Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gate 1999
Uploaded by
tonykallada0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views8 pagesLimit of the function trn is 1.2. The function f(x) = e' is (a) even (e) Neither even nor odd (d) None of the above 1.3. Number of inflection points for the curve y = x + 2 x'is 1.5. Number of terms in the expansion of general determinant of order n is 1.7. Characteristic strength of concrete is defined as that compressive strength below which not more than (a) 10"10 of results
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLimit of the function trn is 1.2. The function f(x) = e' is (a) even (e) Neither even nor odd (d) None of the above 1.3. Number of inflection points for the curve y = x + 2 x'is 1.5. Number of terms in the expansion of general determinant of order n is 1.7. Characteristic strength of concrete is defined as that compressive strength below which not more than (a) 10"10 of results
Copyright:
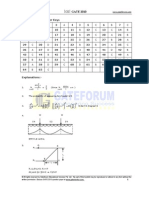
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views8 pagesGate 1999
Uploaded by
tonykalladaLimit of the function trn is 1.2. The function f(x) = e' is (a) even (e) Neither even nor odd (d) None of the above 1.3. Number of inflection points for the curve y = x + 2 x'is 1.5. Number of terms in the expansion of general determinant of order n is 1.7. Characteristic strength of concrete is defined as that compressive strength below which not more than (a) 10"10 of results
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
GATE-1999
CIVIL ENGINEERING
Duration : Three hours
Maximum marks 150
SECTION A. (75 Marks)
1. This question consisis of 35 (Thitty five) multiple
choice type sub-questions, each carrying one mark.
The answer to the multiple choice questions MUST
be written only in the boxes corresponding to the
question by writing 4, B,C, or Din the answer book,
(35x1=35),
41.1. Limit of the function =
1
@ 5 wo
We @a
1.2. The function f(x) = eis,
(@) Even
@ Oda
© Neither even nor odd
@ None of the above
1.3. If Ais any nxn matricand kisa scalar, |kAl=a[Al,
where ais
(@) kn ®t
(ok (@ kin
(nn?
14, The infinite series )°
om
(2n}!
() Diverges
(@) Oscillates
(a) Converges
(9 Is unstable
1.5, Number of inflection points for the curve
xis
3 1
(an @ (n+ ay
1.6. Number of terms in the expansion of general
determinant of order nis
@ an Wat
@a @ (n+?
17. Two perpendicular axes x and y of a section are
called principal axes when
(@) Moments of inertia about the axes are equal
=I)
() Product moment of inertia ([,) is zero
(© Product moments of inertia (I, « ,) is zero
(@) Moment of inertia about one of the axes is
greater than the other
1L8. In section, shear centre isa point through which, f
the resultant load passes, the section ‘wll not be
subjected to any
(@) Bending
(© Compression
() Tension.
(@ Torsion
19. For a fixed beam with span L, having plastic
moment capacity of M,, the ultimate central
concentrated load will be
4M,
M,
() p
@ Og
P
L
8M,
@
L
1.10. In reinforced concrete, pedestal is defined as
compression member, whose effective length does
not exceed its dimension by
(© 3 times
( 8 times
(0) 12 times
(©) I6times
1.11. The mirimum area of tension reinforcement in a
beam shall be greater than
0.85 bd 0875,
Me o
fo) 0.04 bd (d)
1.12. The characteristic strength of concrete is defined as
that compressive strength below which not more
than
(2) 10% of results fall
(6) 2% of results fall
1.13. Maximum strain at the level of compression stee!
for a rectangular section having effective cover to
compression sieelas and neutral axis depth from
compression face x, i8
(0) 5% of results fall,
(4) None of these
@
(@) 0.0035 0-4) @) 0.002 6-2)
(9 0.0035 0 - 2) (@) 0.002 ( 7
1.14. A ste! beam supporting loads from: the floorslab as,
‘well as from wall is termed as
© Lintel boom
(i) Header beam
() Stringerbeam
(© Spandrel beam
1.15. The problem of lateral buckling ean arise only in
those steel beams which have
(a) moment of inertial about the bonding axis larger
than the other
(6) moment of inertial about the bending axis
smoller than the other
(© fully supported compression flange
(@ none of these
1.16. The values of liquid limit and plasticity index for
soils having common geological origi:
restricted locality usually define
(@) azone above A - line
(@) a staright line parallel to A line
(© a straight line perpendicular to A -line
* @) points may be anywhere in the plasticity chart
1L.17. The toughness index of clayey soils is given by
(@) Plasticity index/Flow index
(0) Liquid limit Plastic limit
(6) Liquidity index/Plastie limit
(@) Plastic limit/Liquidity index
1.18. Principle involved in the relationship between
submerged unit weight and saturated weight of a
soil is based on
(@) Equilibrium of floating bodies
() Archimedes’ principle
(©) Stokes’ law
(@) Darey’s law
1.19, For an anisotropic soil, permeabilities in x and y
directions are k, and k, respectively in a two
dimensional flow. The effective permeability k,, or
the soil is given by
k,
(a) ky +k, ® 5
© Kk? kh @ tk ky
1.20. Cohesion in soil
(@) decreases active pressure and increases passive
resistance
@) decreases both active pressure and passive
resistance
(©) increases the active pressure and decreases the
passive resistance
@ increases both active pressine and passive
resistance
1.21. Consolidation in soils
(@) ‘isa function fo the effective stress
(8) does not depend on the present stress
(©) isa function of the pore waler pressure
(@) 18a function of the total stress
1.22. The sequent depth ratio oF a hydraulic jamp in a
rectangular horizontal channel is 10:30. The Froude
‘Number at the beginning of the jump is
(a) 5.64 ) 7.63
(©) 8.05, @) 13.61
1.23. Inan iceberg, 15% of the valume projects above the
sea surface. It the specific weight of sea water ig
10.5 KN/m?, the specific weight of iceberg in
KN/m is
(@ 1252 © 981
© 893 (@ 7.83
1.24. The ordinate ofthe Instantaneous Unit Hydrograph
(UH) of acaichment atany time tis
(2) the slope of the I-hour unit hydrograph at that
time
(® the slope of the direct runoff unit hydrograph
at that time
(©) difference in the slope of the $ - curve and 1+
hour unit hydrograph
(@) the slope of the § - curve with effective rainfall
intensity of Lem /hr
1.25. An isochrone is a line on the basin map.
{a} joining raingauge stations having equal rainfall
duration
() joining points having equal rainfall depth ina
given lime interval
© joining points having equal time of travel of
surface runoff to the catchment outlet
(2) joining ponts which are at equal distance from
the catchment outlet.
1.26. In a steady radial flow into an intake, the velocity
is found to vary as (1/r?), where ris the radial
ance, The acceleration ofthe flow is proportional
to
1
Oe Op
a L
Ox >
1.27. 4 soil formation through which only seepage is
possible, being partly permeable and capable of
giving insignificant yield, is classified as
@) Aquifer (6) Aquitard
(© Aquifuge (@) Aquiclude
1.28. Temporary hardness in water is caused by the
presence of
(@ Bicarbonates of Ca and Mg
(0) Sulphates of Ca and Mg
(6) Chlorides of Ca and Mg
(@) Nitrates of Ca and Mg
1.29. Blue baby disease (methaemoglobinemia) in
children is caused by the presence of excess
(@ Chlorides () Nitrates
(c) Fluoride (@) Lead
1.30. Standard 5-day BOD of a waster water sample is
nearly x% of the ultimate BOD, where x is
@) 48 Oss
© 68 @n
131. The minimum dissolved oxygen content (ppm) in
a river necessary for the survival of aquatic life is
@o (2
os ws
1.32. Chlorine is sometimes used in sewage treatment
{@) to avoid flocculation
(b) to increase biological activity of bacteria
(c) toavoid bulking of activated sludge
(2) tohelp in grease separation
1.33, The total length (in km) of the existing National
Highways in India isin the range of
(@) 15,000 to 25,000 (@) 25,000 to 35,000
(© 35,000 to 45,000 (4) 45,000 t0 55,000
1.34, The relationship between the length (1) and radits
(8) of an ideal transition curve is given by
@lor ier
@1«t Wied
F 7
1.85. Rapid curing cutback bitumen is produced by
lending bitumen with
(a) Kerosene
(©) Benzene
(©) Diesel
(d) Petrol
2. This question consists of 20 (Twenty) multiple choice
type sub-questions, each carrying TWO marks, The
ansivers to the multiple choice questions MUST be
written only in the boxes corresponding to the
question number writing A, B,C of Din the answer
book (20% 2=40)
21. If cis a constant, solution of the equation
oy ayy:
See teyis
(@) y=sin@x+0) ® y=cos (x +0)
(0 ystan(x+o) @ysete
pad
22. Theeguation 1 1 | represents. parabola
ye x
passing through the points
(} @,1),.2,(0,~1) @) (0,0), 1, 1),(1,2)
(©) 1), ©0223) @) (1,2), 2,0, 0,0)
2.3, The Laplace transform of the function
{() =k O ig fans
“Gm 8, S00
m
300mm dia, 700m
=F soos
16, The inflow hydrograph for a river reach is given,
below. Route this flood to a downstream point of
the river using Muskingham method of flood
routing. Assume that the initial flood discharge at
the downstream point is equal to 100 m’/s. For the
river reach, Muskingham coefficient (K) = 18hours
and weighing factor (x) = 0.3. Use a routing period
of 12 hours.
Time(hours) [0 [12 [ 24] 36] 48
Inflow (m/s) [00 [750 [780 [ 470] 270
17. Fig. 9shows the section (non -overflow portion) of a
straight gravity dam built with concrete
Considering water pressure and uplift pressure, and
neglecting the other external forces acting on the
dam, check whether the resultant passes through
the middle third of the base for the reservoir full
condition, In the figure, RL stands for Reduced
Level in metres and MWL stands for Maximum
Water Level. (Unit weight of water is 1000 kg/m?
and that of concrete is 2400 kg/m’)
18. A rectangular sedimentation tank is designed fora
surface overflow. raié (surface loading) of
12,000 litre/heur/m?, What percentage of the
suspended particles of diameter (a) 0.003 mm and
(2) 12 mm will be removed inthe tank. Appropriate
expressions forsellling velocity (V,, mm/s) may be
selected from the formulate given below.
Kinematic viscosity (nu) of water = 0.897 mim?/s.
Specific gravity of particles = 2.65.
mF
Stroke’s: V, Xen
oe
Ag.
Hazen’s: 20-9] Gy
where Re is the Reynolds number.
(3.33 gd (s- 1)?
19, Design a septic tank for a colony of 200 people. The
colony is supplied water at a rate of 135 litres/
person/day. Assume a detention period of 24 hours
andl 75% of the water becomes waste water. The
ank is cleaned once in a year. The rate of deposition
of sludge is 40 litres/ person years. Depth of tank
isto be kept as 2.0 in. Provide a free board of 0.3 m.
Length to breath ratio may be kept as 3: 1
20. The driver of a car, applied brakes and barely
avoided hitting an obstacle on the road. The vehicle
left skic marks of tyres on the road for a length of
25m. There was aspeed limit restriction of 55 kmph
for that road, Was the driver of theear violating the
limit if he was travelling on
@ level road
(0) a4% downgrade
Also compute the average decleration rate
developed (in the process of braking) on the level
road. Assume the longitudinal coefficient of friction
between the tyres and the road surface as 0.5.
21, On a two-lane two-way highway, a car A was
following a trick B and both were travelling at a
speed of 40 kmph. While looking for an opprotunity
to overtake the truck, the driver of the car A saw
another car C coming from the opposite direction.
At that moment, the distance between A and C was
450 m. After an initial hesitation period of two
seconds, the driver of car A started the overtaking,
operation, The distance between A and B at that
instance was 30 m. A overtook B by accelerating at
an uniform rate of 1.20 m/sec?. When the
overtaking operation was completed, there was a
distance of 25 m between B and A. Determine the
distance between the two cars (A and C) at the
instance of completion of the overtaking action. The
distance between different vehicles given are as
‘measured from the front the bumper of one vehicle
to the front bumper of another vehicle. Design
22. A ortion of a highway is to be consteueted with
25 cm thick plain cement comcrete slab. The design
traific intensity is estimated to be 3000 commercial
vehicles per day. Using the data given below, cheek,
the adequacy of the slab thickness as per IRC : 58.
1988 procedure.
Dimensions of slab
5m 3.5m
Design wheel load, P = 5100kg,
Design tyre pressure, p =7.2 kg/cm?
kg/cm?
Flexural strength of concrete = 40 kg fem"
Foundation strength,
Elastic modulus value of concrete,
E=30x 10% kg/cm?
Poisson’s ratio of concrete, u = 0.15
Coefficient of thermal expansion of concrete,
a= 10x 104*/°C
Maximum value of temperature differential in the
slab, At=15°C
Radius of relative stiffness, | = 90.3 cm
Radius of tyre contact area, a= 15 em
Radius of equivalent distribution of pressure,
b=145em
‘Use the following expressions wherever necessary
Edge stress (due to load) in kg/cm?
P
=0526 {7 (0541) (+1080 i + logo b-o4048)
‘Comet stress (due to load) in kg/cm?
Hee
Edge stress (due to temperature differential) in
kg/en? = BSE
Bradbury coefficients (C) may be taken as 0.72 and
0.43.
speed of the highway is 80 kmph.
ANSWERS
MW @ 120 13@) 14@ 15.6) 160 170 18@ 19.@ 1100
TAL (@) 112.) 13a) 144. (@) 15.6) 146.) 1.:17.@) 1.18. (%) 19. 1208)
121. (6) 1.22.06) 123.(6) 124.) 1.25.) 126.(@) 127.) 128.4) 138.(8) 1.30.6)
13L 6) 182) 133.0) 134 138.(a)
2A() 22.0) 23.2) 24.5) 25.) 26.) -27.(0)-28.(6) -2.9.(d) 2.0.10)
2A (4) 242.) 293.6) 244.() 2.78.6) 2.26, (@) 2.17.(c) 2.18.(8) 2.19. (d) 2.20.(a)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Psalm 112 - Psalm 112 - Praise The LORDDocument2 pagesPsalm 112 - Psalm 112 - Praise The LORDtonykalladaNo ratings yet
- RCC - Properties of Steel and ConcreteDocument17 pagesRCC - Properties of Steel and Concretenitishpathak79No ratings yet
- (Entrance-Exam - Net) - GATE Civil Engineering Sample Paper 1Document13 pages(Entrance-Exam - Net) - GATE Civil Engineering Sample Paper 1rajuramaiah2091% (32)
- GATE: 2008 Ce: Civil Engineering Q.1 (A) P: Dy y DXDocument15 pagesGATE: 2008 Ce: Civil Engineering Q.1 (A) P: Dy y DXamitk1986No ratings yet
- Generalized Event Tree Algorithm and Software For Dam Safety RiskDocument135 pagesGeneralized Event Tree Algorithm and Software For Dam Safety RisktonykalladaNo ratings yet
- Ce 2007Document15 pagesCe 2007GTSNo ratings yet
- Design of Slabs 2 2 2Document6 pagesDesign of Slabs 2 2 2tonykalladaNo ratings yet
- Payment AcknowledgementDocument1 pagePayment AcknowledgementtonykalladaNo ratings yet
- (WWW (1) .Entrance-Exam - Net) - GATE Civil Engineering Sample Paper 2Document12 pages(WWW (1) .Entrance-Exam - Net) - GATE Civil Engineering Sample Paper 2ईशान्त शर्माNo ratings yet
- Gate Ce 2004Document10 pagesGate Ce 2004mitulkingNo ratings yet
- Gate Ce 2002Document9 pagesGate Ce 2002amitk1986No ratings yet
- GATE CE 2003 Question PaperDocument12 pagesGATE CE 2003 Question Paperbhustlero0oNo ratings yet
- Gate 2000Document9 pagesGate 2000tonykalladaNo ratings yet
- Gate 2001Document10 pagesGate 2001tonykalladaNo ratings yet
- Economics Notes For B.tech StudentsDocument83 pagesEconomics Notes For B.tech Studentsrohith198980% (5)
- GATE CE 1997 Question PaperDocument8 pagesGATE CE 1997 Question Paperbhustlero0oNo ratings yet
- 2010 SolutionsDocument9 pages2010 SolutionstonykalladaNo ratings yet
- Kerala University B.Tech Nov 2010 Exam Time TableDocument11 pagesKerala University B.Tech Nov 2010 Exam Time TablemidhunlalgNo ratings yet
- GIS Describes Our WorldDocument21 pagesGIS Describes Our WorldtonykalladaNo ratings yet
- Gate Syllubus, Civil EngineeringDocument4 pagesGate Syllubus, Civil Engineeringlokesh2325No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)