Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cheat
Uploaded by
Aparna SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cheat
Uploaded by
Aparna SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
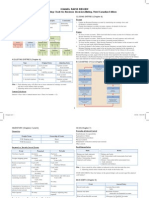
BALANCE SHEET QUICKLY FINDING NET INCOME ESSENTIAL RATIOS
Assets NI = Revenue - ( COGS + Other Expenses ) Type Ratio Numerator Denominator Intuition
Current Assets NI = ∆RE + Div Profitability Return on Equity (ROE) NI Avg. SE
+ Cash NI = ∆A - ∆L - ∆CC + Div Return on Assets (ROA) NI + Interest Exp.(1-Tax Rate) Avg. Total Assets (>) Measures a firm's performance in using assets to generate earnings
+ Short-term investments ∆C = ∆L + ∆SE - ∆N$A Profit Margin for ROA NI + Interest Exp.(1-Tax Rate) Net Sales (>) Measures a firm's ability to control expenses relative to sales
+ Accounts receivable Return on Sales NI + Interest Exp.(1-Tax Rate) Net Sales
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts (ADA) INDIRECT CASH FLOW STATEMENT Return on Capital Equity (ROCE) NI - (Preferred Dividends) Avg. Equity (>) Measures a firm's performance in using financing assets to generate earnings
+ Deferred Tax Assets Net Income Profit Margin for ROCE NI - (Preferred Dividends) Sales (>) Indicates the portion of the sales dollar that is left over for the common shareholder
+ Inventory Gross Margin Gross Profit Sales
- Accumulated Amortization (Bond Interest) Adjustments for Operating Activities Gross Profit Sales - COGS
+ Prepaid expenses + Depreciation Expense Leverage Common Equity Leverage NI NI + Interest Exp.(1-Tax Rate)
+ Total Current Assets + Amortization Expense Capital Structure Leverage Avg. Total Assets Avg. SE Indicates proportion of assets provided by common shareholders vs. creditors
- Gain on Sale of Machinery Debt / Equity Ratio Avg. Total Liabilities Avg. SE The more stable a firm's earnings and cashflows, the higher debt ratio deemed acceptable
Long-term Investments - Increase in Accounts Receivable Solvency Long-term debt ratio Long-Term Liabilities Total Assets Proportion of a firm's long-term financing provided by debt-holders
+ Long-term notes receivable + Increase in ADA Current ratio Current Assets Current Liabilities (prefer > 1) Indicates a firm's ability to meet short-term obligations
+ Land - Increase in Inventory Quick ratio Cash + Marketable Securities + Net A/RCurrent Liabilities (>) A Measurement of Liquidity
+ Marketable Securities + Increase in Accounts Payable CFO to CL Ratio Cash Flow From Operations Average Current Liabilities (>40%) Indicates a firm's ability to meet short-term obligations
+ Marketable Securities Adjustments + Increase in Deferred Taxes or Taxes Payable CFO to Total Liabilities Ratio Cash Flow From Operations Total Liabilities Considers availability of Liquid Assets to cover Debt
+ Total Long-term investments - Increase in Prepaid Expenses Asset Turnover Interest Coverage Ratio NI + Tax Exp. + Interest Exp. Interest Exp. (>) Indicates relative protection operating profitability provides to bondholders
+ Increase in Deferred Revenue A/P Turnover Ratio COGS Avg. A/P
Property, Plant, & Equipment + Increase in Interest Payable Days A/P Outstanding 365 A/P Turnover Ratio
+ Property + Increase in Wages payable Receivable turnover Net Credit Sales Avg. A/R
+ Plant Net cashflow from operating activities A/R Turnover Sales Avg. A/R (>) Indicates how quickly a firm collects cash
- Accum. depreciation (Property/Plant) Days Receivable Outstanding 365 A/R Turnover Ratio
+ Equipment Adjustments for Investing Activities Inventory turnover COGS Avg. Inventory Increases caused by inventory shortages could signal a loss of customers
- Accum. depreciation (Equipment) - Cash paid for land Days Inventories Held 365 Inventory Turnover Ratio
+ Total Property, plant, and equipment - Cash paid for PPE Fixed assets turnover Sales Avg. Fixed Assets Low or decreasing may indicate a firm preparing for growth
+ Sale of machinery Total assets turnover Sales Avg. Total Assets (>) Measures a firm's ability to generate sales from a particular level of asssets
Intangible Assets - Capital Expenditures Financial Earning per share (EPS) NI Avg. # of Shares Outstanding Has limited use in comparing firms
+ Goodwill - Cash paid for intangibles Price / Earning Ratio (PE) Market Price per Share Earnings per Share (> Indicates Growth) How much investors are willing to pay per $1 of earnings
+ Patent + Sale of intangible assets Dividend Yield Ratio Dividends per Share Market Price per Share
+ Trademark + Proceeds form sale of investment securities Return on Investment (ROI) Market Price1 – Market Price0 + Dividends
Market Price0
+ Total intangible assets Net cashflow from investing activities Dupont Analysis RoE (NE+IE)/(Assets) x [NI/(NI+IE) x Assets/SE] The DuPont ratio, while not the end in itself, is an excellent way to get a quick snapshot view of the
Total Assets RoE Operating Performance x Capital Structure overall performance of a firm in three of the four critical areas of ratio analysis, profitability,
Adjustments for Financing Activities Operating Performance Profit Margin for ROA x Asset Turnover operating efficiency and leverage. By identifying strengths and/or weaknesses in any of the three
Liabilities + Proceeds from issuing equity Capital Structure Common Equity Leverage Ratio x Capital Structure Leverage areas, the DuPont analysis enables the analyst to quickly focus his or her detailed study on a
Current Liabilities: + Cash from debt financing ROA Profit Margin for ROA x Total Asset Turnover Ratio particular spot, making the subsequent inquiry both easier and more meaningful.
+ Accounts payable - Principal payment on short-term notes ROA Return on Sales x Total Asset Turnover Ratio
+ Wages payable - Principal payment on long-term debt ROCE Profit Margin for ROCE x Total Assets Turnover x Capital Structure Leverage
+ Taxes Payable - Cash Dividends to stockholders
- Deferred Tax Liabilities - Principal payment on notes payable REVENUE RECOGNITION CRITERIA ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS ACCOUNTING INVENTORY ACCOUNTING
+ Interest payable Net cashflow from financing activities 1. Significant portion of production and sales effort complete Balance Sheet Basic Inventory Calculation
+ Short-term notes payable 2. The amount of revenue can be objectively measured Beginning Balance Cash A/R -ADA =RE COGS = Purchases + Production - ∆ Inventories
+ Current maturities of long-term debts Cash/Cash equivalents at beginning of year 3. The major portion of the cost has been incurred and the Credit Sale + credit sale + credit sale Beginning Inventory + Purchases - Ending Inv = COGS
+ Deposits + Net cashflow for operating activities remaining
costs can be reasonably estimated Bad Debt Expense +BDE (BDE) End Inv FIFO = Beg Inv FIFO + Inputs - COGS FIFO
+ Warranties + Net cashflow from investing activities 4. The eventual collection of cash is reasonably assured Cash Collection + cash (cash) End Inv LIFO = Beg Inv LIFO + Inputs - COGS LIFO
+ Deferred revenues + Net cashflow from financing activities Write Off (WO) (WO) No Effect EI FIFO - EI LIFO = BI FIFO - BI LIFO + COGS LIFO - COGS FIFO
+ Other payables Cash/Cash equivalents at end of year CASH PAYMENT VS. REVENUE RECOGNITION Recovery (a) + recovery + recovery No Effect ∆ LIFO Reserve = COGS LIFO - COGS FIFO
+ Total current liabilities Cash received CONCURRENT TO earning Rev. Recovery (b) + recovery (recovery) No Effect Inventory EB = Inventory BB + Purchases + Production - COGS
DIRECT CASH FLOW STATEMENT Prior Period Ending Balance EB EB EB EB Balance Sheet Effects Increase
Long-term Liabilities: Current Period + Cash (A) = + Rev. (SE) Reverse Engineering ADA and A/R Purchase Materials RMI
+ Long-term notes payable Operating Activities Subsequent Estimation Methods: Aging, Historical Estimation. Convert using algebra Use Raw Materials WIP
+ Bonds payable + Cash Collections from Sales Cash received BEFORE earning Rev. 1. Mention “I assume all the sales were on account.” Complete Production FGI
+ Bond Premium + Cash Collections from A/R Prior Period + Cash (A) = + Def. Rev. (L) 2. [B/S] Pick BB & EB of Accounts Receivable and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. Sell Inventory Cash
- Bond Discount - Cash paid to suppliers Current Period 0 = - Def. Rev. (-L) + Rev. (SE) Usually the A/R values on BS are “Net” values including ADA. Pay Manufacturing Wages WIP
+ Mortgage payable - Cash paid to employees Subsequent 3. [Income S.] Pick sales (net revenue) value (assuming all on account). Depreciate Asset (Capitalize) WIP -Accum Dep
+ Total Long-term liabilities - Cash paid to selling activities Cash received AFTER earning Rev. 4. [Schedule] Pick “Bad Debt Expense”, “Write-Off” (if any), and “Recovery” (if any). Cost Flow Summary
Total Liabilities - Cash paid to interest and taxes Prior Period 5. [Calc] Calculate a missing cell in ADA column (normally “Write-off”). LIFO: Last In First Out; COGS are assumed = costs of most
- Cash paid for inventory Current Period + A/R (A) = + Rev. (SE) 6. [Calc] Calculate a missing cell in A/R column (normally “Cash-collected”). recently purchased units in the financial records
Stockholders' Equity: Net cashflow from operating activites Subsequent + Cash (A) - A/R (-A) = 0 7. [Check] Check if values in each column match. FIFO: First In First Out; COGS are assumed = cost of oldest
+ Common Stock CASH PAYMENT VS. EXPENSE RECOGNITION available units in financial records
+ Preferred Stock Investing activities Cash paid CONCURRENT TO using resource to generate rev PROPERTY PLANT & EQUIPMENT ACCOUNTING Averaging: COGS are assumed to be equal to a per-unit
+ Additional Paid in Capital - Cash paid for land Prior Period Depreciation Methods weighted average cost at the end of the period
+ Treasury Stock - Cash paid for PPE Current Period - Cash (-A) = + Exp. (-SE) Straight-Line (Purchase - Salvage) / (Estimated Useful Life) Comparing LIFO and FIFO
+ Other Comprehensive Income + Sale of machinery Subsequent Double-Declining (2 * Book Value) / (Estimated Useful Life) LIFO provides better balance sheet by increasing ROA
+ Retained earnings - Capital Expenditures Cash paid BEFORE using resource to generate revenue Percent (Purchase - Salvage) / (Amount Used / Total Amount) FIFO provides better Income Statement by decreasing COGS
+ Dividends Payable - Cash paid for intangibles Prior Period - Cash (-A) + Productive Asset (A) = 0 Purchase Price Calculation and increasing Net Income
+ Total stockholders' equity + Sale of intangible assets Current Period - Productive Asset (-A) = + Exp. (-SE) Purchase Asset Price + Installation Costs + Transportation Costs NI (FIFO) = NI (LIFO) + LIFO Reserve – Additional Tax
Total Stockholders' Equity + Proceeds form sale of investment securities Subsequent Construct Asset Direct Construction Costs + Financing Costs (Capitalize Interest) = NI (LIFO) + (1 – tax rate) * LIFO Reserve
Net cashflow from investing activities Cash paid AFTER using resource to generate revenue Balance Sheet ∆ LIFO Reserve = COGSLIFO - COGSFIFO
INCOME STATEMENT Prior Period Beginning Balance Cash PPE - Accum. Dep. RE COGSFIFO = COGSLIFO - ∆ LIFO Reserve
Sales Financing Activities Current Period 0 = + Accrued Liability (L) + Exp. (-SE) Acquisition (purchase) +purchase Cumulative LIFO Reserve = FIFO Inventory - LIFO Inventory
- Discounts + Proceeds from issuing equity Subsequent - Cash (-A) = - Accrued Liability (-L) Depreciation + depr exp (depr exp) Effect of Liquidating LIFO Layers
- Returns + Cash from Debt financing Write Down + depr exp (depr exp) 1. Decrease LIFO COGS (possibly less than FIFO)
The "Productive Asset" could be inventory, Prepaid Insurance,
Net Sales - Principal payment on short-term notes Disposal + cash (disposal) (accum dep) + gain on sale 2. Increase profitability (Offset goes to Net Income)
PP&E, etc. In the case of PP&E, we would reduce the value of
- Cost of Good Sold (COGS) - Principal payment on long-term debt Ending Balance EB EB EB EB 3. Decrease LIFO reserve
the asset through the contra-asset Accumulated Depreciation.
Gross Profit - Cash Dividends to stockholders Reverse Engineering PPE 4. Decrease turnover ratio
The "Accrued Liability" could be Accounts Payable, Accrued
- SG&A - Principal payment on notes payable Wage Expense, Interest Payable, etc 1. [B/S] Pick BB and EB of “Gross PPE” and “Accumulated depreciation.” Cost of Sales = LIFO RESERVE lower
- Wage Expense Net cash flow from financing activities (Sometimes this information is in foot notes) Income before tax provision = LIFO RESERVE higher
- Rent Expense 2. [SCF] Pick “Additions to PPE” (Investing section), “Depreciation” (Operating section) Provision for Income taxes = t * LIFO RESERVE
- Interest Paid Cash/Cash equivalents at beginning of year REVENUE RECOGNITION & TAXES and “Write down” (if any. Operating section). Same Income as before or NI = (1 – t) * LIFO RESERVE
- R&D Expense + Net cashflow for operating activities 1. All cash revenue collections are considered taxable revenue 3. [SCF] Pick “Proceeds from sales of PPE” (meaning cash received. Investing section) Effects of Changing Prices
- Depreciation Expense + Net cashflow from investing activities regardless of timing and “gain/loss” (Operating section) Comparing P Rising
- Amortization Expense + Net cashflow from financing activities 2. Collecting cash before recognizing revenue creates a 4. [Calc] Calculate depreciation value for disposal (use Acc. Dep’n column) COGS LIFO > FIFO LIFO < FIFO
Operating Profit Cash/Cash equivalents at end of year asset (DTA) 5. [Calc] Calculate BV for disposal (use Disposal row) Pre-Tax Income LIFO < FIFO LIFO > FIFO
+ Other revenues 3. Recognizing revenue before collecting payment creates a 6. [Check] Check if the Gross PPE column is balanced. Tax Expense LIFO < FIFO LIFO > FIFO
- Other expenses STATEMENT OF RETAINED EARNINGS deferred tax liability (DTL) Tax Implications EB Inventory LIFO < FIFO LIFO > FIFO
- Disposals Beginning Retained Earnings Balance Depreciation is accounted for using more rapid methods when accounting for taxes ITO LIFO > FIFO LIFO < FIFO
Income Before Taxes + Net Income Non-cash Transactions Omitted from SCF Taxes paid to the IRS is based on accellerated depreciation schedule Tax Impact
- Taxes - Dividends Acquisition of assets by assuming liabilities or by issuing equity Difference builds a timing-related Deferred Tax Asset that is later decremented Cumulative Tax Savings = Tax Rate * Cumulative LIFO Reserve
Net Income Ending Retained Earnings Balance Exchanges of non-monetary assets Tax Saving per year = Tax Rate * ∆ LIFO Reserve
Refinancing of long-term debt
ACCOUNTING FOR SHARES OF STOCK Conversion of debt or preferred stock to common stock
Issues Proceeds = # Shares * Par Value + APIC Authorized > Issued > Outstanding Issuance of equity securities to retire debt
You might also like
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesAccounting Cheat Sheetopty100% (15)
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAccounting Cheat Sheetanoushes1100% (2)
- General Accounting Cheat SheetDocument35 pagesGeneral Accounting Cheat SheetZee Drake100% (5)
- Finance Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFinance Cheat SheetMarc MNo ratings yet
- Dividend Discount and Residual Income Models ExplainedDocument2 pagesDividend Discount and Residual Income Models ExplainedMohammad DaulehNo ratings yet
- FAR NotesDocument163 pagesFAR NotesClaire Antonette Limpangog100% (1)
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance - FormulasDocument3 pagesCorporate Finance - FormulasAbhijit Pandit100% (1)
- ACCT 101 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageACCT 101 Cheat SheetAndrea NingNo ratings yet
- Classification of AccountsDocument3 pagesClassification of AccountsSaurav Aradhana100% (1)
- Basic Everyday Journal EntriesDocument2 pagesBasic Everyday Journal EntriesMary73% (15)
- Intermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cheat SheetsDocument4 pagesAccounting Cheat SheetsGreg BealNo ratings yet
- Wallace Wattles - Science of Getting LoveDocument13 pagesWallace Wattles - Science of Getting LovePannir Joe80% (5)
- Defining Heads of Charge and Deductions S10(1Document2 pagesDefining Heads of Charge and Deductions S10(1Jean Pingfang Koh100% (3)
- ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2Document1 pageACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2jieboNo ratings yet
- Fnce 100 Final Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFnce 100 Final Cheat SheetToby Arriaga100% (2)
- Corporate Finance Math SheetDocument19 pagesCorporate Finance Math Sheetmweaveruga100% (3)
- Cheat Sheet Exam 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet Exam 1Shashi Gavini Keil100% (2)
- Cheat Sheet For AccountingDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet For AccountingshihuiNo ratings yet
- Class of AccountsDocument5 pagesClass of AccountssalynnaNo ratings yet
- CorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2Document2 pagesCorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2subtle69100% (4)
- Account ClassificationDocument2 pagesAccount ClassificationMary96% (23)
- Get UnstuckDocument136 pagesGet UnstuckIshmo Kueed100% (2)
- Kelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Document2 pagesKelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Kelly Koh100% (4)
- Cheat Sheet Final - FMVDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet Final - FMVhanifakih100% (2)
- Microeconomics Formulas & ConceptsDocument20 pagesMicroeconomics Formulas & Conceptsgavka100% (1)
- Bec Review SheetDocument7 pagesBec Review Sheettrevor100% (1)
- Seeds of EnlightmetDocument12 pagesSeeds of EnlightmetIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- ManifestingDocument65 pagesManifestingahmedekram100% (12)
- Account ClassificationDocument3 pagesAccount ClassificationUsama MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Accounting Journal Entries Flowchart PDFDocument1 pageAccounting Journal Entries Flowchart PDFMary75% (4)
- Spiritual EvolutionDocument8 pagesSpiritual EvolutionIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Financial AccountingDocument1 pageCheat Sheet For Financial Accountingmikewu101No ratings yet
- Key Financial Ratios BreakdownDocument25 pagesKey Financial Ratios Breakdownwinnerme100% (1)
- Basic Impact of Everyday Journal Entries On The Income StatementDocument2 pagesBasic Impact of Everyday Journal Entries On The Income StatementMary100% (1)
- Financial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian EditionDocument6 pagesFinancial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian Editionapi-19743565100% (1)
- Closing Journal EntriesDocument1 pageClosing Journal EntriesMary91% (11)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Ultimate Accounting Guide SheetDocument1 pageUltimate Accounting Guide SheetMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay67% (6)
- Corporate FinanceDocument24 pagesCorporate Financeapi-3719687100% (3)
- BVA CheatsheetDocument3 pagesBVA CheatsheetMina ChangNo ratings yet
- Bec Notes 17Document87 pagesBec Notes 17Pugazh enthi100% (2)
- The PowerofGratitudeDocument18 pagesThe PowerofGratitudeluckyfolks100% (1)
- Inventory Turnover Cost of Sales / Avg Inventory High Is Effective Inv MGMT Days of Inventory On Hand (DOH) 365/inv TurnoverDocument3 pagesInventory Turnover Cost of Sales / Avg Inventory High Is Effective Inv MGMT Days of Inventory On Hand (DOH) 365/inv Turnoverjoe91bmwNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementsDocument1 pageFinancial StatementsMary100% (4)
- Asset Conversion CycleDocument12 pagesAsset Conversion Cyclessimi137No ratings yet
- Robert Dilts - AnchoringDocument8 pagesRobert Dilts - AnchoringJulio PaulinNo ratings yet
- Accounting formulas guideDocument6 pagesAccounting formulas guideGabriel100% (2)
- Linux Sysadmin CommandsDocument436 pagesLinux Sysadmin CommandsIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- Reg Notes 17Document184 pagesReg Notes 17shaji irumbanamNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cheat Sheet FinalsDocument5 pagesAccounting Cheat Sheet FinalsRahel CharikarNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAccounting Cheat SheetvgirotraNo ratings yet
- Written Communications Memo on IFRS BenefitsDocument9 pagesWritten Communications Memo on IFRS Benefitscpa2014No ratings yet
- Cfa Level I - Us Gaap Vs IfrsDocument4 pagesCfa Level I - Us Gaap Vs IfrsSanjay RathiNo ratings yet
- Chap-2 Quản trị tài chínhDocument12 pagesChap-2 Quản trị tài chínhQuế Anh TrươngNo ratings yet
- Working Capital MGTDocument12 pagesWorking Capital MGTssimi137No ratings yet
- Ananta-02 - Mengenal Laporan Keuangan, Pajak, Dan Free Cash FlowDocument40 pagesAnanta-02 - Mengenal Laporan Keuangan, Pajak, Dan Free Cash FlowKania SyahraNo ratings yet
- 25th Aug 2014 Lect: Current Time InvestDocument3 pages25th Aug 2014 Lect: Current Time InvestGaurav SomaniNo ratings yet
- A Boat Called FreedomDocument4 pagesA Boat Called FreedomIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- Core JDBCDocument45 pagesCore JDBCIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- Java: Generics and AnnotationsDocument34 pagesJava: Generics and AnnotationsIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- RESTful Web ServicesDocument148 pagesRESTful Web ServicessmsbariNo ratings yet
- Matrix Algebra For Beginners, Part I Matrices, Determinants, InversesDocument16 pagesMatrix Algebra For Beginners, Part I Matrices, Determinants, InversesPhine-hasNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Technology: A Crash Course: Tables, Records, and ColumnsDocument5 pagesRelational Database Technology: A Crash Course: Tables, Records, and ColumnsIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- JoinDocument10 pagesJoinkardeslerim123No ratings yet
- Portscan TechDocument10 pagesPortscan TechIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- A Beginner S Guide To Effective Programming: Mahindra Satyam Learning WorldDocument265 pagesA Beginner S Guide To Effective Programming: Mahindra Satyam Learning WorldIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- Unix ToolboxDocument56 pagesUnix ToolboxtipusNo ratings yet
- Raise Your Vibration Shape Your RealityDocument12 pagesRaise Your Vibration Shape Your Realitymelamin1980janNo ratings yet
- Bank SmartDocument2 pagesBank SmartIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- The Aloha SpiritDocument5 pagesThe Aloha SpiritIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- Your Invisible PowerDocument77 pagesYour Invisible PowerEU_SUNT_IUBIRENo ratings yet
- Calling C++ DLL From ExcelDocument5 pagesCalling C++ DLL From Excelsingamit2335No ratings yet
- Chakra MedDocument7 pagesChakra MedIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- MeditationbasicsDocument59 pagesMeditationbasicsangelicgirl100% (4)
- The Rosicrucian Cosmo-Conception: by Max HeindelDocument32 pagesThe Rosicrucian Cosmo-Conception: by Max HeindelIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- Parenting 40 To DoDocument9 pagesParenting 40 To DoIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- The Age of ReasonDocument102 pagesThe Age of ReasonbomcdreamyNo ratings yet
- Emersonr1664316643 8Document136 pagesEmersonr1664316643 8Željko MijićNo ratings yet