Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Outline With Edited Program
Uploaded by
WanAthirah WanKamalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Outline With Edited Program
Uploaded by
WanAthirah WanKamalCopyright:
Available Formats
SCHOOL OF ARCHITECTURE, BUILDING & DESIGN Modern Architecture Studies in Southeast Asia (MASSA) Research Unit Bachelor of Science
(Honours) (Architecture)
ASIAN ARCHITECTURE [ARC 2213] Credit hours: 3 Prerequisite: None
__________________________________________________________________________________ L ectu rer: n ooridayu AHMAD Y US UF , shahrianne SHAH, noorazahanim Abstract The subject explores the history of South, Southeast and East Asian architecture as a whole within a systematic treatment of architectural design and construction, building science and technology, garden design and city planning through three key themes: tradition, modernity and globalization. These themes will guide the organization of weekly lecture and seminar sessions, which will proceed from the establishment of a basic theoretical apparatus to the examination of specific cases. Students will develop a written synopsis of a designated reading, an oral presentation of a specific discussion in relation to the designated reading, and an in-depth analytical research paper on the designated topic. Teaching Objectives To develop critical perspectives on architecture and urbanism in situations where tradition, modernity and globalization intersect through an exploration of the history of South, Southeast and East Asian architecture To provide tools for the analysis of specific architectural situations that inform third year design studios To formulate questions and issues based on cross cultural awareness
Learning Outcomes Upon successful completion of this module, students will be able to: 1. Describe the historical development of the main strands of Asian architecture 2. Identify a broad range of issues related to the historical and chronological transitions of Asian architectural history 3. Interpret architectural language in relation to the development of Asian architecture and urbanism based on the themes of tradition, modernity and globalization 4. Analyze and discuss the relationship between architecture and its social, cultural and intellectual context within the Asian region 5. Differentiate the way in which many varied factors contribute to the development of Asian architecture and urbanism 6. Produce, orally and in writing, a critical interpretation of Asian architecture and urbanism in relation to relevant theories within the contemporary discourse of architecture Modes of Delivery This is a 3 credit hour subject held over 14 weeks. The mode of delivery will be in the form of Lectures, Tutorials and Self-study. The breakdown of the hours is as follows:
TU Bachelor of Science (Honours) (Architecture) 1|P age
Contact Hours Lecture: Tutorial: Self Study: 2 hours/week 2 hours/week 2 hour/week
General Rules and Regulations Late Submission Penalty The School imposes a late submission penalty for work submitted late without a valid reason e.g. a medical certificate. Any work submitted after the deadline (which may have been extended) shall have the percentage grade assigned to the work on face value reduced by 10% for the first day and 5% for each subsequent day late. A weekend counts as 1 day. Individual members of staff shall be permitted to grant extensions for assessed work that they have set if they are satisfied that a student has given good reasons. The Board of Examiners may overrule any penalty imposed and allow the actual mark achieved to be used if the late submission was for a good reason. Absenteeism at intermediate or final presentations will result in zero mark for that presentation. Attendance and Participation Attendance is compulsory. Any student who arrives late after the first half-hour of class will be considered as absent. A minimum of 80% attendance is required to pass this subject and/or be eligible for the final examination. You are expected to attend and participate actively in class. The lectures and tutorials will assist you in expanding your ideas and your research progression. Your work will be graded based on your performance throughout the semester. Your class participation is as important as the end product. It is compulsory for the student to attempt and submit all assessment components including portfolio. Failing to do so will result in failing the subject irrespective of the marks earned. It is also compulsory for the student to attend the final examination. Being absent from the final exam will result in failing the subject even though the student has achieved more than 50% in the overall assessment. Plagiarism (TU Student Handbook 2011) Plagiarism, which is an attempt to present another persons work as your own by not acknowledging the source, is a serious case of misconduct which is deemed unacceptable by the University. "Work" includes written materials such as books, journals and magazine articles or other papers and also includes films and computer programs. The two most common types of plagiarism are from published materials and other students works a. Published Materials In general, whenever anything from someone elses work is used, whether it is an idea, an opinion or the results of a study or review, a standard system of referencing should be used. Examples of plagiarism may include a sentence or two, or a table or a diagram from a book or an article used without acknowledgement. Serious cases of plagiarism can be seen in cases where the entire paper presented by the student is copied from another book, with an addition of only a sentence or two by the student. While the former can be treated as a simple failure to cite references, the latter is likely to be viewed as cheating in an examination. Though most assignments require the need for reference to other peoples works, in order to avoid plagiarism, students should keep a detailed record of the sources of ideas and findings and ensure that these sources are clearly quoted in their assignment. Note that plagiarism refers to materials obtained from the Internet too.
TU Bachelor of Science (Honours) (Architecture) 2|P age
b. Other Students Work Circulating relevant articles and discussing ideas before writing an assignment is a common practice. However, with the exception of group assignments, students should write their own papers. Plagiarising the work of other students into assignments includes using identical or very similar sentences, paragraphs or sections. When two students submit papers which are very similar in tone and content, both are likely to be penalised.
Student Centered Learning Approach This subject uses the Student-centered Learning (SCL) approach. Utilization of this method embodies most of the principles known to improve learning and to encourage students participation. SCL requires students to be active, RESPONSIBLE participants in their own learning and the teachers are to facilitate the students learning process. Various teaching and learning strategies such as experiential learning, problem-based learning, site visits, group discussions, presentations, working in group and etc. will be employed to facilitate the learning process for this module. In SCL students are to be: active in their own learning self-directed to be responsible to enhance their learning abilities able to cultivate skills that are useful in todays workplace active knowledge seekers active players in a teamwork
Blackboard 7 (BB7) Blackboard 7 (BB7) will be used as a communication tool and information portal for students to access subject materials, project briefs, assignments and announcements.
Contact Lecturer: Nooridayu Ahmad Yusuf Office Hours Students are encouraged to visit the instructor/lecturer/tutor concerned for assistance during office hours. If the office hours do not meet the student's schedule, it is suggested that the student notify the instructor, and set appointment times as needed. Types of Assessment and Feedback Each student will be graded in the form of formative and summative assessments. Formative assessments will provide information to guide the student in the research process. This form of assessment will be conducted through Interim Critique/Review sessions. Summative assessment will inform the student about the level of understanding and performance capabilities achieved at the end of each project with form of a final examination. nooridayu.yusuf@taylors.edu.my
TU Bachelor of Science (Honours) (Architecture)
3|P age
Assessment Plan Assessments Type Learning outcomes 4,5,6 Marks 10% 10% 10% 20% 30% 10% 10% Pass/Fail 100% Presentation Submission 17 Mar 2011 7 Apr 2011 14 Apr 2011 28 Apr 2011 9 Jun 2011 9 Jun 2011 24 Mar 2011 26 May 2011 9 Jun 2011
Project 1
Individual
Project 2 Online tutorials Portfolio Total
Group Individual Individual
3 1,2 1-6
Coursework This module will be graded in the form of coursework and final examination. It consists of 2 projects, a midterm test, final examination and a portfolio submission. Project 1: Research Paper: Literature Review This project involves producing, orally and in writing, a critical interpretation of Asian architecture and urbanism in relation to relevant theories within the contemporary discourse of architecture. Students are required to produce a paper (2,000 to a maximum of 2,500 words, double spaced) on an issue or contemporary architecture practice in Asia. The paper should not focus on a survey of the contemporary scene but rather critically examine a practice or an issue (or several related issues), which inform our reading of the emergent Asian architectural and urban landscape. The final topic of the paper should be evolved in discussion and consultation with the tutors and should be finalized by the third week of the course. Students will present the summary of the paper with images in class which contains an outline of the paper covering issues and themes explored, as well as a bibliography. Project 2: Case study This project will involve an interpretation of architectural language in relation to the development of Asian architecture and urbanism based on themes of tradition, modernity and globalization. Students are required to select specific site in Asia as a case study to conduct a self-investigation through observation and documentation in which an oral and visual presentation would be the final outcomes. Online tutorials Tutorial questions will be provided weekly based on assigned readings to further increase students architectural theory vocabulary and enhance the understanding of the subject. Taylors Graduate Capabilities Portfolio (P/F) The portfolio is an edited document to include all the work produced in this module. Visual diary and process of work (packaged) are to be included as part of the portfolio submission. The portfolio should be an A3 bounded document and well-crafted. Images, drawings, text and so on must be well edited, legible and composed. Text should be kept minimal .
TU Bachelor of Science (Honours) (Architecture)
4|P age
Student Input Student participation is encouraged through various means. In this module, students have the opportunity to participate in the following ways: Students ideas and questions are welcomed, valued and encouraged. Student input is sought to understand their perspectives, ideas and needs in planning subject revision. Students are offered opportunities to give feedback with the assurance that issues will be addressed in response to that feedback. Students reflect on their performance in personal portfolios. Student evaluation allows their views and experiences about the sessions are actively sought and used as an integral part of improvement in teaching and continuous improvement. Marks and Grading Table (Revised as per 2011 programme guide) Assessments and grades will be returned within 2 weeks of your submission. You will be given the grades and necessary feedback for each submission. The grading system is shown below: Grade Grade Marks Definition Description Points A 80 100 4.00 Excellent Evidence of original thinking; demonstrated outstanding capacity to analyze and synthesize; outstanding grasp of module matter; evidence of extensive knowledge base Evidence of good grasp of module matter; critical capacity and analytical ability; understanding of relevant issues; evidence of familiarity with the literature Evidence of grasp of module module; critical capacity and analytical ability, reasonable understanding of relevant issues; evidence of familiarity with the literature Evidence of some understanding of the module matter; ability to develop solutions to simple problems; benefitting from his/her university experience
AB+ B BC+ C D+ D DF
75 79 70 74 65 69 60 64 55 59 50 54 47 49 44 46 40 43 0 39
3.67 3.33
Very Good
Good 3.00 2.67 2.33 2.00 1.67 1.33 1.00 0.00 Fail Marginal Pass Pass
Evidence of minimally acceptable familiarity with module matter, critical and analytical skills
Insufficient evidence of understanding of the module matter; weakness in critical and analytical skills; limited or irrelevant use of the literature Withdrawn from a module before census date, typically mid semester Withdrawn after census date, typically mid semester An interim notation given for a module where a student has not completed certain requirements with valid reason or it is not possible to finalise the grade by the published deadline Given for satisfactory completion of practicum Given for a module where attendance is for information only without earning academic credit
5|P age
WD F(W) IN P AU
0 -
0.00 -
Withdrawn Fail Incomplete Pass Audit
TU Bachelor of Science (Honours) (Architecture)
Recommended Reading Main References : 1. 2. 3. Abel, Chris. 1997. Architecture & Identity: Towards a Global Eco-Culture. Avon Books. Findley, Lisa. 2005. Building Change: Architecture, Politics and Cultural Agency. Routledge. Kostoff, Spiro. 1999. The City Shaped: Urban Patterns and Meanings Through History. Thames and Hudson. Meng, Tan K. 2000. Asian Architects 1. Select Books. Meng, Tan K. 2001. Asian Architects 2. Select Books. Inglis, Kim. 1997. Tropical Asian Style. Perplus Editions. Khan, Hasan-Uddin. 1995 Contemporary Asian Architects. Taschen Ching, Francis D.K. 2007. A Global History of Architecture. Wiley Lim, William S.W. 2000. World Architecture 1900 2000: A Critical Mosaic: Southeast Asia and Oceania. Thomson Gale.
Additional References :
4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
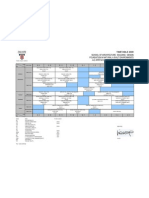
Module Schedule Week/Date Week 1 (3 Mar 2011) Description Subject introduction Lecture 1 Introduction: Asia Project 1: Briefing Lecture 2 History of architecture and urbanism in the South, Southeast and East Asian Region Project 1: Tutorial 1: What is literature review Lecture 3 Vernacular Architecture Project 1 Review: Submission of topic and issue Plagiarism and Referencing Workshop
Week 2 (10 Mar 2011)
Week 3 (17 Mar 2011)
Week 4 (24 Mar 2011) Week 5 (31 Mar 2011)
Lecture 4 Architecture, Ornamentation and Symbolism Project 1: Tutorial 2: Proposal Revision (Session 1) Lecture 5 Architecture and Anthropology Project 1: Tutorial 2: Proposal Revision (Session 2) Project 1 Review: Submission of proposal (Session 1) Briefing on presentation and abstract writing Project 1: Tutorial 3: What is an Abstract? (Session 1 & 2) Project 1 Review: Submission of proposal (Session 2) Project 1: 10%
6|P age
Week 6 (7 April 2011)
Project 1: 10%
Week 7 (14 April 2011)
TU Bachelor of Science (Honours) (Architecture)
Semester break (18 to 22 April 2011) Week 8 Project 1: Presentation (Session 1) (28 April 2011) Online Tutorial 1 Project 2: Briefing Project 1: Presentation (Session 2) Project 1: Submission of abstract (Session 1) Project 2: Tutorial 1: Site Lecture 7 Post modernity, Post-Culturalism and Globalization in the Transformation of Asian Architecture and Urbanism Project 1: Submission of abstract (Session 2) Project 2: Study Trip 1 (Local site Kuala Lumpur) Online tutorial 2 Project 1: Tutorial 4: Final Review (Session 1) Project 2: Study Trip 2 (Overseas site TBC) Lecture 8 Complexities of Tradition, Modernity and Globalization Project 1: Tutorial 4: Final Review (Session 2) Project 2: Tutorial 2: Analysis of findings Project 2: Tutorial 3: Using of multimedia Project 1: Submission (Session 1) Presentation and submission of Project 2 Project 1: 20% Project 2: 30% Project 1: 20% Project 1: 10% Project 1: 10% 10%
Week 9 (5 May 2011)
Project 1: 10% Project 1:10%
Week 10 (12 May 2011)
Week 11 (19 May 2011)
10%
Week 12 (26 May 2011)
Week 13 (2 June 2011) Week 14 (9 June 2011)
Project 1: Submission (Session 2) Note: This module outline is subject to change within short notice
TU Bachelor of Science (Honours) (Architecture)
7|P age
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Oku ParkingDocument1 pageOku ParkingWanAthirah WanKamalNo ratings yet
- The Significance of MinaretDocument9 pagesThe Significance of MinaretWanAthirah WanKamalNo ratings yet
- The Significance of MinaretDocument9 pagesThe Significance of MinaretWanAthirah WanKamalNo ratings yet
- Green ScreenDocument24 pagesGreen ScreenWanAthirah WanKamalNo ratings yet
- La Deee Dam Dee DamDocument1 pageLa Deee Dam Dee DamWanAthirah WanKamalNo ratings yet
- Latest Timetable FNBE July09Document1 pageLatest Timetable FNBE July09WanAthirah WanKamalNo ratings yet
- Steel Ribs PDFDocument1 pageSteel Ribs PDFWanAthirah WanKamalNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Grade 12 Schedule of Prefinal Exams Term 1 AY 2021-2022Document4 pagesGrade 12 Schedule of Prefinal Exams Term 1 AY 2021-2022Joshua ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson Plan in English Q3-Week 5-FinalDocument5 pagesCot Lesson Plan in English Q3-Week 5-Finalcatherine caytunaNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Events: in Collaboration With Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, IndiaDocument10 pagesSchedule of Events: in Collaboration With Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, IndiaLalitha RajaNo ratings yet
- February 2013 Full IssueDocument144 pagesFebruary 2013 Full IssuechioNo ratings yet
- Addressing Barriers To LearningDocument508 pagesAddressing Barriers To LearningNadine100% (1)
- Doctors and ProgrammeDocument28 pagesDoctors and ProgrammePabitra ThapaNo ratings yet
- B M S College of Engineering: (Autonomous Institution Under Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum)Document2 pagesB M S College of Engineering: (Autonomous Institution Under Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum)Anil FkNo ratings yet
- Summer 2013Document20 pagesSummer 2013Ahmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 Lesson Plan 1Document6 pagesCot 2 Lesson Plan 1Alma RayosoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication (Gec-Pc)Document3 pagesPurposive Communication (Gec-Pc)Hanna Jane CabasagNo ratings yet
- Revista de Geomorfologie NR 15 2013 Miscallanea PoseaDocument4 pagesRevista de Geomorfologie NR 15 2013 Miscallanea PoseaElena.Loredana ManeaNo ratings yet
- Reflection - SeasonsDocument2 pagesReflection - Seasonsapi-295500001100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Home Economics 7Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Home Economics 7Gwyneth Queen GalvadoresNo ratings yet
- First Oral Exam PetDocument2 pagesFirst Oral Exam PetDafne MoralesNo ratings yet
- BISP DeputationDocument3 pagesBISP DeputationAadil HaroonNo ratings yet
- Activity Guide and Evaluation Rubric - Unit 2 - Task 3 - Contrasting Teaching ApproachesDocument6 pagesActivity Guide and Evaluation Rubric - Unit 2 - Task 3 - Contrasting Teaching Approachesjaider gòmez vegaNo ratings yet
- Water Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesWater Lesson Planapi-272576800No ratings yet
- Odd and Even NumbersDocument4 pagesOdd and Even NumbersSukmaning TyasNo ratings yet
- Speaking CardsDocument19 pagesSpeaking CardsLiliana BritesNo ratings yet
- The Importance Role of Education For LifeDocument3 pagesThe Importance Role of Education For LifeMuhammad Nur SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Training Session Evaluation Form InstructionsDocument8 pagesTraining Session Evaluation Form Instructionsaaronjules100% (1)
- Oc ApplicpackDocument10 pagesOc ApplicpackRaviNo ratings yet
- 8607 Fields Notes +observation ReportsDocument34 pages8607 Fields Notes +observation ReportsKuku gagaNo ratings yet
- Performance Indicator I.Instructional Competence 10 8 6 4 2: Total Score Sub-Rating (Total Score/16x5% or 40%)Document3 pagesPerformance Indicator I.Instructional Competence 10 8 6 4 2: Total Score Sub-Rating (Total Score/16x5% or 40%)siopaupaoNo ratings yet
- Learning and Transfer of Training: 6 Edition Raymond A. NoeDocument51 pagesLearning and Transfer of Training: 6 Edition Raymond A. NoeanujdeshmukhNo ratings yet
- cb21 Childcare LadderDocument2 pagescb21 Childcare Ladderapi-214405982No ratings yet
- Government Orders 106Document3 pagesGovernment Orders 106nani20032010No ratings yet
- Designation LetterDocument2 pagesDesignation LetterbabyroseNo ratings yet
- Edtpa LessonsDocument12 pagesEdtpa Lessonsapi-279312232No ratings yet
- Letters Seeking PermissionDocument9 pagesLetters Seeking PermissionJagannath BasuNo ratings yet