Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Waves
Uploaded by
RohmaAfzalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Waves
Uploaded by
RohmaAfzalCopyright:
Available Formats
questionbase.50megs.
com GCSE Revision Notes
Physics Revision Notes – Waves
1. All waves carry energy from one place to another. There are two types of waves:
• Transverse waves have vibrations perpendicular to the direction of travel (e.g. all
electromagnetic waves).
• Longitudinal waves have vibrations in the same direction as that in which they are travelling
(e.g. sound waves).
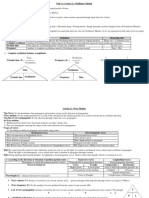
2. The following words are used to describe waves:
• Amplitude – the distance from the horizontal axis to the peak (in m).
• Wavelength (λ) – the distance from peak to peak, or trough to trough (in m).
• Frequency – the number of complete waves per second (in Hz).
• Period – the time taken for one complete wavelength (in s).
3. All waves can be reflected, refracted and diffracted:
• Reflection – a wave bouncing off a surface.
• Refraction – a wave bending when it passes through a different medium.
• Diffraction – a wave spreading out when it passes through a narrow gap.
4. The wave formula:
Velocity (m/s) = Frequency (Hz) × Wavelength (m) – v = f × λ
5. Sound is a longitudinal wave:
• The amplitude is related to its volume (a higher amplitude means a higher volume).
• The wavelength is related to its pitch (a shorter wavelength means a higher pitch).
6. Sound is produced by objects vibrating:
• The strings on a violin.
• The surface of a drum.
• The air in a trumpet.
• The reeds in an oboe.
7. A cathode ray oscilloscope shows sounds as transverse waves:
8. Ultrasound is a high frequency sound wave, and is used in industry, medicine, quality control and
sonar by transmitting the waves, and observing the way in which they are reflected back.
9. The Earth consists of a crust, a mantle, a liquid outer core, and a solid inner core.
10. There are two types of seismic waves:
• P-waves are longitudinal. They travel through solids and liquids and are fast.
• S-waves are transverse. They will only travel through solids and are slower than p-waves.
11. Properties of reflection:
• The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
• An image is virtual, laterally inverted, and the same distance from the mirror as the object.
12. Properties of refraction:
• If a wave enters a denser medium (e.g. a perspex block), it will be bent towards the normal.
The emerging ray will come out at the same angle, but displaced.
• A prism can be used to split white light into the visible spectrum.
• When a wave passes into a different medium, it will either slow down or speed up.
13. Properties of total internal reflection:
• Total internal reflection is when a wave reflects off the inside of a block, rather that
refracting out of it.
• The critical angle for perspex is about 43°.
• This principle is used in fibre optics (e.g. with endoscopes in medicine).
You might also like
- Physics Revision Notes - WavesDocument1 pagePhysics Revision Notes - WavesAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Physics WavesDocument1 pagePhysics Waveshmatara8No ratings yet
- Physics O Level Notes 3Document3 pagesPhysics O Level Notes 3Vr Gaming100% (1)
- Physic Notes DefinitionsDocument5 pagesPhysic Notes Definitionsfatimawaqar657No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Waves - Edexcel Physics IGCSE PDFDocument5 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 3 Waves - Edexcel Physics IGCSE PDFMemory Tawananyasha MutongiNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Waves - Edexcel Physics IGCSE PDFDocument5 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 3 Waves - Edexcel Physics IGCSE PDFFahimDayhanNo ratings yet
- CTSC Waves Lightandsound 160521134455Document42 pagesCTSC Waves Lightandsound 160521134455Kimberly Anne PagdangananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 WavesDocument53 pagesChapter 14 WavesAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument52 pagesWavesapi-508592459100% (1)
- MET 413 PPT - Module 2Document52 pagesMET 413 PPT - Module 2sandeep.vishnu007No ratings yet
- WavesDocument52 pagesWavesapi-245497801No ratings yet
- Waves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingDocument40 pagesWaves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingGellirose S. Bantayan100% (1)
- Waves and Optics Class Notes Part 1Document3 pagesWaves and Optics Class Notes Part 1reeta ramNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAMmvWiE21x9s8IcZ9sLu5Zv LYs7X0uGL z1zGCRmgkHXeIiP x0MAKBAlCjOUWUfjru7 DRzwvegmOwAzUTNk Ha2kgzqlcv V65u4j WlZO8U ADGcYh MYja7W7jpgun1AB0owZODocument48 pagesACFrOgAMmvWiE21x9s8IcZ9sLu5Zv LYs7X0uGL z1zGCRmgkHXeIiP x0MAKBAlCjOUWUfjru7 DRzwvegmOwAzUTNk Ha2kgzqlcv V65u4j WlZO8U ADGcYh MYja7W7jpgun1AB0owZOAmish ShahNo ratings yet
- Waves 100Document6 pagesWaves 100Brook Rene JohnsonNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument16 pagesWavesgabezneNo ratings yet
- Radiation: Information From The CosmosDocument56 pagesRadiation: Information From The Cosmosglydel fedelicioNo ratings yet
- Light PresentationDocument63 pagesLight PresentationJylle Vernie HembraNo ratings yet
- For Reporting Waves PowerPoint 1Document117 pagesFor Reporting Waves PowerPoint 1Laly AracielNo ratings yet
- Waves PowerPointDocument97 pagesWaves PowerPointAirene Mariel MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Wave NotesDocument66 pagesWave NotesKwame Pee100% (1)
- UTZ Lec 1Document4 pagesUTZ Lec 1Ann BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Waves Sound Light PowerPointDocument54 pagesWaves Sound Light PowerPointRonel DecastroNo ratings yet
- Rarefactions.: Electromagnetic Waves. Although Electromagnetic Waves Do Not Need ADocument3 pagesRarefactions.: Electromagnetic Waves. Although Electromagnetic Waves Do Not Need AVerynNo ratings yet
- Nature of Light PPT FinalDocument58 pagesNature of Light PPT FinalMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Waves and Optics SummaryDocument10 pagesWaves and Optics Summaryandrew.mooreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Student HandoutDocument19 pagesLecture 1 - Student HandoutJeric LumantasNo ratings yet
- IB PH SL Waves NotesDocument13 pagesIB PH SL Waves NotesT-girlNo ratings yet
- Chapter SevenDocument10 pagesChapter Sevensaed cabdiNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Cbse WavesDocument9 pages11 Physics Cbse Wavesvickyvicky0022okNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3Jaima Nahin NisheNo ratings yet
- Waves PowerPointDocument97 pagesWaves PowerPointkeishalorenzo13No ratings yet
- Physics Notes - Waves Part 2Document5 pagesPhysics Notes - Waves Part 2ankur11783officialNo ratings yet
- Physics Vibration and WavesDocument41 pagesPhysics Vibration and WavesRebeca RiveraNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 1 - WAVES - BasicsDocument24 pagesGrade 1 1 - WAVES - BasicsDannyelle BaileyNo ratings yet
- Properties of WavesDocument8 pagesProperties of Wavesjames paulo abandoNo ratings yet
- WAVESDocument2 pagesWAVESBetina MellaNo ratings yet
- Waves sc7 1 1Document77 pagesWaves sc7 1 1uy.cuencosultanNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument27 pagesWavesmeganekokun kawaiiNo ratings yet
- Waves PowerpointDocument68 pagesWaves PowerpointMadana R naikNo ratings yet
- Waves Homework From The Book:: MechanicalDocument11 pagesWaves Homework From The Book:: MechanicalMaha Letchumy BalakeristananNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and WavesDocument38 pagesVibrations and WavesKiara De LeonNo ratings yet
- Null 2Document2 pagesNull 2Tinevimbo ChimusuwoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 WavesDocument10 pagesChapter 7 WavesLucas ShazNo ratings yet
- Waves and SoundDocument17 pagesWaves and SoundMUHAMMAD DANIYAL KANDANo ratings yet
- My Physics NotesDocument6 pagesMy Physics NotesShayne WongNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument41 pagesWavesMimi CiervaNo ratings yet
- Wave MotionDocument19 pagesWave MotionRovshen BayramovNo ratings yet
- Waves and LightDocument21 pagesWaves and LightTheEinsteinofTomorrowNo ratings yet
- HPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 8-1Document31 pagesHPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 8-1Praise NehumambiNo ratings yet
- Optics - Igbala VeysalzadeeDocument117 pagesOptics - Igbala VeysalzadeeMəhəmməd MustafazadəNo ratings yet
- HPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 3Document22 pagesHPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 3Praise NehumambiNo ratings yet
- PH 11 Waves NotesDocument11 pagesPH 11 Waves NotesTikeshwar Sharma100% (1)
- Physics G7 Week 27 B2 Ch.14 SoundDocument43 pagesPhysics G7 Week 27 B2 Ch.14 SoundAyesha DuaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - WavesDocument26 pagesTopic 4 - WaveseisnNo ratings yet
- 2 (2) 5olasaDocument11 pages2 (2) 5olasaolosschool123No ratings yet
- Waves, Sound & Music: (In One-Dimension, Mainly)Document30 pagesWaves, Sound & Music: (In One-Dimension, Mainly)Adal GanisNo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics 3: Wavefunctions, Superposition, & Virtual ParticlesFrom EverandQuantum Mechanics 3: Wavefunctions, Superposition, & Virtual ParticlesNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics 5: Entanglement, EPR, Teleportation, & Advanced TopicsFrom EverandQuantum Mechanics 5: Entanglement, EPR, Teleportation, & Advanced TopicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Biology 405 Organic Evolution Lab ManualDocument9 pagesBiology 405 Organic Evolution Lab ManualZielonaZabaNo ratings yet
- 644296ee86310talwa G-4 For Iron-Manganese ProposalDocument25 pages644296ee86310talwa G-4 For Iron-Manganese Proposalamit kumar guptaNo ratings yet
- CH 22 CW PuzzleDocument2 pagesCH 22 CW PuzzleGavanDusbabekNo ratings yet
- Peru Short Course-Pakalnis PDFDocument404 pagesPeru Short Course-Pakalnis PDFKennet WoNo ratings yet
- 006 Blasting TechnologyDocument5 pages006 Blasting TechnologyKenny CasillaNo ratings yet
- Refining Well Log Interpretation Techniques For Determining Brackish Aquifer Water QualityDocument191 pagesRefining Well Log Interpretation Techniques For Determining Brackish Aquifer Water QualityXaviier PerezzNo ratings yet
- Origins of Life On The Earth and in The CosmosDocument585 pagesOrigins of Life On The Earth and in The CosmosSveti Jeronim100% (3)
- Kadri2015 PDFDocument35 pagesKadri2015 PDFSoltani AkRêmNo ratings yet
- Thunder Healing's - Crystals & Stones Metaphysical and General KnowDocument301 pagesThunder Healing's - Crystals & Stones Metaphysical and General KnowIyerBG100% (1)
- Leach Et Al. 2010 PDFDocument33 pagesLeach Et Al. 2010 PDFJulio RamiroNo ratings yet
- Calcareous and Ultramafic MetDocument13 pagesCalcareous and Ultramafic MetFelichi Dacumos BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- Earthen DamsDocument26 pagesEarthen DamsSarfaraz Ahmed BrohiNo ratings yet
- Second Division: Republic of The Philippines Supreme Court ManilaDocument41 pagesSecond Division: Republic of The Philippines Supreme Court Manilayazi08No ratings yet
- 28BIBLIOGRAFIADocument10 pages28BIBLIOGRAFIAFabio Pava CelyNo ratings yet
- Advance Retrofitting Techniques For Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument13 pagesAdvance Retrofitting Techniques For Reinforced Concrete StructuresSoumya GoraiNo ratings yet
- 02-Petroleum GeologyDocument48 pages02-Petroleum GeologyWaqas Sadiq100% (2)
- Fracture Characterization and Modelling of A Tight Carbonate ReservoirDocument16 pagesFracture Characterization and Modelling of A Tight Carbonate ReservoirAhmad AdvinNo ratings yet
- SonamargDocument38 pagesSonamargHemant MishraNo ratings yet
- 25-Karl Gunnar Holter PHD Project SproytemembranDocument57 pages25-Karl Gunnar Holter PHD Project SproytemembranBerkan KayadanNo ratings yet
- Management of Tailings and Waste Rock in Mining ActvitiesDocument557 pagesManagement of Tailings and Waste Rock in Mining ActvitiesPaula TrindadeNo ratings yet
- Typical Values of The Coefficient of Volume Compressibility, M (After Carter 1983) MDocument21 pagesTypical Values of The Coefficient of Volume Compressibility, M (After Carter 1983) MTuanQuachNo ratings yet
- Master1 AM CoursesDocument3 pagesMaster1 AM CoursesParokotil MidhunNo ratings yet
- Why Re-FracDocument45 pagesWhy Re-Fracrobertobg1No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The Geologic Time ScaleDocument18 pagesLesson 4 - The Geologic Time ScalePat Hadji AliNo ratings yet
- SDCASSADDocument10 pagesSDCASSADJhan Carlos CNo ratings yet
- River Training Structures - GroynesDocument17 pagesRiver Training Structures - GroynesShabana Khan67% (3)
- 1st LPDocument6 pages1st LPAYUBAN, April RoseNo ratings yet
- Practical Methods Manual of Soil Science.Document239 pagesPractical Methods Manual of Soil Science.chia jalelNo ratings yet
- V. S.Raju - Geotechnical Engineering Practice With Focus On Soil Investigations Plus Case StudiesDocument40 pagesV. S.Raju - Geotechnical Engineering Practice With Focus On Soil Investigations Plus Case StudiesSorabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Earth Bund PDFDocument105 pagesEarth Bund PDFKrishna SwaroopNo ratings yet