Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 11
Uploaded by
Jamaliah DaudOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap 11
Uploaded by
Jamaliah DaudCopyright:
Available Formats
T ER
AP
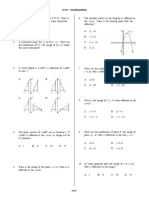
11 Transformations
CH
1. State the transformation involved if P′ is the image of P.
Q
P
P′
2. For the diagram given, figure Q′ is the image of Q under a transformation. State
(a) the transformation involved
(b) the image of point R
M N
Q R
U V S
Q′ W
3. Based on the given transformation, draw the images or the objects for each of the
following.
(a) K ′ is the image of K when K is reflected about the line RS.
K
S
55 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
(b) K ′ is the image of K that was rotated 270° about point B in an anticlockwise
direction.
K′
B
4. State whether the following represents a translation or not. Write either “u” or “2” in
the box given.
C′
5. Draw the image of the following translation represented by the direction line RS.
R A
–4
6. Draw the image of the object under the translation 1 3 2.
y
x
0
2 4 6
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 56
7. State the direction and the distance of the movement of the following translation.
N′
8. Given that A′ is the image of A under a translation. Write the translation in the form
a
1 b 2.
A
A′
6
9. Find the coordinates of the image of point B(–2, 3) under translation 1 –4 2 .
–3
10. Find the coordinates of the object of point Q′(7, 9) for translation 1 8 2.
–2 5
11. A point, Q, is under a translation of 1 2 and then 1 2 . The final image of Q is (7, 4).
3 –1
(a) Determine the coordinates of Q.
(b) State the equivalent single translation for Q.
12. Draw the image of the given object under a reflection about line PQ.
57 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
13. For the following object and its image, construct the axis of reflection, RS.
14. Given that N′ is the image of N under a reflection. Describe the reflection completely.
E H D
N′
F C
N
A G B
15. For each of the points A, B, C and D shown in the diagram, mark the images obtained
when the points are reflected about y-axis. Hence, state the coordinates of the images.
y Coordinates of point Coordinates of image
5
A
4 (a) A(2, 4)
3
B
2
1
D (b) B(–2, 2)
x
–4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5
–1
–2 (c) C(–1, –3)
–3
C
–4
(d) D(1, 1)
16. A point K(3, −4) is mapped to its image K′ under a reflection about x-axis. K′ is then
mapped to K′′ under a reflection about the y-axis.
(a) State the coordinates of K′′.
(b) Describe one reflection which maps K to K′′.
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 58
17. Draw the image of the object under a rotation through 90° anticlockwise about the centre
O.
O
18. M′ is the image of M under a rotation. Mark the centre of rotation as O in the diagram
and hence, state the angle and direction of the rotation.
(a) Angle of rotation:
(b) Direction:
M′
M
19. Mark and state the coordinates of the images of points R and S under a rotation through
90° clockwise about the point (2, 3).
y
R
6
5
4
3
2
1
S
x
0 1 2 3 4 5
20. Mark and state the coordinates of the objects of points T′ and U′ under a rotation through
90° anticlockwise about the point (–2, 1).
y
4
3
2
1 U′
x
–5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1
–1
–2
T′
–3
–4
59 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
21. Given S′ is the image of S under a rotation. Describe the rotation completely.
I H
B S
C D G
S′ F
A E
22. A point M(3, 1) is under a rotation through 90° anticlockwise about the point (0, −1).
The image M′ is then mapped to M′′ under a rotation 180° about the point (1, 2). Find the
coordinates of M′ and M′′.
23. State whether the following transformation is an isometry.
24. In the diagram, complete the pattern by drawing the images of the object under a
2
translation 1 2 three times.
0
y
0 x
25. State whether the following pair of diagrams are congruent.
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 60
26.
3 cm S
P
5 cm
Q R
Parallelogram PQRS experiences a reflection along the line QR. Calculate the perimeter of
the whole diagram formed.
27.
Q L
I
M P
O
J N K
IJKL is a rectangle with sides 5 units and 3 units respectively. M, N, P and Q are midpoints
of the respective sides.
(a) ∆OKL is the image of ∆IJO under a rotation through about the point
.
(b) The midpoint of diagonals JL and IK is point .
(c) ∠IOJ = and ∠IOL = .
(d) The perimeter of IJKL = .
(e) The area of ∆IJL = The area of .
(f) A rectangle like IJKL has axes of symmetry.
61 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
You might also like
- Is The Image of PDocument7 pagesIs The Image of PAnonymous bwVxI8Y8WNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Transformations "Translations"Document139 pagesUnit 1: Transformations "Translations"ARNOLD NOVEMRINo ratings yet
- MaTh 7.5 ExamplesDocument2 pagesMaTh 7.5 ExamplesCA-Math-TeachNo ratings yet
- Math+ Grade+7 Ch+8++Reflections+and+TranslationsDocument28 pagesMath+ Grade+7 Ch+8++Reflections+and+TranslationsLBM PLAYZNo ratings yet
- Translation:: A B C DDocument4 pagesTranslation:: A B C DDiMangNo ratings yet
- MODULE 11 - TransformationDocument12 pagesMODULE 11 - Transformationhasnitajb100% (1)
- Transformations III Module - Latest Edition (2020)Document12 pagesTransformations III Module - Latest Edition (2020)shamirraNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Anthony Butler - 1 - ReflectionsDocument3 pagesKami Export - Anthony Butler - 1 - ReflectionsAnthony ButlerNo ratings yet
- THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY PROBLEMSDocument25 pagesTHREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY PROBLEMSmohd atifNo ratings yet
- A5 Matrices With Transformation MSDocument6 pagesA5 Matrices With Transformation MSDua LatifNo ratings yet
- Modul 11 Topic: Transformations: AnswerDocument12 pagesModul 11 Topic: Transformations: AnswerAnonymous PPYjNttNo ratings yet
- Transformations: Nur Akma BT Makhtar D20081032217Document17 pagesTransformations: Nur Akma BT Makhtar D20081032217WaniAimiNo ratings yet
- Topical Test 8: Transformations IDocument5 pagesTopical Test 8: Transformations ISabariah OsmanNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Reflection: AB A'B', BC B'C' and CA C'A'. A' and A Are The Same Distance From The MirrorDocument8 pages3.2 Reflection: AB A'B', BC B'C' and CA C'A'. A' and A Are The Same Distance From The MirrorZ AliNo ratings yet
- Refl: On: FFLFFLDocument5 pagesRefl: On: FFLFFLWong Yu XuanNo ratings yet
- Q15 TransformationsDocument6 pagesQ15 Transformationsg-54230731No ratings yet
- Unit 5.2 - Reflections - Review WorksheetDocument2 pagesUnit 5.2 - Reflections - Review WorksheetPhop SattayayutNo ratings yet
- MATRICES-AND-TRANSFORMATIONS-QDocument5 pagesMATRICES-AND-TRANSFORMATIONS-Qwambuieccra79No ratings yet
- CEMKS3 E7 GM4 1 ItDocument3 pagesCEMKS3 E7 GM4 1 ItHan Yuan YapNo ratings yet
- 2 Transformations AssignmentDocument5 pages2 Transformations Assignmentrohitrgt4uNo ratings yet
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)Document21 pages2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Probset101 BDocument2 pagesProbset101 BRaymond OndesimoNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument3 pagesReflectiondevit siahaanNo ratings yet
- T K B A Y: Review 3 TrigonometryDocument4 pagesT K B A Y: Review 3 Trigonometryjiaying liNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect 5 Transformations)Document11 pagesPractice Makes Perfect 5 Transformations)dikwanzNo ratings yet
- A2AS MATH Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2014 13507Document8 pagesA2AS MATH Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2014 13507qekosaduNo ratings yet
- Base 2 Base 5 234 2345 1025 933 712 1001011 : 1) Convert The Following Number BasesDocument2 pagesBase 2 Base 5 234 2345 1025 933 712 1001011 : 1) Convert The Following Number BasesLyna NaderNo ratings yet
- Matematik c123Document2 pagesMatematik c123Lyna NaderNo ratings yet
- PS 1 (A)Document2 pagesPS 1 (A)Fredie LeeNo ratings yet
- Sets Worksheet 1Document10 pagesSets Worksheet 1johncarpusampofoNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMATIONS Form 2Document34 pagesTRANSFORMATIONS Form 2Rosmah Abdullah87% (15)
- Topic: Transformation Answer All Questions.: 1 A) B) C) PDocument8 pagesTopic: Transformation Answer All Questions.: 1 A) B) C) Pwhy daNo ratings yet
- 29. Transformations1Document8 pages29. Transformations1MURALEE A/L VEERAMALAI MoeNo ratings yet
- Tranformation 27 October 2023Document10 pagesTranformation 27 October 2023Taamilchelvi saravananNo ratings yet
- Topic: Transformation Answer All Questions.: 1 A) B) C) PDocument8 pagesTopic: Transformation Answer All Questions.: 1 A) B) C) Pwhy daNo ratings yet
- HCI H2 2021 Prelim P2 QNDocument6 pagesHCI H2 2021 Prelim P2 QNCheesy ONENo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument2 pagesAssignment IPLAVAK DASNo ratings yet
- HL Calculus 1 Bank PDFDocument4 pagesHL Calculus 1 Bank PDFibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- 14.1 Notes 2011Document20 pages14.1 Notes 2011elssiechrissNo ratings yet
- Vectors Problems SolutionsDocument4 pagesVectors Problems SolutionsSonika MalyalaNo ratings yet
- S4 to S5 Mathematics Compulsory Summer HomeworkDocument32 pagesS4 to S5 Mathematics Compulsory Summer Homework(PCM) Pang Chun ManNo ratings yet
- 2016 Pape1 To 2018 PDFDocument29 pages2016 Pape1 To 2018 PDFNancy Sikazwe100% (1)
- Trapezium ABCD coordinates and gradientDocument12 pagesTrapezium ABCD coordinates and gradientAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- Pastpaper DoubtsDocument34 pagesPastpaper DoubtsArishaNo ratings yet
- SOL. Vector (PART 3)Document10 pagesSOL. Vector (PART 3)devli falduNo ratings yet
- Ans f5 MM Bab5 Part 1Document11 pagesAns f5 MM Bab5 Part 1Law KellyNo ratings yet
- (A) Transformations (Rotation) 2 Marks 1: AnswerDocument2 pages(A) Transformations (Rotation) 2 Marks 1: AnswerIzzati NorNo ratings yet
- Bending StressDocument66 pagesBending StressNathaniel TayNo ratings yet
- STD 10 Maths Part 2 PDFDocument178 pagesSTD 10 Maths Part 2 PDFBLESSY MATHAINo ratings yet
- Jawahar Science College, Neyveli: Section-B (5x5 25) Answer All QuestionsDocument2 pagesJawahar Science College, Neyveli: Section-B (5x5 25) Answer All QuestionsRajasekar GNo ratings yet
- Transformation NotesDocument12 pagesTransformation NotespapersculptorNo ratings yet
- Seminar 07Document3 pagesSeminar 07GabiandoNo ratings yet
- 1 Raffles Institution H2 Further Mathematics 2017 Preliminary Exam Paper 1 QuestionDocument5 pages1 Raffles Institution H2 Further Mathematics 2017 Preliminary Exam Paper 1 QuestionYao Le Titanium ChenNo ratings yet
- 12 Periodic Relationships: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument6 pages12 Periodic Relationships: Trigonometric FunctionsSıla DenizNo ratings yet
- Vector NotesDocument35 pagesVector NotesjhdmssNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- SBP 2011 Addmaths 2 AnsDocument12 pagesSBP 2011 Addmaths 2 AnsJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- SBP 2011 Addmaths 1 AnsDocument6 pagesSBP 2011 Addmaths 1 Answanil1994No ratings yet
- Circles: CH CHDocument4 pagesCircles: CH CHJamaliah Daud100% (1)
- Chap 07Document2 pagesChap 07Jamaliah Daud0% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect 6 (Square, Square Roots, Cubes & Cube Roots)Document2 pagesPractice Makes Perfect 6 (Square, Square Roots, Cubes & Cube Roots)dikwanzNo ratings yet
- The EnvelopeDocument3 pagesThe EnvelopeJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect 1 Fraction Amp DecimalDocument4 pagesPractice Makes Perfect 1 Fraction Amp DecimalChik Zulkhairi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect 7 (Algebra)Document8 pagesPractice Makes Perfect 7 (Algebra)dikwanzNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect 3 (Loci in Two Dimensions)Document7 pagesPractice Makes Perfect 3 (Loci in Two Dimensions)dikwanzNo ratings yet
- Chap 12Document3 pagesChap 12surayailaNo ratings yet
- Chap 08Document6 pagesChap 08Jamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Chap 09Document2 pagesChap 09Jamaliah Daud67% (3)
- Intercept Are BestDocument3 pagesIntercept Are BestJamaliah Daud100% (1)
- Linear ProgramDocument3 pagesLinear ProgramJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions-FormativeDocument1 pageTrigonometric Functions-FormativeJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- About PrismDocument3 pagesAbout PrismJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Basic IndicesDocument2 pagesBasic IndicesJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Compound InterestDocument3 pagesCompound InterestJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Soalan Peperiksaan Matematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 1Document4 pagesSoalan Peperiksaan Matematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 1syukrie377% (35)
- Quadratic Graphs & EquationsDocument2 pagesQuadratic Graphs & EquationsJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Chap 04Document2 pagesChap 04cenkodok_gandumNo ratings yet
- FINAL REPORT Service Quality 2009Document13 pagesFINAL REPORT Service Quality 2009Jamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Latihan Matematik Tingkatan 2 Chap02 Square, Square Root, Cube and Cube RootDocument3 pagesLatihan Matematik Tingkatan 2 Chap02 Square, Square Root, Cube and Cube RootEzra Loganathan MuniandiNo ratings yet
- Chap 06Document2 pagesChap 06Jamaliah Daud50% (2)
- Mathematics Chapter3 PPPMRDocument3 pagesMathematics Chapter3 PPPMRMuralitharan SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions-FormativeDocument1 pageTrigonometric Functions-FormativeJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Chap 05Document4 pagesChap 05Jamaliah Daud100% (5)
- Chap 01Document4 pagesChap 01Jamaliah Daud76% (33)
- Trigonometric Functions-SummativeDocument1 pageTrigonometric Functions-SummativeJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Transversal Line AnglesDocument14 pagesTransversal Line AnglesNevitaNo ratings yet
- NSEJS GEOMETRY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONSDocument6 pagesNSEJS GEOMETRY PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONSgobinda prasad barmanNo ratings yet
- Geometry Activity Sheets Identify 2D and 3D FiguresDocument5 pagesGeometry Activity Sheets Identify 2D and 3D Figureskris100% (1)
- Tutorial 8-Development of SurfacesDocument2 pagesTutorial 8-Development of SurfacesrudranshNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P2 GR 10 Exemplar 2012 EngDocument11 pagesMathematics P2 GR 10 Exemplar 2012 EngZingce PeterNo ratings yet
- KOM Lect13Document24 pagesKOM Lect13Pranav C PNo ratings yet
- SMO Junior 2015Document6 pagesSMO Junior 2015yeeluv9950% (2)
- Quadrilateral - Angles: A) Find The Measure of The Indicated Angle in Each QuadrilateralDocument2 pagesQuadrilateral - Angles: A) Find The Measure of The Indicated Angle in Each QuadrilateralAngel AngiaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Mathematics Student Practice Test BookletDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Mathematics Student Practice Test BookletDaniel TrencheskiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Homework PacketDocument8 pagesUnit 7 Homework PacketAliRazaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Grade 09 Maths Third Term Paper English Medium Royal CollegeDocument7 pages2021 Grade 09 Maths Third Term Paper English Medium Royal Collegeshenalijayasundara05No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument180 pagesTrigonometrynalluri_08No ratings yet
- Geometry Prelim 1 Question PaperDocument7 pagesGeometry Prelim 1 Question PaperManoj HassineNo ratings yet
- Inmo-2012 Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Mathematical Olympiad (INMO) With SolutionsDocument6 pagesInmo-2012 Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Mathematical Olympiad (INMO) With SolutionsAkshay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document8 pagesModule 5Benson MataNo ratings yet
- ProjectionsDocument8 pagesProjectionsThariq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Understanding Numbers and Basic Geometrical ConceptsDocument40 pagesUnderstanding Numbers and Basic Geometrical ConceptsSagar AhirNo ratings yet
- Hellenic Mathematical Competitions 2009 - BookletDocument33 pagesHellenic Mathematical Competitions 2009 - BookletestoyanovvdNo ratings yet
- MathsLinks 7B Homework AnswersDocument16 pagesMathsLinks 7B Homework AnswersRacingToTheLightNo ratings yet
- Math-Grade 5 - Q3 - 2022-2023Document126 pagesMath-Grade 5 - Q3 - 2022-2023Avegail AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Math's B (May) Test – 4Document2 pagesMath's B (May) Test – 4TanzimNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical GeometryDocument14 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical GeometryAnil CharayaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - HW #4Document2 pagesKami Export - HW #4hprabhuNo ratings yet
- Geometry theorems and propertiesDocument9 pagesGeometry theorems and propertiesgvinothkumargvkNo ratings yet
- Arihant 40 Days Crash Course For JEE Main Mathematics Crackjee Xyz 021 024Document4 pagesArihant 40 Days Crash Course For JEE Main Mathematics Crackjee Xyz 021 024shantanu99hazra5No ratings yet
- Crystal Structure VisualizationDocument22 pagesCrystal Structure VisualizationMirtunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Philippine Math Exam Covers Polynomials, Volume, ConversionDocument2 pagesPhilippine Math Exam Covers Polynomials, Volume, ConversionMarie TamondongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Revisit The Primary Trigonometric Ratios: Warm UpDocument3 pagesLesson 1: Revisit The Primary Trigonometric Ratios: Warm Upapi-532096792No ratings yet
- Activity 7 Class 11Document1 pageActivity 7 Class 11DevanshNo ratings yet
- SPM Additional Mathematical Formulae PDFDocument2 pagesSPM Additional Mathematical Formulae PDFJames SimNo ratings yet