Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ansys Tutorial-6
Uploaded by
Amit PalaliyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ansys Tutorial-6
Uploaded by
Amit PalaliyaCopyright:
Available Formats
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
NonLinear Materials
Introduction
This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to describe how to include material
nonlinearities in an ANSYS model. For instance, the case when a large force is applied resulting in a stresses
greater than yield strength. In such a case, a multilinear stress-strain relationship can be included which follows
the stress-strain curve of the material being used. This will allow ANSYS to more accurately model the plastic
deformation of the material.
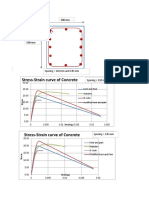
For this analysis, a simple tension speciment 100 mm X 5 mm X 5 mm is constrained at the bottom and has a
load pulling on the top. This specimen is made out of a experimental substance called "WhoKilledKenium".
The stress-strain curve for the substance is shown above. Note the linear section up to approximately 225 MPa
where the Young's Modulus is constant (75 GPa). The material then begins to yield and the relationship
becomes plastic and nonlinear.
Preprocessing: Defining the Problem
1. Give example a Title
Utility Menu > File > Change Title ...
/title, NonLinear Materials
2. Create Keypoints
Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Keypoints > In Active CS
/PREP7
K,#,X,Y
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
We are going to define 2 keypoints (the beam vertices) for this structure to create a beam with a
length of 100 millimeters:
Keypoint Coordinates (x,y)
1 (0,0)
2 (0,100)
3. Define Lines
Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Lines > Lines > Straight Line
Create a line between Keypoint 1 and Keypoint 2.
L,1,2
4. Define Element Types
Preprocessor > Element Type > Add/Edit/Delete...
For this problem we will use the LINK1 (2D spar) element. This element has 2 degrees of freedom
(translation along the X and Y axis's) and can only be used in 2D analysis.
5. Define Real Constants
Preprocessor > Real Constants... > Add...
In the 'Real Constants for LINK1' window, enter the following geometric properties:
i. Cross-sectional area AREA: 25
ii. Initial Strain: 0
This defines an element with a solid rectangular cross section 5 x 5 millimeters.
6. Define Element Material Properties
Preprocessor > Material Props > Material Models > Structural > Linear > Elastic > Isotropic
In the window that appears, enter the following geometric properties for steel:
i. Young's modulus EX: 75e3
ii. Poisson's Ratio PRXY: 0.3
Now that the initial properties of the material have been outlined, the stress-strain data must be
included.
Preprocessor > Material Props > Material Models > Structural > Nonlinear > Elastic >
Multilinear Elastic
The following window will pop up.
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
Fill in the STRAIN and STRESS boxes with the following data. These are points from the
stress-strain curve shown above, approximating the curve with linear interpolation between
the points. When the data for the first point is input, click Add Point to add another. When
all the points have been inputed, click Graph to see the curve. It should look like the one
shown above. Then click OK.
Curve
Strain Stress
Points
1 0 0
2 0.001 75
3 0.002 150
4 0.003 225
5 0.004 240
6 0.005 250
7 0.025 300
8 0.060 355
9 0.100 390
10 0.150 420
11 0.200 435
12 0.250 449
13 0.275 450
To get the problem geometry back, select Utility Menu > Plot > Replot.
/REPLOT
7. Define Mesh Size
Preprocessor > Meshing > Manual Size > Size Cntrls > Lines > All Lines...
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
For this example we will specify an element edge length of 5 mm (20 element divisions along the
line).
8. Mesh the frame
Preprocessor > Meshing > Mesh > Lines > click 'Pick All'
LMESH,ALL
Solution: Assigning Loads and Solving
1. Define Analysis Type
Solution > New Analysis > Static
ANTYPE,0
2. Set Solution Controls
{ Select Solution > Analysis Type > Sol'n Control...
The following image will appear:
Ensure the following selections are made under the 'Basic' tab (as shown above)
A. Ensure Large Static Displacements are permitted (this will include the effects of large
deflection in the results)
B. Ensure Automatic time stepping is on. Automatic time stepping allows ANSYS to determine
appropriate sizes to break the load steps into. Decreasing the step size usually ensures better
accuracy, however, this takes time. The Automatic Time Step feature will determine an
appropriate balance. This feature also activates the ANSYS bisection feature which will
allow recovery if convergence fails.
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
C. Enter 20 as the number of substeps. This will set the initial substep to 1/20 th of the total
load.
D. Enter a maximum number of substeps of 1000. This stops the program if the solution does
not converge after 1000 steps.
E. Enter a minimum number of substeps of 1.
F. Ensure all solution items are writen to a results file. This means rather than just recording the
data for the last load step, data for every load step is written to the database. Therefore, you
can plot certain parameters over time.
Ensure the following selection is made under the 'Nonlinear' tab (as shown below)
A. Ensure Line Search is 'On'. This option is used to help the Newton-Raphson solver converge.
B. Ensure Maximum Number of Iterations is set to 1000
NOTE
There are several options which have not been changed from their default values. For more
information about these commands, type help followed by the command into the command line.
3. Apply Constraints
Solution > Define Loads > Apply > Structural > Displacement > On Keypoints
Fix Keypoint 1 (ie all DOFs constrained).
4. Apply Loads
Solution > Define Loads > Apply > Structural > Force/Moment > On Keypoints
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
Place a 10,000 N load in the FY direction on the top of the beam (Keypoint 2).
5. Solve the System
Solution > Solve > Current LS
SOLVE
The following will appear on your screen for NonLinear Analyses
This shows the convergence of the solution.
General Postprocessing: Viewing the Results
1. To view the element in 2D rather than a line: Utility Menu > PlotCtrls > Style > Size and Shape and
turn 'Display of element' ON (as shown below).
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
2. View the deflection contour plot
General Postproc > Plot Results > Contour Plot > Nodal Solu... > DOF solution, UY
PLNSOL,U,Y,0,1
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
Other results can be obtained as shown in previous linear static analyses.
Time History Postprocessing: Viewing the Results
As shown, you can obtain the results (such as deflection, stress and bending moment diagrams) the same way
you did in previous examples using the General Postprocessor. However, you may wish to view time history
results such as the deflection of the object over time.
1. Define Variables
{ Select: Main Menu > TimeHist Postpro. The following window should open automatically.
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
If it does not open automatically, select Main Menu > TimeHist Postpro > Variable Viewer
{ Click the add button in the upper left corner of the window to add a variable.
{ Select Nodal Solution > DOF Solution > Y-Component of displacement (as shown below) and
click OK. Pick the uppermost node on the beam and click OK in the 'Node for Data' window.
{ To add another variable, click the add button again. This time select Reaction Forces > Structural
Forces > Y-Component of Force. Pick the lowermost node on the beam and click OK.
{ On the Time History Variable window, click the circle in the 'X-Axis' column for FY_3. This will
make the reaction force the x-variable. The Time History Variables window should now look like
this:
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
2. Graph Results over Time
{ Click on UY_2 in the Time History Variables window.
{ Click the graphing button in the Time History Variables window.
{ The labels on the plot are not updated by ANSYS, so you must change them manually. Select
Utility Menu > Plot Ctrls > Style > Graphs > Modify Axes and re-label the X and Y-axis
appropriately.
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/NonLinearMat/NonLine...
This plot shows how the beam deflected linearly when the force, and subsequently the stress, was
low (in the linear range). However, as the force increased, the deflection (proportional to strain)
began to increase at a greater rate. This is because the stress in the beam is in the plastic range and
thus no longer relates to strain linearly. When you verify this example analytically, you will see the
solutions are very similar. The difference can be attributed to the ANSYS solver including large
deflection calculations.
Command File Mode of Solution
The above example was solved using a mixture of the Graphical User Interface (or GUI) and the command
language interface of ANSYS. This problem has also been solved using the ANSYS command language
interface that you may want to browse. Open the file and save it to your computer. Now go to 'File > Read
input from...' and select the file.
Copyright © 2003 University of Alberta
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Save My Exams (Physics Notes) - Work, Energy & PowerDocument38 pagesSave My Exams (Physics Notes) - Work, Energy & Powervihaan.nemaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of SOMDocument10 pagesBasic Concept of SOMO20 0023 Chandrasekaran. S. [PT]No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials I-1Document67 pagesStrength of Materials I-1Adebisi IbraheemNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Science: Y. Garbatov, C. Guedes Soares, J. Parunov, J. KodvanjDocument8 pagesCorrosion Science: Y. Garbatov, C. Guedes Soares, J. Parunov, J. KodvanjSachin SukumaranNo ratings yet
- Affect of Acid and Alkaline On Tensile Stength of Fibers.Document26 pagesAffect of Acid and Alkaline On Tensile Stength of Fibers.Pranjal Mehta57% (70)
- Chap 3Document63 pagesChap 3snupisnupNo ratings yet
- Module #6aDocument17 pagesModule #6akamel touilebNo ratings yet
- Design Segmental Precast Linning Tunnel LiningDocument29 pagesDesign Segmental Precast Linning Tunnel LiningMirna KristiyantoNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument6 pagesStress and StrainTugas00No ratings yet
- Nonlinear Strain Hardening Parameter Comparison For Stainless SteelDocument7 pagesNonlinear Strain Hardening Parameter Comparison For Stainless SteelSavalia HardikNo ratings yet
- Modified Syllabus of B.Tech (Civil Engg.) : Third SemesterDocument13 pagesModified Syllabus of B.Tech (Civil Engg.) : Third SemesterTarunNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structures ModuleDocument48 pagesDesign of Steel Structures ModuledagbaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials CH 3Document12 pagesMechanics of Materials CH 3Adrian MackNo ratings yet
- Basic of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity and Its CalculationDocument23 pagesBasic of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity and Its CalculationAshutosh RaiNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument31 pagesElasticityMUNTASIRNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument115 pagesSyllabusmaxie1024No ratings yet
- Design of Pressure Vessels Under ASME Section VIIIDocument124 pagesDesign of Pressure Vessels Under ASME Section VIIIfqadir100% (6)
- Tensile Mechanical Properties of The Electro-Welded Wire MeshesDocument11 pagesTensile Mechanical Properties of The Electro-Welded Wire MeshesCamilo Gonzalez100% (1)
- Introduction To RC DesignDocument67 pagesIntroduction To RC Designsiti HawaNo ratings yet
- ASTM E8 E8M 2021 Tension Testing of Metallic MaterialsDocument30 pagesASTM E8 E8M 2021 Tension Testing of Metallic MaterialsSuvro ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium Elasticity and Fracture: Physics For EngineersDocument19 pagesStatic Equilibrium Elasticity and Fracture: Physics For EngineersYeho ShuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17-Physics of Solids Important Questions With AnswersDocument30 pagesChapter 17-Physics of Solids Important Questions With AnswersManoNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials NotesDocument66 pagesStrength of Materials NotesHimanshu MishraNo ratings yet
- Confined Concrete Models PDFDocument4 pagesConfined Concrete Models PDFTushar SawaseNo ratings yet
- Student Assignment Cover SheetDocument11 pagesStudent Assignment Cover SheetAhmed AdelNo ratings yet
- MS, TMT, CTDDocument5 pagesMS, TMT, CTDAbdul BasitNo ratings yet
- 54-Analysis of Structural Crashworthiness of Double-Hull Ships in Collision and Grounding - Bin LiuDocument19 pages54-Analysis of Structural Crashworthiness of Double-Hull Ships in Collision and Grounding - Bin LiuNguyễn Huy VũNo ratings yet
- Constitiutive Modelling ConcreteDocument37 pagesConstitiutive Modelling ConcreteGaby GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Photo ElasticityDocument1,102 pagesPhoto ElasticityJacobo Zapata RojasNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study of Pile-Up in Bulk Metallic GlassDocument9 pagesNumerical Study of Pile-Up in Bulk Metallic GlassAditya DeoleNo ratings yet