Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Appraising Employee Performance
Uploaded by
Rona Richard0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views3 pagesA good performance appraisal must be as simple as possible. It must provide the basis or standards for appraisingbsatisfactory performance. The most common practice is for the manager to rate his subordinates.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA good performance appraisal must be as simple as possible. It must provide the basis or standards for appraisingbsatisfactory performance. The most common practice is for the manager to rate his subordinates.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views3 pagesAppraising Employee Performance
Uploaded by
Rona RichardA good performance appraisal must be as simple as possible. It must provide the basis or standards for appraisingbsatisfactory performance. The most common practice is for the manager to rate his subordinates.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
APPRAISING EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE
• Performance appraisal may be defined as the method by which, through
observation by the appraiser, the individual worker’s efficiency in performing
his duties and responsibilities during a given period is evaluated on the basis
of predetermined performance standards or established goals mutually set by
the employeeand his supervisor
WHY STUDY PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL
• Understand the objectives and principles of appraising the performance of
employees
• Know the different types of performance rating plan that will fit a company
• Learn how to formulate and install an employee appraisal program in a
company
• Learn how to evaluate the performance of an employee and communicate
the results of the appraisal in a way that the employee will understand and
accept them
PERFORMANCE DISTINGUISHED FROM DUTIES
• Duties and responsibilities- what should be done, the rendering of what is due
any person or organization, and the fulfillment of moral obligations.
• Performance- how much should be done or accomplished, its quality, and the
manner in which it is done
THE OBJECTIVES OF AN EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE RATING SYSTEM
1. Providing feedback on employee performance
2. Basis for personnel action
3. Management guide in employee counseling and discipline
4. Promotion of better employee-employer relations
5. Improvement of supervision by making the supervisor better aware of his
duties.
6. Development of employees and supervisors
7. As an agent of change
8. Identification of training needs and management development
9. Facilitate organizational diagnosis and development
METHODS USED IN PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL
1. Rank Order Method
2. Paired Comparison Method
3. Forced Distribution System
4. Narrative Essay
5. Graphic Rating Scale
6. Preference Checklist Method
7. Crirical Incidents
8. Rating Scale Method
9. Weighing
10.Management by Objectives or Results Oriented Method
QUALITIES OF A GOOD APPRAISAL FORM
1. It must be as simple as possible
2. It must provide the basis or standards for appraisingbsatisfactory
performance
3. It must be flexible
4. It must be thorough
5. It must provide for a definite control over personal biases and
prejudices
6. Whenever possible, it should provide for two or more independent
evaluations of each employee
7. It must provide for a training program for supervisors who will rate
their subordinates.
WHO WILL DO THE RATING
• The most common practice is for the employees immediate supervisor to do
the rating inasmuch as it is he who assigns the work to the employee and
gives the instructions on how it should be done.
• Nevertheless, current trends point to the use of multi-raters: peers,
subordinates, clients, and the individual himself.
COMMON ERRORS IN RATING
1. Discrepancies in interpreting the meaning of factors
2. The halo effect
3. Logical error
4. Blaming subordinates for errors that are not their fault
5. Leniency
6. Severity
7. Central tendencies
8. Bias and prejudice
9. Previous performance bias
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Evaluating Training Programs The Four Levels by Kirkpatrick: Sajid Mahsud Abdul AzizDocument30 pagesEvaluating Training Programs The Four Levels by Kirkpatrick: Sajid Mahsud Abdul AzizSajid MahsudNo ratings yet
- Data Gathering ProcedureDocument3 pagesData Gathering ProcedureMichelle MahingqueNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE DLL February 19-23, 2019Document2 pagesSCIENCE DLL February 19-23, 2019Geraldine Dioquino RosalesNo ratings yet
- Preventing Compassion FatigueDocument31 pagesPreventing Compassion Fatigueshannon_cortez_375% (4)
- Behavioural Excess Is An Undesirable Target Behaviour The Person Wants To Decrease in FrequencyDocument10 pagesBehavioural Excess Is An Undesirable Target Behaviour The Person Wants To Decrease in FrequencyGodwin EzekielNo ratings yet
- WPP Aunz Academy Booklet CMPSD2Document45 pagesWPP Aunz Academy Booklet CMPSD2Mohd. ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- ITL 600 Group Presentation Week 3Document11 pagesITL 600 Group Presentation Week 3Lisa CarsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Aid: Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing 1: Lester R. L. LintaoDocument14 pagesLecture Aid: Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing 1: Lester R. L. LintaoEsarpy (Nana)No ratings yet
- Dll-Finalized Cot 1Document2 pagesDll-Finalized Cot 1Rose Caro100% (1)
- Nielsen, T.Document10 pagesNielsen, T.Amanda MunizNo ratings yet
- Empirically Supported Complexity: Rethinking Evidence-Based Practice in PsychotherapyDocument6 pagesEmpirically Supported Complexity: Rethinking Evidence-Based Practice in PsychotherapyPedro VargasNo ratings yet
- Six Key Elements in Organizational DesignDocument4 pagesSix Key Elements in Organizational DesignAnonymous KL1eXHNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Reciprocal TeachingDocument36 pagesThe Impact of Reciprocal Teachingborgek11100% (2)
- HRM Reference NotesDocument29 pagesHRM Reference NotesSaher KapdiNo ratings yet
- LinkedIn Article - Leadership BehaviorsDocument3 pagesLinkedIn Article - Leadership BehaviorsAL-HAMD GROUP100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument9 pagesDaily Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJhinete Rizada EstoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan GNM I Year Psychology (Frustration)Document8 pagesLesson Plan GNM I Year Psychology (Frustration)Anonymous 0C4OZmRNo ratings yet
- Theories of MotivationDocument21 pagesTheories of Motivationankushsingh00771% (7)
- Listening - Artefact 2 GruffaloDocument5 pagesListening - Artefact 2 Gruffaloapi-551140746No ratings yet
- Managing Performance Through Training and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesManaging Performance Through Training and DevelopmentHusain KitabiNo ratings yet
- Leadership-Scenario 1: Running Head: ASSESSMENT 2 CAFSDocument7 pagesLeadership-Scenario 1: Running Head: ASSESSMENT 2 CAFSSarah MNo ratings yet
- Internship EssaysDocument5 pagesInternship EssaysJoshua GonsherNo ratings yet
- Donner Hannah Classroom Observation Reflection Lai574Document7 pagesDonner Hannah Classroom Observation Reflection Lai574api-302206294No ratings yet
- Sport Psychology: Sabrina JefferyDocument13 pagesSport Psychology: Sabrina Jefferycsarimah csarimah100% (1)
- Lesson 1Document2 pagesLesson 1Leonora Erika RiveraNo ratings yet
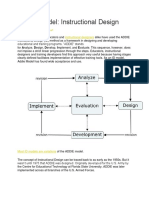
- ADDIE ModelDocument12 pagesADDIE ModelMel Bautista DomingoNo ratings yet
- Contoh - Laporan - Bab 2Document3 pagesContoh - Laporan - Bab 2Ayu komala sariNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesRutchelNo ratings yet
- The General Management in Basket GmibDocument50 pagesThe General Management in Basket GmibSneha ChuriwalNo ratings yet
- 07 TP HRMDocument1 page07 TP HRMRhealyn Jane MirafloresNo ratings yet