Professional Documents
Culture Documents
One Page
Uploaded by
sat2007Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
One Page
Uploaded by
sat2007Copyright:
Available Formats
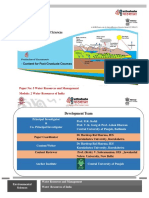
A study on the evaluation of ground water potential and vulnerability in Trichirappalli District.
Water is essential for human life .The demand for water has already increased tremendously over the years due to population explosion, industrialization, urbanization, expanding agriculture and economic development. At the same time the available surface and ground water resources are indiscriminately polluted by improper disposal of municipal, industrial and agricultural waste into water bodies. This leads to water quality deterioration creating new challenges on water conservation and management. In view of present situation sustainable management of water supporting natural environment has gained great importance. Therefore an assessment of availability of water resources is imperative. Tiruchirappalli district is centroid of Tamilnadu state located in Cauvery river basin. It sustains a population of 24,18,366 as per 2001 census in an area of 4,40,383 sqkm. The district is divided into 14 blocks. On the basis of ground water development 4 blocks are categorized as overexploited and 1 as critical and rest as safe. Several studies have shown that some blocks could be vulnerable to water level depletion. The present study is proposed to assess the ground water potential. The study also envisages an appropriate mathematical equations describing the groundwater regime in terms of observable such as groundwater levels or concentrations of pollution etc., A sensitivity analysis of the model to identify those parameters which need to be estimated more accurately and to evolve efficient management options to protect the groundwater. The primary objective of vulnerability assessment is to identify places that are most susceptible to harm and identify vulnerability reducing actions.
(M. Nirmala Devi)
Kearey, Philip, Michael Brooks, and Ian Hill. An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration, 3rd ed. Oxford, U.K.: Blackwell, 2002. Stone, William. J. Hydrogeology in Practice: A Guide to Characterizing Groundwater Systems. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1998.
Read more: Groundwater Supplies, Exploration for - river, depth, salt, types, plants, source http://www.waterencyclopedia.com/Ge-Hy/GroundwaterSupplies-Exploration-for.html#ixzz1GsTfDrSw
.
Water resources are sources of water that are useful or potentially useful to humans. Uses of water include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities. Virtually all of these human uses require fresh water. 97% of water on the Earth is salt water, and only 3% is fresh water of which slightly over two thirds is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps.[1] The remaining unfrozen freshwater is mainly found as groundwater, with only a small fraction present above ground or in the air.[2]
Foster, Stephen, Albert Tuinhof, Karin Kemper, Hector Garduno, and Marcella Nanni. 2002. Groundwater Management Strategies. GWMATE Briefing Note 3. Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools series. Online at http://www.worldbank.org/ gwmate. IWMI (International Water Management Institute). 2002. Innovations in Groundwater Recharge. IWMI-Tata Water Policy Briefing, No. 1. Available online at http://www.iwmi.cgiar.org/ waterpolicybriefing/files/wpb01.pdf. Murray Rust, H., and E. Vander Velde. 1992. Conjunctive Use of Canal and Groundwater in Punjab, Pakistan: Management and Policy Options. Advancements in IIMIs Research 1992. A Selection of papers presentedat the Internal Program Review. Colombo, Sri Lanka: International Irrigation Management Institute. Shah, T. 2003. Decentralized Water Harvesting and Groundwater
Water is one of the most essential natural resources for sustaining life and it is likely to become critically scarce in the coming decades, due to continuous increase in its demands, rapid increase in population and expanding economy of the country.
Groundwater Resources of India, Central Groundwater Board,
New Delhi, 1995. 11. Theme paper Five Decades of Water Resources Development in India, Indian Water Resources Society, Roorkee, 1998.
Fetter, C.W. 2001. Applied Hydrogeology (Fourth Edition). Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. Freeze, R.A., and J.A. Cherry. 1979. Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey. Hansel, A.K., and W.H. Johnson. 1996. Wedron and Mason Groups: Lithostratigraphic Reclassification of Deposits of the Wisconsin Episode, Lake Michigan Lobe Area. Illinois
Ahmad Jamrah & Ahmed Al-Futaisi & Natarajan Rajmohan & Saif Al-Yaroubi
Published online: 20 December 2007 # Springer Science + Business Media B.V. 2007
You might also like
- Water Demand All SlidesDocument23 pagesWater Demand All Slidesrajat debnathNo ratings yet
- Rainwater HarvestingDocument55 pagesRainwater Harvestingnur67% (3)
- Lecture NotesDocument71 pagesLecture NotesBernard Palmer89% (9)
- Development Economics Project: Research Proposal ONDocument8 pagesDevelopment Economics Project: Research Proposal ONNatalia PatnaikNo ratings yet
- First Draft Intro RRL PDFDocument34 pagesFirst Draft Intro RRL PDFleo besa100% (1)
- Full Disclosure 2019Document114 pagesFull Disclosure 2019Mail and GuardianNo ratings yet
- Water Resource EngineeringDocument29 pagesWater Resource EngineeringRamesh DaundkarNo ratings yet
- UK Rainwater Harvesting Literature Review - Bradford UniversityDocument59 pagesUK Rainwater Harvesting Literature Review - Bradford UniversityFree Rain Garden Manuals92% (13)
- Hidden ConsequencesDocument80 pagesHidden ConsequencesDanielle DacuanNo ratings yet
- Water Recycle and Reuse NIMMS University PDFDocument8 pagesWater Recycle and Reuse NIMMS University PDFDennis KorirNo ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation ManuscriptDocument6 pagesDrip Irrigation ManuscriptSam Edwin Moses100% (1)
- Section BDocument112 pagesSection BFredrick MashingiaNo ratings yet
- Rejuvenation of Water Bodies in Kerala-A Case Study of Kanampuzha River at Kannur DistrictDocument4 pagesRejuvenation of Water Bodies in Kerala-A Case Study of Kanampuzha River at Kannur DistrictAnshuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Article 2Document10 pagesArticle 2abhinav.bhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- E6 106 18 Solar DistillationDocument10 pagesE6 106 18 Solar DistillationghostamirNo ratings yet
- 1513074387paper5module40 Etext 2Document19 pages1513074387paper5module40 Etext 2Piyush TripathiNo ratings yet
- Drinking WaterDocument9 pagesDrinking WaterSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- The Role of Hydropower in Visions of Water Resources Development For Rivers of Western NepalDocument29 pagesThe Role of Hydropower in Visions of Water Resources Development For Rivers of Western NepalNeeraj BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Sociolog 3Document16 pagesSociolog 3lucifer morningstarNo ratings yet
- Ce 507 Ce51fc1 TitleDocument2 pagesCe 507 Ce51fc1 TitleAyessaDelCastilloPiguerraNo ratings yet
- Develop To Model Assess of River Basins in TamilnaduDocument10 pagesDevelop To Model Assess of River Basins in TamilnaduInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Planning For Water Resources Development: Presented byDocument38 pagesPresentation On Planning For Water Resources Development: Presented byMunmun BasumataryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-5. EditedDocument34 pagesChapter 1-5. EditedBasa, Rica Mae P.No ratings yet
- Surveillance of Drinking Water Quality For Safe Water Supply-A Case Study From Shillong, IndiaDocument22 pagesSurveillance of Drinking Water Quality For Safe Water Supply-A Case Study From Shillong, IndiaHakimi BobNo ratings yet
- Stakeholder Participation in Water Resource Management Drop of LifeDocument6 pagesStakeholder Participation in Water Resource Management Drop of LifeEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- D019851821 PDFDocument4 pagesD019851821 PDFDharma KrisnahadiNo ratings yet
- Corrected Order 1Document6 pagesCorrected Order 1nelsonchaga001No ratings yet
- NRM - WaterDocument10 pagesNRM - WaterD.Sreenivasa ReddyNo ratings yet
- Reshma G Renjini S Christopher Kurian Sreenath N Joji Isac P V Rahini Amol KhanwalkarDocument31 pagesReshma G Renjini S Christopher Kurian Sreenath N Joji Isac P V Rahini Amol KhanwalkarManoj SatishNo ratings yet
- A Study On Water Resource Management and Its Issues in IndiaDocument4 pagesA Study On Water Resource Management and Its Issues in IndiaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Chm092: Assignment 1 Sustainable Development Goals 6 (SDG 6)Document15 pagesChm092: Assignment 1 Sustainable Development Goals 6 (SDG 6)Izzatul Najihah AzhamNo ratings yet
- Divyanshu Singh - B059 SocioDocument15 pagesDivyanshu Singh - B059 Sociolucifer morningstarNo ratings yet
- An Analysisof Demandand Supplyof Waterin IndiaDocument8 pagesAn Analysisof Demandand Supplyof Waterin IndiaSavita BartwalNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General: Department of Civil Engineering, MIT MYSOREDocument26 pages1.1 General: Department of Civil Engineering, MIT MYSOREThanuj MurthyNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Conservation in Kerala Policies and Practice With Special Emphasis On Ground Water Conservation in IndiaDocument38 pagesGround Water Conservation in Kerala Policies and Practice With Special Emphasis On Ground Water Conservation in IndiaS.Alec Knowle100% (1)
- WaterDocument3 pagesWaterKevinjosh FriginalNo ratings yet
- Neccesity of Water Managament in India - 100244Document8 pagesNeccesity of Water Managament in India - 100244muralidharankonar1No ratings yet
- C A KomolafeDocument10 pagesC A KomolafeAdewale Adefemi JonathanNo ratings yet
- A Research Paper On:: Sociology Semester - 3Document16 pagesA Research Paper On:: Sociology Semester - 3lucifer morningstarNo ratings yet
- JADS 13-1-11 Page 156-162Document7 pagesJADS 13-1-11 Page 156-162Abebe MengistuNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Planning The Challenges of Water Resources Engineers in UgandaDocument11 pagesWater Resources Planning The Challenges of Water Resources Engineers in UgandakamagaraNo ratings yet
- Water Quality Mapping of Coastal Aquifers in Central Part of Penisular India Using Geographic Information SystemDocument5 pagesWater Quality Mapping of Coastal Aquifers in Central Part of Penisular India Using Geographic Information SystemIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of Sustainable Use of WastewaterDocument22 pagesSWOT Analysis of Sustainable Use of WastewaterNisar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Course 6 Yacob Water Governance 2022Document9 pagesCourse 6 Yacob Water Governance 2022eyobNo ratings yet
- Water Recycle and Reuse - A Case Study of NMIMS University CampusDocument8 pagesWater Recycle and Reuse - A Case Study of NMIMS University CampusinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Water Quality Assessment of A River Using Deep Learning Bi-LSTM Methodology: Forecasting and ValidationDocument15 pagesWater Quality Assessment of A River Using Deep Learning Bi-LSTM Methodology: Forecasting and ValidationSakshi KhullarNo ratings yet
- Course 5 Water Governance 2022Document10 pagesCourse 5 Water Governance 2022eyobNo ratings yet
- Evs Water Pollution Mrityunjaya Thakur 1986Document31 pagesEvs Water Pollution Mrityunjaya Thakur 1986Gautam DohareyNo ratings yet
- Working Paper 140Document29 pagesWorking Paper 140Sugirtha NamachivayamNo ratings yet
- Ijseer 2014 3 (4) 178 184Document7 pagesIjseer 2014 3 (4) 178 184Aprill ApriiliantyNo ratings yet
- Sociology II Research PaperDocument45 pagesSociology II Research PaperB Amandeep Yadav 1036No ratings yet
- Water: Water Supply and Water ScarcityDocument16 pagesWater: Water Supply and Water ScarcityLal ChandNo ratings yet
- October 2015: Velu Ethirajan Nethaji MariappanDocument15 pagesOctober 2015: Velu Ethirajan Nethaji MariappanN .PERUMAL RAJANo ratings yet
- 12 Desalination Advance Water Treatment Economics FinancingDocument34 pages12 Desalination Advance Water Treatment Economics Financingleo besaNo ratings yet
- Module 1. Overview of ASCOTs Vision Mission AgEn 101Document11 pagesModule 1. Overview of ASCOTs Vision Mission AgEn 101John Lester AlforteNo ratings yet
- 1520396302paper5module2 EtextDocument20 pages1520396302paper5module2 EtextPiyush TripathiNo ratings yet
- Ecologically Sustainable Water Management: Managing River Flows For Ecological IntegrityDocument19 pagesEcologically Sustainable Water Management: Managing River Flows For Ecological IntegrityilanatzubaNo ratings yet
- Water PDFDocument8 pagesWater PDFShaikhsamiyanNo ratings yet
- ILR Booklet - Printable FormatDocument8 pagesILR Booklet - Printable FormatSangeetha SriramNo ratings yet
- Group 9 - Essay 1Document6 pagesGroup 9 - Essay 1Priyam MrigNo ratings yet
- Krishna River ReportDocument142 pagesKrishna River ReportPrasanth M SNo ratings yet
- Water Management Problems and Challenges in India: An Analytical ReviewDocument29 pagesWater Management Problems and Challenges in India: An Analytical ReviewKripa PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1 Background of The StudyDocument29 pagesChapter One 1.1 Background of The StudyCephas StoneNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Potable WaterDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Potable Waterfvf3f9h1100% (1)
- Sustainable Water Management in Smallholder Farming: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandSustainable Water Management in Smallholder Farming: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- The World's Water 2008-2009: The Biennial Report on Freshwater ResourcesFrom EverandThe World's Water 2008-2009: The Biennial Report on Freshwater ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Wright Water 2013Document166 pagesWright Water 2013Chuma747No ratings yet
- 773 Final Emp Existing Engen Fuel Storage Depot Continued Operations in KeetmanshoopDocument29 pages773 Final Emp Existing Engen Fuel Storage Depot Continued Operations in KeetmanshoopBabacar DieyeNo ratings yet
- BSBSUS301 BSBADM311 Student Book V1.0715 PDFDocument177 pagesBSBSUS301 BSBADM311 Student Book V1.0715 PDFjosebravo16100% (4)
- Speech by Governor James Ongwae During World Water Day 2018 CelebrationsDocument8 pagesSpeech by Governor James Ongwae During World Water Day 2018 CelebrationsJamesOngwaeNo ratings yet
- Jordan's Second National Communication To The United Nations Framework Convention On Climate ChangeDocument166 pagesJordan's Second National Communication To The United Nations Framework Convention On Climate ChangeddiabNo ratings yet
- Toppeta Report 005 2010Document9 pagesToppeta Report 005 2010Gabriel Isaac Gonzalez0% (1)
- Natural ResourceDocument30 pagesNatural ResourcejdidiwoodkdorNo ratings yet
- The Lake Challa Water Resources Integrated Development ProjectDocument100 pagesThe Lake Challa Water Resources Integrated Development ProjectrajfabNo ratings yet
- Importance and Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesDocument14 pagesImportance and Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studiessuparswa100% (2)
- Quality Requirements For Beneficial Use of WaterDocument8 pagesQuality Requirements For Beneficial Use of WaterJerome PalicteNo ratings yet
- Individual Reading For Middle EastDocument1 pageIndividual Reading For Middle Eastmysharona76No ratings yet
- Draft Agenda 5FME of 26012024Document5 pagesDraft Agenda 5FME of 26012024VozpopuliNo ratings yet
- Bengaluru LakesDocument16 pagesBengaluru LakesDavidNo ratings yet
- Irrigation 2017-2018 PDFDocument26 pagesIrrigation 2017-2018 PDFUmer QureshiNo ratings yet
- Integrated Water Resource Management-A New Way ForwardDocument24 pagesIntegrated Water Resource Management-A New Way ForwardRizka Dwi WildaniNo ratings yet
- The Turkana County Water Sector Plan Final 23022018Document48 pagesThe Turkana County Water Sector Plan Final 23022018lex tec0% (1)
- HB 4944 - DWRWRC BillDocument47 pagesHB 4944 - DWRWRC Billpaomillan0423No ratings yet
- DAO 90-34 - Revised Water Usage and Classification Water Quality Criteria Amending Section Nos 68 and 69, Chapter III of The 1978 NPCC Rules and RegulationsDocument11 pagesDAO 90-34 - Revised Water Usage and Classification Water Quality Criteria Amending Section Nos 68 and 69, Chapter III of The 1978 NPCC Rules and RegulationsPacific Spectrum100% (4)
- Tri-Tech Infrastructure (India) Private LimitedDocument8 pagesTri-Tech Infrastructure (India) Private LimitedLalit Mohan SenapatiNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 PDFDocument54 pagesLec 1 PDFshahid aliNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Brochure of Varanasi District, U.P.: Title Page NoDocument18 pagesGround Water Brochure of Varanasi District, U.P.: Title Page Notaryesh jangidNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Drinking-Water Quality: Surveillance and Control of Community SuppliesDocument28 pagesGuidelines For Drinking-Water Quality: Surveillance and Control of Community SuppliesJin SiclonNo ratings yet
- DhuleDocument19 pagesDhuleBobby MathewNo ratings yet
- Water Code of The Philippines: Atty. Elenito M. BagalihogDocument37 pagesWater Code of The Philippines: Atty. Elenito M. BagalihogArnold Magdalita FranciscoNo ratings yet