Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reported Speech Inglese
Uploaded by
GiacoMinus GelmettiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reported Speech Inglese
Uploaded by
GiacoMinus GelmettiCopyright:
Available Formats
1
REPORTED SPEECH IN ENGLISH
1. Quando la reggente presenta un verbo al presente, futuro o passato prossimo, il
tempo verbale della frase riferita rimane invariato.
Es. Mark: “I don't want to go to school” Mark says he don't want to go to school
2. Quando la reggente presenta un verbo al passato, il tempo verbale della frase
riferita necessita di cambiamenti.
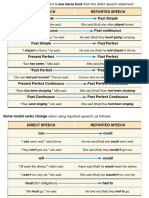
Direct speech Indirect speech
Present simple Past simple
He said “I go to school” He said he went to school
Present continuous Past continuous
He said “I'm going to school” He said he was going to school
Present perfect Past perfect
He said “I've gone to school” He said he had gone to school
Past simple Past perfect
He said “I went to school” He said he had gone to school
Past perfect Past perfect (No Change)
He said “I had gone to school” He said he had gone to school
Modal Verb
Direct speech Indirect speech
1
Will Would+B.I./Would+Past infinitive.1
He said “I will go to school” He said he would go / would have gone to school
Can Could
He said “I can go to school” He said he could go to school
Must Had to
He said “I must go to school” He said he had to go to school
Shall Should
He said “What shall we learn?” He aked what we should learn
May Might
He said “May I open the door” He asked if he might open the door
Would Would (No Change)
He said “I would go to school” He said he would go to school
Could Could (No Change)
He said “I could go to school” He said he could go to school
Had to Had to (No Change)
He said “I had to go to school” He said he had to go to school
Should Should (No Change)
He said “I should go to school” He said he should go to school
1
Con Will solitamente si utilizza il Present conditional (Would+B.I.), ma quando vogliamo specificare che non
è avvenuta l' azione descritta si usa il Past conditional (Would+Past infinitive)
Giacomo Gelmetti Inglese
2
Conditional
Direct speech Indirect speech
Zero conditional Zero conditional (No Change)
He said “If water reaches 100°, it boils” He said if water reaches 100°, it boils
First conditional Second conditional
He said “If it rains, i will stay at home” He said if it rained, he would stay at home
Second conditional Second conditional
He said “If I was young, I was able to walk” He said if he was young, he was able to walk
Third conditional Third conditional
He said “If I had seen Mara, I would have told her” He said if he had seen Mara, he would have told
Time change
Direct speech Indirect speech
This (evening, day, morning,...) That (evening, day, morning,...)
Today2 Yesterday/That day2
Tommorrow The following day
Yesterday The day before
Last (week, Friday, year,...) The previous (week, Friday, year,...)
Next (week, Friday, year,...) The following (week, Friday, year,...)
A year ago A year before
Here There
2
Con “today” si usa “that day” se ci si riferisce ad una azione avvenuta nello stesso giorno nel quale si riporta
la frase (nell' arco di 24 ore) altrimenti si utilizza “yesterday”
Giacomo Gelmetti Inglese
You might also like
- Modern Chinese (BOOK 2) – Learn Chinese in a Simple and Successful Way – Series BOOK 1, 2, 3, 4From EverandModern Chinese (BOOK 2) – Learn Chinese in a Simple and Successful Way – Series BOOK 1, 2, 3, 4Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Indirect Speech Lesson With ExercisesDocument10 pagesIndirect Speech Lesson With Exercisesmohammad515No ratings yet
- Direct IndirectDocument10 pagesDirect IndirectSujot TumbadeNo ratings yet
- Tense Change D and IDDocument4 pagesTense Change D and IDkunti robiyatunNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechRiskaMeilaniNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechMiljanaNo ratings yet
- Exercitii Gramatica EnglezaDocument3 pagesExercitii Gramatica EnglezaMaryleNo ratings yet
- A. Making Conclusion With Modal Verbs: Must Be ' and CAN'T BE .'Document7 pagesA. Making Conclusion With Modal Verbs: Must Be ' and CAN'T BE .'Karlina DewiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech: Instructor: Usama MuneerDocument26 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech: Instructor: Usama MuneerDoctor Muhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument20 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJelena MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument14 pagesReported SpeechBryan Anthony Aranda CastilloNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech Grade 9 NewDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech Grade 9 NewRumesh MadusankaNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument16 pagesDirect & Indirect SpeechPaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNa100% (3)
- Direct and IndirectDocument11 pagesDirect and IndirectYita Gayatri WillyaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 35 Reported Speech PDFDocument11 pagesLesson 35 Reported Speech PDFArianneNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech With ExercisesDocument13 pagesReported Speech With ExercisesCarlosaradasNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechYefer romañaNo ratings yet
- Mateo REPRTED SPEECH NewDocument11 pagesMateo REPRTED SPEECH NewemanuelNo ratings yet
- Rules of The Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesRules of The Reported SpeechMiguel Jose Quijada BetancourtNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJohann Alwi Candyn'machineloverNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech StatementsDocument12 pagesReported Speech Statements6IM12 Franco Guadarrama Andrea SophiaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechIvy Yiing100% (1)
- Reported or Indirect Speech WorshopDocument6 pagesReported or Indirect Speech WorshopMARÍA FERNANDA VASQUEZ MOLINANo ratings yet
- Cours Anglais ST1 S1 2Document14 pagesCours Anglais ST1 S1 2ghofranesdeNo ratings yet
- General RevisionDocument20 pagesGeneral RevisionJESuisAhmedNo ratings yet
- Direct speech-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesDirect speech-WPS OfficeAshiq Superior collegeNo ratings yet
- Narration Gyan ArpanDocument10 pagesNarration Gyan ArpanAnu KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 35 Reported Speech PDFDocument11 pagesLesson 35 Reported Speech PDFlauriig1312No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechVaishali RaviNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech Garde XiDocument44 pagesDirect Indirect Speech Garde XiJoy JRNo ratings yet
- Estilo Indirecto (Reported Speech) : Can Could Must Had To May MightDocument2 pagesEstilo Indirecto (Reported Speech) : Can Could Must Had To May MightmifernandezfNo ratings yet
- Indirect SpeechDocument12 pagesIndirect SpeechElaine OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Menn Mennn NennneeDocument6 pagesMenn Mennn NennneeMelanie LopezNo ratings yet
- B1 Grammar Reported SpeechDocument1 pageB1 Grammar Reported SpeechSagine FlerivalNo ratings yet
- ComparativesDocument2 pagesComparativesInés Amaya DíazNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument19 pagesReported Speechumurita37No ratings yet
- "I Often She Said (That) She OftenDocument5 pages"I Often She Said (That) She OftenKiberSalo322No ratings yet
- MEETING 10 - 11 REPORTED SPEECH (New)Document25 pagesMEETING 10 - 11 REPORTED SPEECH (New)AiluNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect Narrations - Spoken English With Azhar NawazDocument27 pagesDirect & Indirect Narrations - Spoken English With Azhar NawazazharnawazNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech For FCEDocument4 pagesReported Speech For FCEMarinaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument9 pagesReported SpeechSubashini ChryshanthusNo ratings yet
- Gómez Henao, J. I. (2019) - Reported Speech. University of Antioquia.Document18 pagesGómez Henao, J. I. (2019) - Reported Speech. University of Antioquia.Daniel ArenasNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument21 pagesDirect and Indirectgeetaryan01No ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument8 pagesDirect & Indirect SpeechSecurity Check-upNo ratings yet
- Direct SpeechDocument46 pagesDirect Speechparthagarwal759No ratings yet
- Toefl Preparation Paper Assignments "Direct-Indirect Speech"Document6 pagesToefl Preparation Paper Assignments "Direct-Indirect Speech"Siti Ramlah SiregarNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech and Phrasal VerbsDocument11 pagesReported Speech and Phrasal VerbsTarik AattaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument9 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechEncik HkNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect (Or Reported) Speech. IntroductionDocument12 pagesDirect and Indirect (Or Reported) Speech. IntroductionJavier LeonNo ratings yet
- Grammar Basics-Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesGrammar Basics-Reported SpeechSilvia TripodiNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument20 pagesReported SpeechLinda FatmasariNo ratings yet
- DirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Document17 pagesDirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Puja RatanNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument10 pagesReported SpeechAlbertoyJavier Sancho CamposNo ratings yet
- Use Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesUse Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechIeva VaičikauskaitėNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech TeoriaDocument4 pagesReported Speech TeoriasilviaNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech / Quoted Speech: For ExampleDocument6 pagesDirect Speech / Quoted Speech: For ExamplesaigovindarajanNo ratings yet
- Statements, Questions, and Commands/requests.: Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesStatements, Questions, and Commands/requests.: Reported SpeechVanja Đorđevic100% (1)
- Reported Speech: But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in The ReportedDocument5 pagesReported Speech: But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in The ReportedHamalahamaNo ratings yet
- No Mistakes Grammar Bites, Volume VI, Passed and Past, and Into, In To and InFrom EverandNo Mistakes Grammar Bites, Volume VI, Passed and Past, and Into, In To and InNo ratings yet