Equations For Pipe Network - OsamaDocument30 pagesSystem of Equations For Pipe Network - OsamasamadonyNo ratings yet
- EGR231 Lecture24Trusses Method of SectionsDocument7 pagesEGR231 Lecture24Trusses Method of Sectionssamadony0% (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing 6th Edition Keltner Test BankDocument35 pagesPsychiatric Nursing 6th Edition Keltner Test Bankfrustumslit.4jctkm100% (26)
- Atls 1Document5 pagesAtls 1Mega MalyndaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nutrition and Nutritional Disorders: PediatricsDocument4 pagesPediatric Nutrition and Nutritional Disorders: Pediatricsapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Investigations For Diseases of The Tongue A Review PDFDocument6 pagesInvestigations For Diseases of The Tongue A Review PDFShantanu DixitNo ratings yet
- Assessmen Ttool - Student AssessmentDocument5 pagesAssessmen Ttool - Student AssessmentsachiNo ratings yet
- HRFuture Sept 2020 MJLKJDocument59 pagesHRFuture Sept 2020 MJLKJGlecy KimNo ratings yet
- MHFL Functional FoodsDocument24 pagesMHFL Functional FoodsZekel HealthcareNo ratings yet
- Al Shehri 2008Document10 pagesAl Shehri 2008Dewi MaryamNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Pediatric Cardiology Division University of Sumatera UtaraDocument40 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Pediatric Cardiology Division University of Sumatera UtaraHanda YaniNo ratings yet
- 80-Article Text-264-1-10-20200729Document6 pages80-Article Text-264-1-10-20200729ulfaNo ratings yet
- Psihogeni Neepileptički Napadi Kao Dijagnostički Problem: AutoriDocument4 pagesPsihogeni Neepileptički Napadi Kao Dijagnostički Problem: AutorifhdhNo ratings yet
- OGL 481 Pro-Seminar I: PCA-Ethical Communities Worksheet Erica KovarikDocument4 pagesOGL 481 Pro-Seminar I: PCA-Ethical Communities Worksheet Erica Kovarikapi-529016443No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Pharmacy Law and Ethics Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document4 pagesChapter 14 Pharmacy Law and Ethics Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Shamant TNo ratings yet
- Physio Ex Exercise 6 Activity 4Document5 pagesPhysio Ex Exercise 6 Activity 4Roland Calipayan Jr.No ratings yet
- Drug Study Kalium DuruleDocument2 pagesDrug Study Kalium DuruleGrant Kenneth Dumo AmigableNo ratings yet
- REAL in Nursing Journal (RNJ) : Penatalaksanaan Pasien Rheumatoid Arthritis Berbasis Evidence Based Nursing: Studi KasusDocument7 pagesREAL in Nursing Journal (RNJ) : Penatalaksanaan Pasien Rheumatoid Arthritis Berbasis Evidence Based Nursing: Studi Kasustia suhadaNo ratings yet
- NOAA Sedimento 122 Squirt CardsDocument12 pagesNOAA Sedimento 122 Squirt CardshensilNo ratings yet
- Guide To Referencing and Developing A BibliographyDocument26 pagesGuide To Referencing and Developing A BibliographyAHSAN JAVEDNo ratings yet
- Charakam Sidhistanam: Vamana Virechana Vyapat SidhiDocument45 pagesCharakam Sidhistanam: Vamana Virechana Vyapat Sidhinimisha lathiffNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Fundamental Nursing Skills and Concepts Tenth EditionDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Fundamental Nursing Skills and Concepts Tenth Editionooezoapunitory.xkgyo4100% (41)
- Botany (Virus)Document48 pagesBotany (Virus)Madhuri DeviNo ratings yet
- New TNMDocument157 pagesNew TNMShouvik ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Endocervical PolypDocument2 pagesEndocervical PolypRez007No ratings yet
- MadRiverUnion01 13 21editionDocument8 pagesMadRiverUnion01 13 21editionMad River UnionNo ratings yet