Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brain
Uploaded by
Brqwert12Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain
Uploaded by
Brqwert12Copyright:
Available Formats
1. The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
Functions: receives, process, interprets, stores incoming information,
send outs messages to muscles, glands, internal organs.
2. The peripheral nervous system consists of all the nerve tissue in the
body.
Functions:
Sensory neurons: bring input to skin, muscles, and organs
Motor neurons: carry output to muscles, glands, organs
3. These are both subdivision of the PNS. The somatic nervous system
handles voluntary muscle movements and transmission of sensory
information, connects to sensory receptors and skeletal muscles. The
autonomic nervous system handles involuntary internal organ
functions, regulates blood vessels, glands, and organs. Influenced by
emotional states: sympathetic and parasympathetic.
4. Sympathetic nervous system mobilizes body for action and
parasympathetic nervous system slows action
5. A neuron consists of dendrites, a cell body and an axon.
The synaptic vessels at the axon terminal are filled with a
neurotransmitter. When the signal reaches the axon terminal, it cause
the vessels to release in the gap between the neurons which is the
synaptic cleft. These molecules then drift across the gap to reach their
destination on the receiving neuron.
6. Myelin Sheath has insulation consisting mainly of fatty material
around some axons. It ensures that the signal doesn’t leak out and
allows the signal to move quickly down the axon.
In Multiple Sclerosis is a neurological disorder where the myelin
sheath is destroyed in patches. The body’s immune systems attacks
the glial cells by attacking the signal transmission.
7. Stem cells are immature cells that renew themselves and have
potential to develop into mature cells.
Neurogenisis is the formation of new neurons, which can even occur
in the adult brain, in case of brain damage.
8. Neurons in a new born is widely spaced, but immediately being to
form new connections and the unused synaptic connection are pruned
away.
Brain Plasticity is when our brains are constantly changing as a
function of our learning experiences and stored memories. Maybe
even new brain cells will be produced by brain stimulation.
9. Neurons communicate using two types of signal transmission:
Excitatory msgs – increases likelihood that receiving neuron will fire
Inhibitory msgs – decreases likelihood that receiving neuron will fire
A neuron either fires or not is the all or non principle
10. Neurotransmitters are neurons that connect to each other but do not
physically touch but rather use a chemical messenger to
communicate. They are a versatile courier.
Serotonin – sleep, mood, appetite
Dopamine – movement, learning, memory, emotion
Acetylcholine – muscle action, memory, cognition
Norepinephrine – heart rate, learning, memory, emotion
GABA – inhibitory neurotransmitter
Glutamate – major neurotransmitter
11. Endorphins is a chemical substance in the nervous system, similar I
structure and action to opiates. Involved in pain reduction, pleasure,
and memory.
12. Hormones are long distance messengers secreted by the endocrine
gland that affect the functioning of other organs.
Psychologists are specifically interested in melatonin, oxytocin,
adrenal hormones, and sex hormones
Melatonin – secreted by the pineal gland, regulates biological rhythms
and promotes sleep
Oxytocin – is secreted by the pituitary gland, enhances uterine
contractions during childbirth
Adrenal Hormones – produced by adrenal glands, is related to
emotion and stress
Sex Hormones – secreted by tissue in gonads, androgens, estrogens,
and progesterone
13. Psychologists study the brain using many methods such as:
Lesion method – damaging or removing section of the brain
Electroencephalography (EEG) – needle electrodes and
microelectrodes into a single cell
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) – wire coil around persons
magnetic field
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) – injections of glucose like
substances contain radio active elements
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – uses magnetic fields and
special radio tissues
14. Localization of function means when different parts of the brain
performs different tasks
15. 1. The brain stem – rises out of the spinal cord
a. Medulla – regulates automatic functions, such as breath and
heart rate
b. Pons – regulates sleeping, waking and dreaming
c. Reticular Activating Sys (RAS) – network of neurons, connects
with higher areas of the brain; screens information, alertness
2. Cerebellum – on top of the brain stem; regulates movement and
balance and involved in simple responses
3. Thalamus – relays motor impulses out of brain, directs incoming
sensory messages to higher centers
4. Hypothalamus and pituitary gland
a. Hypothalamus – associated with survival drives such as,
hunger, thirst, emotion, sex, and reproduction, body temp
b. Pituitary Gland – ‘master gland’ regulated by hypothalamus
5. Limbic System – loosely interconnected structures involved in
emotions
a. Amygdala – evaluates sensory info to determines its importance
b. Hippocampus – allows formation and storage of new memories
6. Cerebrum – site of higher forms of thinking
a. Divided into two halves or cerebral hemispheres that are
connected by a band of fibers called the corpus callosum
b. Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body
c. Each hemisphere has somewhat different talents (lateralization)
7. Cerebral Cortex – layers of densely packed cells covering cerebrum
a. Occipital lobes – contain visual cortex
b. Parietal lobes – contain somatosenory cortex
c. Temporal lobes – involved in memory, perception, and emotion
d. Frontal lobes – contain motor cortex; responsible for making
plans and thinking creatively, Broca’ area (Speech production)
16. Its enables us to form spatial memories so that we can navigate
through our environment and also enables ur to form new memories
about facts and events.
17. Occipital lobes – contain visual cortex
Parietal lobes – contain somatosenory cortex
Temporal lobes – involved in memory, perception, and emotion
Frontal lobes – contain motor cortex; responsible for making
plans and thinking creatively, Broca’ area (Speech production)
18. The two hemispheres communicate via the opus callosum. The right
hemisphere is nonverbal: is better at spatial-visual tasks, facial
recognition, and the creation and appreciation of ar and music. The
left hemisphere is verbal: to excel at languages and verbal activities,
logical, symbolical, and sequential tasks.
19. Split brain surgery is surgery in which the corpus callosum is
severed. Stopping the spread of electrical activity from one side of the
brain to the other.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- How PETCO Manages Ethical Concerns of StakeholdersDocument2 pagesHow PETCO Manages Ethical Concerns of Stakeholdersyashnegi.847268No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Queen ManualDocument25 pagesA Queen ManualAle BioleNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Pathophysiology of Postpartum Hemorrhage and Third Stage of LaborDocument7 pagesPathophysiology of Postpartum Hemorrhage and Third Stage of Labornouval_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Quiz Report-2Document12 pagesQuiz Report-2Nadiya RashidNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Poultry Welfare Developing CountriesDocument12 pagesPoultry Welfare Developing CountriesshamalaksNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Exercise 7.2 - ElectrocardiogramDocument2 pagesExercise 7.2 - ElectrocardiogramKevin F. CortesNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Zebra PDFDocument10 pagesZebra PDFelmond mortaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- SCIENCE FORM 2 (Chapter 1) NOTESDocument41 pagesSCIENCE FORM 2 (Chapter 1) NOTESRamanath Ram100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
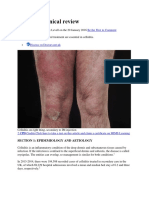
- Cellulitis: Clinical Review: Be The First To CommentDocument9 pagesCellulitis: Clinical Review: Be The First To CommentAnonymous 1nMTZWmzNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Lindane and Permethrin Insecticides for Scabies and LiceDocument4 pagesLindane and Permethrin Insecticides for Scabies and LicevellaparadithaNo ratings yet
- Many Different Uses For YL Lavender OilDocument8 pagesMany Different Uses For YL Lavender OilLena WolfeNo ratings yet
- Socio-Economic Profile and Constraints Faced byDocument5 pagesSocio-Economic Profile and Constraints Faced byAmandeep Singh GujralNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Oral Patho Q AnswerDocument10 pagesOral Patho Q AnswerAnȜ'am Abu Ȝ'leonNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Killer Whales (Orcas) Unsuccessful Births by Mother's NameDocument2 pagesKiller Whales (Orcas) Unsuccessful Births by Mother's NameThe Orca Project Corp100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Body Fluid Electrolytes Acid Base BalanceDocument2 pagesBody Fluid Electrolytes Acid Base BalanceMarzanul Islam AnikNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Anatomy and Physiology of the HeartDocument56 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Heartamjad khan100% (1)
- These Nouns Are The Names For A Collection of Things. Which Are True?Document11 pagesThese Nouns Are The Names For A Collection of Things. Which Are True?Muhammad Ariff Aizuddin AbdullahNo ratings yet
- What Is Dairy RanchingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Dairy RanchingBright SamuelNo ratings yet
- Dental Pulp TissueDocument77 pagesDental Pulp TissueJyoti RahejaNo ratings yet
- Vertigo and ImbalanceDocument19 pagesVertigo and ImbalanceDiena HarisahNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Darwins Voyage PowerPoint For WebsiteDocument38 pagesDarwins Voyage PowerPoint For WebsiteEko SujatmikoNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Mother Tincture Management PDFDocument62 pagesMother Tincture Management PDFParag Mhatre100% (3)
- Ambahan: Ambahans Inscribed On Plants in A Bamboo Grove (Source: Antoon Postma)Document10 pagesAmbahan: Ambahans Inscribed On Plants in A Bamboo Grove (Source: Antoon Postma)Mernie Grace DionesioNo ratings yet
- Capybara SchoolprojectDocument3 pagesCapybara SchoolprojectTom HoldaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Pericoronitis Is Defined As The Inflammation of The Soft Tissues of Varying Severity Around An Erupting or Partially Erupted Tooth With Breach of The FollicleDocument7 pagesPericoronitis Is Defined As The Inflammation of The Soft Tissues of Varying Severity Around An Erupting or Partially Erupted Tooth With Breach of The FollicleRavan WidiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal LepraDocument20 pagesJurnal LepraCalvin AffendyNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam Grade 10 Animal ProductionDocument4 pages3rd Quarter Exam Grade 10 Animal Productionbella flor villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Grabovoi NumbersDocument29 pagesGrabovoi Numberssillyminds100% (3)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Early Human DietsDocument3 pagesEarly Human DietsDouglas CamposNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: An OrientationDocument59 pagesThe Human Body: An OrientationShery Han Bint HindawiNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)