Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answers Nerve Stimulate I.e., Action Potential Generated
Uploaded by
Muhammad ArsalanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers Nerve Stimulate I.e., Action Potential Generated
Uploaded by
Muhammad ArsalanCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers
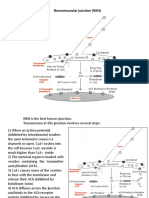
Nerve stimulate i.e., action potential generated
1) ACh dissociates from binding sites a) (23) Na+ influx to create action potential
2) ACh in synaptic cleft b) (8)Ca2+ binds to troponin
3) AChE fragments neurotransmitter c) (28) RMP goes from –90mV to +75mV
4) action potential to muscle fiber ceases d) (24) nerve stimulus proceeds
Action potential at Varicosity
5) ATP bound to myosin heads is hydrolyzed to e) (29) synaptic end bulbs also called
ADP by ATPase varicosity
6) binding of neurotransmitter to ligand-gated f) (12) Ca2+ released
ion channels
7) binding sites on the actin are exposed g) (31) to stimulate ACh filled vesicles to be
released
8) Ca2+ binds to troponin h) (2) ACh in synaptic cleft
9) Ca2+ lost from troponin i) (6) binding of neurotransmitter to ligand-
gated ion channels
Action potential stimulate the muscle fiber
10) Ca2+ pumped back into SR (ATP used) j) (35) wave of action potentials spreads in all
directions along membrane
11) Ca2+ released k) (30) T tubules stimulated to open voltage-
regulated ion gates
12) Ca2+ released l) (34) voltage-gated calcium channels open
13) calsequestrin binds Ca2+ m) (11) Ca2+ released
14) contraction over n) (17) from the SR into the cytosol
15) crossbridges are formed o) (1) ACh dissociates from binding sites
16) fragments are reabsorbed p) (3) AChE fragments neurotransmitter
17) from the SR into the cytosol q) (16) fragments are reabsorbed
Muscle contraction started
18) K+ diffuses outward r) (8) Ca2+ binds to troponin
19) muscle fiber excited s) (33) troponin-tropomyosin shifts
20) muscle fibrils relax t) (7) binding sites on the actin are exposed
21) myosin head cocks and attaches to actin u) (19) muscle fiber excited
22) myosin releases actin v) (5) ATP bound to myosin heads is hydrolyzed to
ADP by ATPase
23) Na+ influx to create action potential w) (21) myosin head cocks and attaches to
actin
24) nerve stimulus proceeds x) (15) crossbridges are formed
25) nerve stimulus stops y) (27) power stroke
26) new ATP added z) (22) myosin releases actin
27) power stroke aa) (26) new ATP added
28) RMP goes from –90mV to +75mV bb) (25) nerve stimulus stops
29) synaptic end bulbs cc) (4) action potential to muscle fiber ceases
Contraction over due to the cease of action potential
30) T tubules stimulated to open voltage- dd) (14) contraction over
regulated ion gates
31) to stimulate ACh filled vesicles to be released ee) (13) calsequestrin binds Ca2+
32) tropomyosin slides back over the myosin ff) (10) Ca2+ pumped back into SR (ATP used)
binding sites on actin
33) troponin-tropomyosin shifts gg) (9) Ca2+ lost from troponin
34) voltage-gated calcium channels open hh) (32) tropomyosin slides back over the
myosin binding sites on actin
35) wave of action potentials spreads in all ii) (20) muscle fibrils relax
directions along membrane
You might also like
- Bio201 Exam 2 Master With AnswersDocument12 pagesBio201 Exam 2 Master With AnswersRicha Rala100% (1)
- Muscle MCQs - AnswerDocument41 pagesMuscle MCQs - AnswerMohit Balboa90% (79)
- Muscle MCQs Answer PDFDocument41 pagesMuscle MCQs Answer PDFHarun Mohamed50% (2)
- Collection of Problems in Classical Mechanics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandCollection of Problems in Classical Mechanics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 5 - Nerve - MuscleDocument11 pages5 - Nerve - Musclesame200100% (1)
- Quiz Cardiovascular Part 1 of 3Document30 pagesQuiz Cardiovascular Part 1 of 3MedShare90% (10)
- Neurophysiology: Dr. Irbab HawariDocument32 pagesNeurophysiology: Dr. Irbab Hawaritrisna satriana100% (1)
- CNS Stimulants: College of Pharmacy Department of PharmacologyDocument20 pagesCNS Stimulants: College of Pharmacy Department of PharmacologyDrDeepak PrasharNo ratings yet
- MC Chapter 48 TestDocument14 pagesMC Chapter 48 Testbori0905100% (2)
- Physiology MCQ - Muscles and NervesDocument10 pagesPhysiology MCQ - Muscles and NervesJoseph90% (10)
- Cardiology Mcq's Part - 1Document31 pagesCardiology Mcq's Part - 1aymenNo ratings yet
- Phsio EXITABLEDocument12 pagesPhsio EXITABLEmohammedNo ratings yet
- RECEPTORSDocument22 pagesRECEPTORSpharmazone4u100% (1)
- 2Document17 pages2이어진No ratings yet
- 2 With No AnswerDocument16 pages2 With No Answer이어진No ratings yet
- SKN Test XiiDocument10 pagesSKN Test XiiKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Tut Physiology 2Document7 pagesTut Physiology 2Ghaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- ECE795 Math Practice PDFDocument12 pagesECE795 Math Practice PDFadiazNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Jam 2009Document8 pagesJam 2009sairajdreamNo ratings yet
- 12th Phy QP Set 1 To 5Document21 pages12th Phy QP Set 1 To 5Samiullah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Physio Recalls 1Document3 pagesPhysio Recalls 1Philip Kyle OpinionNo ratings yet
- NMJ+Muscle Contraction PDFDocument4 pagesNMJ+Muscle Contraction PDFRajat AgrawalNo ratings yet
- NROSCI 1012 - Lecture 23Document3 pagesNROSCI 1012 - Lecture 23HonzaNo ratings yet
- E-CAT 2013 Collected MCQS: UET ECAT 2013 Past PaperDocument6 pagesE-CAT 2013 Collected MCQS: UET ECAT 2013 Past PaperOmmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Neurobiology, Physiology, and BehaviorDocument9 pagesNeurobiology, Physiology, and BehaviorcindyucdNo ratings yet
- Untitled11 PDFDocument15 pagesUntitled11 PDFElizabeth LeonNo ratings yet
- 5 Sets Model Questions of PhysicsDocument27 pages5 Sets Model Questions of Physicsdast DonNo ratings yet
- Physics M. PalanichamyDocument4 pagesPhysics M. PalanichamyphysicspalanichamyNo ratings yet
- Ecat 2013Document6 pagesEcat 2013Asad ullahNo ratings yet
- (Nalomkanq Dan Optiu Tuaas: N 2) (XT) B Lza) 3XDocument3 pages(Nalomkanq Dan Optiu Tuaas: N 2) (XT) B Lza) 3XDelita WnNo ratings yet
- 2009Document8 pages2009Udaibir PradhanNo ratings yet
- E-CAT 2013 Collected MCQS: 2/sinx B) Tan2xDocument6 pagesE-CAT 2013 Collected MCQS: 2/sinx B) Tan2xRidda AfzalNo ratings yet
- Class Test Neuron and Nerve ImpluseDocument2 pagesClass Test Neuron and Nerve ImplusesikanderNo ratings yet
- Qui 1 UcpDocument1 pageQui 1 Ucpdjun033No ratings yet
- Hodgkin Huxley Neuron ModelDocument9 pagesHodgkin Huxley Neuron ModelSomnath SandeepNo ratings yet
- Nuclear and Particle Physics QuestionsDocument41 pagesNuclear and Particle Physics QuestionsSid KNo ratings yet
- Ecat 2013 FinalDocument7 pagesEcat 2013 FinalAitazaz AhsanNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Three of The Following:: Maximllmmarks: 300Document6 pagesAnswer Any Three of The Following:: Maximllmmarks: 300RATNADEEP BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Aieee Paper 2007Document10 pagesAieee Paper 2007Protyay ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering Volume 13, Number 3, June 2016Document11 pagesMathematical Biosciences and Engineering Volume 13, Number 3, June 2016The great PNo ratings yet
- Part - I (MCQ) (Compulsory)Document2 pagesPart - I (MCQ) (Compulsory)rohitmodikNo ratings yet
- Physic 12 Sample PaperDocument5 pagesPhysic 12 Sample PaperDeep ChovatiyaNo ratings yet
- A, A, A B) A, A, A C) A, A, A D) A, A, ADocument18 pagesA, A, A B) A, A, A C) A, A, A D) A, A, Avenki786No ratings yet
- IES CONV Electronic Comm. 1998Document9 pagesIES CONV Electronic Comm. 1998gateandiesNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Assig (Xi 2021-23) (Print) 26 08 21Document3 pagesAtomic Structure Assig (Xi 2021-23) (Print) 26 08 21Ramkrushna khandareNo ratings yet
- VSAT Class 12 NEET Sample QuestionsDocument9 pagesVSAT Class 12 NEET Sample QuestionsHarsh AnandNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Waves (QB)Document16 pagesMechanical Waves (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Computational Biology, Part 20: Neuronal ModelingDocument34 pagesComputational Biology, Part 20: Neuronal ModelinghanifsharNo ratings yet
- 04 - Physics - July 2007Document6 pages04 - Physics - July 2007Bernardo Gonzalez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Physics McqsDocument42 pagesPhysics McqsRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- SNC1D - Final Exam: Review Questions: Unit 1: Sustainable EcosystemsDocument5 pagesSNC1D - Final Exam: Review Questions: Unit 1: Sustainable EcosystemsAsad CheemaNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 SEM1 (2023-2024) NewDocument3 pagesAssignment2 SEM1 (2023-2024) Newbhushanhimanshu538No ratings yet
- BME Capstone Final Examination - SolutionDocument8 pagesBME Capstone Final Examination - SolutionTín Đức ĐoànNo ratings yet
- Gate Mock Test1Document17 pagesGate Mock Test1Gopinathan SudheerNo ratings yet
- Physics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyDocument4 pagesPhysics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyRAVINDRA WAYKOLENo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper Higher Secondary - Second Year - PhysicsDocument6 pagesModel Question Paper Higher Secondary - Second Year - Physicsbindum_9No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Reduced Syllabus Model Question Paper EM 220586Document2 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Reduced Syllabus Model Question Paper EM 220586karthi1234No ratings yet
- Atomic and Nuclear Physics TutorialsDocument4 pagesAtomic and Nuclear Physics TutorialsEinstein Ocs Ogbu Chukwudi StephaneNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 12 PDFDocument12 pagesPaper 2 12 PDFSatwant KaurNo ratings yet
- EIL Aptitude Paper 1Document11 pagesEIL Aptitude Paper 1Anoop VermaNo ratings yet
- 2physics ClassXII Sample Paper 2008Document6 pages2physics ClassXII Sample Paper 2008hi_gauravaroraNo ratings yet
- Computational NeuroendocrinologyFrom EverandComputational NeuroendocrinologyDuncan J. MacGregorNo ratings yet
- Sulfated Ash TestDocument1 pageSulfated Ash TestMuhammad Arsalan100% (1)
- Tazobactum (Drug Monograph)Document2 pagesTazobactum (Drug Monograph)Muhammad Arsalan100% (1)
- OndensetronDocument1 pageOndensetronMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Tranexamic Acid: Pharmacological EffectsDocument1 pageTranexamic Acid: Pharmacological EffectsMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument1 pageParacetamolMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- StandardizationDocument3 pagesStandardizationMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Brief OverView of Rheology and ViscosityDocument2 pagesBrief OverView of Rheology and ViscosityMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument1 pageOmeprazoleMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- ItraconazoleDocument1 pageItraconazoleMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Folinic AcidDocument1 pageFolinic AcidMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- MeropenemDocument1 pageMeropenemMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- ImipenemDocument1 pageImipenemMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesLevofloxacinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- FilgastrinDocument1 pageFilgastrinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Co AmoxiclavDocument1 pageCo AmoxiclavMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- FluconazoleDocument1 pageFluconazoleMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Disease ProfilesDocument5 pagesDisease ProfilesMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Diclofenac SodiumDocument1 pageDiclofenac SodiumMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument1 pageCeftriaxoneMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- FexofenadineDocument1 pageFexofenadineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument2 pagesDexamethasoneMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- ClindamycinDocument1 pageClindamycinMuhammad Arsalan100% (1)
- CyclosporineDocument2 pagesCyclosporineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- CiprofloxacinDocument1 pageCiprofloxacinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument1 pageAmlodipineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- AcyclovirDocument1 pageAcyclovirMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- BeclomethasoneDocument1 pageBeclomethasoneMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- CefiximeDocument1 pageCefiximeMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- AmikacinDocument1 pageAmikacinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Aspirin (Acetyl-Salicylic Acid) Drug MonographDocument1 pageAspirin (Acetyl-Salicylic Acid) Drug MonographMuhammad Arsalan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Febrile SeizuresDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of Febrile SeizuresJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesNo ratings yet
- ERQ NeurotransmissionDocument2 pagesERQ NeurotransmissionPhương Anh Cao HoàngNo ratings yet
- CNS NeurotransmitterDocument67 pagesCNS NeurotransmitterGreenNo ratings yet
- The Action PotentialDocument6 pagesThe Action PotentialMagias FCNo ratings yet
- Intercellular CommunicationDocument8 pagesIntercellular CommunicationDina MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (Science Assignment)Document6 pagesNervous System (Science Assignment)Emylya HasnirNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology: Nervous CoordinationDocument39 pagesA Level Biology: Nervous CoordinationAhmedNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Midterm ReviewDocument4 pagesAP Psychology Midterm ReviewPostcardsFromAlbertaNo ratings yet
- Pex 03 06Document6 pagesPex 03 06aexillis100% (3)
- Signals and ReceptorsDocument28 pagesSignals and ReceptorsEmilio MurciaNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics - Screening MethodsssDocument37 pagesAnxiolytics - Screening MethodsssKarthiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Neural and Hormonal CommunicationDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Neural and Hormonal CommunicationAmmar SmadiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of SeizuresDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of SeizuresironNo ratings yet
- Solinas2019 Article DopamineAndAddictionWhatHaveWe PDFDocument36 pagesSolinas2019 Article DopamineAndAddictionWhatHaveWe PDFBobNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12 - Coordination & ResponseDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 12 - Coordination & ResponseHAJAR LENNo ratings yet
- File 0147Document6 pagesFile 0147Tassnime SebaeiNo ratings yet
- Pharma Graphs-1Document22 pagesPharma Graphs-1Aranya BhandaryNo ratings yet
- Summary NeurobiologyDocument42 pagesSummary NeurobiologytjNo ratings yet
- 4 Reflexes Lecture Notes RevisedDocument9 pages4 Reflexes Lecture Notes RevisedKristina CabanezNo ratings yet
- Types of Receptors and Their Properties: Noman AnwarDocument21 pagesTypes of Receptors and Their Properties: Noman AnwarNoman AnwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biology and BehaviorDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Biology and BehaviorLexie PepeNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonist: Persiapan CBT September 2020 Bimo Kusumo BhirowoDocument16 pagesAdrenergic Agonist: Persiapan CBT September 2020 Bimo Kusumo BhirowoDendyNo ratings yet
- 2 PharmacodynamicsDocument51 pages2 PharmacodynamicsKriziaoumo P. Orpia100% (1)
- NeurotransmitterDocument72 pagesNeurotransmitterrara pramei100% (1)
- ThresholdDocument10 pagesThresholdFelisitasDianaEffendiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System FundamentalsDocument29 pagesNervous System FundamentalsSarosh MajeedNo ratings yet