Professional Documents
Culture Documents
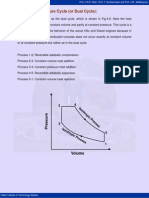
Diesel Cycle
Uploaded by
kingking21177Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diesel Cycle
Uploaded by
kingking21177Copyright:
Available Formats
Gas Power Cycles Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M .
Mallikarjuna
4.5 Air Standard Diesel Cycle:
Air standard diesel cycle is a idealized cycle for diesel engines. It is as shown on P-v
and T-s diagrams. The processes in the cycle are as follows:
2 3
Volume
2
4
Entropy
Fig.4.5. Air standard diesel cycle on p-v and T-s diagrams.
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Gas Power Cycles Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M . Mallikarjuna
Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic Compression.
Process 2-3: Constant pressure heat addition.
Process 3-5: Reversible adiabatic Compression.
Process 4-1: Constant volume heat rejection.
Consider ‘m’ kg of working fluid. Since the compression and expansion processes are
reversible adiabatic processes, we can write,
Heat sup plied = m Cp ( T3 - T2 ) = ( h3 - h2 )
Heat rejected = m Cv ( T4 - T1 ) = ( u4 - u1 )
Workdone = m Cp ( T3 - T2 ) - m C v ( T4 - T1 )
Now, we can write, thermal efficiency as,
m Cp ( T3 - T2 ) - m C v ( T4 - T1 )
ηth =
m Cp ( T3 - T2 )
1 ⎛ T4 - T1 ⎞
= 1 - ⎜ ⎟
γ ⎝ T3 - T2 ⎠
v1 v
T2 = T1 r γ -1 ; r = = 4
v2 v2
T3 v
= 3 = rc = cutoff ratio
T2 v2
T3 = rc T2 = rc T1 r γ -1
γ -1 γ -1
⎛v ⎞ ⎛v ⎞
T4 = T3 ⎜ 3 ⎟ = T3 ⎜ 4 ⎟
⎝ v4 ⎠ ⎝ v3 ⎠
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Gas Power Cycles Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M . Mallikarjuna
1-γ 1- γ
⎛v v ⎞ ⎛r ⎞
= T3 ⎜ 4 . 2 ⎟ = T3 ⎜ ⎟
⎝ v 2 v3 ⎠ ⎝ rc ⎠
1- γ
γ -1 ⎛ r ⎞
= rc T1 r ⎜ ⎟ ; T4 = rcγ T1
⎝ rc ⎠
1 ⎧⎪ rcγ T1 - T1 ⎫⎪
Hence, ηth = 1 - ⎨ ⎬
γ ⎩⎪ rc r γ -1 T1 - r γ -1 T1 ⎭⎪
⎧⎪ r γ -1 ⎫⎪
= 1 - r1-γ ⎨ c ⎬
⎪⎩ γ ( rc -1) ⎭⎪
From the above equation, it is observed that, the thermal efficiency of the diesel engine
can be increased by increasing the compression ratio, r, by decreasing the cut-off ratio,
α2, or by using a gas with large value of γ. Since the quantity (rγ-1)/γ(rp-1) in above
equation is always greater than unity, the efficiency of a Diesel cycle is always lower
than that of an Otto cycle having the same compression ratio. However, practical Diesel
engines uses higher compression ratios compared to petrol engines.
Mean effective Pressure:
Net workdone
mep =
Displacement volume
m Cp ( T3 - T2 ) - m C v ( T4 - T1 )
=
v1 - v 2
⎛ v ⎞ ⎛ 1⎞
v1 - v 2 = v1 ⎜ 1 - 2 ⎟ = v1 ⎜1 - ⎟
⎝ v1 ⎠ ⎝ r⎠
⎛ r - 1⎞
= m R T1 ⎜ ⎟
⎝ r ⎠
m C v ( γ -1) T1 ⎛ r - 1 ⎞
= ⎜ ⎟
P1 ⎝ r ⎠
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Gas Power Cycles Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M . Mallikarjuna
m Cp ( T3 - T2 ) - m C v ( T4 - T1 )
mep =
⎛ γ - 1⎞⎛ r - 1⎞
m C v T1 ⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟
⎝ P1 ⎠ ⎝ r ⎠
⎛ P r ⎞ ⎛ 1 ⎞ ⎪⎧ ⎛ T3 - T2 ⎞ ⎛ T4 - T1 ⎞ ⎪⎫
= ⎜ 1 ⎟⎜ ⎟ ⎨γ ⎜ ⎟-⎜ ⎟⎬
⎝ r - 1 ⎠ ⎝ γ - 1 ⎠ ⎪⎩ ⎝ T1 ⎠ ⎝ T1 ⎠ ⎭⎪
= P1 r ⎨
c (
⎧ γ r γ -1 ( r - 1) - r γ - 1 ⎫
⎪ c )
⎪
⎬
⎪⎩ ( r - 1)( γ - 1)
⎭⎪
Difference between Actual Diesel and the Otto Engines:
Otto Engine Diesel Engine
1. Homogenous mixture of fuel and air 1. No carburetor is used. Air alone is
formed in the carburetor is supplied supplied to the engine cylinder. Fuel is
to engine cylinder. injected directly into the engine
cylinder at the end of compression
stroke by means of a fuel injector.
Fuel-air mixture is heterogeneous.
2. Ignition is initiated by means of an 2. No spark plug is used. Compression
electric spark plug. ratio is high and the high temperature
of air ignites fuel.
3. Power output is controlled by varying 3. No throttle value is used. Power output
the mass of fuel-air mixture by is controlled only by means of the
means of a throttle valve in the mass of fuel injected by the fuel
carburetor. injector.
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
You might also like
- Otto CycleDocument5 pagesOtto CycleSaraju NandiNo ratings yet
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- Limited Pressure CycleDocument4 pagesLimited Pressure Cyclecasu19No ratings yet
- 2 Carnot CycleDocument6 pages2 Carnot CycleSamujawal Kumar SumanNo ratings yet
- Stirling CycleDocument3 pagesStirling CycleRon QuerubinNo ratings yet
- Stirling CycleDocument6 pagesStirling CycleChristian_Joe__9147No ratings yet
- Working Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsFrom EverandWorking Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ic Engine Cycles 1Document85 pagesIc Engine Cycles 1jhpandiNo ratings yet
- IC Engines 2012 Edition Theory & QuestionsDocument178 pagesIC Engines 2012 Edition Theory & Questionskumarrohit91No ratings yet
- Principle of TurbomachineryDocument159 pagesPrinciple of TurbomachinerySharath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lecture Notes OnDocument200 pagesLecture Notes Onananth k r100% (3)
- Engineering Council Certificate Level Thermodynamic, Fluid and Process Engineering C106 Tutorial 5 - Ideal Engine CyclesDocument14 pagesEngineering Council Certificate Level Thermodynamic, Fluid and Process Engineering C106 Tutorial 5 - Ideal Engine CyclesDipeshNo ratings yet
- The Traveling Engineers' Association to Improve the Locomotive Engine Service of American RailroadsFrom EverandThe Traveling Engineers' Association to Improve the Locomotive Engine Service of American RailroadsNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine Ignou NotesDocument16 pagesIc Engine Ignou NotesRakesh JhaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Engine CycleDocument20 pagesIdeal Engine CycleMulugeta WoldeNo ratings yet
- Air Standed Cycles Lec-7Document20 pagesAir Standed Cycles Lec-7pleasename1No ratings yet
- Air-Standard Cycles and Their AnalysisDocument40 pagesAir-Standard Cycles and Their AnalysisSrimanthula Srikanth100% (1)
- Cycles PDFDocument10 pagesCycles PDFratchagarajaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gas Power CyclesDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Gas Power CyclesN S SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- City and Guilds 9210 Level 6 Module - Unit 128 Applied ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesCity and Guilds 9210 Level 6 Module - Unit 128 Applied ThermodynamicsAlaa ShammaaNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDocument68 pagesGas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyAbraham HutomoNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines: LecturDocument32 pagesInternal Combustion Engines: LecturPuneet GargNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentmonotoshNo ratings yet
- Air Standard Assumptions:: EN560: Foundation For Energy TechnologyDocument5 pagesAir Standard Assumptions:: EN560: Foundation For Energy TechnologypoojaNo ratings yet
- Compression Ignition Engine Modelling PDFDocument8 pagesCompression Ignition Engine Modelling PDFmechveenaNo ratings yet
- Brayton CycleDocument5 pagesBrayton CycleAnonymous yorzHjDBd100% (1)
- Review of Air Standard Cycle (Analysis) :otto & Diesel CyclesDocument13 pagesReview of Air Standard Cycle (Analysis) :otto & Diesel CyclessomechnitjNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleAnonymous BHBWQIcClNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleSami UllahNo ratings yet
- 2 Rankinecycle-2Document4 pages2 Rankinecycle-2Anonymous gS6JtOfaNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 Rankinecyclesoubhadra nagNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerDocument4 pages5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerVidyut KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleJohn FredyNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleMantript SinghNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerDocument4 pages5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerSasi GunaNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITDocument47 pagesGas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITmohan govindasamyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Software: Brayton Cycle (Gas Turbine) For Propulsion Application AnalysisDocument16 pagesEngineering Software: Brayton Cycle (Gas Turbine) For Propulsion Application AnalysisHeni HtiraNo ratings yet
- Gas Natural TransmisionDocument43 pagesGas Natural Transmisionangel3reyesNo ratings yet
- Turbine: The Effect of Friction On The Joule CycleDocument13 pagesTurbine: The Effect of Friction On The Joule CycleGeorge AniborNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 40: Internal Combustion EngineDocument9 pagesModule 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 40: Internal Combustion EngineAryyama JanaNo ratings yet
- Otto CycleDocument28 pagesOtto CycleNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: A Model Energy Conversion System: Operation and Analysis of A Stirling EngineDocument11 pagesExperiment 2: A Model Energy Conversion System: Operation and Analysis of A Stirling Enginetimur_okNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Regenerative Gas Turbine Cycle For Performance EvaluationDocument10 pagesAnalysis of A Regenerative Gas Turbine Cycle For Performance EvaluationbensouiciNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument163 pagesRefrigerationali105No ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDocument68 pagesGas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyManjunatha TnNo ratings yet
- Engineering Software: Brayton Cycle (Gas Turbine) For Propulsion Application AnalysisDocument16 pagesEngineering Software: Brayton Cycle (Gas Turbine) For Propulsion Application AnalysisagoezNo ratings yet
- Air Cycle Refrigeration Systems (Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur)Document15 pagesAir Cycle Refrigeration Systems (Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur)emawz21No ratings yet
- Different Type of Air Standard (Otto and Diesel Cycle)Document23 pagesDifferent Type of Air Standard (Otto and Diesel Cycle)Irteza HossainNo ratings yet
- Gas - Turbine - CycleDocument41 pagesGas - Turbine - CycleKalpaniNo ratings yet
- Exam Title: IAS4Sure Prelims 2018 - Test 1 Email Contact: Correct Answer: B Your Answer: D ExplanationDocument72 pagesExam Title: IAS4Sure Prelims 2018 - Test 1 Email Contact: Correct Answer: B Your Answer: D ExplanationSanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- Find The Number of Triangles in The Given Figure Count The Number of TrianglesDocument5 pagesFind The Number of Triangles in The Given Figure Count The Number of TrianglesSanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- Mine - Plan A ReviewDocument107 pagesMine - Plan A ReviewSanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- Traditional Agriculture in India - High Yields and No Waste - Satavic FarmsDocument13 pagesTraditional Agriculture in India - High Yields and No Waste - Satavic FarmsSanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- Omr Sheet: Maulana Azad National Urdu UniversityDocument2 pagesOmr Sheet: Maulana Azad National Urdu UniversitySanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- UPSC Mains Blank Answer SheetsDocument11 pagesUPSC Mains Blank Answer SheetsRahul Yadav67% (3)
- Geography FOR UPSCDocument6 pagesGeography FOR UPSCSanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- Natural VentilationDocument26 pagesNatural VentilationSanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- GCSE Geography Instant RevisionDocument131 pagesGCSE Geography Instant RevisionCasey Rodriguez100% (13)
- Big Picture - Goods and Services Tax': GST: What's The Point of Conflict Now?Document2 pagesBig Picture - Goods and Services Tax': GST: What's The Point of Conflict Now?Sanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare Geography Optional For UPSC MainsDocument31 pagesHow To Prepare Geography Optional For UPSC MainsSanjeev Prakash0% (2)
- Installation of The Generator and Control Panel Components For Dynamic Gas BlendingDocument49 pagesInstallation of The Generator and Control Panel Components For Dynamic Gas Blendingالمهندسوليدالطويل100% (1)
- Biodiesel Production Through Waste Cooking OilDocument15 pagesBiodiesel Production Through Waste Cooking OilYan's Senora BescoroNo ratings yet
- Shamshad Ali Elect EngrDocument4 pagesShamshad Ali Elect Engrرضا سلطانNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering, LNCT Bhopal Material and Energy Balance Lab (CM - 404)Document3 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering, LNCT Bhopal Material and Energy Balance Lab (CM - 404)Anonymous FWlt8YNo ratings yet
- The "New Energy Economy": An Exercise in Magical ThinkingDocument24 pagesThe "New Energy Economy": An Exercise in Magical ThinkingManhattan InstituteNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor BrosurDocument6 pagesAir Compressor BrosurFick Ry'sNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Fire 2009 PDFDocument7 pagesCatalogo Fire 2009 PDFPatricia J ÁngelesNo ratings yet
- Jetstream Europe Brochure EnglishDocument6 pagesJetstream Europe Brochure EnglishFernando ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Directive056 April2014Document339 pagesDirective056 April2014geverett2765No ratings yet
- 39.0046 - Issue7 - July2002 - FMQ 10&FMQ 8 36&FMQ 7 42 - Install&OperateInstructionsDocument30 pages39.0046 - Issue7 - July2002 - FMQ 10&FMQ 8 36&FMQ 7 42 - Install&OperateInstructionsSubuk T. RathodNo ratings yet
- Parker Compound NL153-70 - Material ReportDocument2 pagesParker Compound NL153-70 - Material ReportWMC_PMNo ratings yet
- Hanboens Profile Rev7Document45 pagesHanboens Profile Rev7Md NazriNo ratings yet
- Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument32 pagesVapour Liquid EquilibriumHaseen Kaur0% (1)
- Automotive TechnologyDocument11 pagesAutomotive TechnologyDhasarathan Krishnan100% (9)
- Fuel Supply System in Petrol EnginesDocument54 pagesFuel Supply System in Petrol EnginesKLUniveristy86% (14)
- A Idade Decisiva - Meg JayDocument57 pagesA Idade Decisiva - Meg JayjardelbrunoNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Product Distribution and Operational Performance in The Downstream Sector of Oil and Gas Petroleum Industry in Nigeria Abigal ODE (PH.D)Document14 pagesPetroleum Product Distribution and Operational Performance in The Downstream Sector of Oil and Gas Petroleum Industry in Nigeria Abigal ODE (PH.D)AndualemNo ratings yet
- Soal Percepatan Sept 19Document14 pagesSoal Percepatan Sept 19Lucia SudiyatiNo ratings yet
- Keystone Fig. 60 Butterfly ValveDocument8 pagesKeystone Fig. 60 Butterfly ValveCarlos GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Basic Course of Drilling ProcedureDocument4 pagesBasic Course of Drilling ProcedureAli Samani100% (2)
- CC Y C" #$ %&'' (!') ' +Document11 pagesCC Y C" #$ %&'' (!') ' +pinky_marian17100% (3)
- IBIX 9 25 Scheda GBDocument2 pagesIBIX 9 25 Scheda GBkdhakane9460No ratings yet
- API Asme StampsDocument4 pagesAPI Asme StampsHerdiana Kristi100% (1)
- Eor Potential For Dulang FieldDocument8 pagesEor Potential For Dulang FieldnikenanthaNo ratings yet
- Control Room Operator: J.Bala DineshDocument5 pagesControl Room Operator: J.Bala DineshDonNo ratings yet
- Good Research Project Chitunha ShapazDocument22 pagesGood Research Project Chitunha ShapazTinashe Christopher MatongoNo ratings yet
- Amine Gas Sweetening Systems PsDocument3 pagesAmine Gas Sweetening Systems Pscanada_198020008918No ratings yet
- High Cost of Quick Turnarounds and Erroneous Procedures: Petr LenfeldDocument11 pagesHigh Cost of Quick Turnarounds and Erroneous Procedures: Petr Lenfeldkirandevi1981No ratings yet
- An Atmospheric Crude Tower RevampDocument6 pagesAn Atmospheric Crude Tower RevampMarlon ArteagaNo ratings yet
- Clause No. Exhaust Gas System, HRSG and Auxiliaries (M2) Exhaust Gas SystemDocument19 pagesClause No. Exhaust Gas System, HRSG and Auxiliaries (M2) Exhaust Gas SystemSIVA50% (2)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestFrom EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerFrom EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Small Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsFrom EverandSmall Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsNo ratings yet
- CDL Study Guide 2024-2025: Everything You Need to Know to Pass the Commercial Driver’s License Exam on your First Attempt, with the Most Complete and Up-to-Date Practice Tests - New VersionFrom EverandCDL Study Guide 2024-2025: Everything You Need to Know to Pass the Commercial Driver’s License Exam on your First Attempt, with the Most Complete and Up-to-Date Practice Tests - New VersionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- How to Fabricate Automotive Fiberglass & Carbon Fiber PartsFrom EverandHow to Fabricate Automotive Fiberglass & Carbon Fiber PartsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Allison Transmissions: How to Rebuild & Modify: How to Rebuild & ModifyFrom EverandAllison Transmissions: How to Rebuild & Modify: How to Rebuild & ModifyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Troubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesFrom EverandTroubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Modern Engine Blueprinting Techniques: A Practical Guide to Precision Engine BlueprintingFrom EverandModern Engine Blueprinting Techniques: A Practical Guide to Precision Engine BlueprintingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- The Little Black Book of Motorcycle WisdomFrom EverandThe Little Black Book of Motorcycle WisdomRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- OBD-I and OBD-II: A Complete Guide to Diagnosis, Repair, and Emissions ComplianceFrom EverandOBD-I and OBD-II: A Complete Guide to Diagnosis, Repair, and Emissions ComplianceNo ratings yet
- Why We Drive: Toward a Philosophy of the Open RoadFrom EverandWhy We Drive: Toward a Philosophy of the Open RoadRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Competition Engine Building: Advanced Engine Design and Assembly TechniquesFrom EverandCompetition Engine Building: Advanced Engine Design and Assembly TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Automotive Master Technician: Advanced Light Vehicle TechnologyFrom EverandAutomotive Master Technician: Advanced Light Vehicle TechnologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesFrom EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Powder Coating: A How-to Guide for Automotive, Motorcycle, and Bicycle PartsFrom EverandPowder Coating: A How-to Guide for Automotive, Motorcycle, and Bicycle PartsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- High-Performance Cams & Valvetrains: Theory, Technology, and Selection: Theory, Technology, and SelectionFrom EverandHigh-Performance Cams & Valvetrains: Theory, Technology, and Selection: Theory, Technology, and SelectionNo ratings yet