Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Precalcsolution
Uploaded by
timepratiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Precalcsolution
Uploaded by
timepratiCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 1261: Calculus I Brown
Precalculus Review Solutions
Functions
1. Write the denition of function.
Solution. See page 11.
2. Suppose f(x) = 2x
2
x
3
+ 1. Evaluate the following.
(a) f(3) = 18
(b) f(5) f(2) = 41
(c) f(5 2) = 18
(d) f(u+v) = 2u
2
+4uv+2v
2
u/3v/3+1
(e) f(x+h) = 2x
2
+4xh+2h
2
x/3h/3+1
(f)
f(x + h) f(x)
h
= 4x + 2h 1/3, h = 0
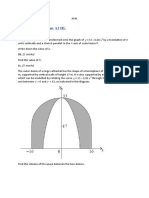
3. State, in order, the transformations you would apply to the graph of y = sin x in order to obtain the
graph of f(x) =
1
2
sin
x
4
. Sketch the graph of y = f(x).
Solution. 1) Compress vertically by a factor of 2. 2) Shift to the right /4 units.
4. Suppose f(x) =
x
2
+ x 3
x + 2
and g(x) =
x + 3
x
2
4
.
(a) State the domains of f and g.
Solution. Domain of f = {x|x = 2}; Domain of g = {x|x = 2}
(b) Find
f
g
(x) and state its domain.
Solution.
f
g
(x) =
(x
2
+ x 3)(x 2)
x + 3
; Domain of
f
g
= {x|x = 2, x = 2, x = 3}
(c) Find (f g)(x) and state its domain.
Solution. (f g)(x) =
(x + 3)
2
+ (x + 3)(x
2
4) 3(x
2
4)
2
(x + 3)
2
(x
2
4) + 2(x
2
4)
2
;
Domain of f g =
x|x = 2,
1
41
4
1
Linear and Exponential Change
5. What characterizes a linear function? Explain how you would determine whether or not a table of
values exhibits linear change. Explain how you would determine whether a linear function is increasing
or decreasing.
Solution. A linear function has a constant rate of change, or slope, m. Each time the input x is
increased by one, we add the exact same amount, m, to f(x). f(x + 1) = f(x) + m for all x. A linear
function is increasing if m > 0 and decreasing if m < 0.
6. What characterizes an exponential function? Explain how you would determine whether or not a
table of values exhibits exponential change. Explain how you would determine whether an exponential
function is increasing or decreasing.
Solution. An exponential function has the property that if the input x is increased by one, we multiply
f(x) by the same amount a. f(x+1) = f(x) a for all x. An exponential function is increasing if a > 1
and decreasing if 0 < a < 1.
Note. For linear functions, the dierence between successive outputs is constant. For exponential
functions, the quotient of successive outputs is constant.
7. Suppose you purchase an item for $1000.
(a) If your items value decreases by $100 each year, nd the value, V (t), t years after it was purchased.
Solution. V (t) = 1000 100t
(b) If your items value decreases by 10% each year, nd the value, V (t), t years after it was purchased.
Solution. V (t) = 1000(0.9)
t
(c) What kind of decay is exhibited by each of the above models?
Solution. Part (a) is linear, and part (b) is exponential.
2
Inverses
8. Explain why a function must be one-to-one in order to have an inverse.
Solution. A function has the property that each input has exactly one output. A one-to-one function
has the additional property that each output corresponds to exactly one input. The inverse of a
function f eectively switches the inputs and outputs of f, so that the outputs of f become in inputs
of f
1
and vice versa. If f were not one-to-one, then there would be at least one output with at least
two dierent inputs, e.g. f(a) = f(b) = d even though a = b. But then the inverse would send the
input d to two dierent outputs a and b. Hence the inverse would not be a function, so the only way
to ensure that the inverse is itself a function is to require the original function f to be one-to-one.
9. Find the inverse of f(x) =
10 3x.
Solution. f
1
(x) =
1
3
x
2
10
3
, x 0
10. How is the logarithm function f(x) = log
a
x dened? Find its domain and range.
Solution. The function f(x) = log
a
x is dened to be the inverse of y = a
x
. The domain of f is (0, )
and the range of f is (, ).
11. Solve the inequality 2 < ln x < 9 for x.
Solution. e
2
< x < e
9
12. Find the exact value of each expression.
(a) sin
2
3
3
2
(b) sec
13
4
2
(c) cos
1
3
2
=
5
6
(d) tan
1
(1) =
4
(e) csc
csc
1
3
2
=
3
2
(f) cos(sin
1
x) =
1 x
2
3
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Derivation of Endurance Curves From Fatigue Test Data, Including Run-OutsDocument39 pagesDerivation of Endurance Curves From Fatigue Test Data, Including Run-OutscumtjerryNo ratings yet
- Math Let Reviewer 42 Advanced AlgebraDocument3 pagesMath Let Reviewer 42 Advanced Algebrajohn johnNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry, Volume 1Document286 pagesPhysical Chemistry, Volume 1Almira Bhel Morquianos50% (2)
- Docu54199 OneFS 7.1.1 CLI Administration GuideDocument864 pagesDocu54199 OneFS 7.1.1 CLI Administration GuidetimepratiNo ratings yet
- NetBackup AdminGuide CloudDocument77 pagesNetBackup AdminGuide CloudAdriana Hernandez YescasNo ratings yet
- Organizational DevelopmentDocument35 pagesOrganizational DevelopmentUmesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Symantec Veritas NetbackupDocument24 pagesSymantec Veritas NetbackuptimepratiNo ratings yet
- How To Update NetBackup For A Replaced Tape Drive Without Deleting and Re-Adding The DriveArticle-SymantechTECH34296Document3 pagesHow To Update NetBackup For A Replaced Tape Drive Without Deleting and Re-Adding The DriveArticle-SymantechTECH34296timepratiNo ratings yet
- Math 322 Complex Analysis Notes 0Document7 pagesMath 322 Complex Analysis Notes 009polkmnpolkmnNo ratings yet
- Liz AssetDocument32 pagesLiz AssetssfofoNo ratings yet
- Math Biostatistics Boot Camp 1Document3 pagesMath Biostatistics Boot Camp 1Jerry Taylor100% (1)
- Mathematical Expressions: Technical NoteDocument4 pagesMathematical Expressions: Technical NoteHayyan SabilNo ratings yet
- Ai HLDocument6 pagesAi HLaaryamann guptaNo ratings yet
- Manual Calculadora Casio fx100S PDFDocument48 pagesManual Calculadora Casio fx100S PDFAgapornisNo ratings yet
- An Article On Optics of Paint Layers: Paul Kubelka Franz Munk August, 1931Document16 pagesAn Article On Optics of Paint Layers: Paul Kubelka Franz Munk August, 1931JimmyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 4: Algorithm ComplexityDocument34 pagesLecture Week 4: Algorithm ComplexityMaham uroojNo ratings yet
- TCD CS 2006 46Document10 pagesTCD CS 2006 46masterhacksNo ratings yet
- Algorithm and Architecture For Logarithm, Exponential, and Powering ComputationDocument12 pagesAlgorithm and Architecture For Logarithm, Exponential, and Powering ComputationAnjuJoseTomKarukappallilNo ratings yet
- Sales Force Useful Formula FieldsDocument91 pagesSales Force Useful Formula FieldsAndrea Steffania Paez BarollettaNo ratings yet
- Compound InterestDocument31 pagesCompound InterestShane Louise VasquezNo ratings yet
- Grade (10) Chapter - 12 CalculusDocument33 pagesGrade (10) Chapter - 12 CalculusZakir Amad 32No ratings yet
- 1-Complexity Analysis Basics-23-24Document74 pages1-Complexity Analysis Basics-23-24walid annadNo ratings yet
- 114 Handy Formulae For Quantitative Aptitude Problems: Author: Sagar SonkerDocument26 pages114 Handy Formulae For Quantitative Aptitude Problems: Author: Sagar SonkerdskrishnaNo ratings yet
- MCV4U Homework GuideDocument8 pagesMCV4U Homework GuideChristian KapsalesNo ratings yet
- MATH1009 Test 1 SolutionsDocument3 pagesMATH1009 Test 1 SolutionsfatdogeNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Notes - 6.9 Notes - Logs With Other Bases-KeyedDocument2 pagesDay 1 Notes - 6.9 Notes - Logs With Other Bases-Keyedmika piusNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ProblemsDocument12 pagesMathematical ProblemsMorakinyo Douglas ElijahNo ratings yet
- Calculus II - Transcendental FunctionsDocument62 pagesCalculus II - Transcendental FunctionsQisthi Al Hazmi Hidayatur-RohmanNo ratings yet
- Matematika I Statistika Za IMQFDocument208 pagesMatematika I Statistika Za IMQFGo WolowitzNo ratings yet
- Major Steps in Well Log StudiesDocument8 pagesMajor Steps in Well Log StudiesHafiz AsyrafNo ratings yet
- Big O Notation (Compatibility Mode)Document10 pagesBig O Notation (Compatibility Mode)Ofif MurtessaaNo ratings yet
- Norton Media Library: The Facts of Economic GrowthDocument200 pagesNorton Media Library: The Facts of Economic GrowthwbboothNo ratings yet
- Basic MT F3 Notes PDFDocument297 pagesBasic MT F3 Notes PDFClemence TafitiNo ratings yet
- GENMATH ABM Boyle - Logarithmic Inequalities and Their GraphsDocument36 pagesGENMATH ABM Boyle - Logarithmic Inequalities and Their GraphsKaela SamonteNo ratings yet
- Baranyi Et Al 1993 A Non-Autonomous Differential Equation To Model Bacterial Growth PDFDocument17 pagesBaranyi Et Al 1993 A Non-Autonomous Differential Equation To Model Bacterial Growth PDFCarlos AndradeNo ratings yet