Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Form 4 Annual Teaching Plan (2011)
Uploaded by
debbycley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views13 pagesThe document outlines a science teaching plan for Form 4 students over 13 weeks. It covers topics in scientific investigation, the human body systems, heredity and variation. Some key learning objectives are to understand cell division, genetic inheritance, sex determination and the causes and effects of genetic variation and mutation. Students will learn through various thinking strategies like analysis, comparison and group activities to develop scientific attitudes.
Original Description:
annual plan
Original Title
f4 2011
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines a science teaching plan for Form 4 students over 13 weeks. It covers topics in scientific investigation, the human body systems, heredity and variation. Some key learning objectives are to understand cell division, genetic inheritance, sex determination and the causes and effects of genetic variation and mutation. Students will learn through various thinking strategies like analysis, comparison and group activities to develop scientific attitudes.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views13 pagesScience Form 4 Annual Teaching Plan (2011)
Uploaded by
debbycleyThe document outlines a science teaching plan for Form 4 students over 13 weeks. It covers topics in scientific investigation, the human body systems, heredity and variation. Some key learning objectives are to understand cell division, genetic inheritance, sex determination and the causes and effects of genetic variation and mutation. Students will learn through various thinking strategies like analysis, comparison and group activities to develop scientific attitudes.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
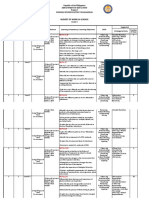
SCIENCE FORM 4 ANNUAL TEACHING PLAN (2011)
MONTH / THEME / LEARNING AREA / THINKING SKILLS SUGGESTE SCIENTIFIC
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES / LEARNING OUTCOMES / THINKING D T&L ATTITUDES AND
STRATEGIES ACTIVITIES NOBLE VALUES
THEME : INTRODUCING SCIENCE
Week 1 – 2 LEARNING AREA : 1. SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION
(03/01 – • Analyzing • Being
• Making Discussion systematic
14/01) 1.1 : Analyzing method of scientific investigation
conclusions • Being
• explain the steps in scientific investigation objective
• Relating
• carry out a scientific investigation
• write a report on a scientific investigation
• explain the importance of scientific
investigation
1.2 : Realizing the need to practice scientific
attitudes and noble values when
carrying out scientific investigation
• identify scientific attitudes and noble values
practised by scientists
• explain the need to practise scientific
attitudes and
noble values when carrying out a scientific
investigation
• practise scientific attitudes and noble values
when
carrying out a scientific investigation
THEME : MAINTENANCE AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
LEARNING AREA : 1. BODY COORDINATION
Week 3 – 7 1.1 : Understanding body coordination
• Analyzing Slide • Being
(17/01 – • describe what body coordination is presentation
• Making responsible
18/02) • identify the body systems that control and about the
conclusions
regulate coordination • Comparing Discussion safety of
• state the importance of body coordination and oneself,
contrasting Mind others and
1.2 : Understanding the human nervous system
• Synthesizin mapping/ the
• identify the component parts of the human concept environment
nervous system g
mapping • Being
• Visualizing
• state the function of each component part of thankful to
• Generating
the nervous system Groupwork & God
ideas
• state what a neurone is presentation • Thinking
• Evaluating
• identify the parts of a neurone rationally
• state the function of each part of the • Being
neurone confident
and
• identify the different types of the neurone independent
• state the function of each type of neurone
• compare and contrast different types of
neurone
1.3 : Analyzing nervous coordination
• state what receptors and effectors are
• state the functions of receptors and effectors
• explain with examples what a reflex action is
• describe a reflex arc
• illustrate the path taken by an impulse in the
reflex arc
1.4 : Understanding the role of proprioceptors in
maintaining balance and coordination
• explain what proprioceptors are
• explain the importance of proprioceptors
1.5 : Understanding the human brain and its
complexity
• identify the main parts of the human brain
• state the main functions of each part of the
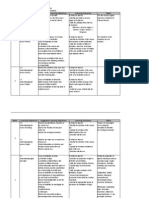
THEME : MAINTENANCE AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
Week 8 – 13 LEARNING AREA : 2. HEREDITY AND VARIATION
(21/02 –
• Analyzing Slide • Realizing
108/04) 2.1 : Understanding cell division
• Grouping presentation that science
• state what genes, deoxyribonucleic acids is a means to
and classifying
(DNA) and chromosomes are Group understand
• Comparing
• describe relationship between gene, DNA and discussion nature
and chromosome contrasting • Being
• state what mitosis is • Synthesizin Internet thankful to
research God
• describe the process of mitosis g
• state what meiosis is • Visualizing • Appreciati
• Generating ng the
• describe the process of meiosis contribution
ideas
• compare and contrast mitosis with meiosis of science
• explain the importance of mitosis and and
meiosis technology
2.2 : Understanding the principles and
mechanism of inheritance
• explain what dominnat genes and recessive
genes are
• identify dominant traits and recessive traits
in human
• illustrate the mechanism of inheritance of
traits using
a schematic diagram
• predict the genotype and phenotype ratios
of a monohybrid cross
2.3 : Understanding sex determination and the
occurrence of twins in human beings
• explain what sex chromosomes are
• explain how sex is determined
• explain the formation of identical and non-
identical twins
• compare and contrast between identical and
non-identical twins
• explain what siamese twins are
2.4 : Understanding mutation
• state what mutation is
• state the types of mutation
• list exampels of mutation
• identify causes of mutation
• state the advantages and disadvantages of
mutation
2.5 : Evaluating the effects of genetic research
on human life
• list the contributions of genetic research in
various fields
• explain selective breeding in plants and
livestock
• state the importance of selective breeding in
plants and livestock
• describe the technology used for selective
breeding
• present arguments for and against genetic
research
2.6 : Analyzing variation among living things
• state what variation is
• list variation in humans
• classify variation into continuos and
discontinuos variation
• compare and contrast continuous and
discontinuous variation
• identify factors that cause variation
• explain the importance of variation
2.7 : Realizing the need to adhere to a code of
ethics in genetic research
• explain how the misuse of knowledge in the
field of
• genetics can endanger life
• describe the importance of establishing and
adhering to
• ethics and morals in scientific research for the
benefit of mankind
March
Week 10 UJIAN GERAK MAHIR
(07/03 –
11/03)
Week 11 MID – SEM BREAK
(12/03 –
18/03)
April - May THEME : MATTER IN NATURE
Week 14 – LEARNING AREA : 1. MATTER AND SUBSTANCE
18
• Analyzing Discussion • Realizing
(04/04 – 1.1 : Analyzing changes in the states of matter
• Grouping that science
06/05) • explain the kinetic theory of matter Experimentin
and classifying is a means to
(a) relate changes in the heat to changes in g understand
• Making
kinetic energy of the particles in matter inferences nature
(b) explain the interconversion of the three • Making • Appreciati
states hypothesis ng the
of matter based on the kinetic theory • Generating balance of
matter ideas nature
1.2 : Understanding the structure of an atom • Evaluating
• describe the structure of an atom
• identify the subatomic particles
• compare and contrast the subatomic
particles
1.3 : Applying the idea of proton number and
nucleon number in atoms of elements
• state what proton number is
• state what nucleon number is
• relate the number of protons, neutrons, and
electrons
in an atom to its proton number and nucleon
number
• deduce the number of protons, electrons and
neutrons in atoms of different elements
• make a generalisation on the numbers of
protons
and electrons in atoms of different elements
• state what isotops are
• give examples of isotopes
1.4 : Understanding the classification of elements
in the Periodic Table
• describe the arrangment of elements in the
Periodic Table
• describe what is meant by groups and
periods in
THEME : ENERGY IN LIFE
Week 19 – LEARNING AREA : 1. ENERGY AND CHEMICAL
27 CHANGES
• Analyzing Experimentin • Realizing
(09/05 –
• Making g that science
08/07) 1.1 : Understanding physical and chemical
hypothesis is a means to
changes Discussion understand
• Generating
• explain whqt physical change is ideas nature
• explain what chemical change is • Sequencing • Appreciati
• give examples of physical changes in daily • Evaluating ng the
life • Predicting contribution
• give examples of chemical changes in life of science
and
• compare and contrast physical changes and technology
chemical changes
1.2 : Analyzing heat change in chemical reactions
• state that chemical reactions involve heat
change
• identify reactions involving heat loss
• identify reactions involving heat gain
• relate changes in temperature of reactants
to exothermic reactions
• relate changes in temperature of reactants
to endothermic reactions
• explain through examples heat changes that
occur during industrial chemical reactions
1.3 : Synthesizing the reactivity series of metals
• describe the reactivity of metals with water
• describe the reactivity of metals with acids
• describe the reactivity of metals with oxygen
• compare and contrast the reactivity of
metals
with water, acids and oxygen
• arrangge metals in order of reactivity
• construct the reactivity series of metals
based on
reactivity of metals and oxygen
• identify the position of carbon in the
reactivity series
Week 20 –
21 FIRST SEMESTER EXAM
(16/05 –
27/05)
Week 22 – MID-YEAR BREAK
23
(30/05 –
10/06)
THEME : ENERGY IN LIFE
LEARNING AREA : 2. NUCLEAR ENERGY
• Analyzing Group • Thinking
2.1 : Understanding radioactive substances
• Predicting discussion rationally
• state what radioactive substances are
• Making • Having
Week 28 – • give examples of radioactive substances Slide
hypothesis critical and
29 • describe the process of radioactive decay presentation analytical
(11/07 – thinking
• name the three types of radioactive
22/07)
radiations
• describe the characteristics of each type of
radioactive radiations
• compare and contrast radioactive radiations
• explain what radioisotopes are
• give examples of radioisotopes
• explain the uses of radioactive substances
2.2 : Understanding the production of nuclear
energy and its uses
• describe the production of nuclear energy
through fission
• describe the production of nuclear energy
through fusion
• state the uses of nuclear energy
• describe the process of generating electricity
from nuclear energy
• explain the effects of nuclear energy
production
2.3 : Awareness of the need for proper handling
of radioactive substances
• state the effects of radioactive radiations on
living things
• describe the correct way of handling
radioactive
• substances and radioactive waste
• explain the need for proper handling in
radioactive
• substances and radioactive waste
THEME : ENERGY IN LIFE
LEARNING AREA : 3. LIGHT, COLOUR, SIGHT
• Synthesizin Discussion • Realizing
Week 30 – 3.1 : Synthesizing the formation of image by
g that science
33 plane mirrors and lenses Slide
• Visualizing is a means to
(25/07 – • state the characteristics of images formed presentation understand
• Attributing
19/08) by a plane mirror nature
• Making
• state the characteristics of images formed hypothesis Experimentin • Appreciati
by a convex lens g ng the
• Generating
• state the characteristics of images formed ideas contribution
by a concave lens • Relating of science
and
• compare and contrast images of distant technology
objects formed by convex • Being
lenses and concave lenses honest and
• draw a labelled ray diagram to show the accurate in
formation of recording
image by light rays passing through a convex and
lens validating
• draw a labelled ray diagram to show the data
formation of
image by light rays passing through a
concave lens
• draw a labelled ray diagram to explain how
characteristics
of images formed by convex lenses vary with
object distance
• determine the focal length of a convex lens
3.2 : Synthesizing the formation of image by
optical instruments
• identify the parts of optical instruments
involved in image formation
• draw ray diagrams for light rays passing
through an
optical instrument
• compare and contrast the mechanisms in
focusing and
controlling the amount of light that enters
human eyes and a camera
Week 35
(29/08 – MID-SEMESTER BREAK
02/09)
September THEME : TECHONOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL
Week 34 – DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY
36 LEARNING AREA : 1. CHEMICALS IN INDUSTRY
(22/08 –
• Analyzing Slide • Realizing
08/09) 1.1 : Understanding the properties of alloys and presentation
• Predicting that science
their uses in industry is a means to
• Making
• state what an alloy is hypothesis Discussion understand
• give example of alloys • Generating nature
• explain how the formation of alloy can ideas Mind • Appreciati
change the mapping ng the
properties of metals balance of
nature
• relate the changes in the properties of
• Being
metals when they are
responsible
converted to alloys to the arrangment of about the
particles in the alloys safety of
• relate the properties of alloys to their uses in oneself,
daily life others and
• describe the importance of alloys in industry the
• state what superconductors alloys are environment
1.2 : Analyzing the production and uses of
ammonia in industry
• list the uses of ammonia and its compounds
in daily life
• describe how ammonia is produced in
industry
• state the factors which affect the production
of ammonia in industry
• state the industral uses of ammonia
• describe how ammonia is used to produce
ammonium salt fertilisers and urea
1.3 : Analyzing the effects of industrial waste
disposal on the environment
• identify manufacturing activities which are
sources of pollution
• explain the effects of improper industrial
waste disposal
• relate the effects of improper industrial
waste
disposal to the survival of living things
• state with examples the methods of
controlling
industrial waste disposal to avoid pollution
1.4 : Realizing the need for preservation and
conservation of the environment from industrial
waste pollution for the well being of mankind
• describe the consequences of uncontrolled
and haphazard
• disposal of industrial waste
• explain the importance of practising
responsible
• way of disposing industrial waste
Week 37 – 42 REVISION
(12/09 –
22/10)
Week 43 – 44 SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION
(24/10 –
04/11)
November – YEAR END SCHOOL’S HOLIDAY
December
Prepared by, Verified by,
____________________ ___________________
(DEBBIE CLEMENT) (JANNIE A. ROMAN)
Head of Science Panel. Head of Department of Science and Mathematics.
SMK Tun Fuad Stephens, Kiulu. SMK Tun Fuad Stephens, Kiulu.
You might also like
- Yearly Plan Science Form 4Document49 pagesYearly Plan Science Form 4Vikneswaran Gunahlan NeshNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 4 2016Document21 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 4 2016Wani MesraNo ratings yet
- Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2011Document28 pagesScience Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2011姚方祥No ratings yet
- Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Pahang Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2010Document28 pagesJabatan Pelajaran Negeri Pahang Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2010Rodzila GhadziNo ratings yet
- Yearly Teaching Plan 2Document1 pageYearly Teaching Plan 2Usop AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work Science 9Document3 pagesBudget of Work Science 9Abe JimenezNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 4 (201 )Document2 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 4 (201 )kudienaNo ratings yet
- Revised Bloom's Taxonomy: Dimaguila, Aaron Garfin, Ma. Rowena Bse-Ss IiiDocument17 pagesRevised Bloom's Taxonomy: Dimaguila, Aaron Garfin, Ma. Rowena Bse-Ss IiiAaron DimaguilaNo ratings yet
- Week Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesDocument35 pagesWeek Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesCatherine LeeNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Vivekananda 2015 Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4Document32 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Vivekananda 2015 Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4Nurul FarhanaNo ratings yet
- K12 Basic Education Curriculum MapDocument10 pagesK12 Basic Education Curriculum MapMary Chriszle Domisiw100% (1)
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010Document28 pagesScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010WanM.Syamim0% (1)
- Sains Tingkatan 4Document33 pagesSains Tingkatan 4Zulkifli Bin JaafarNo ratings yet
- 01 Welcome To The World of PsychologyDocument7 pages01 Welcome To The World of PsychologyTunahan OğuzNo ratings yet
- Psychology Major PO CODocument10 pagesPsychology Major PO COaritrayeebarman05No ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer (UTS)Document3 pagesFinals Reviewer (UTS)Kimberly GuinoNo ratings yet
- SMK Slim Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2011Document29 pagesSMK Slim Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2011Zulkifli Bin JaafarNo ratings yet
- PDF Diss q1 Mod7 Psychoanalysis Rational Choicepdf - CompressDocument22 pagesPDF Diss q1 Mod7 Psychoanalysis Rational Choicepdf - CompressRaiza CabreraNo ratings yet
- 06-F2022 - Midterm#1 ReviewDocument6 pages06-F2022 - Midterm#1 ReviewEmma MahoneyNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide 6 4Document88 pagesTeaching Guide 6 4Saleha Shoaib100% (2)
- F4 Physics Yearly PlanDocument14 pagesF4 Physics Yearly PlansaizassrNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearDocument68 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearNandita Ghosh100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearJerin CyriacNo ratings yet
- BSN SyllabusDocument75 pagesBSN SyllabusEllen ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 4Document33 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 4Abdullah Yusof AzzamNo ratings yet
- Yearly TP f4 2011Document32 pagesYearly TP f4 2011Haffiuzdin Bin Abd AzizNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work f52006Document18 pagesScheme of Work f52006ediNo ratings yet
- RPT Science FRM 2 PZADocument12 pagesRPT Science FRM 2 PZAapeenakallNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 SequenceDocument5 pagesGrade 4 SequenceSarah ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Weekly Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesWeekly Lesson PlanBea DoministoNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM Pilar College Anatomy Physiology Final EditDocument41 pagesMIDTERM Pilar College Anatomy Physiology Final EditYeona BaeNo ratings yet
- 5º - Unit 1 NaturalDocument10 pages5º - Unit 1 Naturalkarina guiradoNo ratings yet
- 1 CLA PrinciplesDocument35 pages1 CLA PrinciplesEira SethiNo ratings yet
- Week Learning Objectives and Outcomes Learning ActivitiesDocument13 pagesWeek Learning Objectives and Outcomes Learning ActivitiesNorazla MustafaNo ratings yet
- Lesson: How Does The Brain Work?Document22 pagesLesson: How Does The Brain Work?yair Enrique Romero OspinoNo ratings yet
- Theory - 60 HoursDocument7 pagesTheory - 60 HoursChenna KeshavaNo ratings yet
- Psychology: PerceptionDocument4 pagesPsychology: Perceptionapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Midtermstudyguide2022!2!2 2 2Document4 pagesMidtermstudyguide2022!2!2 2 2Georgette AyazNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Continuity of Life 1. Body CoordinationDocument3 pagesMaintenance and Continuity of Life 1. Body Coordinationcyberbat2008No ratings yet
- Colourful Spec (Print)Document1 pageColourful Spec (Print)emmaNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes - EDUC 154 Pres.Document6 pagesLearning Objectives Learning Outcomes - EDUC 154 Pres.Kerby Jean GumallaoiNo ratings yet
- Psychology: Placement: First YearDocument8 pagesPsychology: Placement: First YearJerin CyriacNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Lesson PlanDocument25 pagesScience Yearly Lesson PlanfordalNo ratings yet
- Spinal Reflexes: Psychology 372 Physiological PsychologyDocument4 pagesSpinal Reflexes: Psychology 372 Physiological PsychologylinaleenNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction: Learning Objective/sDocument11 pagesModule 1: Introduction: Learning Objective/sRoxie May Theresse AbagatnanNo ratings yet
- Bakai Yearly Plan 2011Document11 pagesBakai Yearly Plan 2011Nurul Shariza Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- Cerebrum AbdullaDocument16 pagesCerebrum AbdullaafssmowNo ratings yet
- PART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesDocument11 pagesPART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesLoLiNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 CS - RS12-If-J-4Document3 pagesPractical Research 2 CS - RS12-If-J-4Lei Lundai-CondinaNo ratings yet
- Ø Creative Presentation of A Neuron and Its PartsDocument12 pagesØ Creative Presentation of A Neuron and Its PartsBryant GonzalesNo ratings yet
- INTELLIGENCE THEORY and WICS MODELDocument12 pagesINTELLIGENCE THEORY and WICS MODELEst LijNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan SC f4Document36 pagesYearly Lesson Plan SC f4Gula MelakaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1Document7 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1Lenny Verra JosephNo ratings yet
- Biology of CognitionDocument67 pagesBiology of CognitionMarcusColacinoLicioNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOPDocument23 pagesPHYSIOPAirame Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Senses and The Brain Lesson Plan GGDocument4 pagesSenses and The Brain Lesson Plan GGCindy Huerta CastilloNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological Principles: Developmental and Social Factors and Individual DifferencesDocument5 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles: Developmental and Social Factors and Individual DifferencesAshley Co TingNo ratings yet
- The Triadic Structure of the Mind: Outlines of a Philosophical SystemFrom EverandThe Triadic Structure of the Mind: Outlines of a Philosophical SystemNo ratings yet
- Selfhood, Identity and Personality StylesFrom EverandSelfhood, Identity and Personality StylesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantdebbycleyNo ratings yet
- Annual Plan 2011 Gantt ChartDocument2 pagesAnnual Plan 2011 Gantt ChartdebbycleyNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 3 Experiment Checklists: Num. Form Activity NotesDocument1 pageBiology Paper 3 Experiment Checklists: Num. Form Activity Notesdebbycley70% (10)
- Science Form 4 Crossword 1-AnsDocument1 pageScience Form 4 Crossword 1-AnsdebbycleyNo ratings yet
- Science Module 2010Document25 pagesScience Module 2010debbycleyNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantdebbycleyNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 Annual Teaching Plan (2011)Document11 pagesScience Form 5 Annual Teaching Plan (2011)debbycleyNo ratings yet
- Science Form 4 Crossword 1-AnsDocument1 pageScience Form 4 Crossword 1-AnsdebbycleyNo ratings yet
- The Role of Hormones in HumanDocument2 pagesThe Role of Hormones in HumandebbycleyNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument5 pagesThe Lymphatic Systemdebbycley100% (1)
- Science Form 5 Problem Solving QuestionsDocument4 pagesScience Form 5 Problem Solving QuestionsdebbycleyNo ratings yet
- IMMUNISATIONDocument1 pageIMMUNISATIONdebbycleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document4 pagesChapter 8debbycley100% (3)
- Chapter 6Document1 pageChapter 6debbycleyNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 Conceptual QuestionDocument8 pagesScience Form 5 Conceptual QuestiondebbycleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter MotionDocument3 pagesChapter MotiondebbycleyNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 Synthetic Materials in IndustryDocument10 pagesScience Form 5 Synthetic Materials in Industrydebbycley100% (11)
- Bio Form4 Chemical Composition in CellDocument11 pagesBio Form4 Chemical Composition in Celldebbycley86% (7)
- Marten Terpstra, Johan G. Van Veen (Auth.), Marten Terpstra, Johan G. Van Veen (Eds.) - Heat Pipes - Construction and Application - A Study of Patents and Patent Applications-Springer NetherlandsDocument391 pagesMarten Terpstra, Johan G. Van Veen (Auth.), Marten Terpstra, Johan G. Van Veen (Eds.) - Heat Pipes - Construction and Application - A Study of Patents and Patent Applications-Springer NetherlandsJed MansouriNo ratings yet
- Ceramem TechDocument17 pagesCeramem TechSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- CHM 201 2019-2020 Note1Document38 pagesCHM 201 2019-2020 Note1Adams TemitopeNo ratings yet
- USC Modeling-Exercises-Tank-Systems PDFDocument3 pagesUSC Modeling-Exercises-Tank-Systems PDFMARK LESTER REALNo ratings yet
- 02 17 EksmalDocument2 pages02 17 Eksmal1aleksandar_t5349No ratings yet
- Rpt-sales-Fundamentals of Sand ControlDocument8 pagesRpt-sales-Fundamentals of Sand ControlDidier MorenoNo ratings yet
- Intertek Minerals Schedule of Services and Charges 2022 AUS PDFDocument60 pagesIntertek Minerals Schedule of Services and Charges 2022 AUS PDFJGGNo ratings yet
- OlraytDocument30 pagesOlraytArjay ArnucoNo ratings yet
- Advance Welding PDFDocument2 pagesAdvance Welding PDFRajeevNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance OF Pharmaceutical Herbal PreparationsDocument20 pagesQuality Assurance OF Pharmaceutical Herbal PreparationsHazrati UmmiNo ratings yet
- Paper ASP PetrofacDocument12 pagesPaper ASP Petrofacbagus yosan setiawanNo ratings yet
- Fill Volume Weight and Other Checks For Parenteral Products During Filling-1Document4 pagesFill Volume Weight and Other Checks For Parenteral Products During Filling-1SolomonNo ratings yet
- The History of Botulinum Toxin From Poison To BeautyDocument3 pagesThe History of Botulinum Toxin From Poison To BeautyElaine MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Physical-Chemical Characterization of Metal Hydroxides Sludge Waste Obtained From ElectrocoagulationDocument19 pagesPhysical-Chemical Characterization of Metal Hydroxides Sludge Waste Obtained From ElectrocoagulationcelestinogarciaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To SS13 ChemistryDocument1 pageA Guide To SS13 Chemistrywhat about the wookiesNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 7Document11 pagesLab Report 7Adel ZeynollaNo ratings yet
- 09 Chapter 2Document45 pages09 Chapter 2Mendoza LhaneNo ratings yet
- Preferred Features Advanced Technology Proven Design: Bulletin 4000Document12 pagesPreferred Features Advanced Technology Proven Design: Bulletin 4000saulomonNo ratings yet
- WKS 8 & 9 - Industrial Dryer 2T 2020-2021Document26 pagesWKS 8 & 9 - Industrial Dryer 2T 2020-2021Mei Lamfao100% (1)
- Sympathic Magic in GURPSDocument8 pagesSympathic Magic in GURPSCptnfiskedrittNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To 3D Printed JewelryDocument69 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To 3D Printed JewelryjpNo ratings yet
- Candace MaharajDocument11 pagesCandace MaharajCharlotte BNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Standard Rating Conditions: Gpm/ton 105.00Document28 pagesTable 1. Standard Rating Conditions: Gpm/ton 105.00Jhon LewisNo ratings yet
- PDS Uracron CS113 S1G-60 Vs 1.1Document1 pagePDS Uracron CS113 S1G-60 Vs 1.1DJOUHRINo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Determination of Corrosion Rate of Metals: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment 1: Determination of Corrosion Rate of Metals: Objective041Mir QazimNo ratings yet
- Self Etching Adhesive On Intact Enamel: Devarasa GM, Subba Reddy VV, Chaitra NLDocument6 pagesSelf Etching Adhesive On Intact Enamel: Devarasa GM, Subba Reddy VV, Chaitra NLNiNis Khoirun NisaNo ratings yet
- DOWSIL™ 982-H Curing Agent Black SDSDocument21 pagesDOWSIL™ 982-H Curing Agent Black SDSAquatic studentNo ratings yet
- Flowserve Reg PumpDocument66 pagesFlowserve Reg Pumpshaad_ksi100% (1)
- React Scales PosterDocument1 pageReact Scales PosterFrancesco ManiscalcoNo ratings yet
- Snake-Out MSDSDocument8 pagesSnake-Out MSDSRamdas NagareNo ratings yet