Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carl Zeiss C80
Uploaded by
gstabOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carl Zeiss C80
Uploaded by
gstabCopyright:
Available Formats
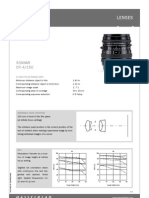
This Planar jens is eharaeterized by an extremely uniform edge-to- Apart tram the Planar f/3.
f/3.5-1 00 mm this jens is standard outfit of the
edge sharpness at full aperture, owing to the exeellent eorreetion of Hasselblad 500 C and 500 EL eameras.
aillens aberrations. As indieated by its name, the anastigmatie
flatness of the image fjeld is outstanding. The jens is suited tor almost any task in general photography.
~
The foeallength eorresponds approximately to the diagonal of the
6 x 6 em format.
74,9 to film
~
$
,r'-
N 51.7
Number of jens elements: 7 Diataneerange: co to 0.9 m
Number of eomponents: 5 Automatie depth-of-field indieation für z = 0.06 mm *)
f-number: 2.8 Position of entranee pupil: 26.6 mm behind the first jens vertex
Foeallength: 80.5 mm Diameter of entranee pupil: 28.8 mm
Negative size: 56.5 x 56.5 mm Position of exit pupil: 25.7 mm in front of the last
Angular fjeld 2 w: diagonal 52°, side 38° jens vertex
Speetral range: visible speetrum Diameter of exit pupil: 34.5 mm
f-stop seale: 2.8 - 4 - 5.6 - 8 - 11 - 16 - 22 Position of principal plane H: 39.0 mm behind the first lens vertex
Mount: Compur interehangeable reflex shutter Position of prineipal plane H': 10.8 mm in front of the last
size 0 with automatie iris diaphragm jens vertex
Filter mounting: bayonet forHasselblad series 50 Distanee between first and
Weight: 465g last lens vertex: 46.4 mm
*) z = eirele-of-eonfusion diameter
Performance data: PlanarT* f/2.8-80 mm Cat No. 102076
Modulation transter T as a tunction ot image height u White light
Sutorientationtangential- - - - SpatialtrequenciesR = 1O,20 and40 cycles/mm
sagittal
T t-number k = 2.8 T t-number k = 5.6
1,0 1,0
0,8
-- 0,8
0,6 0,6
--
0,4 0,4
~
0,2 0,2
-
10 20 30 40 10 20 30 40
u[mllj] u [mm]
E Relative illuminance
1,0
---- - k=2,S
""- --- k=5,6
o,s "....
....
"
""
.....
0,6
"
1. MTF Diagrams
The image height u - reckoned trom the image center - is entered in
0,4 ~
mm on the horizontal axis ot the graph. The modulation transter T
(MTF = Modulation Transter Factor) is entered on the vertical axis.
Parameters ot the graph are the spatial trequencies R in cycles (line 0,2
pairs) per mm given at the top right hand above the diagrams.
The lowest spatial trequency corresponds to the upper pair ot curves,
the highest spatial trequency to the lower pair. Above each graph the
t-number k is given tor which the measurement was made. 'White"
light means that the measurement was made with a subject 10 20 30 40
illumination having the approximate spectral distribution ot daylight. u [mm]
Unless otherwise indicated, the performance data rater to large object
distances, tor which normal photographic lenges are primarily used.
2. Relative iIIuminance
In this diagram the horizontal axis gives the image height u in mm and : r'5IDrtlon in 1% 01 Image rghl C I I
'E
Cl>
the vertical axis the relative iIIuminance E, both tor tull aperture and a E
"C
moderately stopped-down leng. The values tor E are determined t:
Cl>
taking into account vignetting and natural light decrease. E
01 ---L I I ca
(ij
3. Distortion ()
'E
Here again the image height u is entered on the horizontal axis in mm. J::
()
The vertical axis gives the distortion V in % ot the relevant image 2
height. A positive value tor V means that the actual image point is
-1,0 I I I 1"-- I .9
turther trom the image center than with perfectly distortion-tree Ö
Cl>
imaging (pincushion distortion); a negative V indicates barrel :c
:J
distortion. -2,0 I
I I 1 1 (f)
10 20 30 40
u [mm]
102076-e Printed in West Germany AW 11/81 Po
You might also like
- Distagon3.5 60mm CF 104869 eDocument2 pagesDistagon3.5 60mm CF 104869 eHong Chen0% (1)
- Tele-Arton Tele-Xenar: SchneiderDocument2 pagesTele-Arton Tele-Xenar: SchneiderxOxRAYxOxNo ratings yet
- Leader Test Instruments: Signal Genera TorDocument2 pagesLeader Test Instruments: Signal Genera TorFrancisco GarridoNo ratings yet
- Model Plan de Afaceri - AntreprenoriatDocument24 pagesModel Plan de Afaceri - AntreprenoriatSimona ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- 09 Chapter 16-56 10-23Document10 pages09 Chapter 16-56 10-23Jackson Dias RochaNo ratings yet
- 4005 Solutions V POWDERDocument1 page4005 Solutions V POWDERSereibot YemNo ratings yet
- Pre-wired FCT limit switches under 40 charsDocument2 pagesPre-wired FCT limit switches under 40 charsgiovenzana akshar salesNo ratings yet
- LetItGoHB 34Document1 pageLetItGoHB 34ESCUELA DE MUSICA RITMOSNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Tape Heads GuideDocument6 pagesMagnetic Tape Heads GuidepsychpostersNo ratings yet
- Effects of Pollution on Thames Estuary Ecosystem RecoveryDocument34 pagesEffects of Pollution on Thames Estuary Ecosystem RecoverySuriyah SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Low-Jitter Process-Independent DLL and PLL Based On Self-Biased Techniques (John G. Maneatis)Document10 pagesLow-Jitter Process-Independent DLL and PLL Based On Self-Biased Techniques (John G. Maneatis)Aram ShishmanyanNo ratings yet
- 6786-Article Text PDF-10544-1-10-20130718Document11 pages6786-Article Text PDF-10544-1-10-20130718Alpine.designNo ratings yet
- Code Positions-Nr Parts ListDocument2 pagesCode Positions-Nr Parts ListVijay BhureNo ratings yet
- 44 9nconDocument1 page44 9nconsaubhagya majhiNo ratings yet
- Phase Identification by Selective Etching: January 1986Document11 pagesPhase Identification by Selective Etching: January 1986MarkNo ratings yet
- Plastic Shrinkage Cracking (BPS)Document36 pagesPlastic Shrinkage Cracking (BPS)shingkeongNo ratings yet
- YFVDocument2 pagesYFVTed Thomson100% (1)
- DIN ISO 276811 tolerance chartDocument5 pagesDIN ISO 276811 tolerance chartSugeng Hadi SusiloNo ratings yet
- InputDocument3 pagesInputSugeng Hadi SusiloNo ratings yet
- Ta2 PDFDocument5 pagesTa2 PDFSugeng Hadi SusiloNo ratings yet
- Finished Taiwan Course 5 KLIPPEL - Nonlinear Parameter MeasuremenDocument14 pagesFinished Taiwan Course 5 KLIPPEL - Nonlinear Parameter Measuremen點潔No ratings yet
- Tiny SG90 Servo Motor with High TorqueDocument1 pageTiny SG90 Servo Motor with High TorquewendyNo ratings yet
- A SA-106-9Document1 pageA SA-106-9riyyjuniorNo ratings yet
- Ligeti, Sq2 IIIDocument4 pagesLigeti, Sq2 IIIRiccardo PeruginiNo ratings yet
- Ifr2 - 030413-Matyc Automation SacDocument3 pagesIfr2 - 030413-Matyc Automation SacJoel PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Fgtat enDocument8 pagesFgtat enMarius ClavacNo ratings yet
- STEP Product OverviewDocument7 pagesSTEP Product OverviewTran Nguyen BaNo ratings yet
- LP-G Surface 380 Ground Floor 80 100: Lighting Lighting Lighting SocketDocument1 pageLP-G Surface 380 Ground Floor 80 100: Lighting Lighting Lighting SocketSobhy NadaNo ratings yet
- P.O. Bc23-00002 Drawing For Approval r.0Document1 pageP.O. Bc23-00002 Drawing For Approval r.0Hadjer BouchlaghemNo ratings yet
- Emco325 BroschyrDocument4 pagesEmco325 BroschyrnogesoNo ratings yet
- Solton DISCO64 SchematicsDocument14 pagesSolton DISCO64 SchematicsaccordatorepianoNo ratings yet
- 17PM K016V NMBDocument2 pages17PM K016V NMBMourad BejaNo ratings yet
- AKG C422, C34, C33 Stereophonic Condenser MicrophonesDocument4 pagesAKG C422, C34, C33 Stereophonic Condenser MicrophonesMario CrispiNo ratings yet
- Yhg/Yhf: Plastic Filters - On Line Filter Model 'H''Document2 pagesYhg/Yhf: Plastic Filters - On Line Filter Model 'H''Ted ThomsonNo ratings yet
- T BeamDocument10 pagesT BeamPawan Kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Guide hydrostatic steering units type XYDocument34 pagesGuide hydrostatic steering units type XYKADNo ratings yet
- Lab 2ND SemDocument89 pagesLab 2ND Semseion vaneNo ratings yet
- SparameterDocument4 pagesSparameterBogdan DitaNo ratings yet
- Strength of High-Rise Shear Walls-Rectangular Cross SectionsDocument6 pagesStrength of High-Rise Shear Walls-Rectangular Cross Sectionsmr.xinbombayNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic property chart for waterDocument12 pagesThermodynamic property chart for waterIndah Azhari MawaddahNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internal Combustion Engines Heat TransferDocument1 pageIntroduction to Internal Combustion Engines Heat TransferAmit MondalNo ratings yet
- DIN 7162-1965xDocument6 pagesDIN 7162-1965xAntonio Maestre LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Week 4-6 Convolution CorrelationDocument64 pagesWeek 4-6 Convolution CorrelationSOHAG ALAMNo ratings yet
- CS1 capaNCDTDocument6 pagesCS1 capaNCDTbnp2gffx8fNo ratings yet
- Disaster Preparedness GuideDocument2 pagesDisaster Preparedness GuideWinston Rudio JulioNo ratings yet
- ACS U - 5 Imp MaterialDocument30 pagesACS U - 5 Imp MaterialPrathap VuyyuruNo ratings yet
- Pages From Dorman Longs - Handbook For Constructional Engineers - 1895-53Document1 pagePages From Dorman Longs - Handbook For Constructional Engineers - 1895-53Fornvald TamasNo ratings yet
- Rod1000 2016 enDocument3 pagesRod1000 2016 enjackyNo ratings yet
- Carrier Tabela6 DuctDimensionsDocument5 pagesCarrier Tabela6 DuctDimensionsLuciano Lopes SimõesNo ratings yet
- Installation Instruction: 7/16 DIN Female 7/16 DIN Male N Type Male N Type FemaleDocument2 pagesInstallation Instruction: 7/16 DIN Female 7/16 DIN Male N Type Male N Type FemalenguyentraihdNo ratings yet
- Difuses UltrasonicDocument5 pagesDifuses Ultrasonicradius SuharlinNo ratings yet
- KinoptikDocument7 pagesKinoptikSándor SzabóNo ratings yet
- Spcolumn Manual v4.201 - Page - 102Document1 pageSpcolumn Manual v4.201 - Page - 102anmenglaNo ratings yet
- Pages From Bearings Catalogue XinzhuDocument1 pagePages From Bearings Catalogue XinzhumwendaNo ratings yet
- Toilet Block ModelDocument1 pageToilet Block ModelBhushan KambaleNo ratings yet
- DM-27 Part3Document14 pagesDM-27 Part3Adrian CantaragiuNo ratings yet
- Hikaru Nara (Easy Version)Document9 pagesHikaru Nara (Easy Version)ethanyileishiNo ratings yet
- FASCIKEL 2 - Orbis D.O.O. - Material No Poslovanje (Str. 281-285)Document5 pagesFASCIKEL 2 - Orbis D.O.O. - Material No Poslovanje (Str. 281-285)ResnicaoorozjuNo ratings yet
- Int 0 Char '/0' Float 0 Double 0 Null: G Main (A, B A 10 B 20 G A + B Std::cout A B GDocument17 pagesInt 0 Char '/0' Float 0 Double 0 Null: G Main (A, B A 10 B 20 G A + B Std::cout A B GOleg DudiXNo ratings yet
- How To Read MTF CurvesDocument33 pagesHow To Read MTF CurvesDaffyNo ratings yet
- Erwin Panofsky - Perspective As Symbolic FormDocument99 pagesErwin Panofsky - Perspective As Symbolic Formfrizbi2023No ratings yet
- Minolta Auto Meter VFDocument4 pagesMinolta Auto Meter VFgstabNo ratings yet
- IRF510Document8 pagesIRF510aj_oaomvNo ratings yet
- IRF510Document8 pagesIRF510aj_oaomvNo ratings yet
- Minolta Auto Meter VFDocument4 pagesMinolta Auto Meter VFgstabNo ratings yet
- Hasselblad Cfi 150Document2 pagesHasselblad Cfi 150gstabNo ratings yet
- Carl Zeiss CF150Document2 pagesCarl Zeiss CF150gstabNo ratings yet
- Ilford Film Processing ChartDocument1 pageIlford Film Processing ChartMarkusMayerNo ratings yet
- Ilford Delta 100Document6 pagesIlford Delta 100gstabNo ratings yet
- Quasi VarianceDocument2 pagesQuasi Varianceharrison9No ratings yet
- Lecture Antenna MiniaturizationDocument34 pagesLecture Antenna MiniaturizationJuhi GargNo ratings yet
- Short Term Load Forecast Using Fuzzy LogicDocument9 pagesShort Term Load Forecast Using Fuzzy LogicRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- EO and EO-2 Metric Bite Type Fittings: The Fitting AuthorityDocument62 pagesEO and EO-2 Metric Bite Type Fittings: The Fitting AuthorityZahir KhiraNo ratings yet
- Business Calculus NotesDocument38 pagesBusiness Calculus NotesTom KowalskiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Database: Madda Walabu University College of Computing Department of Information TechnologyDocument46 pagesFundamental of Database: Madda Walabu University College of Computing Department of Information TechnologychalaNo ratings yet
- Transportation Installation R2000iC210FDocument25 pagesTransportation Installation R2000iC210FMeet PAtel100% (2)
- 4PH0 1P Que 20160119 PDFDocument28 pages4PH0 1P Que 20160119 PDFschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Formation and Evolution of Planetary SystemsDocument25 pagesFormation and Evolution of Planetary SystemsLovelyn Baltonado100% (2)
- CREATE A CORRECTLY SCALED NETWORK FROM SCRATCHDocument5 pagesCREATE A CORRECTLY SCALED NETWORK FROM SCRATCHMauricio Senior RamírezNo ratings yet
- Manriding Tirfor O-MDocument16 pagesManriding Tirfor O-MPhillip FrencilloNo ratings yet
- SAP Table BufferingDocument31 pagesSAP Table Bufferingashok_oleti100% (3)
- KENWOOD TK 7302 Manual - ADocument2 pagesKENWOOD TK 7302 Manual - AMas IvanNo ratings yet
- Effect of SR, Na, Ca & P On The Castability of Foundry Alloy A356.2Document10 pagesEffect of SR, Na, Ca & P On The Castability of Foundry Alloy A356.2jose.figueroa@foseco.comNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: Electrolyte AnalyzerDocument25 pagesUser's Manual: Electrolyte AnalyzerNghi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Movie Recommender System: Shekhar 20BCS9911 Sanya Pawar 20BCS9879 Tushar Mishra 20BCS9962Document27 pagesMovie Recommender System: Shekhar 20BCS9911 Sanya Pawar 20BCS9879 Tushar Mishra 20BCS9962Amrit SinghNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagents 1Document17 pagesLimiting Reagents 1Aldrin Jay Patungan100% (1)
- Chapter 11 - MatricesDocument39 pagesChapter 11 - MatricesJhagantini Palanivelu0% (1)
- Chapter 4 Worksheets Algebra 1Document110 pagesChapter 4 Worksheets Algebra 1Amanda GeorginoNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF FLANGED SECTION (EC2) - Updated 020712Document23 pagesANALYSIS OF FLANGED SECTION (EC2) - Updated 020712stoneNo ratings yet
- Template 8dDocument165 pagesTemplate 8dLuis Alberto Quiroz GranadosNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 5439390Document108 pagesGrundfosliterature 5439390ptlNo ratings yet
- What Is Radar and Its FunctionDocument3 pagesWhat Is Radar and Its FunctionJean Maya DiscayaNo ratings yet
- Honeywell VisionPro 8000 Install Manual 69-1706Document20 pagesHoneywell VisionPro 8000 Install Manual 69-1706electrician 15No ratings yet
- Line Tension and Pole StrengthDocument34 pagesLine Tension and Pole StrengthDon BunNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric, Gage, and Absolute PressureDocument13 pagesAtmospheric, Gage, and Absolute PressureJefrie Marc LaquioNo ratings yet
- Cube Nets Non-Verbal Reasoning IntroductionDocument6 pagesCube Nets Non-Verbal Reasoning Introductionmirali74No ratings yet
- Lewis Structures and Shape of Molecules and HybridizationDocument12 pagesLewis Structures and Shape of Molecules and HybridizationsanjuanaomiNo ratings yet
- Use Jinja2 To Create TemplatesDocument44 pagesUse Jinja2 To Create TemplatesmNo ratings yet