Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solid, Liquid, Gas Explanation Text
Uploaded by
nettextsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solid, Liquid, Gas Explanation Text
Uploaded by
nettextsCopyright:
Available Formats
100
Solid Liquid Gas
Figure 5–2 The states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
forms are called the states of matter. Matter assumes one of these states de-
pending on its temperature (Figure 5–2). The three different states have
the following distinct characteristics.
Solids have a definite shape and volume. Ice is an example of a solid.
Liquids have a definite volume but not a definite shape; they take the
shape of their containers. Water is an example of a liquid.
Gases do not have a definite volume or shape. They expand easily and
can be compressed. Steam is an example of a gas.
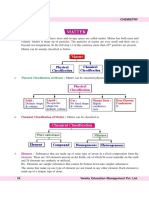
Structure of Matter
Matter can be classified into three main groups: elements, compounds,
and mixtures.
An element is the basic unit of all matter. It is a substance that can-
not be made by the combination of two or more simpler substances, and
the element itself cannot be reduced to simpler substances without a loss
of identity. There are over 90 naturally occurring elements, each with its
5 own distinctive physical and chemical properties. All matter in the univ-
verse is made up of one or more of these different elements.
Each element is identified by a letter symbol, such as O for oxygen, C
for carbon, and H for hydrogen. You can search for these symbols in the
Periodic Table of Elements, found in any chemistry textbook.
There are five elements in the Table that are of special interest to the
esthetician. These elements make up part of the structure of skin, hair, and
nails: carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), and sulfur(S).
Atoms are the structural units that make up elements. Atoms are the
particles from which all matter is composed. An atom is the smallest par-
ticle of an element that still retains the properties of that element. All the
atoms in an element are identical. Atoms cannot be divided into simpler
substances by ordinary chemical means.
Atoms consist of smaller particles: protons, which have a positive elec-
trical charge; neutrons, with a neutral charge; and electrons, with a nega-
Part 2 General Sciences
101
tive charge (Figure 5–3). The number of protons in an atom equals the Carbon Atom
number of electrons. Proton
A molecule is formed by joining two or more atoms chemically. There
are two types of molecules.
Elemental molecules contain two or more atoms of the same element Neutron
that are united chemically. Atmospheric oxygen, in the air we breathe, is
Electron
the elemental molecule O2. The ozone in the atmosphere, which protects
us from ultraviolet radiation, is the elemental molecule O3 (Figure 5–4).
Compound molecules are chemical combinations of two or more
atoms of different elements (Figure 5–5). The compound molecule Figure 5–3 An atom consists of
sodium chloride (NaCl), or common table salt, is a chemical combi- negatively charged electrons, positively
charged protons, and neutral neutrons.
nation of one atom of sodium (Na) and one atom of chlorine (Cl).
A compound is a combination of two or more atoms of different
elements united chemically with a fixed chemical composition, definite
proportions, and distinct properties. The properties of chemical
compounds are different from the properties of the elements from
which they were made. Water (H2O) is a chemical compound. A water
Atomic oxygen
O O O O
Oxygen, O2 Ozone, O3
Figure 5–4 Elemental molecules. 5
Sodium chloride, NaCl
H
H H
O O
O C O
O
Water, H2O Carbon dioxide, CO2 Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2
Figure 5–5 Compound molecules.
Chapter 5 Chemistry for Estheticians
You might also like
- Elements, Compounds, & MixturesDocument72 pagesElements, Compounds, & MixturesWendz ArominNo ratings yet
- Substance A Substance Is Matter Which Has A Specific Composition and Specific PropertiesDocument8 pagesSubstance A Substance Is Matter Which Has A Specific Composition and Specific Propertiesaishajutt041No ratings yet
- Elements Compounds Mixtures 1222945537104981 9Document72 pagesElements Compounds Mixtures 1222945537104981 9is124el6169No ratings yet
- Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument15 pagesElements Compounds and Mixturespeaky blinderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chem IDocument16 pagesChapter 2 Chem IStudy LionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document46 pagesChapter 01dostinNo ratings yet
- Edexcel AS Chemistry Note 1 Definitions of The TermsDocument3 pagesEdexcel AS Chemistry Note 1 Definitions of The TermsSajaniNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Elements ExplainedDocument45 pagesAtoms and Elements ExplainedShereen Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- Global Indian International School Uppal, Hyderabad Subject: Chemistry Chapter 3 .Atoms and MoleculesDocument13 pagesGlobal Indian International School Uppal, Hyderabad Subject: Chemistry Chapter 3 .Atoms and MoleculesKhatrasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 生物與化學Document16 pagesLesson 2 生物與化學邱崇閔No ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument51 pagesChem NotesHannah RossNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaDocument75 pagesChemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaJESPHER GARCIANo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Matter, molecules and periodic tableDocument40 pagesLecture 3 - Matter, molecules and periodic tableNaff WariNo ratings yet
- Most Molecular Compounds (I.e. Involving Chemical Bonds) Contain Only Non-Metallic ElementsDocument6 pagesMost Molecular Compounds (I.e. Involving Chemical Bonds) Contain Only Non-Metallic ElementsFavogaNo ratings yet
- CHEM1100 Notes-ModifiedDocument86 pagesCHEM1100 Notes-ModifiedDeepika VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Molecules and CompoundsDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Molecules and CompoundsChristian JamesNo ratings yet
- The Differences Between A Compound and A MixtureDocument27 pagesThe Differences Between A Compound and A Mixturearies triwidajatiNo ratings yet
- GED Chemistry Note1 (Atoms, Molecules and Their Properties)Document6 pagesGED Chemistry Note1 (Atoms, Molecules and Their Properties)Shahadat Hussain Parvez100% (1)
- U2l2 150725104221 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument23 pagesU2l2 150725104221 Lva1 App6891 PDFBernadett JoseNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL SYMBOLS & FORMULASDocument7 pagesCHEMICAL SYMBOLS & FORMULASeverithingwithbNo ratings yet
- 02 Lesson 2 Chemical BondingDocument23 pages02 Lesson 2 Chemical BondingAnnabel PatarataNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Bohr Model of AtomsDocument31 pagesAtoms and Bohr Model of Atomsogedengbed28No ratings yet
- BL Skill CH 3 Notes and TFDocument5 pagesBL Skill CH 3 Notes and TFapi-329922192No ratings yet
- Basic Definitions of Structure of MatterDocument6 pagesBasic Definitions of Structure of MatterÏt's RîçkgãrçīäNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Matter and Life: What Is Chemistry and Why Is It Important?Document17 pagesChapter One: Matter and Life: What Is Chemistry and Why Is It Important?knitwitchrnNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument2 pagesVolcanoJhaynnon AniezNo ratings yet
- Y9 Chemistry Revision Booklet PDFDocument17 pagesY9 Chemistry Revision Booklet PDFRamesh Adwani0% (1)
- Reviewer in General Chemistry 2Document77 pagesReviewer in General Chemistry 2Ana Marie100% (1)
- ICSE Class 9ch 1 (Language of Chemistry)Document20 pagesICSE Class 9ch 1 (Language of Chemistry)Swati 06No ratings yet
- Fundamental Chemical ConceptsDocument21 pagesFundamental Chemical Conceptsapi-26291674No ratings yet
- Fundamental Chemical ConceptsDocument21 pagesFundamental Chemical Conceptsapi-26291674No ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction in Water Desalination:: Dr. Adnan O. Alhathal Fall 2021/2022Document25 pagesChapter One Introduction in Water Desalination:: Dr. Adnan O. Alhathal Fall 2021/2022Hydar MohammedNo ratings yet
- HTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFDocument82 pagesHTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFayoubNo ratings yet
- CHEMDocument31 pagesCHEMSheena Ann L. LLarenasNo ratings yet
- C16 14a Pt3 Atomic TheoryDocument49 pagesC16 14a Pt3 Atomic TheoryJohn Michael AlcachupasNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument10 pagesAtoms and MoleculesUtsav Kumar MathurNo ratings yet
- Periodic-Table-and-Elements-TES-uploadDocument127 pagesPeriodic-Table-and-Elements-TES-upload18811301255No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesCHEMISTRYblessing akataNo ratings yet
- Compounds and Chemical FormulasDocument35 pagesCompounds and Chemical Formulasjolina OctaNo ratings yet
- Che101 Chap 2Document60 pagesChe101 Chap 2Ruhi AfsaraNo ratings yet
- Presented by GROUP 5Document10 pagesPresented by GROUP 5cq8bvzccw9No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Composition of MatterDocument8 pagesChemistry: Composition of Matterrica marieNo ratings yet
- Chemical CompoundsDocument37 pagesChemical Compoundsyawev55732No ratings yet
- Demo ChemDocument25 pagesDemo ChemCalixTroy AgustinNo ratings yet
- Naming and Writing Formulas of Inorganic CompoundsDocument14 pagesNaming and Writing Formulas of Inorganic CompoundsArvin CoirneNo ratings yet
- Structure 1 Models of Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument18 pagesStructure 1 Models of Particulate Nature of Matter Notesphooi.sheng-ernNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Chemistry Is TheDocument12 pagesEtymology: Chemistry Is Thejet999999999_8091324No ratings yet
- Class Ix Chapter 3Q QND Answer With NumericalsDocument17 pagesClass Ix Chapter 3Q QND Answer With NumericalsABHAY PRATAP SINGH TOMARNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument46 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pureparamjeet164No ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument41 pagesClassification of MatterRicardo Jr. Uy100% (1)
- CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER RevisedDocument23 pagesCLASSIFICATION OF MATTER RevisedTrisha Rae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Structure of AtomDocument16 pagesClass 7 Structure of AtomGaganNo ratings yet
- 1 Molecules of LifeDocument127 pages1 Molecules of LifeRana FatimaNo ratings yet
- Bio 110 - Ch2Document30 pagesBio 110 - Ch2محسن الشاطريNo ratings yet
- CHP 8 Covalent BondDocument58 pagesCHP 8 Covalent BondKatherine Lai Kwan CHANNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument36 pagesTopic 2 Atoms, Elements and Compoundsadamskbd100% (1)
- C4 Chemistry SRP MaterialDocument11 pagesC4 Chemistry SRP MaterialDhaksheysh.NNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument47 pagesAtoms, Molecules and Ionszekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- Proportional and Non Proportional RelationshipsDocument11 pagesProportional and Non Proportional RelationshipsnettextsNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Sequences As Linear FunctionsDocument15 pagesArithmetic Sequences As Linear FunctionsnettextsNo ratings yet
- Review For Direct VariationDocument2 pagesReview For Direct VariationnettextsNo ratings yet
- Regular ER VerbsDocument3 pagesRegular ER Verbsswatson033No ratings yet
- Color Handouts - GoogleDocument6 pagesColor Handouts - GooglenettextsNo ratings yet
- Slope and Rate of ChangeDocument6 pagesSlope and Rate of ChangenettextsNo ratings yet
- Slope and Rate of ChangeDocument6 pagesSlope and Rate of ChangenettextsNo ratings yet
- Places WorksheetDocument9 pagesPlaces WorksheetnettextsNo ratings yet
- History of Atomic Theory Power PointDocument28 pagesHistory of Atomic Theory Power PointnettextsNo ratings yet
- Rooms of A House-GoogleDocument3 pagesRooms of A House-GooglenettextsNo ratings yet
- Regular ER VerbsDocument3 pagesRegular ER Verbsswatson033No ratings yet
- Gas Laws-Wiki 0Document2 pagesGas Laws-Wiki 0nettextsNo ratings yet
- Plot Diagram TemplateDocument1 pagePlot Diagram TemplatenettextsNo ratings yet
- Theme WorksheetDocument2 pagesTheme WorksheetnettextsNo ratings yet
- Literary ElementsDocument2 pagesLiterary ElementsnettextsNo ratings yet
- Literary ElementsDocument2 pagesLiterary ElementsnettextsNo ratings yet
- Theme WorksheetDocument2 pagesTheme WorksheetnettextsNo ratings yet
- FreezingDocument1 pageFreezingnettextsNo ratings yet
- FreezingDocument1 pageFreezingnettextsNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws-Wiki 0Document2 pagesGas Laws-Wiki 0nettextsNo ratings yet
- Plot - Elements of Plot StructureDocument3 pagesPlot - Elements of Plot StructurenettextsNo ratings yet
- Character Analysis WorksheetDocument1 pageCharacter Analysis WorksheetnettextsNo ratings yet
- Plot Diagram TemplateDocument1 pagePlot Diagram TemplatenettextsNo ratings yet
- LitelementsDocument5 pagesLitelementsapi-275654604No ratings yet
- Diagram of The PlotDocument1 pageDiagram of The PlotnettextsNo ratings yet
- Graphing Linear Equations WorksheetDocument2 pagesGraphing Linear Equations WorksheetnettextsNo ratings yet
- Literary Elements WorksheetDocument3 pagesLiterary Elements WorksheetnettextsNo ratings yet
- Spanish #Document1 pageSpanish #nettextsNo ratings yet
- Linear Eq NotesDocument4 pagesLinear Eq NotesnettextsNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws-Wiki 0Document2 pagesGas Laws-Wiki 0nettextsNo ratings yet
- For Coin & Blood (2nd Edition) - SicknessDocument16 pagesFor Coin & Blood (2nd Edition) - SicknessMyriam Poveda50% (2)
- Installation Instruction XALM IndoorDocument37 pagesInstallation Instruction XALM IndoorVanek505No ratings yet
- Digital Communication Quantization OverviewDocument5 pagesDigital Communication Quantization OverviewNiharika KorukondaNo ratings yet
- Supplier GPO Q TM 0001 02 SPDCR TemplateDocument6 pagesSupplier GPO Q TM 0001 02 SPDCR TemplateMahe RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Suband Coding in MatlabDocument5 pagesSuband Coding in MatlabZoro Roronoa0% (1)
- Exor EPF-1032 DatasheetDocument2 pagesExor EPF-1032 DatasheetElectromateNo ratings yet
- Bandung Colonial City Revisited Diversity in Housing NeighborhoodDocument6 pagesBandung Colonial City Revisited Diversity in Housing NeighborhoodJimmy IllustratorNo ratings yet
- APC Smart-UPS 1500VA LCD 230V: Part Number: SMT1500IDocument3 pagesAPC Smart-UPS 1500VA LCD 230V: Part Number: SMT1500IDesigan SannasyNo ratings yet
- (Bio) Chemistry of Bacterial Leaching-Direct vs. Indirect BioleachingDocument17 pages(Bio) Chemistry of Bacterial Leaching-Direct vs. Indirect BioleachingKatherine Natalia Pino Arredondo100% (1)
- FALL PROTECTION ON SCISSOR LIFTS PDF 2 PDFDocument3 pagesFALL PROTECTION ON SCISSOR LIFTS PDF 2 PDFJISHNU TKNo ratings yet
- AAU5243 DescriptionDocument30 pagesAAU5243 DescriptionWisut MorthaiNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper #1 - Introduction To Action ResearchDocument1 pageReflection Paper #1 - Introduction To Action Researchronan.villagonzaloNo ratings yet
- Domingo V People (Estafa)Document16 pagesDomingo V People (Estafa)Kim EscosiaNo ratings yet
- Put The Items From Exercise 1 in The Correct ColumnDocument8 pagesPut The Items From Exercise 1 in The Correct ColumnDylan Alejandro Guzman Gomez100% (1)
- Drafting TechnologyDocument80 pagesDrafting Technologyong0625No ratings yet
- Failure Analysis Case Study PDFDocument2 pagesFailure Analysis Case Study PDFScott50% (2)
- Political Reporting:: Political Reporting in Journalism Is A Branch of Journalism, Which SpecificallyDocument6 pagesPolitical Reporting:: Political Reporting in Journalism Is A Branch of Journalism, Which SpecificallyParth MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lady Allen On Froebel Training School, Emdrup, CopenhagenDocument5 pagesLady Allen On Froebel Training School, Emdrup, CopenhagenLifeinthemix_FroebelNo ratings yet
- Kahveci: OzkanDocument2 pagesKahveci: OzkanVictor SmithNo ratings yet
- Weekly Choice - Section B - February 16, 2012Document10 pagesWeekly Choice - Section B - February 16, 2012Baragrey DaveNo ratings yet
- Gi 007 Gerund InfinitiveDocument2 pagesGi 007 Gerund Infinitiveprince husainNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods: Jeffrey R. ChasnovDocument60 pagesNumerical Methods: Jeffrey R. Chasnov2120 sanika GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Product CycleDocument2 pagesProduct CycleoldinaNo ratings yet
- Henny Penny 500-561-600 TM - FINAL-FM06-009 9-08Document228 pagesHenny Penny 500-561-600 TM - FINAL-FM06-009 9-08Discman2100% (2)
- ULN2001, ULN2002 ULN2003, ULN2004: DescriptionDocument21 pagesULN2001, ULN2002 ULN2003, ULN2004: Descriptionjulio montenegroNo ratings yet
- Creatures Since Possible Tanks Regarding Dengue Transmission A Planned Out ReviewjnspeDocument1 pageCreatures Since Possible Tanks Regarding Dengue Transmission A Planned Out Reviewjnspeclientsunday82No ratings yet
- Guide to Fair Value Measurement under IFRS 13Document3 pagesGuide to Fair Value Measurement under IFRS 13Annie JuliaNo ratings yet
- NOTE CHAPTER 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and EquationDocument10 pagesNOTE CHAPTER 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and EquationNur AfiqahNo ratings yet
- DSE61xx Configuration Suite Software Manual PDFDocument60 pagesDSE61xx Configuration Suite Software Manual PDFluisNo ratings yet
- Mythi From AndromedaDocument383 pagesMythi From AndromedaRico MinnerNo ratings yet