Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients
Uploaded by
msubbiahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients
Uploaded by
msubbiahCopyright:
Available Formats
Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients in Heat Exchangers
U U
Type Application and Conditions 2 1) Btu/(ft2 °F
W/(m K)
h)1)
Tubular, heating or
Gases at atmospheric pressure inside and outside tubes 5 - 35 1-6
cooling
Gases at high pressure inside and outside tubes 150 - 500 25 - 90
Liquid outside (inside) and gas at atmospheric pressure inside
15 - 70 3 - 15
(outside) tubes
Gas at high pressure inside and liquid outside tubes 200 - 400 35 - 70
Liquids inside and outside tubes 150 - 1200 25 - 200
Steam outside and liquid inside tubes 300 - 1200 50 - 200
1500 -
Tubular, condensation Steam outside and cooling water inside tubes 250 - 700
4000
Organic vapors or ammonia outside and cooling water inside
300 - 1200 50 - 200
tubes
steam outside and high-viscous liquid inside tubes, natural
Tubular, evaporation 300 - 900 50 - 150
circulation
steam outside and low-viscous liquid inside tubes, natural
600 - 1700 100 - 300
circulation
steam outside and liquid inside tubes, forced circulation 900 - 3000 150 - 500
Air-cooled heat
Cooling of water 600 - 750 100 - 130
exchangers2)
Cooling of liquid light hydrocarbons 400 - 550 70 - 95
Cooling of tar 30 - 60 5 - 10
Cooling of air or flue gas 60 - 180 10 - 30
Cooling of hydrocarbon gas 200 - 450 35 - 80
Condensation of low pressure steam 700 - 850 125 - 150
Condensation of organic vapors 350 - 500 65 - 90
1000 -
Plate heat exchanger liquid to liquid 150 - 700
4000
Spiral heat exchanger liquid to liquid 700 - 2500 125 - 500
condensing vapor to liquid 900 - 3500 150 - 700
Notes:
1) 1 Btu/(ft2 °F h) = 5.6785 W/(m2 K)
2) Coefficients are based on outside bare tube surface
You might also like
- Overall Heat TransferDocument9 pagesOverall Heat TransferRahul S. ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Coeficientes de Calor 2Document3 pagesCoeficientes de Calor 2Hector BarriosNo ratings yet
- Engineering Page - Heat Exchangers - Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients PDFDocument2 pagesEngineering Page - Heat Exchangers - Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients PDFJahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- HeatExchanger Part2Document81 pagesHeatExchanger Part2mohammad abusarhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Coefficients for Submerged CoilsDocument70 pagesHeat Transfer Coefficients for Submerged CoilsAdam JinNo ratings yet
- HVAC ASSIGNMENT - HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENTSDocument29 pagesHVAC ASSIGNMENT - HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENTSNeerajaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Heat Transfer Rates for Steam and Fluid SystemsDocument19 pagesCalculating Heat Transfer Rates for Steam and Fluid SystemsEnes BayramNo ratings yet
- Burner Start-Up Quick Guide: Appendix ADocument3 pagesBurner Start-Up Quick Guide: Appendix ADIAGNENo ratings yet
- Convective Heat Transfer Coefficients Table Chart - Engineers Edge - WWW - EngineersedgeDocument4 pagesConvective Heat Transfer Coefficients Table Chart - Engineers Edge - WWW - Engineersedgenikhil3005No ratings yet
- Increasing Heat Exchanger PerformanceDocument13 pagesIncreasing Heat Exchanger Performanceimtinan mohsinNo ratings yet
- HF 745 02 T eDocument4 pagesHF 745 02 T eNuñez JesusNo ratings yet
- Type Application and Conditions: W/ (M K) Btu/ (FT °F H)Document2 pagesType Application and Conditions: W/ (M K) Btu/ (FT °F H)Debkumar958No ratings yet
- ITT Standard Gould SpecDocument12 pagesITT Standard Gould SpecDendi DenisNo ratings yet
- Appendix B & CDocument3 pagesAppendix B & CJohn Louie PimentelNo ratings yet
- Koefisien hukum Newton untuk aliran cairan dan gasDocument3 pagesKoefisien hukum Newton untuk aliran cairan dan gasnoviNo ratings yet
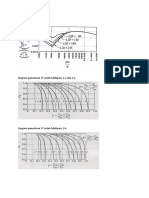
- Penentuan Koefisien H: Diagram Penentuan FT Untuk Multipass 1-2 Dan 1-4Document3 pagesPenentuan Koefisien H: Diagram Penentuan FT Untuk Multipass 1-2 Dan 1-4Novianti NoviNo ratings yet
- Parker B Series Ball ValvesDocument12 pagesParker B Series Ball ValvesCesar ZarateNo ratings yet
- HeatPump enDocument4 pagesHeatPump enArunee SombatjindaNo ratings yet
- Gas Quality INGAA Presentation 2004Document34 pagesGas Quality INGAA Presentation 2004sabrineNo ratings yet
- UFK W AftercoolerDocument3 pagesUFK W AftercoolerLiem NguyenNo ratings yet
- MidsemwasteheatrecoveryDocument11 pagesMidsemwasteheatrecoveryPranav OmkarNo ratings yet
- Setyo KalorDocument2 pagesSetyo KalorstyoNo ratings yet
- Ebara PumpDocument25 pagesEbara PumpMark CentenoNo ratings yet
- Fluxes: Forms of Filler MetalsDocument7 pagesFluxes: Forms of Filler MetalsWilly UioNo ratings yet
- 02 - Cabin Slim Ac Ug 2 D - 21 enDocument13 pages02 - Cabin Slim Ac Ug 2 D - 21 enkdc termice100% (1)
- الرسومات و الجداول الخاصة بالمبادل الحراريDocument11 pagesالرسومات و الجداول الخاصة بالمبادل الحراريمحمد عليNo ratings yet
- Sheet-3: Thermodynamic properties of water and refrigerant-12Document3 pagesSheet-3: Thermodynamic properties of water and refrigerant-12Kerro MankoNo ratings yet
- Some Practical Considerations in The Design of Steam Injection WellsDocument8 pagesSome Practical Considerations in The Design of Steam Injection Wellsfjflores26No ratings yet
- Different Types of Refrigeration SystemDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of Refrigeration SystemRavi Shankar67% (3)
- How To Select The Right Flange Gasket - Projectmaterials PDFDocument1 pageHow To Select The Right Flange Gasket - Projectmaterials PDFWiskusa NarudeanNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Cracking in Recovery BoilersDocument23 pagesCorrosion and Cracking in Recovery BoilersAndy Herdyal SitumorangNo ratings yet
- 9000 SeriesDocument32 pages9000 SeriesTechnical A-Star Testing & Inspection MalaysiaNo ratings yet
- LPG Flex ENDocument4 pagesLPG Flex ENSEBASDAZACNo ratings yet
- Multi-Rifled Boiler Tubes for Power GenerationDocument8 pagesMulti-Rifled Boiler Tubes for Power GenerationAgniva DuttaNo ratings yet
- Ex Air Vortex TubeDocument8 pagesEx Air Vortex TubeSyed AmirNo ratings yet
- 2015 L14 Distillation Applications - Refinery Distillation PDFDocument27 pages2015 L14 Distillation Applications - Refinery Distillation PDFfegcopNo ratings yet
- Dehumidifiers for radiant cooling systems with heat recoveryDocument6 pagesDehumidifiers for radiant cooling systems with heat recoveryNikosNo ratings yet
- Spray Water - Rev 00Document2 pagesSpray Water - Rev 00Jacky KaruppaiahNo ratings yet
- Survey of KEBO Products for Boiler, Cooling and Industrial Water TreatmentDocument3 pagesSurvey of KEBO Products for Boiler, Cooling and Industrial Water TreatmentCarlos TomeyNo ratings yet
- Is S SE E E SE S SE S SE S: Water Storage - CalorifierDocument4 pagesIs S SE E E SE S SE S SE S: Water Storage - CalorifierJust RysdanNo ratings yet
- Air Treatment Product Line Cross ReferenceDocument1 pageAir Treatment Product Line Cross Referenceingenieria_377024831No ratings yet
- Data Sheet-FIREMIKS-FM-14000-GP-F-Aut 2016-02-23Document3 pagesData Sheet-FIREMIKS-FM-14000-GP-F-Aut 2016-02-23appril26No ratings yet
- CLM Series Steam & Water BoilersDocument4 pagesCLM Series Steam & Water BoilersAlexánder Muñoz FerrerNo ratings yet
- Madukismo Water TreatmentDocument119 pagesMadukismo Water TreatmentFadli Ryan ArikundoNo ratings yet
- Catalog Deaerator, Model Deg 8000 PDFDocument2 pagesCatalog Deaerator, Model Deg 8000 PDFHưng QuangNo ratings yet
- Valve Classification SchedulesDocument1 pageValve Classification SchedulesAbd Elrahman HamdyNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Cooling Units For Door or Wall Mounting: Characteristics M.U. EMO04BM1B EMO04CM1B Accessories/OptionsDocument1 pageOutdoor Cooling Units For Door or Wall Mounting: Characteristics M.U. EMO04BM1B EMO04CM1B Accessories/OptionsTomasz KownackiNo ratings yet
- Iti Thermjet Usa (Eclipse)Document38 pagesIti Thermjet Usa (Eclipse)exergicNo ratings yet
- Sno Service Pipe Material: 4. Non Ibr PipingsDocument1 pageSno Service Pipe Material: 4. Non Ibr PipingsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Network Synthesis (HENS/)Document56 pagesHeat Exchanger Network Synthesis (HENS/)vijendra mauryaNo ratings yet
- Chloride Ball Valve FLVDocument7 pagesChloride Ball Valve FLVLenin MagañaNo ratings yet
- Etaline Type SeriesDocument48 pagesEtaline Type SeriesChristopher Greg PermisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Shreshth BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Dati Tecnici TB EDocument2 pagesDati Tecnici TB ExilentstrikeNo ratings yet
- Assignment EN674: Submitted by Puja Koch Roll No-184351012Document9 pagesAssignment EN674: Submitted by Puja Koch Roll No-184351012puja kochNo ratings yet
- Engineering Page - Heat Exchangers - Typical Overall Heat Transfer CoefficientsDocument2 pagesEngineering Page - Heat Exchangers - Typical Overall Heat Transfer CoefficientsNiaz HasanNo ratings yet
- Catalog Ava Air Valve Dok DoakDocument1 pageCatalog Ava Air Valve Dok Doakazlen494No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Non-Stationary Heat Transfer Through Walls, Measurement of Thermal Conductivity, Heat Transfer with Two Phase RefrigerantsFrom EverandHeat Transfer: Non-Stationary Heat Transfer Through Walls, Measurement of Thermal Conductivity, Heat Transfer with Two Phase RefrigerantsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- Guide to preventing corrosion, scale and carryover in boiler feedwater systemsDocument25 pagesGuide to preventing corrosion, scale and carryover in boiler feedwater systemsSree SureshNo ratings yet
- PpiDocument17 pagesPpinithiyanandhamNo ratings yet
- RER Mod5@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument13 pagesRER Mod5@AzDOCUMENTS - inMizan SalimNo ratings yet
- 14 Purgadores Ayvaz PDFDocument13 pages14 Purgadores Ayvaz PDFjoaquin torrano veraNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design Engineer ResumeDocument4 pagesMechanical Design Engineer ResumeAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Esb Series: Gas or LPG 3-Pass Steam BoilerDocument25 pagesEsb Series: Gas or LPG 3-Pass Steam BoilerMohamed Fazil100% (1)
- Gas TurbinesDocument21 pagesGas TurbinesG Vengat VinayagamNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual: General Safety InformationDocument56 pagesInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Manual: General Safety InformationCarlos GonzalezNo ratings yet
- GN08.2279 USD2461b (1) EKV BRDocument16 pagesGN08.2279 USD2461b (1) EKV BRHassan HoudoudNo ratings yet
- ETD - Question BankDocument6 pagesETD - Question BankGopinath VNo ratings yet
- How To Preserve HRSGDocument6 pagesHow To Preserve HRSGBaran ShafqatNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q4 Mod9Document24 pagesSci9 Q4 Mod9Harold Emmanuel M. LlonaNo ratings yet
- Dryness Fraction of Steam LabDocument17 pagesDryness Fraction of Steam LabRoneil Napier100% (3)
- Concordia MECH 351 Thermodynamics IIDocument3 pagesConcordia MECH 351 Thermodynamics IImralex11No ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram Design CriteriaDocument16 pagesProcess Flow Diagram Design CriteriaGabriele GabrieleNo ratings yet
- RS 1500 Sulphur GranulatorDocument4 pagesRS 1500 Sulphur GranulatorvzgscribdNo ratings yet
- Design Practices - SVsDocument12 pagesDesign Practices - SVsagarwalashwin32No ratings yet
- ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RENEWABLE ENERGY GeothermalDocument8 pagesENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RENEWABLE ENERGY GeothermalTegar Putra Adi PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Equilibrium and Heat TransferDocument20 pagesThermal Equilibrium and Heat TransferTS ShongNo ratings yet
- Apv - Evaporator HandbookDocument68 pagesApv - Evaporator HandbookJosiane CostaNo ratings yet
- Wet Lay Up in BoilerDocument5 pagesWet Lay Up in BoilersprotkarNo ratings yet
- Cussons: Engineering Education & Training DivisionDocument16 pagesCussons: Engineering Education & Training DivisionJawwad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument22 pagesUnit IIamarkp204No ratings yet
- Flare System Design For A Refinery Mega ComplexDocument4 pagesFlare System Design For A Refinery Mega Complexroberdani12100% (1)
- Downstream GP Index SummaryDocument6 pagesDownstream GP Index Summarycorey jacobsNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Condensers: Design Features & Performance IssuesDocument58 pagesPower Plant Condensers: Design Features & Performance IssuesAyush ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Final Mill Tariniggng ReportDocument53 pagesFinal Mill Tariniggng ReportPriyanka VishnoiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Gas Turbine Cycles For Power GenerationDocument10 pagesAdvanced Gas Turbine Cycles For Power GenerationRenzo Alexander RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Report On Basic Operation of Vindhyachal Super Thermal Power StationDocument36 pagesReport On Basic Operation of Vindhyachal Super Thermal Power Stationsaurabhk_103No ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Training FileDocument69 pagesThermal Power Plant Training FileAbhishek Kumar YadavNo ratings yet