Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microbe Mission
Uploaded by
Grant NicholasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microbe Mission
Uploaded by
Grant NicholasCopyright:
Available Formats
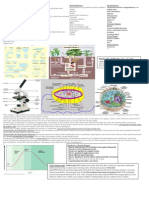
BACTERIA!
• bacillus is rod-shaped
• coccus is ball-shaped
• spirilium is spiral-shaped
• vibrio is comma-shaped
• cocco-bacillus is ovoid-shaped
• other combinations
(mostly spherical, rod, and spiral)
Gram positive bacteria
• stain purple under Gram stain
• have a thick bilayer wall of the
polymer peptidoglycan.
Gram negative bacteria
• stain red
• have a thin layer of this polymer and an
additional lipopolysaccharide outer layer,
LPS,
• often endotoxic - capable of initiating
inflammation and cell-mediated immune
responses
• e.g., Salmonella, Shigella, and
Escherichia.
Some are photoautotrophic - make their own food
as plants and give off oxygen – Cyanobacteria are
also aerobic – use oxygen for respiration Purple
and green bacteria
are anaerobic
• Some are chemoautotrophic - synthesize their own
food using energy from chemical reactions
ANIMAL-LIKE PROTISTS (PROTOZOA) – important for recycling in nitrogen and sulfur cycles
Amoeba • Some have flagella - rotates like a tiny outboard
• Protozoa means “little animal” – act like tiny animals - Eukaryotic motor, others secrete a slime layer and move
• Hunt other microbes for food over surfaces like slugs, while others are immobile.
• Mainly feed on bacteria, also other protozoa and some algae • Some form spores
• Digest food in digestive organelles
• Ciliates, Amoebaes, Flagellates – organized by mode of
transportation
• Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena are examples ARCHAEA
• Most are not harmful – a few are harmful • Are Prokaryotic
• Certain protozoa can cause dysentery and malaria • Similar to bacteria in many characteristics
• Cell walls lack peptidoglycan + other differences
FUNGI Yeast • Origin very old - during formation of the earth
• Cellular level, more like animals than plants – Eukaryotic • Extremely tolerant to heat, acid, and toxic gases
• Can’t synthesize their own food • Found in extreme habitats in anaerobic environments to produce
• Single celled as yeast or multicellular clusters as molds & mushrooms methane, high salt concentrations or hot acid environments
• Multicellular ones form filament like strands – hyphae • Involved in carbon & nitrogen cycles, assist in digestion, & can be
• Grow best in slightly acidic environment – can grow in low moisture used in sewage treatment
• Live in soil, on plants & animals, in fresh & salt water
• One teaspoon of topsoil has about 120,000 fungi ALGAL PROTISTS (ALGAE)
• Baker’s yeast for bread and brewing, some fungi are used for antibiotics, others • Are Eukaryotic
are • Found in fresh and salt water environments
decomposers in the ecosystem • Can live on rocks, trees, and in soils with enough moisture
• Some cause disease in humans, animals and plants – ruin ¼ to ½ of fruits & • Can carry on photosynthesis – produce large amount of oxygen
vegetables per year for life on earth
• Diatoms, Volvox, Clamydomonas , Spirogyra
VIRUSES • Shells of diatoms – silica – mined to make abrasives
• Are acellular • Algal blooms can use up oxygen in water – harming other organisms as fish
• Consists of a piece of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) encased in protein
and in some cases a membrane-like envelope
• They come in many shapes
• Found anywhere there are cells to infest PRIONS
• Exist to reproduce – must take over a suitable host cell • proteinaceous infectious particles, associated with a number of diseases such as
• Uses the cell machinery of the host cell to reproduce o Creutzfeld-Jacob disease (CJD) in humans
o Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome (GSS) in humans
o Alpers syndrome (in infants),
o Fatal Familial Insomnia (FFI) in humans
o Kuru in humans
o Scrapie in sheep,
o Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) or Mad Cow Disease in cattle
o Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) in wild ungulates such as Mule deer and elk
• These diseases are characterized by loss of motor control, dementia, paralysis, wasting
and
eventually death.
You might also like
- Microbe Mission Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesMicrobe Mission Cheat Sheetgangakolli100% (3)
- Microscopes, Prions, Bacteria, Fungi, ProtistsDocument2 pagesMicroscopes, Prions, Bacteria, Fungi, Protistsbookguynelson75% (4)
- Anatomy and Physiology Science Olympiad 2024 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Science Olympiad 2024 Cheat Sheetgfzmrtqj54No ratings yet
- Science Olympiad: Forensics Note SheetDocument2 pagesScience Olympiad: Forensics Note Sheetbasm100% (3)
- Ecology Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesEcology Cheat SheetJorge Aka-angel0% (2)
- Meteorology Cheat Sheet SciOlyDocument2 pagesMeteorology Cheat Sheet SciOlySaanvi0% (2)
- Reach For The Stars SciO Reference SheetDocument8 pagesReach For The Stars SciO Reference SheetAmanda Liu100% (1)
- MM Cheat Sheet 2011Document2 pagesMM Cheat Sheet 2011Jayanthi RameshNo ratings yet
- Disease Detectives - NotesDocument3 pagesDisease Detectives - NotesAshwin KaliyaperumalNo ratings yet
- 120 313 Mycology MaielloDocument3 pages120 313 Mycology MaielloBen100% (1)
- Manual Electricty and MagnetismDocument13 pagesManual Electricty and MagnetismDennis Cosmod100% (1)
- Testing of Semifinished Products of Thermoplastics Bases - Indications Directive DVS 2201-1Document4 pagesTesting of Semifinished Products of Thermoplastics Bases - Indications Directive DVS 2201-1OscarNo ratings yet
- Social Media and Loneliness - Why An Instagram Picture May Be Worth More Than A Thousand Twitter WordsDocument13 pagesSocial Media and Loneliness - Why An Instagram Picture May Be Worth More Than A Thousand Twitter WordsCarlos Leite Filho100% (1)
- PacificGoldenPlover Microbe Mission Practice TestDocument5 pagesPacificGoldenPlover Microbe Mission Practice TestsandeeptaraNo ratings yet
- Microbe MissionDocument1 pageMicrobe MissionGrant Nicholas100% (1)
- Scioly 2012 Microbe MissionDocument2 pagesScioly 2012 Microbe Missionedguchi19100% (3)
- Weather Systems Vocab Updated 12-31-14Document5 pagesWeather Systems Vocab Updated 12-31-14api-260201978No ratings yet
- Practice TestDocument3 pagesPractice TestNur Banu SimsekNo ratings yet
- Solubility Tests Identify Common Solids & LiquidsDocument4 pagesSolubility Tests Identify Common Solids & LiquidssNo ratings yet
- Microscope Skills ReviewDocument5 pagesMicroscope Skills Reviewapi-329085879No ratings yet
- Weather Study GuideDocument2 pagesWeather Study Guideapi-296852092100% (1)
- Dichotomous Key To OrdersDocument15 pagesDichotomous Key To OrdersHuyền Nguyễn Thị ThanhNo ratings yet
- Familiar Weather TopicsDocument17 pagesFamiliar Weather Topicsapi-217675974No ratings yet
- Forensics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesForensics Cheat SheetJacob ShawNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument18 pagesBiotechnologyZanib SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Practical Microbiology Exam Revision: Slide Spots CollectionDocument40 pagesPractical Microbiology Exam Revision: Slide Spots Collectionعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- Viruses: Key Characteristics!Document7 pagesViruses: Key Characteristics!Melody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Science Chapter 2 MicrooganismDocument9 pagesClass 8 - Science Chapter 2 MicrooganismwandererNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitology PDFDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology PDFArianna Aparte AvenidoNo ratings yet
- Arthro 1Document55 pagesArthro 1MenDel Icj IcjiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerNathaniel FerrerNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Archaebacteria and Eubacteria ComparisonDocument34 pagesKingdom Archaebacteria and Eubacteria ComparisonGena Clarish CarreonNo ratings yet
- STDs and Common Diseases: Transmission, Symptoms and PreventionDocument1 pageSTDs and Common Diseases: Transmission, Symptoms and PreventionAnkita ShirahattiNo ratings yet
- Archaebacteria Are The Oldest Organisms Living On The EarthDocument4 pagesArchaebacteria Are The Oldest Organisms Living On The EarthTon TonNo ratings yet
- Microbiology NotesDocument1 pageMicrobiology NotesGlecy Ann MagnoNo ratings yet
- Pollution Is The Introduction of Contaminants Into A Natural Environment That Causes Instability, DisorderDocument16 pagesPollution Is The Introduction of Contaminants Into A Natural Environment That Causes Instability, DisorderJassi Layal100% (2)
- Virus, Viroids and PrionsDocument29 pagesVirus, Viroids and PrionscatherinejoaquinNo ratings yet
- Botany Chapter 1 Notes PDFDocument2 pagesBotany Chapter 1 Notes PDFSUDHIR MISHRANo ratings yet
- Parasitology: An Introduction to Nematodes, Cestodes, Trematodes and ProtozoaDocument8 pagesParasitology: An Introduction to Nematodes, Cestodes, Trematodes and ProtozoaRuthenie RedobleNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Classification Observation of Microorganisms by Microscopy-1Document47 pagesBacterial Classification Observation of Microorganisms by Microscopy-1lutfiyecelik18No ratings yet
- Medical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyDocument3 pagesMedical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyLaiza JanelleNo ratings yet
- Basic Microbiology Part-3Document5 pagesBasic Microbiology Part-3raifbinrafiNo ratings yet
- BIO204 - Chapter 2Document1 pageBIO204 - Chapter 2Holin DolanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 5Document13 pagesChapter 4 5Johana Pinagayao AngkadNo ratings yet
- Ch. 21: Vascular Plants Without Seeds: ConceptsDocument4 pagesCh. 21: Vascular Plants Without Seeds: ConceptsNexNo ratings yet
- Micr Lec - MidtermsDocument20 pagesMicr Lec - Midtermsyvette montesNo ratings yet
- Micro para ReviewerDocument4 pagesMicro para ReviewerMelo MedecieloNo ratings yet
- Biology Kingdom SystemDocument41 pagesBiology Kingdom SystemDBT1A F2020 LinaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotes Structure and Function of Prokaryotic CellDocument40 pages1.2 Prokaryotes Structure and Function of Prokaryotic Celljumbergy01No ratings yet
- 3.kingdom Plantae NIE Class 11Document10 pages3.kingdom Plantae NIE Class 11Sasuke UchihaNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument14 pagesBiology NotesWoo wooNo ratings yet
- Micro Para 1Document6 pagesMicro Para 1glen bert banuaNo ratings yet
- Cell: Parts and Their FunctionsDocument12 pagesCell: Parts and Their FunctionsAllex Leigh DominguezNo ratings yet
- Week 2 LectureDocument8 pagesWeek 2 Lecturekimmynemil80No ratings yet
- MicroPara 02 - Classification and NomenclatureDocument41 pagesMicroPara 02 - Classification and NomenclatureJianne CaloNo ratings yet
- Form Three Biology NotesDocument88 pagesForm Three Biology NotesTowera KamphanjeNo ratings yet
- Final Notebook BioDocument16 pagesFinal Notebook Biolorina p del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Anaerobes: Definitions EpidemiologyDocument10 pagesAnaerobes: Definitions EpidemiologyKayode AGNo ratings yet
- BscNR24 T4 Characteristics of FungiDocument4 pagesBscNR24 T4 Characteristics of Fungiakoeljames8543No ratings yet
- Key Differences Between Bacteria and CyanobacteriaDocument18 pagesKey Differences Between Bacteria and CyanobacteriaFazal AminNo ratings yet
- BC-312 Microorganism ImportanceDocument3 pagesBC-312 Microorganism ImportanceAjay MahaichNo ratings yet
- 2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFDocument18 pages2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFSean SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- TDT4171 Artificial Intelligence Methods Task 5 Creating A Decision Support SystemDocument12 pagesTDT4171 Artificial Intelligence Methods Task 5 Creating A Decision Support SystemKermess McNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Wire Reference Guide: WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611 WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611Document1 pageThermocouple Wire Reference Guide: WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611 WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611Mohamed MaltiNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis AND Similarity: Chapter-5. (Frank White)Document46 pagesDimensional Analysis AND Similarity: Chapter-5. (Frank White)ShujaAmjadNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing TechniquesDocument34 pagesDigital Image Processing Techniquesaishuvc1822No ratings yet
- State Standards: Common CoreDocument24 pagesState Standards: Common CoreEddy R. VélezNo ratings yet
- Compact GSM II: Installation and Application ManualDocument22 pagesCompact GSM II: Installation and Application ManualleonardseniorNo ratings yet
- Live load and wind pressure on sloping roofsDocument11 pagesLive load and wind pressure on sloping roofsAbel BerhanemeskelNo ratings yet
- PT32 12Document3 pagesPT32 12sergiuserbanNo ratings yet
- Lectures Accompanying The Book - Solid State Physics - An (PDFDrive)Document148 pagesLectures Accompanying The Book - Solid State Physics - An (PDFDrive)Raza Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Collet Chuck Catalog 2007 PDFDocument28 pagesCollet Chuck Catalog 2007 PDFAlexandru Marius-catalinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1bekemaNo ratings yet
- Is 14416 1996Document20 pagesIs 14416 1996kaustavNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Hazardous Area ClassificaDocument106 pagesHazardous Area Hazardous Area ClassificaHedi Ben MohamedNo ratings yet
- TCP Operational Overview and The TCP Finite State Machine (FSM)Document4 pagesTCP Operational Overview and The TCP Finite State Machine (FSM)Mayank JaitlyNo ratings yet
- KX DT543Document74 pagesKX DT543Uriel Obregon BalbinNo ratings yet
- Lubricants For Cement ProductionDocument21 pagesLubricants For Cement Productiongrameshkreddy2013100% (1)
- Alkali MetalsDocument12 pagesAlkali MetalsSaki Sultana LizaNo ratings yet
- NCERT: Why Is Steel More Elastic Than Rubber?Document7 pagesNCERT: Why Is Steel More Elastic Than Rubber?Satyam RaiNo ratings yet
- Rigid PavementDocument100 pagesRigid PavementJAY GANDHI100% (1)
- Ajmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalDocument45 pagesAjmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalNikita KadamNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument69 pagesMachine DesignSushant TiwariNo ratings yet
- 250+ C Programs for Practice PDF Free DownloadDocument13 pages250+ C Programs for Practice PDF Free Downloadsubhanshu sahuNo ratings yet
- CC5291-Design For Manufacture Assembly and Environments QBDocument11 pagesCC5291-Design For Manufacture Assembly and Environments QBYuvaraj Yuvi0% (1)
- Chapter 3 Step Wise An Approach To Planning Software Projects 976242065Document31 pagesChapter 3 Step Wise An Approach To Planning Software Projects 976242065RiajiminNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC Study GuideDocument4 pagesAP Calculus BC Study GuideHarshil SahaiNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument6 pagesConnective TissuecrtgyhujikNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Paper 1 Marking Scheme Asumbi Girls Final Prediction 2022Document4 pagesBIOLOGY Paper 1 Marking Scheme Asumbi Girls Final Prediction 2022balozi training InstituteNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument45 pagesSeminar Reportmanaskollam0% (1)