Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differential Diagnosis of Chronic IBD Types and Ot
Uploaded by
Pises PisespongsaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differential Diagnosis of Chronic IBD Types and Ot
Uploaded by
Pises PisespongsaCopyright:
Available Formats
Colitis—Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Other Forms of Colitis
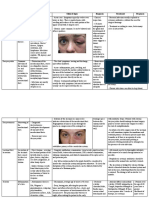
쐍 12.9 cont.
d e
d, e Florid inflammation in anastomotic region. d View into the ascending colon toward f Chronic ulcer at ileocolonic anastomosis,
anastomosis. e View into neoterminal ileum, highly florid attack, but without significant no stenosing tendency for years.
narrowing (which, however, is imminent in the course of disease).
Pathological Findings
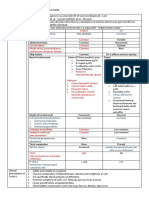
Differential Diagnosis of Chronic IBD Types and Table 12.2 Colonoscopy features for differential diagnosis of UC and
CD (modified according to reference 8)
Other Forms of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Feature Ulcerative colitis Crohn disease
쮿 Differential Diagnosis: Ulcerative Colitis vs. Continuous inflammation always* extremely rarely
Crohn Disease Patchy manifestation no* frequent
III Tables 12.1, 12.2 display major characteristics for distinguishing
Rectal involvement almost always often spared
between the two main types of chronic IBD. Vascular pattern distorted or lost often normal
Diffuse bleeding widespread rare
Vulnerability widespread uncommon
Spontaneous petechiae widespread rare
Granularity widespread less widespread
Table 12.1 Endoscopic differential diagnosis CD−UC (based on refer- Erythema typical less typical
ence 8) Edema present present
Factors supporting a diagnosis Factors supporting a diagnosis
Cobblestoning no typical
of CD of UC
Aphthous erosions no typical
왘 key finding: patchy, discon- 왘 continuous, symmetrical,
Surface ulcerations occasionally frequent
tinuous and segmental diffuse inflammation
spread of inflammation Large ulcers 쏜 1 cm in severe cases common
Long, deep ulcers rare common
왘 areas of normal mucosal in- 왘 mucosa in affected segment
terspersed with ulcerations; noticeably different from the Linear ulcers rare common
or asymmetrical distribution surrounding mucosa, sharp Serpiginous ulcers rare common
of ulcerations in a given demarcation to proximal, Pseudopolyps not infrequent occasionally
segment uninvolved mucosa
Mucosal bridging occasionally occasionally
왘 rectum is spared 왘 diffuse rectal involvement Mucosa surrounding ulcer abnormal normal
왘 ulceration surrounded by 왘 ulceration on a background Sharp demarcation (circu- yes no
relatively normal mucosa, no of diffuse abnormal mucosa lar) to normal tisse
marked increase in vulnera- with reddening, vulnerability, Stricture no common, frequent
bility of surrounding mucosa and granularity
왘 This difference is vital
왘 deep, widespread ulcerations 왘 attention: these factors for the patient: stricture
왘 ulcerations and stenosis or usually support a diagnosis related to UC may be
distortion of the Bauhin valve of UC, but there are always malignant!
exceptions!
* For exceptions, see sections concerning UC.
쐽 106
Search
You might also like
- DeQuervain Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDeQuervain Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Ulcerative Colitis Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Treating And Managing Ulcerative Colitis With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Ulcerative Colitis Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Treating And Managing Ulcerative Colitis With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument13 pagesChapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseNaronana AliNo ratings yet
- Irritant and Allergic Contact Dermatitis Symptoms and LesionsDocument1 pageIrritant and Allergic Contact Dermatitis Symptoms and LesionsJo CanensNo ratings yet
- PAEDS Approach To Crohn's / Ulcerative ColitisDocument4 pagesPAEDS Approach To Crohn's / Ulcerative ColitisVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Ulcer Genitalis EllenoDocument2 pagesUlcer Genitalis EllenoGabriela Sabatini GunawanNo ratings yet
- 5 CD 12th EdDocument12 pages5 CD 12th Edstella.gillesania.chenNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin Infections: Cellulitis Case and OverviewDocument75 pagesBacterial Skin Infections: Cellulitis Case and OverviewmasithaNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.05a Bening Ang Malignant Lesions of The VulvaDocument11 pagesGYNE 4.05a Bening Ang Malignant Lesions of The VulvaGray SnellNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About GangliaDocument2 pagesEverything You Need to Know About GangliaAnonymous eF8cmVvJaNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Intestinal Obstruction and PolypsDocument55 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease Intestinal Obstruction and PolypsLiza Marie IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Disease Etiopathogenesis Clinical Signs Diagnosis Treatment PrognosisDocument7 pagesDisease Etiopathogenesis Clinical Signs Diagnosis Treatment PrognosisKevin Suwandi0% (1)
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseasesDocument30 pagesInflammatory Bowel DiseasesMohammedHuzairIbunuAbidNo ratings yet
- Immune Mediated DisordersDocument153 pagesImmune Mediated DisordersHaroon ButtNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING EVALUATIONDocument2 pagesASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING EVALUATIONJiraGonzalesNo ratings yet
- ULCERDocument19 pagesULCERDivagar MurugavelNo ratings yet
- Immune Mediated DisordersDocument153 pagesImmune Mediated DisordersHaroon ButtNo ratings yet
- 1.02 Sugical Conditions of The Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue (Part2)Document6 pages1.02 Sugical Conditions of The Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue (Part2)Klyn Agagon GayodanNo ratings yet
- Surgery Image BankDocument180 pagesSurgery Image BankRishik RanaNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology NotesDocument79 pagesOphthalmology NotesWise AmroNo ratings yet
- Vulvar Ulcer CausesDocument4 pagesVulvar Ulcer CausesChibiNo ratings yet
- Examination of UlcerDocument14 pagesExamination of UlcerJamshaid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Splenomegaly: Involvement Is CommonDocument1 pageSplenomegaly: Involvement Is CommonMadeline WanhartNo ratings yet
- Red Eye TableDocument2 pagesRed Eye TableFatimah AlsultanNo ratings yet
- Gingival Enlargment: Maryam Aziz Ahmed Fourth Stage Group - CDocument15 pagesGingival Enlargment: Maryam Aziz Ahmed Fourth Stage Group - Cمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Types and Classification of Common UlcersDocument6 pagesTypes and Classification of Common UlcersAhmed Hamed Abdelzaher MohamedNo ratings yet
- Crohn Disease and Ulcerative ColitisDocument3 pagesCrohn Disease and Ulcerative ColitisMike GNo ratings yet
- Diverticular DiseaseDocument30 pagesDiverticular Diseasept.mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Vulvar and Vaginal Benign LesionsDocument8 pagesVulvar and Vaginal Benign LesionsKristine VanzuelaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin Infections: Basic Dermatology CurriculumDocument78 pagesBacterial Skin Infections: Basic Dermatology CurriculumAnthony Bravo CortezNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis Guide: Causes, Types & TreatmentDocument7 pagesOsteomyelitis Guide: Causes, Types & TreatmentMargo Milad Fahim SaadNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin InfectionsDocument73 pagesBacterial Skin InfectionsAnthony Bravo CortezNo ratings yet
- Oral MedicineDocument19 pagesOral MedicineNoura RihanNo ratings yet
- Morning Report, WHC, 12/2/2010Document20 pagesMorning Report, WHC, 12/2/2010Mohit MehtaniNo ratings yet
- Classification of Periradicular Pathosis:: 4-Acute Apical AbscessDocument7 pagesClassification of Periradicular Pathosis:: 4-Acute Apical AbscessOmar MohamedNo ratings yet
- ConjungtivitisDocument86 pagesConjungtivitisIvo AfianiNo ratings yet
- Topic Name: I. A. 1. B. II. A. 1. Iii. IV. VDocument2 pagesTopic Name: I. A. 1. B. II. A. 1. Iii. IV. VRaiMalsiPilarNo ratings yet
- (Iii) Ewing's Sarcoma of Bone: Skeletal DistributionDocument4 pages(Iii) Ewing's Sarcoma of Bone: Skeletal DistributionWaqas HaleemNo ratings yet
- Afecciones Anorrectales Benignas Absceso Perianal, Fístula Anal, Hemorroides, Fisuras y Seno PilonidalDocument7 pagesAfecciones Anorrectales Benignas Absceso Perianal, Fístula Anal, Hemorroides, Fisuras y Seno PilonidalJoshua MaciasNo ratings yet
- External Dacryocystorhinostomy - DCR - Surgery TechniqueDocument14 pagesExternal Dacryocystorhinostomy - DCR - Surgery TechniquekityamuwesiNo ratings yet
- Angle Closure GlaucomaDocument21 pagesAngle Closure Glaucomasri sinagaNo ratings yet
- AAD-BF-Oral-Disease-2Document2 pagesAAD-BF-Oral-Disease-2kahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- Clinical Course Discussion: Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OregonDocument1 pageClinical Course Discussion: Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OregonperjadanutNo ratings yet
- SCROFULODERMADocument25 pagesSCROFULODERMAFaradiba MaricarNo ratings yet
- The Neo Terminal Ileum The Rutgeerts ScoreDocument1 pageThe Neo Terminal Ileum The Rutgeerts Scorecharelle.33No ratings yet
- Pruritus Ani, Hemorroidet EtjDocument4 pagesPruritus Ani, Hemorroidet EtjKreshnik HAJDARINo ratings yet
- Zebra XX, Part 2 PDFDocument3 pagesZebra XX, Part 2 PDFRamona MateiNo ratings yet
- Primary Surgery - AbscessDocument14 pagesPrimary Surgery - Abscessjackblack2001100% (1)
- Inguinal Hernia and Hydrocele: Congenital Hydrocele Presents As A Mass in The Scrotum ShortlyDocument3 pagesInguinal Hernia and Hydrocele: Congenital Hydrocele Presents As A Mass in The Scrotum ShortlyBetão AviãoNo ratings yet
- Classification Criteria For SLEDocument2 pagesClassification Criteria For SLEA. DuqueNo ratings yet
- Skleritis EpiskleritisDocument22 pagesSkleritis EpiskleritisDavi DzikirianNo ratings yet
- Abses DMDocument19 pagesAbses DMAngel MakinNo ratings yet
- Benign Disease of Vulva and Vagina - FavDocument2 pagesBenign Disease of Vulva and Vagina - FavjeccomNo ratings yet
- Type of The Wound-JCF 4thDocument25 pagesType of The Wound-JCF 4thTaufik HidayantoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin Integrity Related To Trauma or Infection: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesImpaired Skin Integrity Related To Trauma or Infection: Objectivesmhean azneitaNo ratings yet
- General Surgery Personal Notes by DR Shariful HalimDocument189 pagesGeneral Surgery Personal Notes by DR Shariful HalimFaruki80% (5)
- Uveitis: Preceptor: Dr. Rahmad Syuhada, SP.M Wulandari, S.Ked 17360077Document23 pagesUveitis: Preceptor: Dr. Rahmad Syuhada, SP.M Wulandari, S.Ked 17360077widya melianitaNo ratings yet
- Neurology CasesDocument16 pagesNeurology Casesphreakyfil100% (1)
- Wounds and BleedingDocument3 pagesWounds and BleedingJames Peter FernandezNo ratings yet
- Digital Healthcare Market Research 3Document33 pagesDigital Healthcare Market Research 3Nero AngeloNo ratings yet
- Emergency Department Approach to Allergic Reactions and AnaphylaxisDocument25 pagesEmergency Department Approach to Allergic Reactions and AnaphylaxisEden FerrerNo ratings yet
- CASE SCENARIO AppendicitisDocument6 pagesCASE SCENARIO AppendicitisJacob Estrada0% (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing Diagnosis List Based On The Nanda-I Nursing Diagnoses (NDS)Document14 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Diagnosis List Based On The Nanda-I Nursing Diagnoses (NDS)Tania sharmaNo ratings yet
- Linear Iga Dermatosis / Chronic Bullous Disease of ChildhoodDocument31 pagesLinear Iga Dermatosis / Chronic Bullous Disease of ChildhoodHoc Lim SeeNo ratings yet
- Evmlu Uganda.2020Document124 pagesEvmlu Uganda.2020ALINOMUGASHA EMMANUELNo ratings yet
- Intellectual and Developmental Disorders: Erlanda RomilusDocument7 pagesIntellectual and Developmental Disorders: Erlanda Romilusapi-247965295No ratings yet
- Single-payer health care reduces inequality gapsDocument52 pagesSingle-payer health care reduces inequality gapsMetelitswagNo ratings yet
- Sjogren 3Document12 pagesSjogren 3Marco Antonio García LunaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Findings in FIP CatsDocument73 pagesUltrasound Findings in FIP Catsludiegues752No ratings yet
- 30613167: Management of Osteitis Pubis in Athletes Rehabilitation and Return To Training - A Review of The Most Recent Literature PDFDocument10 pages30613167: Management of Osteitis Pubis in Athletes Rehabilitation and Return To Training - A Review of The Most Recent Literature PDFRicovially DavyaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in Pregnancy: Management ofDocument8 pagesDiabetes in Pregnancy: Management ofdiana rossNo ratings yet
- Cancer Management in Man Cancer Management in Man Cancer Management in ManDocument305 pagesCancer Management in Man Cancer Management in Man Cancer Management in Manmanu98kkskskskskiwyhNo ratings yet
- Josephine Morrow: Guided Reflection QuestionsDocument3 pagesJosephine Morrow: Guided Reflection QuestionsElliana Ramirez100% (1)
- CONCEPT EpidemilologyDocument13 pagesCONCEPT EpidemilologyKrishnaveni MurugeshNo ratings yet
- CV Elizabeth Beemer James PDFDocument3 pagesCV Elizabeth Beemer James PDFapi-255051459No ratings yet
- Gummin2018 PDFDocument204 pagesGummin2018 PDFAelton AraujoNo ratings yet
- Health Checklist Form For Visitors: Nakaranas Ka Ba NG Mga Sumusunod: Oo HindiDocument2 pagesHealth Checklist Form For Visitors: Nakaranas Ka Ba NG Mga Sumusunod: Oo HindiCoin CharNo ratings yet
- Smoking and Hypertension - UpToDateDocument25 pagesSmoking and Hypertension - UpToDatemehdi.chlif4374No ratings yet
- The Asthma, COPD & Allergic Rhinitis Market Outlook To 2011: HealthcareDocument163 pagesThe Asthma, COPD & Allergic Rhinitis Market Outlook To 2011: HealthcareYuva VikazNo ratings yet
- R G C I & R C: Ajiv Andhi Ancer NstituteDocument7 pagesR G C I & R C: Ajiv Andhi Ancer NstituteShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Excerpt From "Diabetes: A Lifetime of Being Too Sweet"Document9 pagesExcerpt From "Diabetes: A Lifetime of Being Too Sweet"waltcrockerNo ratings yet
- CHF SIM - Preparation Questions and Notes For LPN StudentsDocument3 pagesCHF SIM - Preparation Questions and Notes For LPN Studentsmercy longNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Artificial Respiration and Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Artificial Respiration and Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationMark Kenneth CeballosNo ratings yet
- Breast Examination Prenatal PostpartumDocument2 pagesBreast Examination Prenatal PostpartumMaria Rose Ann YeeNo ratings yet
- Chronic Gastritis and Peptic Ulcer Disease GuideDocument32 pagesChronic Gastritis and Peptic Ulcer Disease GuideDian Ekawati100% (2)
- Ix. Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesIx. Nursing Care PlanJai - HoNo ratings yet
- Arterial Disorders: Arteriosclerosis & AtherosclerosisDocument28 pagesArterial Disorders: Arteriosclerosis & AtherosclerosisManuel Jacob YradNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Rudolf - Instrument Surgical - PT. Graha IsmayaDocument172 pagesCatalogue Rudolf - Instrument Surgical - PT. Graha IsmayayuketamaNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Optimising The Patient Interview & Clinical OutcomesDocument6 pagesA Framework For Optimising The Patient Interview & Clinical OutcomesPipsKhoor FxNo ratings yet