Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Immobility
Uploaded by
Bcoi QuilacioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Immobility
Uploaded by
Bcoi QuilacioCopyright:
Available Formats
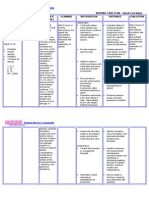
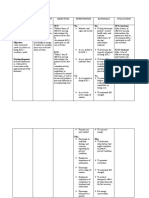
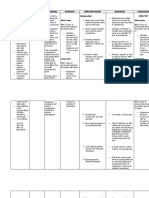
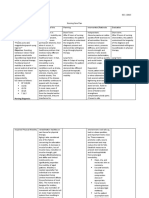
NURSING CARE PLAN
PROBLEM: Immobility
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Impaired physical mobility r/t spinal injury secondary to VA.
GORDONS: Activity-exercise pattern
CAUSE ANALYSIS: The most obvious signs of prolonged immobility are often manifested in the musculoskeletal system. Thus, when the spinal injury happens, a person’s
physical mobility will be impaired. Fundamentals of Nursing by Kozier p 567)
CUES OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE: STO: INDEPENDENT:
Spaced nursing activities. Clustering activities
After 8 hours of effective increases myocardial
NO VERBAL CUES nursing care, patient will be demand and may cause
reposition frequently to promote extreme fatigue. After 8 hours of effective
circulation and relieves pressure Evaluated degree of Level of activity depends nursing care, patient was
on tissues. fracture or injury. on progression of injury. repositioned frequently. And was
Assisted with active/ Improves joint function relieved from pressures on tissue.
OBJECTIVES: LTO: passive ROM as and general stamina.
Reduced skin turgor indicated.
Loss of consciousness After 2 days of nursing care Repositioned frequently Relieves pressure on
GCS-3 implementation, patient will have using adequate tissues and promoted After 2 days of duty with
Negative muscle strength a maintain position of function as personnel. circulation. Proper continued implementation of
evidenced by reduced foot drop. transfer techniques nursing care, patient has a
Presence of cast on upper
left arm prevent shearing abrasion maintained position of function.
Foot drop- 45 degrees of skin.
Positioned with pillows. Promotes joint stability
Provide joint support and maintains proper
with splints. joint position and body
alignment.
Provided footboard. To reduced the foot drop.
REFERENCE: NCP 6th edition by Doenges
You might also like
- Icu NCPDocument8 pagesIcu NCPClaire Nicole ApostolNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationDocument3 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationNur faizah bt azmiNo ratings yet
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Self Care DeficitLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: O Short Term: Short TermDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: O Short Term: Short TermRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Document2 pagesCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungNo ratings yet
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- 12 NCP Spinal Cord InjuryDocument7 pages12 NCP Spinal Cord InjuryDessy Ratna S100% (3)
- Planning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byDocument10 pagesPlanning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility...Document3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility...Christy BerryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryKyla ToledoNo ratings yet
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Document20 pagesSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizNo ratings yet
- Acute PainDocument5 pagesAcute PainJan Heartini SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: OSTEOPOROSIS DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: OSTEOPOROSIS DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Suicidal PatientDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Suicidal PatientJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of DyspneaDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of DyspneaNiel MinatozakiNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINDocument4 pagesDegenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINHermin TorresNo ratings yet
- Spinal Injury Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesSpinal Injury Nursing Care PlanPatricia OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Accident Leads to Multiple Fracture InjuriesDocument2 pagesMotor Vehicle Accident Leads to Multiple Fracture Injuriesjunifer laynoNo ratings yet
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- Disturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPDocument4 pagesDisturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPSamVelascoNo ratings yet
- 3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCDocument5 pages3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Spinal Cord InjuryDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Spinal Cord InjuryDan Leo UnicoNo ratings yet
- MNAP Military Nursing in The Philippines May Be Said To Have Existed As Early As 1896 When The Legendary Tandang Sora Took Care of The Sick and WoundedDocument4 pagesMNAP Military Nursing in The Philippines May Be Said To Have Existed As Early As 1896 When The Legendary Tandang Sora Took Care of The Sick and WoundedarjeighNo ratings yet
- Ncp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDDocument4 pagesNcp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- NCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)Document2 pagesNCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)R Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginDocument3 pagesReflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginRexson Alcantara DalanginNo ratings yet
- NCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityDocument4 pagesNCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityAl-Qadry NurNo ratings yet
- Risk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.Document2 pagesRisk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.eleinsamNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Sto: DX: DX: STO: Goal MetDocument3 pagesSubjective: Sto: DX: DX: STO: Goal MetFaith BugtongNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsDocument1 pageAcute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsAi RouNo ratings yet
- Coa ReviewersDocument269 pagesCoa Reviewersmary ann corsanesNo ratings yet
- Risk For FallsDocument1 pageRisk For FallsEugene UCNo ratings yet
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- Aminogen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAminogen Drug Studymilesmin100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLean Ashly Tuddao Macarubbo0% (1)
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome CASEDocument38 pagesStevens-Johnson Syndrome CASEChristy Rose AgrisNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAngela Neri0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- NCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitArt Christian Ramos0% (1)
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Document3 pagesNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesSelf Care DeficitAddie Labitad100% (2)
- TCP AmoebiasisDocument6 pagesTCP AmoebiasisAristotel CabaisNo ratings yet
- Cancer Pain ManagementDocument8 pagesCancer Pain ManagementMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- NCP Readiness RevisionDocument3 pagesNCP Readiness RevisionimnasNo ratings yet
- Student Centered Objectives-TicudDocument2 pagesStudent Centered Objectives-TicudFely Theresa Lanes LorenoNo ratings yet
- Gout N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageGout N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoDocument1 pageASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoCherie MayNo ratings yet
- Improving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeDocument1 pageImproving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeSelwynVillamorPatenteNo ratings yet
- Geria NCP, Dela CruzDocument7 pagesGeria NCP, Dela CruzStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalGeralyn KaeNo ratings yet
- NCP CVA ImmoblityDocument3 pagesNCP CVA ImmoblityAnalyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Case IcuDocument5 pagesCase IcuTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Subjective: The PatientDocument2 pagesSubjective: The PatientRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Pick UpsDocument4 pagesMagnetic Pick UpslunikmirNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Handbook On Compressors (Of Under Slung AC Coaches) PDFDocument39 pagesMaintenance Handbook On Compressors (Of Under Slung AC Coaches) PDFSandeepNo ratings yet
- 11 Baby Crochet Cocoon Patterns PDFDocument39 pages11 Baby Crochet Cocoon Patterns PDFIoanaNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report Yes-O NDCMC 2013Document9 pagesAccomplishment Report Yes-O NDCMC 2013Jerro Dumaya CatipayNo ratings yet
- AI Model Sentiment AnalysisDocument6 pagesAI Model Sentiment AnalysisNeeraja RanjithNo ratings yet
- SECTION 303-06 Starting SystemDocument8 pagesSECTION 303-06 Starting SystemTuan TranNo ratings yet
- Activities and Assessments:: ASSIGNMENT (SUBMIT Your Answers at EDMODO Assignment Section)Document5 pagesActivities and Assessments:: ASSIGNMENT (SUBMIT Your Answers at EDMODO Assignment Section)Quen CuestaNo ratings yet
- Ricoh 4055 PDFDocument1,280 pagesRicoh 4055 PDFPham Nguyen Hoang Minh100% (1)
- The Apu Trilogy - Robin Wood PDFDocument48 pagesThe Apu Trilogy - Robin Wood PDFSamkush100% (1)
- Panasonic 2012 PDP Troubleshooting Guide ST50 ST Series (TM)Document39 pagesPanasonic 2012 PDP Troubleshooting Guide ST50 ST Series (TM)Gordon Elder100% (5)
- Religion in Space Science FictionDocument23 pagesReligion in Space Science FictionjasonbattNo ratings yet
- Fraktur Dentoalevolar (Yayun)Document22 pagesFraktur Dentoalevolar (Yayun)Gea RahmatNo ratings yet
- Naukri LalitaSharma (3y 4m)Document2 pagesNaukri LalitaSharma (3y 4m)rashika asraniNo ratings yet
- Front Wheel Steering System With Movable Hedlights Ijariie5360Document6 pagesFront Wheel Steering System With Movable Hedlights Ijariie5360Ifra KhanNo ratings yet
- Elevator Traction Machine CatalogDocument24 pagesElevator Traction Machine CatalogRafif100% (1)
- LSUBL6432ADocument4 pagesLSUBL6432ATotoxaHCNo ratings yet
- QP (2016) 2Document1 pageQP (2016) 2pedro carrapicoNo ratings yet
- RPG-7 Rocket LauncherDocument3 pagesRPG-7 Rocket Launchersaledin1100% (3)
- Final Decision W - Cover Letter, 7-14-22Document19 pagesFinal Decision W - Cover Letter, 7-14-22Helen BennettNo ratings yet
- NDE Procedure - Radiographic TestingDocument43 pagesNDE Procedure - Radiographic TestingJeganeswaranNo ratings yet
- Seed SavingDocument21 pagesSeed SavingElectroPig Von FökkenGrüüven100% (2)
- Casio AP-80R Service ManualDocument41 pagesCasio AP-80R Service ManualEngkiong Go100% (1)
- 24.postpartum Period-Physiological Changes in The MotherDocument16 pages24.postpartum Period-Physiological Changes in The MotherHem KumariNo ratings yet
- Tds G. Beslux Komplex Alfa II (25.10.19)Document3 pagesTds G. Beslux Komplex Alfa II (25.10.19)Iulian BarbuNo ratings yet
- Lathe - Trainer ScriptDocument20 pagesLathe - Trainer ScriptGulane, Patrick Eufran G.No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 AP GP PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 10 AP GP PDFGeorge ChooNo ratings yet
- Letter of MotivationDocument4 pagesLetter of Motivationjawad khalidNo ratings yet
- Is.4162.1.1985 Graduated PipettesDocument23 pagesIs.4162.1.1985 Graduated PipettesBala MuruNo ratings yet
- De Thi HSG Tinh Binh PhuocDocument9 pagesDe Thi HSG Tinh Binh PhuocDat Do TienNo ratings yet
- ASA 2018 Catalog WebDocument48 pagesASA 2018 Catalog WebglmedinaNo ratings yet