Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Uploaded by
Apryll Kristin Villaluna Zafe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views5 pagesX. Nursing care plans assessment: y y Restlessness y Rapid shallow breathing y Distended neck veins y Tactile fremitus decreased and breath sounds decreased y RR = 35 cpm y PR=126 y Cyanosis y CTT at the Right NURSING DIAGNOSIS Ineffective breathing pattern related to decreased lung expansion PLANNING Short Term: Within 10-15 minutes of nursing interventions, the client s respiratory rate will decrease from 35-25 cpm
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentX. Nursing care plans assessment: y y Restlessness y Rapid shallow breathing y Distended neck veins y Tactile fremitus decreased and breath sounds decreased y RR = 35 cpm y PR=126 y Cyanosis y CTT at the Right NURSING DIAGNOSIS Ineffective breathing pattern related to decreased lung expansion PLANNING Short Term: Within 10-15 minutes of nursing interventions, the client s respiratory rate will decrease from 35-25 cpm
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views5 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion
Uploaded by
Apryll Kristin Villaluna ZafeX. Nursing care plans assessment: y y Restlessness y Rapid shallow breathing y Distended neck veins y Tactile fremitus decreased and breath sounds decreased y RR = 35 cpm y PR=126 y Cyanosis y CTT at the Right NURSING DIAGNOSIS Ineffective breathing pattern related to decreased lung expansion PLANNING Short Term: Within 10-15 minutes of nursing interventions, the client s respiratory rate will decrease from 35-25 cpm
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
X.
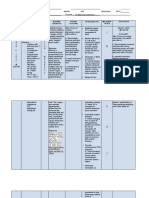
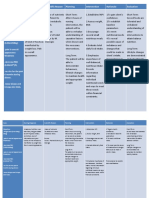
Nursing Care Plans
NURSING
ASSESSMENT PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
Subjective: Ineffective Short Term: Independent : GOALS MET
“Nahihirapan akong breathing pattern Within 10-15 1. Elevated the head of the 1. Provides maximum lung
huminga”, as stated by related to minutes of nursing bed, placed in an upright expansion.
the patient decreased lung interventions, the position.
expansion client’s respiratory
Objective: rate will decrease 2. Instructed pursed-lip 2. To increase oxygen intake
Restlessness from 35-25 cpm breathing. and increase release of Carbon
Rapid shallow dioxide.
breathing Long Term:
Distended neck 3. Kept the room well 3. A well ventilated
veins After 8 hours of ventilated.
environment contributes to
Tactile fremitus nursing
sufficient air circulation.
decreased and interventions, the
breath sounds client’s breathing 3. Assessed chest tube
decreased pattern will be drainage system for the
RR = 35 cpm normal in rate and following:
PR=126 rhythm within the 8
Cyanosis hrs shift. -Secure connection
- A loose connection can allow
CTT at the Right
air entry and positive pressure
in the intrapleural space
resulting in further lung
collapse.
-Kept chest drainage system
below level of chest - This allows mobility while
preventing accidental knock
over of the system.
-Intact water seal -This prevents air entry into
the intrapleural space.
-Presence of air leak or
bubbling in the water seal can indicate clogged or kinked
tube.
Dependent: 1. Enhances oxygen delivery to
the lungs for circulatory
1. Administered supplemental uptake, especially in presence
oxygen at 2-3 LPM by
of reduced ventilation.
cannula as indicated
1.) Monitors effectiveness of
Collaborative:
respiratory therapy and
1. Reviewed chest x-ray reports documents developing
and laboratory studies as complications.
indicated.
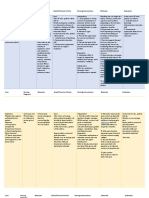
NURSING
ASSESSMENT PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
Subjective: Ineffective tissue Short Term: Independent : GOALS MET
“Nahihirapan siyang perfusion related Within 30 minutes of 1. Administered oxygen at This saturates
huminga tapos to decreased nursing interventions 2-3 LPM as needed circulating hemoglobin
nanlalamig yung mga hemoglobin the client will be able and increases the
kamay niya” concentration to : effectiveness of blood
that is reaching the
Objective: Demonstrate relief ischemic tissues
from chest pain
Capillary Refill=4 secs Demonstrate a This promotes optimal
2. Instructed to assume
RR=35 cpm decrease in the lung ventilation and
an high fowler’s
PR=126 bpm respiratory rate perfusion
position
Restlessness from 35-25 cpm
Nasal flaring Conserves energy and
Cyanosis Long Term: lowers oxygen demand
RBC Count : 2.40x106/ul. After 3 days of of tissues
3. Provided a quiet and
Hemoglobin: 7.8g/dl nursing interventions
calm environment
Cold, clammy skin the client will be able
to: Prevents venous stasis
Demonstrate 4. Encouraged to perform and helps maintain
increased passive ROM exercises muscle tone of
perfusion as on the extremities extremities
manifested by: every 2-4 hours
o Capillary refill <3
secs
o RR= 16-20 cpm 5. Instructed to avoid These activities may
o PR=80-100 bpm measures that may increase ICP and
o Acyanosis increase cardiac further reduce blood
workload such as flow
straining, coughing,
o RBC (4.6-6.2 neck or hip flexion and
x106/ul) and lying supine
hemoglobin (10-
18g/dl) count 6. Encouraged intake of Iron is needed for the
within normal iron rich foods such as production of
parameters green leafy vegetables hemoglobin which in
turn supplies oxygen
to tissues
Dependent:
1. Administered iron Provides supplemental
supplements as iron that can help
indicated improve hemoglobin
level
2. Administered Vitamin C
as indicated Enhances absorption
of iron in the
gastrointestinal tract
You might also like
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- NCP AnxietyDocument3 pagesNCP AnxietyNeil Alcazaren かわいいNo ratings yet
- TPN NCPDocument10 pagesTPN NCPArabylle Maranca AbuelNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPNichole Audrey SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodKit Alizon BarredoNo ratings yet
- Date and Time Focus Data Action Response 12/10/21Document2 pagesDate and Time Focus Data Action Response 12/10/21ANGEL AKIRA TORRESNo ratings yet
- NCP On DyspneaDocument5 pagesNCP On DyspneaDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionSteffiNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPgenevieve kryzleiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetDocument5 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetRussel SantosNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPLouis RoderosNo ratings yet
- DX Fracture PDFDocument8 pagesDX Fracture PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPchesca_paunganNo ratings yet
- Patient X (Cellulitis Right Arm) : Subjective Data Objective Data Assessment Data Plan Intervention EvaluationDocument1 pagePatient X (Cellulitis Right Arm) : Subjective Data Objective Data Assessment Data Plan Intervention EvaluationJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- NCP Imbalanced NutritionDocument7 pagesNCP Imbalanced NutritionNora VarshavskiNo ratings yet
- Mu CostaDocument6 pagesMu Costafarracholidia_867630No ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument7 pagesIneffective Airway Clearanceapi-314849412100% (1)
- No. 9 Legal-Responsibility-Of-NurseDocument23 pagesNo. 9 Legal-Responsibility-Of-NursePawan BatthNo ratings yet
- III. Nursing Care Plan Nursing Priority No. 1: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Accumulation of Secretions Secondary To PneumoniaDocument6 pagesIII. Nursing Care Plan Nursing Priority No. 1: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Accumulation of Secretions Secondary To PneumoniaRae Marie Aquino100% (1)
- Otitis Externa Case StudyDocument5 pagesOtitis Externa Case StudyGino Al Ballano BorinagaNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis & NPI - Edmalyn GozarDocument78 pagesAcute Appendicitis & NPI - Edmalyn GozarKM100% (1)
- NCP Skin IntegityDocument3 pagesNCP Skin Integityclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPDocument7 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- B00K 3 Unit 13Document11 pagesB00K 3 Unit 13Rolli SptNo ratings yet
- NCP Total Hip ReplacementDocument11 pagesNCP Total Hip ReplacementDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- 11 NCP Pressure UlcerDocument6 pages11 NCP Pressure UlcerICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Q A 1Document48 pagesQ A 1ChannelGNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPErica Denice CastilloNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangevanNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN 2 - Written ReportDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN 2 - Written ReportAkira PinedaNo ratings yet
- Health TeachingDocument3 pagesHealth TeachingNyj QuiñoNo ratings yet
- Velez College of Nursing F. Ramos Street, Cebu CityDocument57 pagesVelez College of Nursing F. Ramos Street, Cebu Cityinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- New Revised NCP SurgeryDocument9 pagesNew Revised NCP SurgeryChristina Espiña EjercitoNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching PlanSonia MambaNo ratings yet
- 1.MOD On GERON (1) CommunicationDocument19 pages1.MOD On GERON (1) CommunicationPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNCP Drug StudyAndrea JoyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Coping NCPDocument4 pagesIneffective Coping NCPFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Group Case Study DONEDocument5 pagesGroup 6 Group Case Study DONEE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyFrances Oscar GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Sample Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesSample Teaching Planmine2515No ratings yet
- NCP 2 MiDocument16 pagesNCP 2 MiWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPZmiaNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis NCP FINALDocument6 pagesCholelithiasis NCP FINALShreshthi VermaNo ratings yet
- 4 THE PARTNERSHIP APPROACH TO COMMUNITY HEALTH PRACTICE Mam ThaiDocument14 pages4 THE PARTNERSHIP APPROACH TO COMMUNITY HEALTH PRACTICE Mam ThaiKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPJahmie RiveraNo ratings yet
- Jose Paulo D. Verances, RNDocument5 pagesJose Paulo D. Verances, RNpauloverancesNo ratings yet
- G-CFA Instructor Tab 6-2 Handout 2 Sample Adequate Nursing Care Plan-R6Document2 pagesG-CFA Instructor Tab 6-2 Handout 2 Sample Adequate Nursing Care Plan-R6SriMathi Kasi Malini ArmugamNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Case 2Document3 pagesModule 2 - Case 2Joselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Revised NCPDocument8 pagesRevised NCPKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument4 pagesNCP PainMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMa Virginia Nathalia CreerNo ratings yet
- MODULE-9-Biotechnology, Genetically Modified Organisms, and Gene TherapyDocument5 pagesMODULE-9-Biotechnology, Genetically Modified Organisms, and Gene TherapyKerry NuñezNo ratings yet
- NCP ImmobiltyDocument4 pagesNCP ImmobiltyAlizza Therese Severo AnzanoNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageLaryngeal Cancer Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Secondary To Cellulitis DM Type 2Document3 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion Secondary To Cellulitis DM Type 2MichaelaKatrinaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument4 pagesNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathySapna thakurNo ratings yet
- Requirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaDocument7 pagesRequirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Biostat Final Exam ReviewerDocument5 pagesBiostat Final Exam ReviewerApryll Kristin Villaluna ZafeNo ratings yet
- NCP Interrupted Breast Feeding NCH NICUDocument1 pageNCP Interrupted Breast Feeding NCH NICUApryll Kristin Villaluna ZafeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyApryll Kristin Villaluna ZafeNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument7 pagesNCP FinalApryll Kristin Villaluna ZafeNo ratings yet
- Development and GeneticsDocument67 pagesDevelopment and GeneticsApryll Kristin Villaluna ZafeNo ratings yet
- 4 5803133100506483687Document245 pages4 5803133100506483687Malik HamidNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters Vocabulary Exercises Fun Activities Games Icebreakers Oneonone Activiti 42747Document2 pagesNatural Disasters Vocabulary Exercises Fun Activities Games Icebreakers Oneonone Activiti 42747Andrea Tercero VillarroelNo ratings yet
- E-OLSS: Electronic ControlDocument12 pagesE-OLSS: Electronic ControlSamidiNo ratings yet
- Arts6,4, Week2, Module 2V4Document24 pagesArts6,4, Week2, Module 2V4Loreen Pearl MarlaNo ratings yet
- Astm 2017-F2059Document5 pagesAstm 2017-F2059laythNo ratings yet
- HY-TB3DV-M 3axis Driver PDFDocument10 pagesHY-TB3DV-M 3axis Driver PDFjoelgcrNo ratings yet
- TS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFDocument5 pagesTS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFUnknown Khan100% (3)
- Bahir Dar University BIT: Faculity of Mechanical and Industrial EngineeringDocument13 pagesBahir Dar University BIT: Faculity of Mechanical and Industrial Engineeringfraol girmaNo ratings yet
- How To Eat WellDocument68 pagesHow To Eat WelleledidiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of LaminatedDocument31 pagesAnalysis of LaminatedKaustubh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Banachek UnlimitedDocument34 pagesBanachek UnlimitedserenaNo ratings yet
- Firestone & Scholl - Cognition Does Not Affect Perception, Evaluating Evidence For Top-Down EffectsDocument77 pagesFirestone & Scholl - Cognition Does Not Affect Perception, Evaluating Evidence For Top-Down EffectsRed JohnNo ratings yet
- Egt Margen From The Best ArticalDocument6 pagesEgt Margen From The Best ArticalakeelNo ratings yet
- Listening - Homework 2: Brushes 285 RamdhanieDocument4 pagesListening - Homework 2: Brushes 285 RamdhanieBao Tran NguyenNo ratings yet
- Comparative Performance of Some Cattle Breeds Under Barani Conditions of PakistanDocument4 pagesComparative Performance of Some Cattle Breeds Under Barani Conditions of PakistanMasood HassanNo ratings yet
- Milviz F-15e Poh V 2Document499 pagesMilviz F-15e Poh V 2Jose Ramon Martinez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- CE Review GEOMETRY 2Document6 pagesCE Review GEOMETRY 2Paul Gerard AguilarNo ratings yet
- MiscanthusDocument27 pagesMiscanthusJacob GuerraNo ratings yet
- Updated SAP Cards Requirement JalchdDocument51 pagesUpdated SAP Cards Requirement Jalchdapi-3804296No ratings yet
- (Eng) Zx890lch 5a Ks En316Document13 pages(Eng) Zx890lch 5a Ks En316MC TAK LEENo ratings yet
- Final Thesis - Aris PotliopoulosDocument94 pagesFinal Thesis - Aris PotliopoulosCristinaNo ratings yet
- Illuminati TruthsDocument27 pagesIlluminati TruthsDonnaveo ShermanNo ratings yet
- Approved Project 25 StandardsDocument5 pagesApproved Project 25 StandardsepidavriosNo ratings yet
- CAC Bubble DiagramsDocument12 pagesCAC Bubble Diagramsangst6250No ratings yet
- The Unofficial Aterlife GuideDocument33 pagesThe Unofficial Aterlife GuideIsrael Teixeira de AndradeNo ratings yet
- St. John's Wort: Clinical OverviewDocument14 pagesSt. John's Wort: Clinical OverviewTrismegisteNo ratings yet
- Propert 447-445Document11 pagesPropert 447-445LUNA100% (1)
- Is 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyDocument4 pagesIs 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyCrypto AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case StudyDocument20 pagesClinical Case Studyapi-252004748No ratings yet