Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 14 (A) Add Math - Integrations
Uploaded by
nurulamirahidrisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 14 (A) Add Math - Integrations
Uploaded by
nurulamirahidrisCopyright:
Available Formats
INTEGRATIONS FORM 5
MODULE 14(A)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
TOPIC : INTEGRATIONS
1. 3 3
Given that ∫ 1
g ( x ) dx = 5 and ∫ [3g ( x ) + mx ] dx = 23 , find the value of m.
1
[4 marks]
[Answer : 2 ]
2. k
Given that ∫ −3
(2 x + 2)dx = 5 where k > −3 , find the value of k.
[4 marks]
[Answer : 2 ]
3. 12
Given that ∫ (3 x − 2) 3
dx = k (3 x − 2)n + c , find the value of k and n.
[3 marks]
[Answer : k = -2, n = -2 ]
4. 3
Given that ∫ p
(4 x − 1)dx = 12 , where p > 0, find the value of p.
[4 marks]
[Answer : -1 ]
5. 2 2
Given that ∫ 1
f ( x ) dx = 4 , find the value of h if ∫1
(3f ( x ) − h )dx = 8 .
[4 marks]
[Answer : 4 ]
6. 2x2 − 9
Find the value of ∫ −3 x − 3
dx .
[3 marks]
1
[Answer : 12 ]
2
7. 5 5
Given that ∫ 3
f ( x ) dx = 4 and ∫ [3f ( x ) − kx ] dx = 8 , find the value of k.
3
[3 marks]
1
[Answer : ]
2
8. x dy 1
Given y = , show that = . Hence, find the value of
1 + 2x dx (1 = 2 x )2
2
4 12
∫1
1 + 2 x dx .
[4 marks]
[Answer : 16 ]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK (szk smkpn) Page 1
INTEGRATIONS FORM 5
9.
∫
If 10(5 + x )4 dx = m(5 + x )n + c , find the value of m and n.
[3 marks]
[Answer : m = 2, n = 5 ]
10. 2 5 2 2
Given that ∫ 0
h( x ) dx = ∫
2
h( x ) dx = 7 . Find the value of ∫
0
h( x ) dx + ∫5
h( x ) dx .
[2 marks]
[Answer : 0 ]
11. k 5
Given that ∫ −k
3x −
x2
dx = 10 , find the value of k.
[3 marks]
[Answer : 1 ]
12.
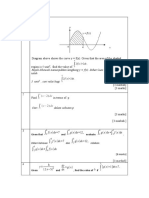
Diagram shows the curve y 2 = 2 x and the straight line y = k . If the area of the
9
shaded region is unit², find the value of k.
2
[4 marks]
[Answer : 3 ]
13.
Diagram shows the graph of the curve y = x 2 and the straight line y + x = 2
which passes through the points A(1,1) and B. Calculate the area of the
shaded region.
[3 marks]
5
[Answer : ]
6
14. x2 dy 2
Given that y =
x+3
and
dx
= g ( x ) , calculate the value of ∫0
2g ( x ) dx .
[3 marks]
8
[Answer : ]
5
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK (szk smkpn) Page 2
INTEGRATIONS FORM 5
15. d 2x − 1 5 2 1
Given that =
dx 3 x + 1 (3 x + 1)2
, find ∫
0 (3 x + 1)2
dx .
[3 marks]
2
[Answer : ]
7
16. x −1 dy
Given that y = 2
and = 2f ( x ) where f ( x ) is a function in terms of x.
x dx
2
Find the value of ∫−2
f ( x ) dx .
[4 marks]
1
[Answer : ]
2
17.
Diagram shows part of the curve y = ( x − 1)( x + 1) . Find the area of the shaded
region.
[3 marks]
8
[Answer : ]
3
18.
Figure shows the curve of y = 4 x 3 and the straight line x = k. If the area of the
shaded region is 81 units², find the value of k.
[4 marks]
[Answer :3]
END OF MODULE
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK (szk smkpn) Page 3
INTEGRATIONS FORM 5
ANSWERS
MODULE 13(A)
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
TOPIC : INTERGRATION
1. 3 3
∫1
3g ( x ) dx + ∫1
mx dx
3
3 mx 2
3 ∫ 1
g ( x ) dx +
2 1
= 23
9 1
3(5) + m − m = 23
2 2
m=2
2. k
∫−3
(2 x + 2)dx = 5
k
x 2 + 2x = 5
−3
k 2 + 2k − 9 = 0
( k − 2)( k + 4) = 0
k =2
3. 12
∫ (3 x − 2) 3 ∫
dx = 12(3 x − 2)−3
12(3 x − 2)−2
= +c
−2(3)
= −2(3 x − 2)−2 + c
k = −2 , n = −2
4. 2 x 2 − x = 12
3
p
2p2 − p − 3 = 0
(2 p − 3)( p + 1) = 0
p = −1
5. 2
∫
2
3 f ( x ) dx − [ hx ]1 = 8
1
3(4) − h = 8
h=4
6. 1
2
= x2 + 3x
2 −3
1 1
= (22 ) + 3(2) − ( −32 ) + 3( −3)
2 2
1
= 12
2
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK (szk smkpn) Page 4
INTEGRATIONS FORM 5
7. 5
∫ [3f ( x ) − kx ] = 8
3
5 5
∫ 3f ( x ) dx − ∫ kx dx = 8
3 3
5
5 kx 2
3 ∫
3 f (x) − =8
2 3
25k 9k
12 − − =8
2 2
1
k=
2
8. 4
12
2
y=
x = ∫
1 1 + 2x
dx
1 + 2x 4 144
dy (1 + 2 x )(1) − x ( 2 )
=
=
1 ∫(1 + 2x )
2
dx
2
dx (1 + 2x ) 4
x
1 = 144
= 1 + 2 x 1
(1 + 2x )2
= 16
9. 10(5 + x )5
= +c
5(1)
= 2(5 + x )5 + c
m=2 , n=5
10. = 7 + ( −7)
=0
11. 3x 2 5
k
+ = 10
2 x −k
3(k )2 5 3( −k )2 5
+ − + = 10
2 (k ) 2 ( −k )
10
= 10
k
k =1
12. k y2
A=
0 2 ∫
dy
k
y3 9
=
3(2) 0 2
k =3
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK (szk smkpn) Page 5
INTEGRATIONS FORM 5
13. 1 1
= ∫ 0
x 2 dx +
2
(1)(1)
1
x3 1
= +
3 0 2
5
=
6
14. x 2
2
= 2
x + 3 0
22
= 2
2+3
8
=
5
15. 2 1 1 2 5
∫0 (3 x + 1)2
dx =
5 ∫ 0 (3 x + 1)2
dx
2
1 2 x − 1
=
5 3 x + 1 0
1 3
= +1
5 7
2
=
7
16. dy
= 2f ( x )
dx
∫
y = 2f ( x ) dx = 2 f ( x ) dx ∫
1
∫ f ( x ) dx = 2 y
1 x − 1 x − 1
= =
2 x 2 2 x 2
2
2 x − 1
∴
−2∫f ( x ) dx = 2
2 x −2
1
=
2
17. 1 2
= ∫−1
( x 2 − 1)dx + ∫
1
( x 2 − 1)dx
1 2
x3 x3
= − x + − x
3 −1 3 1
4 4
= − +
3 3
8
=
3
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK (szk smkpn) Page 6
INTEGRATIONS FORM 5
18. k
= ∫ 0
y dx
k
∫0
4 x 3 dx = 81
k
x 4 = 81
0
k =3
END OF MODULE
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK (szk smkpn) Page 7
You might also like
- Integration: X XDX X XDX Marks)Document10 pagesIntegration: X XDX X XDX Marks)misssarahaikalNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sem 2 Gbs Melaka (Q)Document3 pages2019 Sem 2 Gbs Melaka (Q)Green SlimeNo ratings yet
- INTEGRATIONDocument6 pagesINTEGRATIONIeda WirnaNo ratings yet
- Set 3 P2Document2 pagesSet 3 P2Nicholson NicholsonNo ratings yet
- Mocktest 1Document5 pagesMocktest 1Mapler MapleleafNo ratings yet
- Confidential Section A (45 Marks) : 2020-2-NS-KGVDocument2 pagesConfidential Section A (45 Marks) : 2020-2-NS-KGVvoon sjNo ratings yet
- First Trial Examination 2010 - Paper 1Document2 pagesFirst Trial Examination 2010 - Paper 1Loo Siaw ChoonNo ratings yet
- 2017 2 Joh MuarDocument3 pages2017 2 Joh MuarLee Shi HockNo ratings yet
- Integration: X XDX X XDX Marks)Document10 pagesIntegration: X XDX X XDX Marks)jipunskorzNo ratings yet
- 2014-2-Kelantan-Chung HuaDocument3 pages2014-2-Kelantan-Chung HuaPeng Peng KekNo ratings yet
- Kluang (Q)Document3 pagesKluang (Q)Melody OngNo ratings yet
- CALCULUSDocument52 pagesCALCULUSJoseph TedlaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper: Mathematics - Class XII (Code A)Document23 pagesSample Question Paper: Mathematics - Class XII (Code A)JulioAngelMirandaUbaldoNo ratings yet
- P1-Differentiation and IntegrationDocument5 pagesP1-Differentiation and IntegrationArrow GamingNo ratings yet
- P1 SMK Muhibbah (Q)Document2 pagesP1 SMK Muhibbah (Q)ZurainiNo ratings yet
- 5.0 PSP1Set 3Document11 pages5.0 PSP1Set 33014398No ratings yet
- W22 CHP 3 Integration (Definite Integral)Document9 pagesW22 CHP 3 Integration (Definite Integral)bidarihassanNo ratings yet
- STPM Trial 2009 Matht Q&A (PCGHS, Penang)Document14 pagesSTPM Trial 2009 Matht Q&A (PCGHS, Penang)SimPorNo ratings yet
- Cat 1&2 - Sta 2204Document1 pageCat 1&2 - Sta 2204Lorna Makena KinyuaNo ratings yet
- W21 Chapter 3 IntegrationDocument15 pagesW21 Chapter 3 IntegrationbidarihassanNo ratings yet
- Play With Math: BhagalpurDocument4 pagesPlay With Math: Bhagalpuryogesh amitNo ratings yet
- Tuto 55 AntiderivativesDocument3 pagesTuto 55 AntiderivativesAZRI FIRDAUS이광수No ratings yet
- RevisionDocument2 pagesRevisioncharlene chiaNo ratings yet
- DPP (29 - ) 12th Maths WADocument46 pagesDPP (29 - ) 12th Maths WARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 2015-2-NSembilan-SMK ST Paul - MATHS QADocument8 pages2015-2-NSembilan-SMK ST Paul - MATHS QAVishalinie RamanNo ratings yet
- Integration: X XDX X XDX Marks)Document10 pagesIntegration: X XDX X XDX Marks)Norzulsuriana Binti YahayaNo ratings yet
- Integration SPMDocument2 pagesIntegration SPMMuhammad Mansor BurhanNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument2 pagesAnswer All Questions in This SectionRebornNgNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument2 pagesAnswer All Questions in This SectionJustin NgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9-Integration by Parts-Long DivisionDocument16 pagesLecture 9-Integration by Parts-Long DivisionbananaNo ratings yet
- PG 267/ Eg3. Cos (X) DX 2 .: Area Under The Graph of A Nonnegative FunctionDocument11 pagesPG 267/ Eg3. Cos (X) DX 2 .: Area Under The Graph of A Nonnegative Functionaye pyoneNo ratings yet
- MEI C3 Challenge PaperDocument3 pagesMEI C3 Challenge PaperToby ReicheltNo ratings yet
- Harkness Test 10BDocument1 pageHarkness Test 10BLia CNo ratings yet
- Kelantan STPM 2010 Maths T p1Document3 pagesKelantan STPM 2010 Maths T p1Seow HuaNo ratings yet
- Jan & March 08Document4 pagesJan & March 08Agus LeonardiNo ratings yet
- Sample Test 2 SolDocument6 pagesSample Test 2 Solching chauNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section.: ConfidentialDocument3 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section.: ConfidentialRex KalNo ratings yet
- Dawson College: Department of MathematicsDocument14 pagesDawson College: Department of Mathematicsadcyechicon123No ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM Set 1 - Ques - Final DraftDocument13 pagesFINAL EXAM Set 1 - Ques - Final DraftMuzzammil ZamriNo ratings yet
- 2017-2-Sar-St Thomas-Q&aDocument8 pages2017-2-Sar-St Thomas-Q&aMuhammad IzzuanNo ratings yet
- STPM 2014 - MATHEMATICS T 954/2 (U2) : X X X X X y X X XDocument1 pageSTPM 2014 - MATHEMATICS T 954/2 (U2) : X X X X X y X X X加卡内-张进哲No ratings yet
- Trial STPM P2 2018 SMJK JT SINDocument3 pagesTrial STPM P2 2018 SMJK JT SINMelody OngNo ratings yet
- 2015 2 Per Horley Methodist QaDocument8 pages2015 2 Per Horley Methodist QakartiniNo ratings yet
- (To Do by 29 Mar) Calculus I - Product and Quotient Rule (Practice Problems)Document1 page(To Do by 29 Mar) Calculus I - Product and Quotient Rule (Practice Problems)Claire ChuaNo ratings yet
- SPM Questions: Additional MathematicsDocument2 pagesSPM Questions: Additional MathematicsNurul AtiqahNo ratings yet
- The Second Monthly TestDocument3 pagesThe Second Monthly TestJeremy LingNo ratings yet
- 2016 2 Joh STK Kluang QDocument2 pages2016 2 Joh STK Kluang QNur B TapriNo ratings yet
- Maclaurin QuestionsDocument3 pagesMaclaurin QuestionsSRI SIVABALASUNDRAM A/L KRISHNAN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Harkness Test 9bDocument1 pageHarkness Test 9bLia CNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Kuching Ques&AnsDocument12 pagesTest 2 Kuching Ques&AnsLIM YEE WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- 2015-2-JOHOR-SMKdatoAMARmuar - MATHS QADocument10 pages2015-2-JOHOR-SMKdatoAMARmuar - MATHS QAXue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section x+1 1 X X x+2 Ifx 2 K If X 2Document10 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section x+1 1 X X x+2 Ifx 2 K If X 2郑宏俊No ratings yet
- Due: 1 PM, Thursday, 17 January 2019 Instructions:: Warning!!Document3 pagesDue: 1 PM, Thursday, 17 January 2019 Instructions:: Warning!!Andrew JnrNo ratings yet
- Class Test Differential CalculusDocument5 pagesClass Test Differential CalculusMariyam AfreenNo ratings yet
- Feb 2010 ProblemsDocument1 pageFeb 2010 Problemspaul taniwanNo ratings yet
- Calculus I Product and Quotient Rule Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesCalculus I Product and Quotient Rule Practice ProblemsJohnnas VillamorNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Locus PDFDocument4 pagesLocus PDFPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Noise Attenuation TechniquesDocument2 pagesNoise Attenuation TechniquesadobiNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium II: Physics 106 Lecture 8Document20 pagesEquilibrium II: Physics 106 Lecture 8riyantrin_552787272No ratings yet
- All PastpapersDocument325 pagesAll PastpapersAhmed Masoud100% (7)
- Multipurpose Probabilistic Software For Statistical, Sensitivity and Reliability AnalysisDocument24 pagesMultipurpose Probabilistic Software For Statistical, Sensitivity and Reliability AnalysisAbhishek ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Unit IIDocument93 pagesOperations Management Unit IISheetal VermaNo ratings yet
- G9 MATHS P2 (28 Copies)Document9 pagesG9 MATHS P2 (28 Copies)Straight As StudyNo ratings yet
- Radial and Angular Parts of Atomic OrbitalsDocument3 pagesRadial and Angular Parts of Atomic OrbitalsW47K3R 27886No ratings yet
- Smart Kid Abacus Learning Private LimitedDocument9 pagesSmart Kid Abacus Learning Private Limitedhong lyNo ratings yet
- PSI 3 Course Material v2.1Document16 pagesPSI 3 Course Material v2.1sreenathNo ratings yet
- Bahan Reading Hydraulic PneumaticDocument6 pagesBahan Reading Hydraulic PneumaticAhmad HaritsNo ratings yet
- Design of Experiments: Lecture 1: Introduction (CH 1 DAE) Nitin Padhiyar IIT - GandhinagarDocument9 pagesDesign of Experiments: Lecture 1: Introduction (CH 1 DAE) Nitin Padhiyar IIT - GandhinagarShouharda GhoshNo ratings yet
- Procceding USN ADRI 2020 - FarmanDocument9 pagesProcceding USN ADRI 2020 - Farmanbolo deweNo ratings yet
- 201Document5 pages201Mohan Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Review MaterialDocument5 pagesDifferential Equations Review MaterialIsmael SalesNo ratings yet
- hw11 DallasonnekommtDocument2 pageshw11 DallasonnekommtDan Yapp0% (1)
- Wolfe ConditionsDocument5 pagesWolfe ConditionsRaviKumarNo ratings yet
- Interference of Two Identical Ultrasonic TransmittersDocument5 pagesInterference of Two Identical Ultrasonic TransmittersJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- Equations of Circles PDFDocument4 pagesEquations of Circles PDFMAYNo ratings yet
- CCDocument4 pagesCCferdi tayfunNo ratings yet
- MP ImpDocument2 pagesMP ImpVivek ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Cavidad PrediccionDocument9 pagesCavidad PrediccionLuis MartinezNo ratings yet
- Graph TheoryDocument81 pagesGraph TheoryJohn TeranaNo ratings yet
- Part BDocument16 pagesPart BRamakrishnan Harihara VenkatasubramaniaNo ratings yet
- Bits NozzlesDocument197 pagesBits Nozzlesiman100% (2)
- Air Passenger Demand Forecasting For Planned Airports, Case Study Zafer and OR-GI Airports in Turkey (Planlanan Havalimanlarının Yolcu Talep Miktarlarının Tahmin Edilmesi Zafer Ve OR-Gİ Hava L PDFDocument149 pagesAir Passenger Demand Forecasting For Planned Airports, Case Study Zafer and OR-GI Airports in Turkey (Planlanan Havalimanlarının Yolcu Talep Miktarlarının Tahmin Edilmesi Zafer Ve OR-Gİ Hava L PDFÇağrı KARABİLLİOĞLUNo ratings yet
- SS2 CorrectedDocument15 pagesSS2 CorrectedsunliasNo ratings yet
- Q1 W3 D4 Perform Operations On RAEs MultiplicationDivisionDocument3 pagesQ1 W3 D4 Perform Operations On RAEs MultiplicationDivisionJudith AbogadaNo ratings yet
- A Low-Cost Power-Quality Meter With Series Arc-Fault Detection Capability For Smart GridDocument8 pagesA Low-Cost Power-Quality Meter With Series Arc-Fault Detection Capability For Smart GridBernardMightNo ratings yet
- Madilyn Kendall - Orchard Hideout PortfolioDocument7 pagesMadilyn Kendall - Orchard Hideout Portfolioapi-491224892No ratings yet