Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RS/6000 7044 Model 270: Technical Overview and Introduction
Uploaded by
joandiaz011168Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RS/6000 7044 Model 270: Technical Overview and Introduction
Uploaded by
joandiaz011168Copyright:
Available Formats
RS/6000 7044 Model 270
Technical Overview and Introduction
February 13, 2000
Volker Haug
Jeanine Indest
Scott Vetter
International Technical Support Organization
Austin, TX
IBM
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2000
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
The IBM RS/6000 family is a scalable, software-compatible line of RISC UNIX
workstations, servers, and supercomputers powered by IBMs AIX operating
system. On February 7, 2000, IBM announced two exciting additions to this
family, the 44P Models 170 and 270.
This paper provides a brief history, a general description, and a technical
overview of the 44P Model 270 including: the 64-bit copper technology of the
POWER3-II processor, the error checking and correcting (ECC) memory
subsystem, the advanced packaging design, the built-in service processor, the
sophisticated graphics support, and other selected features.
History
The original 43P Model 140 graphics workstation and entry-level workgroup
server was introduced on October 8, 1996. This uniprocessor system offered a
variety of processing speeds and features. The 43P Model 240 was the first
RS/6000 workstation/workgroup server to offer expandability to 2-way symmetric
multiprocessing (SMP). The 43P Model 150 offered enhanced performance over
the Model 140. The Model 260 is a 1- or 2-way SMP system utilizing the 64-bit
200 MHz POWER3 processor. Both models were introduced on October 5, 1998
and are still available.
General Description
The RS/6000 44P Models 170 and 270 extend the IBM line of powerful and
affordable workstation/workgroup servers with state-of-the-art, 64-bit copper
POWER3-II processors. The 44P family, manufactured in Rochester, Minnesota,
USA and Santa Palomba, Italy, offers ideal solutions for both high-performance
2D or 3D MCAD/CAE users and companies that require a compact system for
commercial computing solutions, such as Lotus Notes Server, business
intelligence, Web server, software development, firewall, high availability
(HACMP), scientific, and technical.
Minimum and Optional Features
The 44P 7044 Model 270 minimum configuration comes with a standard of 256
MB ECC synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM), one 9.1 GB
Ultra SCSI disk drive, a 32X max. speed CD-ROM drive, a 1.44 MB 3.5” diskette
drive, an integrated 10/100 Ethernet controller (AUI and RJ45), an internal Ultra
SCSI controller, an external Ultra2 SCSI controller, a service processor, and an
operator panel. The operator panel has a 2 x 16 backlit LCD for system status
and diagnostic information. Microphone and headphone jacks are built into the
operator panel.
One, two, three, or four 375 MHz POWER3-II 64-bit processors are connected to
an IBM-designed high performance memory/system control chip set. Each
processor has a 4 MB L2 cache. This is the first IBM implementation of copper
technology in an SMP workstation and workgroup server. Refer to “Copper and
CMOS Technology” on page 5 for more information.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2000 1
The memory can be expanded to 8 GB of SDRAM. Two disk bays and three
media bays are offered with the system. Five PCI slots and a variety of PCI
adapters are available. The Model 270 offers integrated ports for tablet (for use
with legacy input devices), keyboard, mouse, two serial (9-pin D-shell), one
parallel (includes advanced features such as ECP, and Bi-Di), and a stereo audio
connections (16 bit stereo, full duplex. Connectors for line in, line out,
microphone, and headphone exist).
The media bay can hold a second CD-ROM drive, a 4 mm or 8 mm tape drive, or
a SCSI disk drive. A media bay mounting kit is required to install a SCSI disk
drive in the media bay.
A mouse and different national keyboards are used as input devices; both are
available in black or ivory. You can also add a Spaceball or a Magellan 3D
(Spacemouse) to your system.
Note
The SCSI disks in the disk bays are not hot-swappable. After AIX is quiesced,
power may remain on while disks are swapped.
Physical Package
The 44P package is the same as used for the 43P Model 260 which is designed
to sit on the floor and out of the way. Figure 1 shows the packaging of the Model
270 without the protective covers.
Two Disk
Bays
Power
Supply CD-ROM
2nd Media
Bay
Diskette
CPU
Cards
Operator
Panel
Memory
Cards
PCI
Cards
Figure 1. 7044-270 Package Layout
2 RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
There is no desktop or rack-mounted option available for this model. The
deskside package has a size of 340 mm W x 713 mm D x 610 mm H (13.4” W x
28.1” D x 24” H), a maximum weight of 45 kg (99 lbs), and is suitable for a quiet
office environment.
The system comes preconfigured with the standard features, leaving one hard
disk bay and one media bay available for customer expansion. Any devices in the
media bays are connected to the internal Ultra SCSI controller (no additional
cable is required).
To connect external SCSI devices to the Ultra2 SCSI adapter’s VHDC, order
# 2118 (mini-68 pin VHDC to 68 pin). This 0.3 m long cable (P/N 76H0518) is not
included with the minimum system configuration.
System Upgrades
The 7044 Model 270 can be upgraded through feature modifications. Additionally,
a 7043 Model 260 upgrade Miscellaneous Equipment Specification (MES) is
available to upgrade an existing 7043 Model 260 to a 7043 Model 270, preserving
the machine type and serial number. The Model 270 is designed for customer
setup of the machine and for subsequent addition of most features (adapters and
devices). However, the 7043-260 is upgraded by the IBM Customer Engineer
(CE).
Note
The 7043 Model 260 to Model 270 upgrade may have limited availability.
Check with your IBM representative for the most current information.
To minimize system downtime, a new chassis will be shipped with new (changed)
electronic components already installed. The CE will move reusable components
from the 260 to the 270. The 260 chassis and replaced parts will be returned to
IBM. This upgrade requires that AIX 4.3.3 or higher be installed. Also, the
firmware must be upgraded and will automatically change system model type and
number to 7043-270 at boot. The upgrade will preserve the customer’s existing
system serial number.
The MES Upgrade Kit contains a mechanical chassis with associated labels and
markings for the 7043-270, processor card, new system planar, new I/O planar,
diskette drive, power supply, and all additional internal cables.
Note
The MES Upgrade Kit only includes one 1-way 375 MHz POWER3-II processor
card. If an existing Model 260 has two processors, an additional 375 MHz
POWER3-II processor card must be ordered to maintain the current processor
configuration.
Architecture and Technical Information
The following sections provide more detailed information about the architecture of
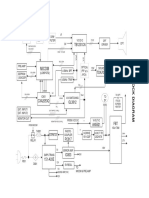
the Model 270. Figure 2 shows the high level system block diagram of the 44P
Model 270 and is the topic of the subsequent discussion.
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview 3
Processor Card Processor Card
4 MB L2 4 MB L2
POWER3 POWER3
375 MHz 375 MHz
32 Bytes 32 Bytes
@ 250 MHz @ 250 MHz
4 MB L2 4 MB L2
POWER3 POWER3
375 MHz 375 MHz
32 Bytes 32 Bytes
@ 250 MHz @ 250 MHz
6xx Data Bus 16 Bytes @ 93.75 MHz
Addr/Cntl
6xx Address Bus 93.75 MHz
Memory Memory Data Bus 16 Bytes @ 93.75 Mhz
Data
Address
Memory Memory
System Planar
256 MB - 4 GB 256 MB - 4 GB
I/O Planar
Integrated Service
PCI Bridge PCI Bridge
Processor
2 PCI Slots
64-bit
ISA Bridge 50 MHz
3 PCI Slots 3.3v
32-bit
10/100 Ultra2 SCSI Ultra-SCSI 33 MHz
Audio Super Ethernet 5.0v
I/O
Figure 2. Model 270 - High-Level System Block Diagram
Processor and Cache
The Model 270 has two processor card slots and will accommodate two different
processor cards, a 1-way and a 2-way (only a 1-way processor card is available
for the 7043-260). Note that slot 1 must have a processor card installed for
normal operations.
If your system unit uses two processor cards, both processor cards must be of
the same clock speed. You cannot interchange processor cards between a Model
260 and Model 270.
Note
Installing a processor card into your system unit may require updating the
firmware. A diskette or CD-ROM is included with your new processor card if
that is required. Check also the following Web page for the latest available
firmware:
http://www.rs6000.ibm.com/support/micro/
4 RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
The Model 270 uses a 64 KB data and a 32 KB instruction 128-way set
associative L1 cache. The L1 cache is effectively supplemented by a 4 MB 4-way
set associative L2 cache, which is located on the processor card (the POWER3
architecture used a 4 MB direct mapped L2 cache, operated at 200 MHz). The
POWER3-II uses a private 32-byte L2 cache bus, operated at 250 MHz. Both the
enhanced clock speed and 4-way set associative L2 cache improve cache
efficiency. The L2 controller uses a least recently used (LRU) algorithm to avoid
replacing recently used cache data and a set prediction mechanism that helps
reduce L2 cache misses.
The current implementation of POWER3-II in the SP node uses 8 MB L2 cache
(POWER3-II design allows up to 16 MB of L2 cache, but no RS/6000s currently
make use of this limit).
POWER3-II Architecture
The processor functional diagram of the POWER3 and the POWER3-II are
similar. However, the use of copper in the POWER3-II represents a new
generation of processing power. Table 1 lists some of the differences between
the POWER3 and the POWER3-II processors. Also, the chart indicates the
direction being taken by this technology. The number of transistors increased in
the POWER3-II due to the enhanced L2 cache controller and minor updates to
handle different bus requirements.
Table 1. Differences POWER3 vs. POWER3-II
Description POWER3 POWER3-II
Chip Die Size 270 mm2 163 mm2
Transistors 15 million 23 million
Power Avg/Max 39W/46W@200 MHz 26W/33W@375 MHz
CMOS Technology 6S2, 5 layers metal 7S, 6 layers metal, copper
interconnect
Lithography 0.25 µm 0.22 µm
Copper and CMOS Technology
Copper is a superior conductor of electricity, making it possible to shrink the
electronic devices even further while increasing performance. It has less
resistance than aluminum and, therefore, allows designs that transmit electrical
signals faster. However, it does not mix as well with silicon, the base material of
semiconductor chips. The IBM researchers found a way to put a microscopic
barrier between the copper and silicon in a way that actually reduced the number
of steps needed to complete a chip. With this development, IBM is able to
squeeze down the widths of copper wires to the 0.2-micron range from the
current 0.35-micron widths - a reduction far more difficult for aluminum. A single
POWER3-II chip contains about 400 meters of copper wiring.
This technology, called CMOS 7S, is the first to use copper instead of aluminum
to create the circuitry on silicon wafers. Copper wires conduct electricity with
about 40 percent less resistance than aluminum. That translates into a speed up
of to 15 percent in processors that contain copper wires.
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview 5
CPU Deallocation
There are two options available to deallocate a CPU:
1. Processor Boot Time Deconfiguration
Processor boot time deconfiguration is a function implemented in the system
and service processor firmware for deallocating processor(s) from the system
configuration at boot time. The objective is to minimize system failure or data
integrity exposure due to a faulty processor.
The processors that are deconfigured remain offline for subsequent reboots
until the faulty processor hardware is replaced. This function provides the
option for a user to manually deconfigure or re-enable a previously
deconfigured processor using the Service Processor menu.
Note
Processor cards only can physically be removed when the power is turned
off to the entire system.
How to Disable the 2nd, 3rd, or 4th Processor Manually
a. The additional processor(s) can be disabled only within the Service
Processor menus. There is no need to remove them from the system. The
cpu_state command, used on the micro-channel SMP servers, is not
supported on the PCI-based systems.
To determine if a processor is enabled or disabled, use the following AIX
commands:
• sar command:
# sar -P ALL 2
AIX volker_270 3 4 00465F2A4C00 02/07/00
10:54:44 cpu %usr %sys %wio %idle
10:54:46 0 0 0 0 100
1 0 0 0 100
- 0 0 0 100
In the above example, you can see two configured processors, which
are shown in the cpu column.
• lsattr command:
# lsattr -E -l proc0
state enable Processor state False
type PowerPC_ POWER3 Processor type False
state enable means that processor #0 is enabled.
# lsattr -E -l proc2
state faulty Processor state False
type PowerPC_ POWER3 Processor type False
state faulty means that processor #2 is disabled.
Note
The processor(s) remain deconfigured until manually reconfigured.
b. There is another option to deconfigure processors manually:
1. Power on your system or, if it is still running, start a reboot.
6 RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
2. As soon as the first screen appears and you hear a beep, press the F1
key to invoke the graphical user interface (GUI) of the System
Management Services (SMS) menu. (Press the number 1 key, if you
have a ASCII terminal attached).
3. The SMS menu displays on your screen. Select the Multiboot option.
4. From the System Management Services Multiboot submenu select OK
Prompt.
5. The Open Firmware prompt appears. At this point, enter the following
command: boot -scpu=X where X can be 1, 2, 3, or 4 and represents the
target number processor(s) to configure. This command will cause the
system to continue the boot process.
You can check how many processors are configured with the sar
command. The lsattr command does not listen the faulty state entry for
any of the deconfigured processor(s).
Note
The processor(s) remain deconfigured until a reboot is invoked.
2. Processor Run-Time Deconfiguration (Dynamic CPU Deallocation)
Dynamic CPU Deallocation, or processor run-time deconfiguration, is a RAS
(Reliability, Availability, Serviceability) enhancement function implemented in
the system firmware, service processor firmware, and AIX operating system
(Version 4.3.3 + APAR IY06844, or later) for dynamically removing CPUs from
the system configuration during run time.
The objective is to minimize system failures or data integrity exposures due to
a faulty processor. The processor to be removed is the one that has
experienced repeated run-time recoverable internal errors (over a predefined
threshold).
When a processor's internal recoverable error reaches a predefined threshold,
the firmware is designed to notify the AIX operating system. The AIX operating
system migrates all software processes and interrupts to another processor
and puts the faulty processor in stop state. CPUs that are deconfigured at
run-time remain offline for subsequent reboots via the CPU Boot Time
Deconfiguration function until the faulty CPU hardware is replaced. The user
can also enable and disable this RAS function via the AIX system
management services.
Currently, the Models 270, S80, and the SP 375 MHz POWER3 SMP Thin and
Wide nodes support Dynamic CPU Deallocation.
CPU Clock Rate
The different processor cards and the processor speeds can be identified by the
SMS Display Configuration menu or by the following AIX command:
lscfg -vp | more
Page down to the Processor Card entry and search for the Product Specification
(ZC) entry. This gives you detailed information about:
PS Processor Clock Speed in Hz, ASCII coded hexadecimal
LB L2 Bus Speed in Hz, ASCII coded hexadecimal
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview 7
SB System Bus Speed in Hz, ASCII coded hexadecimal
NP Number of Processors on Card, ASCII coded hexadecimal
L2 L2 Size in number of Kilobytes, ASCII coded hexadecimal
Following is an example about the processor card information:
Processor Card:
Part Number.................00P2172
EC Level....................D72830
Serial Number...............L200016008
FRU Number..................00P2180
Manufacture ID..............1980
Version.....................RS6K
Product Specific.(ZC).......PS=00165A0BC0,LB=000EE6B280,
SB=00059682F0,NP=02,L2=04096,
PF=764,CL=6,SV=3,VR=3,ER=0000
Product Specific.(ZB).......BC=30602,SG=
Physical Location: P1-C1
For example: PS shows the processor speed in hex-number digit
(0x00165A0BC0 = 375000000 Hz = 375 MHz).
CPU Part Numbers
Due to manufacturing issues the part number of the processor cards might
change. You can determine the part number of the current used processor cards
by the following method:
1. Enter the AIX command: lscfg -vp | more
2. Page down to the Processor Card entry and search for the Product
Specification (ZC) entry.
3. Determine the number of processors by searching for the NP entry:
• 01 = 1-way 375 MHz POWER3-II processor card
• 02 = 2-way 375 MHz POWER3-II processor card
4. Scroll six rows up and determine the appropriate part number.
Memory
The memory subsystem of the Model 270 supports a 128-bit data path to
memory. A minimum of 256 MB of memory is required, and can be expanded to a
maximum of 8 GB SDRAM.
Dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) must be ordered and installed in matched
(size and speed) pairs on the memory cards. Memory cards can be installed in
either slot (or both) on the system board, there is no requirement that one be
installed before the other.
It is recommended that DIMMs be installed starting at the bottom of each card
(card slot J1 and J2) and then moving up. It is also recommended that slots in the
first memory card should be filled before a second memory card is installed.
There is no architectural requirement for this other than to help you organize your
memory. Skipping DIMM slot pairs or partial filling of boards does not enhance or
degrade performance.
8 RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
Slot J15 Slot J16
Slot J13 Slot J14
Slot J11 Slot J12
Slot J9 Slot J10
Slot J8
Slot J7
Slot J6
Slot J5
Slot J4
Slot J3
Slot J2
Slot J1
Figure 3. Memory Card
It is recommended that if only one memory card is installed, it should be installed
in the primary planar slot J2 with the card face down. If a second memory card is
installed, it should be installed in the secondary planar slot J3 with the card face
up (relative to the top of the machine). In reference to memory card planar slots,
there are only two slots J2 and J3. In the case of memory card DIMM slots, there
are 16, J1 through J16, on each memory card.
Memory Boot Time Deconfiguration
Memory boot time deconfiguration is a function implemented in the service
processor firmware for removing a memory segment or DIMM from the system
configuration at boot time. The objective is to minimize system failures or data
integrity exposure due to faulty memory hardware.
The memory segment or DIMM that are deconfigured remain offline for
subsequent reboots until the faulty memory hardware is replaced. The function
provides the option for the user to manually deconfigure or re-enable a previously
deconfigured memory segment/DIMM via the Service Processor menu.
Memory can also be decreased via AIX using the rmss command. This is useful
for certain benchmark simulations.
Note
Memory cards can physically be removed only when the power is turned off to
the entire system.
Memory Interchange with Other Systems
The following comments apply to the different models:
• The 128 MB DIMMs (# 4110) can be interchanged with the Models 170, 260,
270, and F50.
• The 256 MB DIMMs (# 4119) can be interchanged with the Models 170, 260,
and 270.
• The 512 MB DIMMs of the Model 170 (# 4121) can only be used in the Model
170.
• The memory expansion kit of the F50 (# 4093) is different from the one used in
the Model 260 and 270 (# 4098).
16 GB Memory for the Model 270
Currently, there is no support for 512 MB DIMMs.
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview 9
Mixed Sizes of Memory
The system design gives you the flexibility to mix 128 MB and 256 MB SDRAM
DIMMs on the Memory Expansion Kit without loosing performance.
System Bus
The 6XX bus or system bus is optimized for high-performance and
multiprocessing performance. The bus is fully parity checked and each memory
or cache request is range checked and positively acknowledged for error
detection. Any error will cause a machine check condition and is logged in the
AIX error log. The system bus speed is operated with 93.75 MHz.
PCI-Bus, Slots, and Adapters
The Model 270 is compliant with Revision 2.1 of the peripheral component
interconnect (PCI) specifications and implements two peer PCI busses: a 32-bit
data bus operating at 33 MHz and a 64-bit bus operating at 50 MHz. There are
five PCI slots available. Slots one and two are 64-bit and run at 50 MHz and slots
three, four, and five are 32-bit and run at 33 MHz. All slots accept full-sized PCI
adapter cards.
The 7043 Model 260 had three 5.0v PCI slots at 33 MHz (32-bit) and two 5.0v
PCI slots at 50 MHz (64-bit). The 7044 Model 270 contains three 5.0v PCI slots at
33 MHz (32-bit) and two 3.3v PCI slots at 50 MHz (64-bit).
Because of the change in the voltage specification on the two 64-bit slots, only
certain universal PCI adapter cards can be used in these slots. The 64-bit slots
are physically keyed to accept either universal or 3.3v cards only. 5.0v cards will
not seat in the card slots. If you are migrating cards from an existing Model 260,
they must either be placed in the 32-bit slots or in the 64-bit slot if, and only if,
they meet the PCI adapter voltage requirements (see the specifications for the
particular PCI adapters in question).
A variety of graphics, SCSI, LAN, WAN, asynchronous, and SSA adapter cards
can be installed in the 44P Model 270. More specific information about selected
adapters is provided in the next sections.
LAN Adapters
The Model 270 can be connected through the LAN. It supports the following types
of PCI adapters, which are all supported for NIM installations (use chrp as
platform type):
• 25/155 Mbps ATM
• Gigabit Ethernet
• 10/100 Mbps Ethernet
• 4/16 Mbps token ring (100 Mbps token ring is not available at time of
publication)
Graphics Accelerators
A choice of four graphics accelerators are offered for the Model 270. The
GXT130P is an entry-price 2D adapter suitable for business graphics or Internet
applications. The GXT300P is a high-performance, 24-bit color, 2D graphics
accelerator with 3D capability via Softgraphics functions found in the graPHIGS
and OpenGL APIs.
10 RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
The GXT2000P and GXT3000P are full 24-bit capable accelerators and support
the simultaneous execution of both graPHIGS and OpenGL applications.
Currently, the GXT3000P is the most powerful graphics accelerator available.
The maximum number of graphics accelerators supported in this system is four
(the GXT130P is limited to a maximum of three and the GXT3000P is limited to a
maximum of two). Refer to the limitations section of the announcement for details
on limitations associated with graphic accelerators for this system.
A graphics accelerator is not required in the minimum configuration. In order to
attach an ASCII display, either # 3926 or both # 2934 and # 3925 must be
ordered to provide connection. A 9-25 pin serial connector is not included by
default. Determine if the ASCII display you wish to install requires an interposer,
adapter, or both to avoid installation problems.
SSA Adapters
The Advanced SerialRaid Plus Adapter (# 6230) is available for the Model 270.
Optional features include the 128 MB DRAM Option Card (# 6231) and the 32 MB
Fast-Write Cache Option Card (# 6235).
Hot Plug PCI Adapters Capabilities
Hot plug capabilities for PCI adapters are not supported on the Model 270.
Hot plug PCI capabilities are, however, available within the RS/6000 product line.
The RS/6000 SP Expansion I/O Units support hot plug for selected PCI adapters.
This function enables the maintenance of these adapters without powering off the
SP Expansion I/O Unit or the associated SP POWER3 SMP High Node. This
function requires AIX Version 4.3.3 with APAR IY06844.
Service Processor
The Model 270 has an integrated Service Processor that is designed to provide
an immediate means to diagnose, check status, and sense operational conditions
of a remote system, even when the main processor is unavailable.
The Service Processor is a Motorola 68307 processor. The flash memory used
for the storage of the Service Processor programs has increased to 1 MB, and
512 KB of SRAM memory are used for program execution. The additional
memory has allowed enhanced function such as Dynamic CPU Deallocation.
Selected Service Processor Functions
Additional information is provided for the following selected functions:
Fast Boot
Selecting Fast Boot results in several diagnostic tests being skipped and reduces
time for booting. This option has to be activated through the Service Processor
menu. (The SXX series of enterprise sever uses the operator panel to
enable/disable Fast Boot.)
There is a easy way to check Fast Boot enablement without entering the Service
Processor menus. If Fast Boot is enabled, no spinner will appear at the Service
Processor checkpoint E0B0. With the Slow Boot option enabled a spinner
appears at E0B0. A spinner is a single text position on the operator LCD that
cycles through the characters |,/,-, and \ symbolically representing the passage
of time.
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview 11
Processor Boot Time Deconfiguration
Processor boot time deconfiguration allows you to deconfigure processor(s)
without removing them physically. This could be necessary in a benchmark
situation. For more detailed information, refer to “CPU Deallocation” on page 6.
Memory Boot Time Deconfiguration
Memory boot time deconfiguration gives you the option to deconfigure memory
without removing it physically. For more detailed information, see “Memory Boot
Time Deconfiguration” on page 9.
Boot Mode Menu
The Boot Mode menu allows selection of the following boot options:
• Boot to SMS Menu
• Service Mode Boot from Saved List
• Service Mode Boot from Default List
• Boot to Open Firmware
Miscellaneous
The following selected information for DVD, ISA, USB, and Boot support is given:
DVD Support
Currently, DVD drives are not supported in RS/6000 systems.
ISA Support
The Model 270 does not support industry standard architecture (ISA) adapters.
USB Support
The Model 270 does not have integrated Universal Serial Bus (USB) support and
no USB adapters are currently available for use in RS/6000s.
Boot Options and Limitations
Information about boot options is included in the subsequent sections:
Internal Devices
Boot support is available for every internal SCSI disk.
External Devices
Table 2 provides a map that enables you to determine if boot is supported in
external storage devices.
Table 2. Boot Support - External Devices
Does the PCI card have RAID functionality?
yes no
Card is seen as a controller Card is seen as a adapter
no boot support
Does the external device have RAID functionality?
yes no
no boot support (except boot support
Advanced SerialRAID Plus
Adapter1 )
12 RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
Boot Support and Limitations of Storage Adapters for the Model 270
The following adapters support external boot for the Model 270:
• PCI Universal Differential Ultra SCSI Adapter (# 6204)
• PCI Dual Channel Ultra2 SCSI Adapter (# 6205)
• PCI Single-Ended Ultra SCSI Adapter (# 6206)
• Advanced SerialRAID Plus Adapter (# 6230)1
The RS/6000 PCI 3-Channel Ultra2 SCSI RAID Adapter (# 2494) does not
support boot from external devices.
Fast Boot
The Model 270 offers a Fast Boot option. For more detailed information, refer to
“Selected Service Processor Functions” on page 11.
Security
To prevent the system from unauthorized booting from CD-ROM, you can setup a
power-on-password (POP) or a privileged-access password (PAP). In order to
protect the system from unauthorized users removing the battery to delete POP
and PAP, you have to secure the Model 270 with a padlock you provide on the
backside of the Model 270.
The disk drives cage can be protected with a separate padlock.
Software Requirements
AIX 4.3.3 plus APAR IY06844 (AIX 4330-02 Recommended Maintenance Level
for AIX 4.3.3) is required for the Model 270. The GA date is February 18, 2000.
If you are purchasing new RS/6000 systems, the AIX update phases into new
systems starting February 14, and it's available for download at:
http://techsupport.services.ibm.com/rs6k/fixes.html
In North America, you can order CDs by calling (800) 879-2755 or by ordering on
the Web at http://service2.boulder.ibm.com/swdelivery/. In other geographies,
ask your IBM Business Partner or IBM Representative to place a single refresh
System Program Order for 5692-AIX.
For select customer requirements, there is a limited availability of AIX Version
4.3.2 support on the Model 270: PRPQ P91183, AIX 4.3.2 Workstation Support.
1 SSA boot is possible from an Advanced SerialRAID Plus Adapter (# 6230), provided a non-RAID SSA disk is included as part of the
configuration. Other disks associated with the adapter can be RAID but at least one disk must be a non-RAID SSA disk. The non-RAID
SSA disk can be located under the covers of a processor unit or in an external SSA storage unit. If your system is running with AIX 4.3.3
or later software, native boot capability is supported.
For factory system orders with AIX preload requested, an internal SCSI disk drive will be preloaded as the native boot disk even if internal
SSA disk drive(s) are present.
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview 13
Reference
The following sections list additional materials available for further research.
System Documentation
For more detailed information, refer to the following documents:
• 44P Series Model 270 Setup Instructions, SA38-0574
• 44P Series Model 270 User’s Guide, SA38-0573
• 44P Series Model 270 Service Guide, SA38-0572
• RS/6000 Diagnostics Information for Multiple Bus Systems , SA38-0509
• RS/6000 Adapters, Devices and Cables information for Multiple Bus Systems,
SA38-0516
• PCI Adapter Placement Reference Guide, SA38-0538
Select IBM Redbooks
The following IBM Redbooks are related to the material discussed in this paper:
• RS/6000 Systems Handbook, SG24-5120
• RS/6000 43P 7043 Models 150 and 260 Handbook , SG24-5144
• RS/6000 SMP Enterprise Servers Architecture and Implementation ,
SG24-2583
• AIX 4.3 Differences Guide , SG24-2014
• Understanding IBM RS/6000 Performance and Sizing, SG24-4810
Select Internet Links
For more detailed information see the following Web sites:
http://www.rs6000.ibm.com/
http://www.rs6000.ibm.com/hardware/workstations/
http://www.rs6000.ibm.com/resource/hardware_docs/index.html
http://www.rs6000.ibm.com/cgi-bin/ds_form
http://www.rs6000.ibm.com/support/micro/
http://www.ibm.com/servers/aix/
http://www.chips.ibm.com/
http://www.research.ibm.com/topics/serious/chip/
http://www.storage.ibm.com/
http://www.hursley.ibm.com/~ssa/rs6k/
http://www.redbooks.ibm.com/
Sources
The following sources were used in the creation of this publication:
• IBM RS/6000 7044 Model 270 - Announcement Letter
• IBM RS/6000 7043 Model 260 to Model 270 Upgrade - Announcement Letter
• IBM RS/6000 44P Model 270 Workstation - Spec Sheet (G221-7127-01)
• IBM RS/6000 44P Model 270 Server - Spec Sheet (G221-7131-01)
• Blue Logic - CMOS 5SF Technology (G522-0269)
14 RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
• Blue Logic - CMOS 6SF Technology (G522-0261)
• Blue Logic - CMOS 7SF Technology (G522-0357)
Acknowledgements
Assistance creating this white paper came from the following individuals and was
appreciated. Thank you!
Arroyo, Ron IBM Austin
Cocco, Cathy IBM Austin
King, Ken IBM Austin
Peter Lenk IBM Austin
Nguyen, Thoi IBM Austin
Vaden, Mike IBM Austin
Walton, Scott D. IBM Austin
Biographies
Volker Haug is an Advisory I/T Specialist. He has more than 13 years of
experience in the I/T industry, the last 10 of which he has devoted to RS/6000
and AIX systems. He holds a degree in Business Management from the
Berufsakademie in Stuttgart. Volker is the technical leader supporting IBM sales,
Business Partners, and customers with pre-sales consultation and
implementation of client/server environments. His areas of expertise include
RS/6000 workstations and workgroup servers, graphics, MCAD applications, and
AIX systems management. Based in Stuttgart, Germany, he is currently working
for the Web Server Sales RS/6000 and NUMA-Q technical support organization
covering the IBM Europe, Middle East, and Africa Central Region.
Jeanine Indest is an I/T Specialist with the Techline RS/6000 Sales Support
Team, part of the Web Server Sales Americas Organization. She has more than
six years of experience in the I/T industry, the last four of which she has devoted
to RS/6000 and AIX systems. She holds a B.S. degree and a M.A. degree in
Economics from the University of New Orleans. Her current area of expertise is
technical marketing support for Business Partners in the United States for
RS/6000 and NUMA-Q systems.
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview 15
Special Notices
This document was produced in the United States. IBM may not offer the
products, programs, services or features discussed herein in other countries, and
the information may be subject to change without notice. Consult your local IBM
business contact for information on the products, programs, services, and
features available in your area. Any reference to an IBM product, program,
service or feature is not intended to state or imply that only IBMs product,
program, service or feature may be used. Any functionally equivalent product,
program, service or feature that does not infringe on any of IBMs intellectual
property rights may be used instead of the IBM product, program, service or
feature.
Information in this document concerning non-IBM products was obtained from the
suppliers of these products, published announcement material or other publicly
available sources. Sources for non-IBM list prices and performance numbers are
taken from publicly available information including D.H. Brown, vendor
announcements, vendor WWW Home Pages, SPEC Home Page, GPC (Graphics
Processing Council) Home Page and TPC (Transaction Processing Performance
Council) Home Page. IBM has not tested these products and cannot confirm the
accuracy of performance, compatibility or any other claims related to non-IBM
products. Questions on the capabilities of non-IBM products should be addressed
to the suppliers of those products.
IBM may have patents or pending patent applications covering subject matter in
this document. The furnishing of this document does not give you any license to
these patents. Send license inquires, in writing, to IBM Director of Licensing, IBM
Corporation, New Castle Drive, Armonk, NY 10504-1785 USA.
All statements regarding IBMs future direction and intent are subject to change or
withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only. Contact your
local IBM office or IBM authorized reseller for the full text of a specific Statement
of General Direction.
The information contained in this document has not been submitted to any formal
IBM test and is distributed "AS IS". While each item may have been reviewed by
IBM for accuracy in a specific situation, there is no guarantee that the same or
similar results will be obtained elsewhere. The use of this information or the
implementation of any techniques described herein is a customer responsibility
and depends on the customer's ability to evaluate and integrate them into the
customer's operational environment. Customers attempting to adapt these
techniques to their own environments do so at their own risk.
IBM is not responsible for printing errors in this publication that result in pricing or
information inaccuracies.
The information contained in this document represents the current views of IBM
on the issues discussed as of the date of publication. IBM cannot guarantee the
accuracy of any information presented after the date of publication.
All prices shown are IBMs suggested list prices; dealer prices may vary.
IBM products are manufactured from new parts, or new and serviceable used
parts. Regardless, our warranty terms apply.
16 RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
Information provided in this document and information contained on IBMs past
and present Year 2000 Internet Web site pages regarding products and services
offered by IBM and its subsidiaries are "Year 2000 Readiness Disclosures" under
the Year 2000 Information and Readiness Disclosure Act of 1998, a U.S statute
enacted on October 19, 1998. IBMs Year 2000 Internet Web site pages have
been and will continue to be our primary mechanism for communicating year
2000 information. Please see the "legal" icon on IBMs Year 2000 Web site
(www.ibm.com/year2000) for further information regarding this statute and its
applicability to IBM.
Any performance data contained in this document was determined in a controlled
environment. Therefore, the results obtained in other operating environments
may vary significantly. Some measurements quoted in this document may have
been made on development-level systems. There is no guarantee these
measurements will be the same on generally-available systems. Some
measurements quoted in this document may have been estimated through
extrapolation. Actual results may vary. Users of this document should verify the
applicable data for their specific environment.
The following terms are registered trademarks of International Business
Machines Corporation in the United States and/or other countries: ADSTAR, AIX,
AIX/6000, AIXwindows, AS/400, C Set++, CICS, CICS/6000, DB2, ESCON, IBM,
Information Warehouse, Intellistation, LANStreamer, LoadLeveler, Magstar,
MediaStreamer, Micro Channel, MQSeries, Net.Data, Netfinity, OS/2, OS/400,
OS/390, Parallel Sysplex, POWERparallel, RS/6000, S/390, Service Director,
System/390, ThinkPad, TURBOWAYS, VisualAge. The following terms are
trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in the United States
and/or other countries: AIX PVMe, AS/400e, DB2 OLAP Server, DB2 Universal
Database, DEEP BLUE, e-business (logo), eNetwork, GigaProcessor,
HACMP/6000, Intelligent Miner, Network Station, POWER2 Architecture,
PowerPC 604, SmoothStart, SP, Videocharger, Visualization Data Explorer,
WebSphere. A full list of U.S. trademarks owned by IBM may be found at
http://iplswww.nas.ibm.com/wpts/trademarks/trademar.htm.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT and the Windows logo are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States, other
countries, or both. UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other
countries licensed exclusively through The Open Group. Java and all Java-based
trademarks and logos are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United
States, other countries, or both. Lotus, and Lotus Notes are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Lotus Development Corporation. Tivoli, TME, TME 10
and TME 10 Global Enterprise Manager are trademarks of Tivoli Systems, Inc.
Other company, product and service names may be trademarks or service marks
of others.
RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview 17
18 RS/6000 7044 Model 270 Technical Overview
You might also like
- HP C8000 Workstation (AB629A) c8000 - DatasheetDocument2 pagesHP C8000 Workstation (AB629A) c8000 - DatasheetmodsimcaNo ratings yet
- Manual Abit AB-PX5Document90 pagesManual Abit AB-PX5daniel mihaiNo ratings yet
- Athlon Based Dua1Document19 pagesAthlon Based Dua1DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENo ratings yet
- RTC Magazine June 2006Document76 pagesRTC Magazine June 2006Jake NadudiNo ratings yet
- Motherboard components explainedDocument12 pagesMotherboard components explainedTuesept Anne Vargas UrgenteNo ratings yet
- Cisco Media Convergence Server 7845-H1: Product OverviewDocument11 pagesCisco Media Convergence Server 7845-H1: Product OverviewChandrakanth ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Chip SetsDocument29 pagesChip SetsDrift Gee100% (1)
- Power Macintosh 8200 and 8500 Series/WS 8550: Service SourceDocument150 pagesPower Macintosh 8200 and 8500 Series/WS 8550: Service SourceerandolphsavageNo ratings yet
- Sis 5582Document222 pagesSis 5582Luis HerreraNo ratings yet
- Workgroup Server 9650/233Document2 pagesWorkgroup Server 9650/233scriNo ratings yet
- Powermac 7200 SeriesDocument158 pagesPowermac 7200 Seriesyv4hnNo ratings yet
- Motherboard GomaDocument80 pagesMotherboard GomaNoemi VargasNo ratings yet
- Manual M810Document38 pagesManual M810romiyuddinNo ratings yet
- HP and Compaq Desktop PCs - Motherboard Specifications, MS-7184 (AmethystM) - HP® Customer SupportDocument5 pagesHP and Compaq Desktop PCs - Motherboard Specifications, MS-7184 (AmethystM) - HP® Customer SupportNicolas LeguizamonNo ratings yet
- Intel Premiere PCI Motherboard Manual 1994Document31 pagesIntel Premiere PCI Motherboard Manual 1994Sunny DaysNo ratings yet
- MB945 - User Manual - V1.0BDocument77 pagesMB945 - User Manual - V1.0Bpablo salvatierraNo ratings yet
- 570 MMA Announcement Enus 108259Document33 pages570 MMA Announcement Enus 108259hard_uNo ratings yet
- Sis 5597DS20Document331 pagesSis 5597DS20Luis HerreraNo ratings yet
- DataSheet FUJITSU Server PRIMEQUEST 2800B3Document6 pagesDataSheet FUJITSU Server PRIMEQUEST 2800B3Eko PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- 9600 Service ManualDocument150 pages9600 Service ManualElliot Randolph SavageNo ratings yet
- Parts of A System UnitDocument41 pagesParts of A System UnitDebie Catanyag-TorioNo ratings yet
- Ds Celsius r630Document2 pagesDs Celsius r630pcepoxNo ratings yet
- Perform Computer OperationsDocument29 pagesPerform Computer Operationsreynald manzanoNo ratings yet
- Industrial PC Series C61xxDocument4 pagesIndustrial PC Series C61xxHernán MamaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware: Intel AMD Dual CoreDocument6 pagesComputer Hardware: Intel AMD Dual CoreanishklNo ratings yet
- MOTHERBOARDDocument70 pagesMOTHERBOARDCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Digi Lite MotherboardDocument12 pagesDigi Lite Motherboardrajesh_r450No ratings yet
- Manuale Compaq Ipaq - 10832 - CaDocument14 pagesManuale Compaq Ipaq - 10832 - CasimonegalianoNo ratings yet
- X11SCL-F - Motherboards - Products - Super Micro Computer, IncDocument4 pagesX11SCL-F - Motherboards - Products - Super Micro Computer, IncReportNo ratings yet
- ACER Altos R3 Server DatasheetDocument2 pagesACER Altos R3 Server DatasheetDavid JonathanNo ratings yet
- Mother BoardsDocument4 pagesMother BoardsNisha FareenaNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte GA - 586UX User ManualDocument59 pagesGigabyte GA - 586UX User Manualniko99No ratings yet
- Biostar A58ml SpecDocument6 pagesBiostar A58ml SpecAbraham SuarezNo ratings yet
- Manual de La Placa PC 400Document47 pagesManual de La Placa PC 400Esau Jimenez Arevalo0% (2)
- Basic Concepts of The Personal ComputerDocument48 pagesBasic Concepts of The Personal ComputerpfalencarNo ratings yet
- Component of A System Unit - Desktop PCDocument8 pagesComponent of A System Unit - Desktop PCRoger EmbalsadoNo ratings yet
- MB865 User'S Manual: LGA775 Pentium 4 Intel 865G Industrial MotherboardDocument64 pagesMB865 User'S Manual: LGA775 Pentium 4 Intel 865G Industrial Motherboardcharst pNo ratings yet
- Power Macintosh 8600/200Document2 pagesPower Macintosh 8600/200scriNo ratings yet
- mAIN BOARD PC CHIPSDocument39 pagesmAIN BOARD PC CHIPSjotamario007No ratings yet
- HP Integrity Superdome 2Document29 pagesHP Integrity Superdome 2vkky2k8120No ratings yet
- What Is Processor ?Document8 pagesWhat Is Processor ?Arya SinghNo ratings yet
- HP Compaq NC6000 SpecificationsDocument33 pagesHP Compaq NC6000 SpecificationsSamed TalovićNo ratings yet
- Maestro DS081 LITE 1119Document2 pagesMaestro DS081 LITE 1119Carl AzzopardiNo ratings yet
- AMD Athlon: ProcessorDocument10 pagesAMD Athlon: ProcessorGerald CHRISTIENo ratings yet
- Ds Celsius w340Document2 pagesDs Celsius w340Popa Nicolae0% (1)
- Motherboardppt41 160905161959Document39 pagesMotherboardppt41 160905161959Adrian Yan Yan DelaraNo ratings yet
- Rocky 518hv Ver4 0Document33 pagesRocky 518hv Ver4 0allenbaileyNo ratings yet
- Pcchips m900 ManualDocument39 pagesPcchips m900 Manualferangas1733No ratings yet
- Core 2 Quad Processor TechnologyDocument14 pagesCore 2 Quad Processor Technologysubhayu1986No ratings yet
- Icpmb-8660 V1.0Document57 pagesIcpmb-8660 V1.0Rafael SoaresNo ratings yet
- 7521 ServiceManualDocument122 pages7521 ServiceManualRicardo Alexis Fuentes LufittNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Name - Sachin Roll No - 20156 Branch - CseDocument39 pagesMotherboard: Name - Sachin Roll No - 20156 Branch - CseSachin DhamiNo ratings yet
- Components of System UnitDocument8 pagesComponents of System Unitroger_embalsado331988% (16)
- Ta990fxe 20120120Document9 pagesTa990fxe 20120120Caesar ScalettaNo ratings yet
- TCW BookDocument45 pagesTCW Bookمسعود المغيريNo ratings yet
- Trademarks: Mainboard User's ManualDocument43 pagesTrademarks: Mainboard User's Manualjokot42No ratings yet
- AMD Laptop ProcessorsDocument25 pagesAMD Laptop ProcessorsAnithPalat100% (1)
- Reliability, Availability, Serviceability (RAS) : The IbmDocument25 pagesReliability, Availability, Serviceability (RAS) : The IbmChitra VarathanNo ratings yet
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- Nintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8From EverandNintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8No ratings yet
- Atl® Ultramark® 9: SpecificationsDocument1 pageAtl® Ultramark® 9: SpecificationsRicardoRiveraNo ratings yet
- CV Nupur Sahu ECE NITDocument2 pagesCV Nupur Sahu ECE NITvsmishra1992No ratings yet
- Slau 144 JDocument644 pagesSlau 144 JJuan Ricardo Sanchez LopezNo ratings yet
- Ip Book For Class Xii - CbseDocument381 pagesIp Book For Class Xii - CbseSaransh Mehrotra87% (173)
- Types CR, CRC, CRP and CRD Directional Overcurrent Relays: CautionDocument32 pagesTypes CR, CRC, CRP and CRD Directional Overcurrent Relays: CautionRida JavidNo ratings yet
- TV LG KCP 29C85Document18 pagesTV LG KCP 29C85Anonymous lQyR2IWNo ratings yet
- 1.11KV H.g.fuse Unit (Solid Core Type)Document1 page1.11KV H.g.fuse Unit (Solid Core Type)SSK IndustriesNo ratings yet
- ULN2068BDocument6 pagesULN2068BDiego Asicona100% (1)
- Assembly LineDocument8 pagesAssembly LineAnshik YadavNo ratings yet
- AN ESC FAQ V1i1Document52 pagesAN ESC FAQ V1i1shri.bhairavkar6977No ratings yet
- 4500W High Power Class-D Amplifier D4K5 - Electronic CircuitDocument4 pages4500W High Power Class-D Amplifier D4K5 - Electronic CircuitK Raja Sekar71% (7)
- Lexium32i Catalog enDocument38 pagesLexium32i Catalog enСања БанковићNo ratings yet
- Quiz Questions For DLD LabDocument6 pagesQuiz Questions For DLD LabGerald Carson100% (1)
- Dell Inspiron 3520 10316-1 DV15 HR 48.4IP16.011Document60 pagesDell Inspiron 3520 10316-1 DV15 HR 48.4IP16.011Bala MuruganNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument13 pagesPhysics42,Vansh 8th DNo ratings yet
- Transmitter Programming Guide Model: APS 95 BT3Document12 pagesTransmitter Programming Guide Model: APS 95 BT3José olivaNo ratings yet
- 8051 BasicsDocument22 pages8051 BasicsviswapraveenNo ratings yet
- Noise Suppression EMIFILr Capacitor Signal Lines Data SheetDocument2 pagesNoise Suppression EMIFILr Capacitor Signal Lines Data SheetJuan CoronelNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operating Instructions Level-Radar: KROHNE 06/2004 7.02230.32.00Document28 pagesInstallation and Operating Instructions Level-Radar: KROHNE 06/2004 7.02230.32.00Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- A029x163 I7 201902 PDFDocument106 pagesA029x163 I7 201902 PDFFri LayNo ratings yet
- ZTE Product Introduction and Light PON Solution For BalitowerDocument32 pagesZTE Product Introduction and Light PON Solution For BalitowerOrigoAndoraNo ratings yet
- MICROCONTROLLER FAMILY of PIC 18Document29 pagesMICROCONTROLLER FAMILY of PIC 18Taha AssadiNo ratings yet
- Nagaraj CV UpdatedDocument4 pagesNagaraj CV UpdatedNagaraj VjNo ratings yet
- General Wiring Diagram: RelayDocument1 pageGeneral Wiring Diagram: RelayluisNo ratings yet
- Calculate household electric usage and global consumptionDocument2 pagesCalculate household electric usage and global consumptionISsa Qafa'itiNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Audio Transistor Guitar Pre-Amp Circuit Simplest Operating Self BiasDocument2 pagesAmplifier Audio Transistor Guitar Pre-Amp Circuit Simplest Operating Self Biasdreyes2288No ratings yet
- Deh 1350Document60 pagesDeh 1350RafaloganNo ratings yet
- Technical Datasheet Dynameco 200-E03 GBDocument3 pagesTechnical Datasheet Dynameco 200-E03 GBFachlefi Nusantono NusantonoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1 MOBILE NETWORKS 1 NOWDocument13 pagesLecture Notes 1 MOBILE NETWORKS 1 NOWNorris Nana ChinjongNo ratings yet
- DSX1 Digital Signal Cross Connect 103253AEDocument76 pagesDSX1 Digital Signal Cross Connect 103253AEGeoffrey AlleyneNo ratings yet